Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digital currencies and blockchain explained
Uploaded by
MUFAZZAL SADHIQUEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digital currencies and blockchain explained
Uploaded by
MUFAZZAL SADHIQUECopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 - The internet and its uses
5.2 Digital Currency
Learning Objective 16/01/2023
• Understand the concept of a digital currency and how digital currencies are used.
Digital Currency
Currency that exists in electronic form only; it has no physical form and is essentially data
on a database.
It is a method of payment, but rather than exchanging physical coins and bank notes, the
payment is made electronically.
A central bank is needed to act as the "middleman"
Problems with centralization
• Confidentiality (Control of governments and central authorities)
• Security
Crypto Currency
- Use the power of their personal computers to process transactions. The reward for doing
so is that miners receive some of the transaction fees involved in the process of payment
made.
Learning Objective 18/01/2023
• Understand the process of blockchain and how it is used to track digital currency
transactions
Decentralisation - Cryptocurrency
• Traditional digital currencies are regulated by central banks and governments. This
means all transactions and exchange rates are determined by these two bodies.
• Cryptocurrency has no state control and all the rules are set by the cryptocurrency
community itself.
• The cryptocurrency system works by being within a blockchain network which means
it is much more secure.
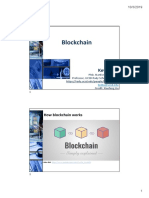
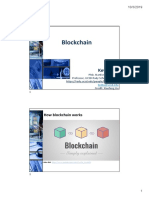
Blockchain
A technology that sits behind all cryptocurrency transactions. It makes all sorts of
cryptocurrency safe to use.
Blockchaining - How cryptocurrency work?
• Blockchain is a decentralised database.
• All the transactions of networked members are stored on this database.
• The blockchain consists of a number of interconnected computers but they are not
connected to a central server.
• All transaction data is stored on all computers in the blockchain network.
Blockchaining - A chain of blocks
• When a new transaction takes place, a new block is created
• Blockchains = A collections of all transactions
What's inside one block?
Learning Objective 19/01/2023
• Explain how a range of solutions are used to help keep data safe from security
threats
Cyber Security
Cyber Security Solutions & Prevention
Access Level
• User will be assigned different levels of access depending on the role they have. It
ensures that users' behaviour can be controlled while they use a computer on a
network.
• When using databases, levels of access are important to determine who has the right to
read, write and delete data.
Anti Malware
Anti Virus
• Anti-virus software are constantly scanning documents, files and also incoming data
from the internet.
• They are designed to detect suspisious activity and files before they are opened or
stored / warn the user against opening the files.
Anti Spyware
Spyware is software that gathers information by monitoring a user’s activities carried out
on their computer.
Authentication
Authentication refers to the ability of a user to prove who they are.
• Password and user names
• Biometrics Authentication
• Two-step verification
• Credit Card & Hotel Card
You might also like
- Blockchain IDocument33 pagesBlockchain Ipumpkin.baba123No ratings yet
- Crypto CurrencyDocument10 pagesCrypto CurrencysaurabhNo ratings yet
- Block Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemDocument21 pagesBlock Chain: BY Mohamed Safwan A Kavin Manoj C M Cse Ii Year Gce, SalemMohamed safwanNo ratings yet
- Using Blockchain in CyberForensicsDocument51 pagesUsing Blockchain in CyberForensicsHimanshi Garg100% (1)
- CryptoDocument12 pagesCryptoParakh Sinha100% (1)
- BCT Unit-1Document43 pagesBCT Unit-1raginiguntupalli12No ratings yet
- Block Chain TechnologyDocument22 pagesBlock Chain TechnologyChaithraNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument11 pagesBlockchain TechnologyASI SASTRAGNA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Cryptocurrency Rotaru GeorgeDocument22 pagesCryptocurrency Rotaru GeorgeGeorge Cristinel RotaruNo ratings yet
- Crypto Coin-Overview of Basic Transaction: January 2017Document6 pagesCrypto Coin-Overview of Basic Transaction: January 2017Cristian S.No ratings yet
- The Blockchain Economy: Decentralized Finance and the Future of MoneyFrom EverandThe Blockchain Economy: Decentralized Finance and the Future of MoneyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument33 pagesBlockchain Technologypawar143omkarNo ratings yet
- CryptocurrencyDocument14 pagesCryptocurrencyAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Blockchain in MarketingDocument14 pagesBlockchain in MarketingSakshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Block Chain ArchitectureDocument2 pagesBlock Chain Architecturectl designerNo ratings yet
