Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joeselle Anne SampagaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joeselle Anne SampagaCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Bio Reviewer II.
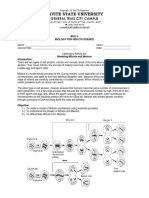
Characteristics of Life
Biology is defined as the study of life. 1. Order - All living things are made up of
Greek words “bios” meaning life one or more cells. Living things are highly
organized and coordinated structures.
“logos” meaning reason or study.
2. Reproduction and Heredity - Living
Divine Creation Theory organisms are able to reproduce by
duplicating their DNA and forming new
- supernatural power of divine being.
cells. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA, the
Extra Terrestrial Origin by Svante Arrhenius material made up of chromosomes that
passes down the genetic information.
- belief that life originated on another planet
outside the Solar System. 3. Growth and Development - Organisms
grow and develop following specific
- meteors or other extraterrestrial bodies. instructions coded for by their genes.
Theory of Biogenesis 4. Sensitivity or Responses - Organisms tend
Francesco Redi to respond and cope up with various external
factors or different environmental stresses.
- belief that life originates from pre-existing
life. Homeostasis - able to regulate internal
environment to maintain appropriate
- maggots in a decaying meat experiment conditions within the body.
"Omne vivum ex vivo" which means “all Thermoregulation - maintaining a specific
life comes from life”. body temperature responsive to
environmental changes.
Theory of Abiogenesis
5. Evolutionary Adaptation - have the ability
- The belief that life arose from inanimate
to adapt and interact with their surroundings
matter after Earth had cooled.
in order to survive and reproduce.
Aleksandr Ivanovich Oparin - John Burton
Permanent - Evolution, Temporary -
Haldane's Theory
Adaptation
“primordial soup theory”
6. Energy Utilization - able to consume and
Stanley Miller - Harold Urey's Experiment convert energy from sun and food for the
following purposes.
III. Cell Biology 1833 - Robert Brown - nucleus in plant cell,
importance of cell creation.
A. Cell Theory - established unifying
standards in the field of biology. 1838 - Matthias Jakob Schleiden - plant
tissues are composed of cell
Cell - basic unit of life
1839 - Theodor Schwann - animal tissues
Unified Cell Theory - Matthias Schleiden are also composed of cell.
(botanist) and Theodor Schwann (zoologist)
- proposed the UCT. 1845 - Carl Heinrich Braun - 2nd part of the
cell theory.
* All organisms are composed of one or
more cells. Cell is the basic unit of life in all 1855 - Rudolf Virchow - 3rd part of the cell
living things. All cells are produced by the theory, stated that cells only come from
division of pre-existing cells. living things.
37.2 Trillion Cells in Human Body Types of Cell
Modern Cell Theory Prokaryotes - Bacterial Cells, do not have a
nucleus, single-celled.
- heredity --- DNA (all cells have chemical
composition and metabolic activities). Eukaryotes - (Plant, Animal, Fungal Cells)
single-celled or multi-celled, has a nucleus.
Uses of Cell
Prokaryotic Cell - first form of life, asexual,
- Disease / Health Medical Research and simpler and smaller, do not have nuclei,
Cures mitochondria, chloroplasts.
- Able to understand how organisms are Binary Fission - divides and duplicates the
created, grow, and die. DNA
Cell Theory Summary - Spherical, Rod-like, Spiral Shape
1596 - Zacharias Jensen - first compound - Plasmids - small circular sections of DNA
microscope, spectacle maker in cytoplasm
1655 - Robert Hooke - a monk, discovered Eukaryotic Cell - larger, have specialized
and coined the term "cell" and viewed the organelles, membrane-bound nucleus,
corks of the cell wall. Used Jensen's enclosing the chromosomes, sexual
Microscope
Chromosomes - thread-like structure made
1670 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek - lenses of up of DNA
microscope, see and draw the first cell
image in 1975 23 pair, 46 total of chromosomes in human
body
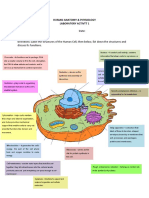
Fungal Cell - similar to plant and animal Anatomy of Animal Cells
Chitin - forms a rigid cell wall between the Lysosomes – digests
cell for correting their shape. Nucleus – control center
Plant and Animal Cells Endoplasmic Reticulum – Lipids/fats, helps
Golgi Bodies function.
Always present in both cells - Cell
membrane, nucleus, nucleoluis, endoplasmic Golgi Bodies (Apparatus) – transports
reticlum, ribosomes, vacuole, mitochondria, proteins
golgi bodies, Nucleolus – production of ribosomes
Always present in Plant Cells - Chloroplasts, Nuclear Envelope – bilayer membrane,
Cell Wall, Plasmodesmata protects the nucleus.
Always present in Animal Cells - Centrioles, Chromosomes – DNA, for traits and
Lysosomes, Centrosomes characteristics
Plant Cell Anatomy
Mitochondria – powerhouse, breaks down
food molecules to make ATP.
ATP – sugar/glucose
Vacuole/Vesicles – fluid, jelly-like,
transport, storage of the cell.
