Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 14 - Chemical Reaction Engineering
Uploaded by
Ashleen MarshallOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 14 - Chemical Reaction Engineering
Uploaded by
Ashleen MarshallCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14
Chemical Reaction Engineering
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
What Actually Drives Reactions?
Is it Energy?
Can We Just Calculate or Measure the Energy
Difference of Reactants and Products and Know
Which Way the Reaction Will Go?
Why do chemical reactions occur??????
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Some Basic Definitions
Le Chatelier's Principle
"If a change is made to a system, the system will respond so as
to absorb the force causing the change.“
Equilibrium
At equilibrium none of the properties of a system change with
time. A system at equilibrium returns to equilibrium if disturbed.
"Stable" describes a system or phase in its lowest energy state.
"Metastable" describes a system or phase in any other energy
state.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Gibbs Free Energy of a Phase
The Gibbs free energy G is the thermodynamic potential that
tells us which way a reaction goes at a given set of physical
conditions--neither the enthalpy change nor the entropy change
for a reaction alone can provide us with this information.
The two measures of energy (enthalpy H and entropic energy
TS) are brought together in the Gibbs free energy equation: (the
chemical potential is the equivalent for a component)
G = U + PV – TS (14.1)
which says that the Gibbs free energy G is the internal energy
U plus the energy gains by virtue of not being allowed to expand
minus the entropic energy TS.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
G is the difference between the heat energy and the entropic
energy.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
How does Gibbs Law relate to the First Law of
Thermodynamics?
H = U + PV
and
dH = dU + PdV + VdP
substitution of dU gives:
dH = T dS + V dP
substituting the above equation into the defined equation for
Gibbs free energy:
dG = V dP – S dT (14.2)
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
These relations indicate that:
the change in Gibbs free energy with respect to pressure is the
molar volume V;
the change in Gibbs free energy with respect to temperature is
minus the entropy S
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Methods of Determining Free Energy from Formation
Data
The defining equation for Gibbs free energy
G = H - TS
can be written as
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
such that the Gibbs free energy of formation ΔGf° is
ΔGf° = ΔHf° - T ΔSf° (14.3)
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Example 14.1:
Determine the Gibbs free energy of formation of anhydrite
(Calcium Sulphate)
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
Methods of Determining Free Energy from Reaction
Data
Gibbs free energy of reaction can be written as the enthalpy
change of reaction minus the entropic energy change of
reaction
ΔGRxn = ΔHRxn – TΔSRxn (14.4)
If the heat energy equals the entropic energy
ΔHRxn = TΔSRxn
then
ΔGRxn = 0
and there is no reaction.
We can now determine whether a given reaction will occur if we
know H and S, and both of these are measurable or can be
calculated.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
If ΔGRxn < 0; Gibbs free energy of the products is lower than the
Gibbs free energy of the reactants, and the reaction moves to
produce more products.
If ΔGRxn > 0; Gibbs free energy of the products is greater than
the Gibbs free energy of the reactants, and the reaction moves
to produce more reactants.
Example 14.2:
Determine the Gibbs free energy for the following reaction at
STP.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
2023
You might also like
- Transformasi LaplaceDocument10 pagesTransformasi LaplacejokerNo ratings yet
- MABE-Unit-1,Subunit-1.2 Gibbs Free Energy, Endergonic & Exergonic Reactions, Standard State Free Energy Changes-ΔG, ΔG0 and ΔG'0, Relationship Between EquiDocument17 pagesMABE-Unit-1,Subunit-1.2 Gibbs Free Energy, Endergonic & Exergonic Reactions, Standard State Free Energy Changes-ΔG, ΔG0 and ΔG'0, Relationship Between EquiffsffgrfNo ratings yet
- What Are Free EnergiesDocument4 pagesWhat Are Free EnergiesBIBI HUDANo ratings yet
- F Thermodynamics of Metal ExtractionDocument17 pagesF Thermodynamics of Metal ExtractionRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Gen_Chem_2-Q4-Week_1Document6 pagesGen_Chem_2-Q4-Week_1Ivyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Derive The Gibbs-Duhem Equation and Give Its Applications?Document4 pagesDerive The Gibbs-Duhem Equation and Give Its Applications?kannan2030No ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy and The Spontaneity of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesGibbs Free Energy and The Spontaneity of Chemical ReactionshlvijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Gibbs-Helmholtz Equation ExplainedDocument9 pagesGibbs-Helmholtz Equation ExplainedM S HaiderNo ratings yet