- Basics of CryptocurrenciesDocument12 pagesBasics of CryptocurrenciesAmulya SNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument14 pagesBlock Chainiqbal ishak100% (1)
- Sid - CryptocurrencyDocument7 pagesSid - Cryptocurrencysp.fdal4jNo ratings yet
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency TechniquesDocument14 pagesBlockchain and Cryptocurrency TechniquesJuma SohnNo ratings yet
- Certified Blockchain ExpertDocument336 pagesCertified Blockchain Expertvathsoo100% (6)
- Crytocurrency Bitcoin and EthereumDocument43 pagesCrytocurrency Bitcoin and EthereumRisheek NayakNo ratings yet
- E CashDocument9 pagesE CashGurpreet BansalNo ratings yet
- FAH - Crypto CurrencyDocument10 pagesFAH - Crypto CurrencyFaisal A. HussainNo ratings yet
- Block ChainDocument16 pagesBlock ChainNirnay PatilNo ratings yet
- Blockchain - A Comprehensive Introduction For Mastering BlockchainFrom EverandBlockchain - A Comprehensive Introduction For Mastering BlockchainNo ratings yet
- Crypto Currency: A Bright Future or Just A Fad?: IntroductionDocument2 pagesCrypto Currency: A Bright Future or Just A Fad?: IntroductionAshi JainNo ratings yet
- Lect1 Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyDocument33 pagesLect1 Introduction To Blockchain TechnologyEdwin FrankNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1From EverandBlockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document58 pagesChapter 4aditsinghonlineNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOCURRENCY (Autosaved)Document26 pagesCRYPTOCURRENCY (Autosaved)Rajni SharmaNo ratings yet
- Web3 Security: Use of Block Chain Technology to Build Secure Web ApplicationsFrom EverandWeb3 Security: Use of Block Chain Technology to Build Secure Web ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Blocchain Fundamentals Module1Document90 pagesBlocchain Fundamentals Module1puneett20012No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About CryptocurrencyDocument31 pagesEverything You Need to Know About CryptocurrencyAvinashNo ratings yet
- Participants BlockchainDocument10 pagesParticipants BlockchainshalyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 updated (1)Document113 pagesUnit 1 updated (1)saurabh tiwariNo ratings yet
- BlockchaniDocument23 pagesBlockchaniOlukoya ModesayoNo ratings yet
- An Improved Banking Application Model Using BlockcDocument21 pagesAn Improved Banking Application Model Using BlockcAakash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Fundamentals and HyperledgerDocument42 pagesBlock Chain Fundamentals and HyperledgerFatema TurnaNo ratings yet
- Digicash CybercashDocument20 pagesDigicash CybercashAnshul GargNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction to Blockchain AnalyticsDocument42 pages1-Introduction to Blockchain AnalyticsTejasruti GeridipudiNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument20 pagesBlockchain Technologyabreham ashebirNo ratings yet
- FOB Chapter-2Document27 pagesFOB Chapter-2Pratik KhuntNo ratings yet
- BlockChain-1 (1) PPTXLDocument18 pagesBlockChain-1 (1) PPTXLPearl ShellNo ratings yet
- Blockchain & CryptocurrencyDocument53 pagesBlockchain & CryptocurrencyTime PassNo ratings yet
- Blockchain SC Technology WP FINAL March 2017 2Document5 pagesBlockchain SC Technology WP FINAL March 2017 2EdwardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - IT in SocietyDocument12 pagesChapter 12 - IT in SocietyJade PumaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain and Operation ManagementDocument18 pagesBlockchain and Operation ManagementFatma HassanNo ratings yet
- Cryptocurrency Trading & Investment Guide for Bulls: 2 in 1 Blockchain & Bitcoin Revolution. How to DeFi and Make Money in Decentralized Finance. Learn Bitcoin and Ethereum and Altcoins.From EverandCryptocurrency Trading & Investment Guide for Bulls: 2 in 1 Blockchain & Bitcoin Revolution. How to DeFi and Make Money in Decentralized Finance. Learn Bitcoin and Ethereum and Altcoins.No ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction Block Chain SecurityDocument4 pages1.1 Introduction Block Chain Securityrajat ghardeNo ratings yet
- Non Financial Applications of BlockchainDocument19 pagesNon Financial Applications of BlockchainHelly MavaniNo ratings yet
- How to Learn About Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies in 48 Hours or LessFrom EverandHow to Learn About Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies in 48 Hours or LessNo ratings yet
- Centralized Power: Prone To Hacks:: Issues With The Current Banking SystemDocument16 pagesCentralized Power: Prone To Hacks:: Issues With The Current Banking SystemVansika SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment System An Implementation Through CryptographyDocument8 pagesElectronic Payment System An Implementation Through CryptographyYamla SrinuNo ratings yet
- BCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayDocument21 pagesBCT Unit-1 21.8.2023 TodayKoti RondiNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOCURRENCY: A DECENTRALIZED DIGITAL CURRENCYDocument23 pagesCRYPTOCURRENCY: A DECENTRALIZED DIGITAL CURRENCYDeepak ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- 2b Blockchain PDFDocument15 pages2b Blockchain PDFjshen5No ratings yet