Plants absorbs energy from the sun and Parts of Chloroplasts
convert it into chemical energy through
Chloroplast – actual sites of photosynthesis
photosynthesis.
Thylakoid – small disk-like, compartment
Animals consume food to acquire usable
which contains the chlorophyll.
energy.
Stroma – inner liquid portion of the
Organelles and Its Function
chloroplast
ORGANELLES are macromolecules within
Non-Membrane-Bound Organelles
the cells which are specialized to perform
specific functions. Ribosome- sites of protein production
Centrioles – move chromosomes around
during cell division.
Cell wall – protects plasma membrane, thick
outer layer made that provide structure and
shape to the cell.
Cell Membrane – plasma membrane, Cilia – short, hair-like structures, move in a
contains contents of the cell, barrier and wave-like rhythmic motion, play a vital role
controller. in cell cycle, cell replication, and daily
development of humans and animals.
Cytoplasm – liquid part of the cell, protects
the cell by keeping all the organelles Flagella - are long whip like structures used
separate from each other. for movement.
Cellular Modification Villi and Microvilli - Villi are finger-like
projections that arise from the epithelial
- Some animal and plant cells undergo layer in some organs. Microvilli are smaller
modification to perform specialized projections that arise from the cell’s surface
functions that promote survival. that also increase surface area allowing
faster and more efficient absorption.
Trichomes - outgrowth of the epidermal
layer that occur on the plant shoot and on Pseudopods - Temporary irregular lobes
the surfaces of the stems and leaves, plays formed by amoebas and some other
important role in heat regulation and water eukaryotic cells used for movement, also
balance. The presence of trichomes can known as false feet. It bulges outward to
make plats prickly or hairy. move the cell or engulf prey.
Root hairs – tip-growing extensions of root
epidermal cells, enhances the ability of the
plant to uptake and absorbs nutrients.
You might also like
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDocument10 pages7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- Pre-test and Post-test ResultsDocument4 pagesPre-test and Post-test ResultsJM MyrtesNo ratings yet
- 21st - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pages21st - 2nd Quarter ReviewerHailie ImperialNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature from the PhilippinesDocument2 pages21st Century Literature from the PhilippinesEvelyn MagbarilNo ratings yet
- Holistic Point of View Partial Point of ViewDocument2 pagesHolistic Point of View Partial Point of ViewFaye MartinezNo ratings yet
- Immaculate Conception Polytechnic Immaculate Conception PolytechnicDocument2 pagesImmaculate Conception Polytechnic Immaculate Conception PolytechnicCharles Sunga100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesGen Bio 1 ReviewerGracia Mae GaciasNo ratings yet
- EAPPREVIEWERDocument4 pagesEAPPREVIEWERIsha GuroNo ratings yet
- 12 Creative Writing Reviewer (1-7)Document6 pages12 Creative Writing Reviewer (1-7)Blessy Myl MagrataNo ratings yet
- Department of Education (Deped)Document6 pagesDepartment of Education (Deped)MARIAN TIMTIMANNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature from Europe and BeyondDocument48 pages21st Century Literature from Europe and BeyondRafaela OngNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework: Importance of Scientific CalculatorDocument3 pagesConceptual Framework: Importance of Scientific CalculatorALLIA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Quarter 2Document11 pages21st Century Quarter 2Al-kyendi IndasanNo ratings yet
- Canonical Authors and Works of Philippine National Artists in LiteratureDocument19 pagesCanonical Authors and Works of Philippine National Artists in LiteratureCris Gacuan0% (1)
- Reading and Writing (4th QTR)Document14 pagesReading and Writing (4th QTR)Sherilyn DiazNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER IN 21st CLPWDocument5 pagesREVIEWER IN 21st CLPWhayme JamesNo ratings yet
- Regional Literature: 21 CenturyDocument59 pagesRegional Literature: 21 CenturyJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 WEEK 2.2: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument4 pagesQuarter 1 WEEK 2.2: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldcarloNo ratings yet
- HOMEof The AshfallDocument4 pagesHOMEof The AshfallJohn John EstiponaNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ReviewerJhon Vincent Draug PosadasNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Lit Q1 Module2 EditedDocument11 pages21st Century Lit Q1 Module2 EditedKhleaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Q1 Module 1 Lesson 3 - CantreDocument2 pages21st Century Q1 Module 1 Lesson 3 - CantreJames Andrei CantreNo ratings yet
- Lopez, Azzia-Stem-IngenuityDocument30 pagesLopez, Azzia-Stem-IngenuityALLIA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- September 3 Colonialisms and CosmopolitanismsDocument4 pagesSeptember 3 Colonialisms and Cosmopolitanismsbea locsinNo ratings yet
- 21clpw ReviewerDocument8 pages21clpw ReviewerpatNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Exploring World LiteratureDocument24 pages21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Exploring World LiteratureJa-dey Harvey JacusalemNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature from the Philippines and BeyondDocument7 pages21st Century Literature from the Philippines and BeyondneaNo ratings yet
- Overcoming adversity through literatureDocument9 pagesOvercoming adversity through literatureLILIAN ROSE DE LARANo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literary Genres OverviewDocument4 pages21st Century Literary Genres OverviewVicki Punzalan100% (1)
