Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BLOOD
Uploaded by
Juana Ilagan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageBLOOD
Uploaded by
Juana IlaganCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Plasma – clear, yellowish fluid component of blood, excluding the suspended corpuscles and cells.
- Consists of about 91% water, 7% proteins, and 2% other substances such as nutrients, gases, ions, and waste
products.
Plasma proteins
1. Albumin – maintain osmotic pressure and act as a transport molecule.
2. Globulin – act as transport molecule. Some are part of the immune system.
3. Fibrinogen – responsible for clot formation.
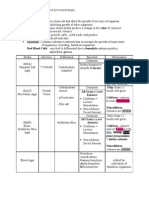
Blood Cells
1. Red blood cells
- Biconcave disk; no nucleus.
- Contains hemoglobin, for transportation of oxygen, and carbonic anhydrase, for transportation of carbon dioxide.
- In response to low blood oxygen levels, the kidneys produce erythropoietin, which stimulates RBC production in
the red bone marrow.
- Worn-out RBC are phagocytized by macrophages.
2. White blood cells – spherical and possess a nucleus.
a. Granulocytes – contains cytoplasmic granules
1. Neutrophil – phagocytizes microorganisms and other foreign substances.
2. Basophil – releases histamine (which promotes inflammation) and heparin (which prevents clot
formation).
3. Eosinophil – reduce inflammation; attacks certain parasites esp. worms.
b. Agranulocytes – cytoplasmic granules are absent.
1. Lymphocytes – produce antibodies and other chemicals responsible for destroying microorganisms. Also
contributes in allergic reactions, graft rejections, tumor control, and even immunity regulation.
2. Monocyte – inactive phagocytic cell that are travelling in the blood stream.
3. Macrophage – active cell that phagocytizes microorganisms, dead cells, cell fragments, and other debris
within tissues.
3. Platelets
- Cell fragments surrounded by plasma membrane.
- Form vessel plugs and release chemicals necessary for blood clotting.
Transfusion – transfer of blood or blood components from one individual to another.
Infusion – introduction of a fluid other than blood, such as a saline or glucose solution, into the blood.
ABO blood groups
1. Type A – A antigen; Anti B antibody
2. Type B – B antigen; Anti A antibody
3. Type AB – both A and B antigen; neither anti A or anti B antibody
4. Type O – neither A or B antigen; both anti A and anti B antibody
Rh antigens
1. Rh +
2. Rh –
Blood typing – determines the ABO and Rh blood groups of a blood sample.
Cross match test – agglutination reactions are tested between donor and recipient blood.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition and FormationDocument27 pagesBlood Composition and Formationchandu ranaNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document35 pagesBlood Part 1Keziah TampusNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- He Hematologic System: Bone MarrowDocument5 pagesHe Hematologic System: Bone MarrowPatricia Mae Loyola FerrerNo ratings yet
- Blood Notes PDFDocument13 pagesBlood Notes PDFsyedurrahman855No ratings yet
- Selflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Document18 pagesSelflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Jeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument56 pagesBloodGail Justine Chongco GonzalesNo ratings yet
- GRP 5 Hematopoietic System ImlanDocument49 pagesGRP 5 Hematopoietic System ImlanSharie Grace ImlanNo ratings yet
- Hematologic SystemDocument81 pagesHematologic Systemseigelystic100% (23)
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument10 pagesBLOODChrisjohn Aster OsioNo ratings yet
- Forensic Existence of Blood As A Dynamic PDFDocument5 pagesForensic Existence of Blood As A Dynamic PDFiqrarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - The Cardiovascular System - Blood Functions of BloodDocument7 pagesChapter 20 - The Cardiovascular System - Blood Functions of Bloodlovelyc95No ratings yet
- Unit 2-Blood Guided NotesDocument5 pagesUnit 2-Blood Guided NotesJeanette IrambonaNo ratings yet
- Blood Overview and IntroductionDocument8 pagesBlood Overview and IntroductionKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument9 pagesComponents of BloodEricBuguinaNo ratings yet
- Physiology - BloodDocument12 pagesPhysiology - BloodHey GoogleNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PhysiologyDocument8 pagesCardiac PhysiologyMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- A. Functions of Blood SystemDocument7 pagesA. Functions of Blood SystemPrant ChikyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 23 BLOOD and URINEDocument31 pagesMODULE 23 BLOOD and URINECrystal ManguneNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Chapter 19 - Blood)Document16 pagesAnaphy (Chapter 19 - Blood)TeresilleNo ratings yet
- Components of BloodDocument9 pagesComponents of Bloodapi-312051183No ratings yet
- Blood 12-6-2018Document42 pagesBlood 12-6-2018Noor Fatima100% (1)
- Blood Overview and IntroductionDocument8 pagesBlood Overview and IntroductionWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - BloodDocument5 pagesChapter 19 - Bloodtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Blood: Figure 1: Shows Separated Blood Layers by CentrifugeDocument7 pagesBlood: Figure 1: Shows Separated Blood Layers by Centrifugeحسين مهديNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsDocument6 pagesBlood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsKids JangNo ratings yet
- Blood ChemistryDocument24 pagesBlood Chemistryflorabelvelasco2No ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood and Body Fluids Mbbsii Bdsii Lecture Note 2019-2020Document39 pagesPhysiology of Blood and Body Fluids Mbbsii Bdsii Lecture Note 2019-2020MUHAMMAD AHMAD HAMMANo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To HematologyJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells, Coagulation.: Teacher: Magdalena Gibas MD PHD Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street No. 6, Dept. of PhysiologyDocument7 pagesBlood Cells, Coagulation.: Teacher: Magdalena Gibas MD PHD Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street No. 6, Dept. of PhysiologysenjicsNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics and VolumeDocument10 pagesPhysical Characteristics and Volumedeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Transportform5 120218082802 Phpapp01Document107 pagesChap1 Transportform5 120218082802 Phpapp01Santhiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Blood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaDocument10 pagesBlood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document29 pagesBlood Part 1raneem fakhouriNo ratings yet