- 2b Blockchain PDFDocument15 pages2b Blockchain PDFjshen5No ratings yet
- Cryptocurrency: Frequently Asked Questions and Answers on Crypto Trading and InvestingFrom EverandCryptocurrency: Frequently Asked Questions and Answers on Crypto Trading and InvestingNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticDocument3 pagesElectromagneticMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- Golf SolutionDocument6 pagesGolf SolutionMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- 5.3 Cyber Security - ThreatsDocument3 pages5.3 Cyber Security - ThreatsMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- Mufazzal Sadhique 11 C 20720 D&T Final Project Word) )Document31 pagesMufazzal Sadhique 11 C 20720 D&T Final Project Word) )MUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- Exterior Design Of A Luxury BuildingDocument29 pagesExterior Design Of A Luxury BuildingMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- ARAB UNITY SCHOOL ISLAMIC STUDIES SYLLABUSDocument1 pageARAB UNITY SCHOOL ISLAMIC STUDIES SYLLABUSMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledMUFAZZAL SADHIQUENo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Humber - Ca/myhumberDocument4 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Humber - Ca/myhumberRodrigo MartinezNo ratings yet
- Envr71000 - Introduction To Environmental Health - Assignment 1 - Jaimie ShortDocument4 pagesEnvr71000 - Introduction To Environmental Health - Assignment 1 - Jaimie Shortapi-290283518No ratings yet
- Nobody Does It Better and Indian Hospitality Will Leave You Feeling Better Too.Document2 pagesNobody Does It Better and Indian Hospitality Will Leave You Feeling Better Too.Abhijeet UmatheNo ratings yet
- Flaws in India's Coal Allocation ProcessDocument12 pagesFlaws in India's Coal Allocation ProcessBhaveen JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ciril Report 2019Document44 pagesCiril Report 2019Aloka MajumderNo ratings yet
- BISE MultanDocument617 pagesBISE MultanZubair NadeemNo ratings yet
- All Grown Up - BareDocument9 pagesAll Grown Up - BareNiamh HawkesNo ratings yet
- The Illumined Man Knows Worldly Enjoyment Is UnrealDocument4 pagesThe Illumined Man Knows Worldly Enjoyment Is UnrealMadhulika Vishwanathan100% (1)
- G47.591 Musical Instrument Retailers in The UK Industry Report PDFDocument32 pagesG47.591 Musical Instrument Retailers in The UK Industry Report PDFSam AikNo ratings yet
- So Ping Bun's Warehouse Occupancy DisputeDocument4 pagesSo Ping Bun's Warehouse Occupancy DisputeVincent BernardoNo ratings yet
- Jasa Vol. 3 (1) Jul-Sep 2013Document4 pagesJasa Vol. 3 (1) Jul-Sep 2013AdityaKumarNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Crisis in the PhilippinesDocument37 pagesConstitutional Crisis in the Philippineslee viceNo ratings yet
- Brainy kl8 Short Tests Unit 5 Lesson 5Document1 pageBrainy kl8 Short Tests Unit 5 Lesson 5wb4sqbrnd2No ratings yet
- Aerographer's Mate Second Class, Volume 2Document444 pagesAerographer's Mate Second Class, Volume 2Bob Kowalski100% (2)
- Final ProposalDocument3 pagesFinal ProposalMadhurima GuhaNo ratings yet
- PIMENTELDocument5 pagesPIMENTELChingNo ratings yet
- Otamias V RepublicDocument2 pagesOtamias V RepublicCassandra Layson75% (4)
- Understanding Diverse LearnersDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Diverse LearnersMerry Grace Aballe Abella100% (2)
- The Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning - Lesson 2bDocument18 pagesThe Role of Marketing in Strategic Planning - Lesson 2bAnonymous lNV4yt0No ratings yet
- 55 CD 383294930 Py 4Document4 pages55 CD 383294930 Py 4api-309385698No ratings yet
- SnowflakeDocument6 pagesSnowflakeDivya SrijuNo ratings yet
- Problem 12Document2 pagesProblem 12Alyssa Jane G. AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 3 Factors That Contribute To Gender Inequality in The ClassroomDocument3 pages3 Factors That Contribute To Gender Inequality in The ClassroomGemma LynNo ratings yet
- Topic Name:: Google Inc. (2010) : The Future of The Internet Search EngineDocument27 pagesTopic Name:: Google Inc. (2010) : The Future of The Internet Search EngineasmshihabNo ratings yet
- ScanCentral Guide 20.2.0Document80 pagesScanCentral Guide 20.2.0Nabil El FilaliNo ratings yet
- Calpers Public Employees' Retirement FundDocument30 pagesCalpers Public Employees' Retirement FundEpicDoctor0% (1)
- 24 Nov 1997 Male GEN: Communication Address GATE Exam DetailsDocument1 page24 Nov 1997 Male GEN: Communication Address GATE Exam DetailsAr Tanmaye MahajanNo ratings yet
- Motion To Approve Compromise AgreementDocument3 pagesMotion To Approve Compromise Agreementcheryl annNo ratings yet
- The Global Diamond Industry: So-Young Chang MBA '02Document17 pagesThe Global Diamond Industry: So-Young Chang MBA '02Pratik KharmaleNo ratings yet
- Briefing The Yemen Conflict and CrisisDocument36 pagesBriefing The Yemen Conflict and CrisisFinlay AsherNo ratings yet