- Gibb-Free-Energy LessonDocument35 pagesGibb-Free-Energy LessonJessabelle MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Physics - Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesPhysics - Second Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Duhem Equation For Extended Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesGibbs Duhem Equation For Extended Nonequilibrium ThermodynamicsSergioNo ratings yet
- Lectura FisicoquimicaDocument5 pagesLectura FisicoquimicaMaria Claudia MartinezNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free EnergyDocument4 pagesGibbs Free EnergyFernando100% (1)
- Ch16ProblemsDocument31 pagesCh16ProblemschicknaliaNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Equation Explains How Enthalpy of Reaction Varies With TemperatureDocument2 pagesKirchhoff's Equation Explains How Enthalpy of Reaction Varies With TemperatureRajesh Jadhav100% (1)
- Bio EnergeticsDocument50 pagesBio EnergeticsAkinleye peterNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - ApuntesDocument13 pagesThermodynamics - ApuntescerenautaNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law ExplainedDocument3 pagesHess's Law ExplainedSyed Waqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free EnergyDocument8 pagesGibbs Free EnergyAditya ShanmukhaNo ratings yet
- Gibbs (Free) EnergyDocument6 pagesGibbs (Free) EnergySantino MusaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 IM Chang 11eDocument4 pagesChapter 17 IM Chang 11eSelma MeloNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q4 Week 1 1Document12 pagesGen Chem 2 Q4 Week 1 1Andrhea Peralta100% (1)
- 1-Intr To Meta 2023-2024Document36 pages1-Intr To Meta 2023-2024lou765500No ratings yet
- The Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)Document15 pagesThe Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)MANISHNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free EnergyDocument4 pagesGibbs Free Energyzakirno19248No ratings yet
- KJM4120 Ch3 Defect EquilibriaDocument31 pagesKJM4120 Ch3 Defect EquilibriaMohamed Elsherif100% (1)
- Free Energy, Entropy and SpontaneityDocument4 pagesFree Energy, Entropy and SpontaneityKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Need For Free Energy FunctionDocument3 pagesNeed For Free Energy FunctionMadhavanIceNo ratings yet
- Gibbs-Duhem Equation ExplainedDocument2 pagesGibbs-Duhem Equation ExplainedSiddharth SureshNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Duhem EquationDocument1 pageGibbs Duhem EquationSiddharth SureshNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#7Document15 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#7Maqsood Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
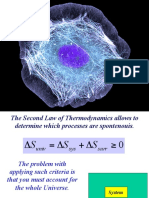
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics allows to determine which processes are spontenouisDocument12 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics allows to determine which processes are spontenouisBelaliaNo ratings yet
- Topic 17Document5 pagesTopic 17Er. Sanjay SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Thermodynamics Test Paper QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter-6 Thermodynamics Test Paper QuestionsNevin ShajiNo ratings yet
- The Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)Document11 pagesThe Gibbs Function (Gibbs Energy)saadNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Crib SheetDocument5 pagesPhysical Chemistry Crib SheetMuhammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Mysteries: FugacityDocument14 pagesThermodynamic Mysteries: FugacityAmro Ismail KashtNo ratings yet
- Alberty 1997Document10 pagesAlberty 1997rosendo rojas barraganNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium ChapterDocument17 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chapter강정우No ratings yet
- LESSON 05 Unit 04 Gibbs Free EnergyDocument9 pagesLESSON 05 Unit 04 Gibbs Free EnergyalvrzmjNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy S&G 06Document13 pagesEnthalpy S&G 06OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Cet-I Unit 4Document22 pagesCet-I Unit 4mathanm1101No ratings yet
- Mid Term3 Review 15Document32 pagesMid Term3 Review 15Jeremy SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Sem2 - 20142015Document32 pagesWeek 11 - Sem2 - 20142015HakashiMirudoNo ratings yet
- 3 Entropy NotesDocument23 pages3 Entropy NotesZubaer Rahman0% (1)
- MH Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions (Chemical Thermodynamics)Document6 pagesMH Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions (Chemical Thermodynamics)Gaming with MokshithNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة السابعةDocument12 pagesالمحاضرة السابعةZaynab JasimNo ratings yet
- 14 - Thermodynamics and MetamorphismDocument17 pages14 - Thermodynamics and MetamorphismsundalmixmailNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operation Part - 1Document7 pagesMass Transfer Operation Part - 1mohammed mahadi.aNo ratings yet