- SR NO NO: Review of Anatomy and Physiology of BloodDocument14 pagesSR NO NO: Review of Anatomy and Physiology of BloodPdianghunNo ratings yet
- Blood: TransportationDocument29 pagesBlood: TransportationShobhit GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Blood Reviewer 1Document6 pagesBlood Reviewer 1tokzzNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 pagesLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Body Fluids: BloodDocument17 pagesBody Fluids: BloodSiti Nor AiniNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael WindelspechtDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Human Biology 16th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael WindelspechtRobertLynchwxey100% (41)
- Blood HBDocument31 pagesBlood HBBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Histology of Blood Histology of Blood VesselsDocument6 pagesHistology of Blood Histology of Blood VesselsgerginNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Module: Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyDocument179 pagesEndocrine System Module: Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyƯớc Của BếttingNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument11 pagesBLOODshapan biswaNo ratings yet
- Blood NotesDocument4 pagesBlood NotesChelsa LeyritanaNo ratings yet
- BLOOD PresentationDocument33 pagesBLOOD PresentationLezlie Jane SahaliNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculatoryDocument5 pagesBlood CirculatoryRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyRao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument14 pagesBody FluidsathuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Circultion1Document17 pagesAnatomy Circultion1Keinneth JacobNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument38 pagesBloodchukwukerechimezirimNo ratings yet
- Compostion Structure and Functions of BloodDocument4 pagesCompostion Structure and Functions of BloodchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII BloodDocument11 pagesChapter VII BloodTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Exams: Scarlet RedDocument2 pagesBiology Lecture Exams: Scarlet RedEmsii DelfinoNo ratings yet
- University of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonDocument45 pagesUniversity of Guyana School of Medicine Med 1106 - Physiology I DR Kalima ThompsonKNo ratings yet
- Blood OutlineDocument4 pagesBlood OutlineNurul SyiraNo ratings yet
- Et CareDocument15 pagesEt CarePaulo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kardiomed-700-User ManualDocument87 pagesKardiomed-700-User ManualJulia TimakovaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument8 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Colgate Marketing ReportDocument16 pagesColgate Marketing ReportRaja GuruNo ratings yet
- Darrells ResumeDocument5 pagesDarrells Resumeapi-273253154No ratings yet
- Tumor AngiogenesisDocument35 pagesTumor AngiogenesisDoni Mirza KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Task 1 FinalDocument4 pagesTask 1 FinalAlᎥyⱥภNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiDocument3 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Selected Teaching Strategies Knowledge Regarding Drug Calculation Among B.Sc. N Students in Selected College at ChennaiEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal ChillerDocument24 pagesCentrifugal ChillerARUL SANKARANNo ratings yet
- Checking Vital SighnDocument14 pagesChecking Vital SighnAdimas AnggaraNo ratings yet
- A "What Not To Do" Better Sex GuideDocument9 pagesA "What Not To Do" Better Sex GuideBenson Huang100% (1)
- Internet Addiction Kids and The South Korean Govt Boot CampsDocument5 pagesInternet Addiction Kids and The South Korean Govt Boot Campslgheorma0No ratings yet
- Selective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartDocument2 pagesSelective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartFrankiesgirl6yr100% (6)
- Updated Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)Document54 pagesUpdated Nutrition Spreadsheet (With Workout Tracker)Kit LbjNo ratings yet
- ACLS Pretest Exam AnnotatedDocument21 pagesACLS Pretest Exam AnnotatedMOLLYNo ratings yet
- Summary Report On Health and HygieneDocument4 pagesSummary Report On Health and HygieneVisal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- BNMHGDocument34 pagesBNMHGAnonymous lt2LFZHNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Different Resources of Bioinformatics and Application PDFDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Different Resources of Bioinformatics and Application PDFSir RutherfordNo ratings yet
- Raynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1Document2 pagesRaynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1api-340995574No ratings yet
- Enrolled Nurses FADocument11 pagesEnrolled Nurses FAjoayou23No ratings yet
- Counseling: Counseling Is A Wonderful Twentieth-Century Invention. We Live in A Complex, BusyDocument21 pagesCounseling: Counseling Is A Wonderful Twentieth-Century Invention. We Live in A Complex, BusyAnitha KarthikNo ratings yet
- Ma 00507c Us KXL BrochureDocument8 pagesMa 00507c Us KXL BrochureEng. Rijulesh KaremmalNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesBiotechnologyChrystal Kyla SalengaNo ratings yet
- Recist Criteria - Respon Solid Tumor Pada TerapiDocument18 pagesRecist Criteria - Respon Solid Tumor Pada TerapiBhayu Dharma SuryanaNo ratings yet
- Rockwool Slab Data Sheet - (ProRox Formerly RW Slab)Document7 pagesRockwool Slab Data Sheet - (ProRox Formerly RW Slab)stuart3962No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Lifting OperationsDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment - Lifting OperationsJishad Nalakath83% (87)
- SOP-016-Testing of LPG ResidueDocument9 pagesSOP-016-Testing of LPG ResidueAmnaKamranNo ratings yet
- Starlight ProgramsDocument12 pagesStarlight Programsllacara@nncogannett.comNo ratings yet
- Psychology of ProcrastinationDocument7 pagesPsychology of ProcrastinationPauline Wallin100% (2)
- Aquatics BrochureDocument24 pagesAquatics BrochurethuronNo ratings yet
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (110)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)