- HessDocument3 pagesHessDuchesne SarzaÜNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument10 pagesScriptNamrata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Combustion EngineeringDocument196 pagesCombustion Engineeringdivakarshettyas4029100% (2)
- Chemical PotentialDocument32 pagesChemical PotentialchomNo ratings yet
- Directions: Define The Following Terms Below. Write Your Answer Inside The BoxDocument5 pagesDirections: Define The Following Terms Below. Write Your Answer Inside The BoxLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- Ecuacionde Vant HoffDocument2 pagesEcuacionde Vant HoffJr.JeanNo ratings yet
- The Third Law of Thermodynamics2Document30 pagesThe Third Law of Thermodynamics2Ivvani Aulia PutriNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesGibbs Free Energy: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaglh00No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 NozzlesDocument13 pagesChapter 16 NozzlesAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument20 pagesReciprocating Air CompressorsAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Air CompressorsDocument20 pagesReciprocating Air CompressorsAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Heat EffectsDocument16 pagesCH 13 Heat EffectsAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- CH 10 - Steam As A Working FluidDocument9 pagesCH 10 - Steam As A Working FluidAshleen MarshallNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension StrategiesDocument67 pagesReading Comprehension StrategiesKumar ChetanNo ratings yet
- GTU Affiliated L.D. College of Engineering Report on Online Hotel Management SystemDocument16 pagesGTU Affiliated L.D. College of Engineering Report on Online Hotel Management Systemyashvant thakkarNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Nature of MathematicsDocument3 pagesMeaning and Nature of MathematicsCyril KiranNo ratings yet
- Hospital Visit ReportDocument8 pagesHospital Visit ReportSuraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- F Chart Method Klein Duffie BeckmanDocument10 pagesF Chart Method Klein Duffie BeckmansergioNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Possession - ComplaintDocument5 pagesRecovery of Possession - ComplaintBleizel TeodosioNo ratings yet
- 206841Document1 page206841VinceOnikaa PerryGermanottaNo ratings yet
- Case Application (New Pay Plan) Alizay Waheed Kayani 24347Document2 pagesCase Application (New Pay Plan) Alizay Waheed Kayani 24347Alizay KayaniNo ratings yet
- Feasibility and CONOPSDocument64 pagesFeasibility and CONOPSGhaziAnwarNo ratings yet
- OLD ENGLISH LITERATURE: ELEGIES, RELIGIOUS POEMS, RIDDLES, AND CHARMSDocument6 pagesOLD ENGLISH LITERATURE: ELEGIES, RELIGIOUS POEMS, RIDDLES, AND CHARMSCodruța Elena CociugNo ratings yet
- F&P Level IndicatorsDocument23 pagesF&P Level IndicatorsBen100% (1)
- A Study On Marketing Practices in Select PDFDocument137 pagesA Study On Marketing Practices in Select PDFSadik SadikaramaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Halligan Tuning PDF Zip PDFDocument341 pages2 Halligan Tuning PDF Zip PDFZHNo ratings yet
- 1997 Can LIIDocs 166Document22 pages1997 Can LIIDocs 166BababooeyNo ratings yet
- Core 13 UcspDocument3 pagesCore 13 UcspJanice DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sacred SpaceDocument440 pagesSacred SpaceAbdiel Cervantes HernandezNo ratings yet
- 11 Letter WordsDocument637 pages11 Letter WordstrakdsNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Understanding Culture and Cultural Changes in IndiaDocument45 pagesLec 4 - Understanding Culture and Cultural Changes in Indiabrokenheart1984No ratings yet
- I Began My Training in The Martial AlexandriaDocument2 pagesI Began My Training in The Martial AlexandriagerplaNo ratings yet
- LT033 PDFDocument38 pagesLT033 PDFAlexandr ChuvakovNo ratings yet
- 2 Saliva PhysiologyDocument20 pages2 Saliva PhysiologyvelangniNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ArtDocument2 pagesContemporary ArtXpertz PrintingNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Face Stability PDFDocument208 pagesTunnel Face Stability PDFnumspyNo ratings yet
- MNM3711 International MarketingDocument70 pagesMNM3711 International MarketingKefiloe MoatsheNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDocument13 pagesPROGRAMMING 11 - Q1 - W2 - Mod2 PDFDianne Brucal - MatibagNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Sasmo: secθ + tanθ = q, secθ q. q q q qDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Sasmo: secθ + tanθ = q, secθ q. q q q qAje GhazaNo ratings yet
- Constructing Worlds Photography and ArchDocument6 pagesConstructing Worlds Photography and ArchRodrigo AlcocerNo ratings yet
- Final Merit List of FCPS II Subspecialty Med Allied and Surgery Allied Induction January 2024 1Document5 pagesFinal Merit List of FCPS II Subspecialty Med Allied and Surgery Allied Induction January 2024 1javedkakajNo ratings yet
- REVLONDocument20 pagesREVLONUrika RufinNo ratings yet
- Labor JurisdictionDocument37 pagesLabor JurisdictionChoystel Mae Artigas100% (1)