- Competency Calendar For Creative WritingDocument3 pagesCompetency Calendar For Creative WritingJS SocoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Q1 21st CenturyDocument30 pages2 - Q1 21st CenturyRemmy Lyn MadesNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World: Quarter 1-Module 3 Elements of Philippine Literary GenresDocument18 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World: Quarter 1-Module 3 Elements of Philippine Literary GenresSicnarf RolagNo ratings yet
- 21STDocument2 pages21STJohn Christopher SantosNo ratings yet
- SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL: 21st Century Literature Teaching From The Philippines and The WorldDocument6 pagesSENIOR HIGH SCHOOL: 21st Century Literature Teaching From The Philippines and The Worldkarizajean desalisaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument3 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldEdwin Peralta IIINo ratings yet
- Exogenic and Endogenic Processes NotesDocument10 pagesExogenic and Endogenic Processes NotesMargaret SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Personal Development - Grade 11 PrefinalsDocument11 pagesPersonal Development - Grade 11 PrefinalsPedro HampaslupaNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument10 pages21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldLorinel MendozaNo ratings yet
- 21st-Century-Literature-Q4-Module 1Document8 pages21st-Century-Literature-Q4-Module 1Conrado AreolaNo ratings yet
- Cwmodule5.1 OkDocument16 pagesCwmodule5.1 OkPeng LatosaNo ratings yet
- Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationships: Tree of Life and SystematicsDocument2 pagesSystematics Based On Evolutionary Relationships: Tree of Life and SystematicsPatricia PascualNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World AS Q1Document14 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World AS Q1Gemma Garzon ColasNo ratings yet
- Poetry Elements and GenresDocument8 pagesPoetry Elements and Genresnelia abuevaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century ReviewerDocument4 pages21st Century ReviewerMeljean MurilloNo ratings yet
- Reading & Writing (As) Woman 2Document25 pagesReading & Writing (As) Woman 2Noelle Leslie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EDITED Q1 Module 2 Lesson 2 (Recovered 1)Document22 pagesEDITED Q1 Module 2 Lesson 2 (Recovered 1)Beata Virgo MariaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Division of Bohol Department of Education Region VII, Central VisayasAiram Cristine MargateNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Document20 pages1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Alexa Julienne RazNo ratings yet
- (M5S2-POWERPOINT) Apo On The Wall by BJ PatinoDocument13 pages(M5S2-POWERPOINT) Apo On The Wall by BJ PatinoAlthea Angela BulaclacNo ratings yet
- Eapp - Module 7, 8,9Document9 pagesEapp - Module 7, 8,9mary roseNo ratings yet
- San Pablo Catholic Schools Research ModuleDocument8 pagesSan Pablo Catholic Schools Research ModuleAdrian James NaranjoNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century Literature Week1Document13 pages21ST Century Literature Week1Justine Mae AlveroNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Sept. 17-Sept .22 - 2018 Week 11Document3 pages21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Sept. 17-Sept .22 - 2018 Week 11BernadettePimentelNo ratings yet
- General Santos Doctors' Medical School Foundation, Inc.: Day 1 Day 2Document3 pagesGeneral Santos Doctors' Medical School Foundation, Inc.: Day 1 Day 2Zerimar RamirezNo ratings yet
- Exploring Oppression and Hope in Cirilo F. Bautista's PoetryDocument20 pagesExploring Oppression and Hope in Cirilo F. Bautista's PoetryMariel C. RamosNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes: Name: DateDocument2 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes: Name: DateMacky Diago0% (1)
- Philo Lesson 6Document72 pagesPhilo Lesson 6Reziel RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lengua para Diablo (The Devil Ate My Words) : (Excerpt From Banana Heart Summer)Document14 pagesLengua para Diablo (The Devil Ate My Words) : (Excerpt From Banana Heart Summer)Tim CabralNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Week 2) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonDocument5 pagesLecture 3 (Week 2) : BIOLOGY 201/winter 2018 Dr. Ian FergusonMohammad FotovatNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Activity LabDocument4 pagesCell Division Activity LabSEAN LIBOTNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cells JeopardyDocument55 pagesCells Jeopardyapi-308745623No ratings yet
- Mitosis Cell Division Flash CardsDocument1 pageMitosis Cell Division Flash CardsMark Roger BasilioNo ratings yet
- As Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Document7 pagesAs Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Anonymous fFKqcYNo ratings yet
- Jilbert B. Gumaru, LPTDocument85 pagesJilbert B. Gumaru, LPTJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 4Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 4Ennyliejor Yusay100% (1)
- 4 RNA TransportDocument35 pages4 RNA TransportUmar KhitabNo ratings yet
- Jeopardy GameDocument51 pagesJeopardy Gameapi-459420090No ratings yet
- The Human CellDocument1 pageThe Human CellAira Viloria Orbillo100% (1)
- Cell-Y-Wood Presentation-2Document11 pagesCell-Y-Wood Presentation-2api-358704014No ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument47 pagesPlant CellIraanurainiNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Coloring RevisedDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell Coloring RevisedjosieA_123No ratings yet
- Week 2 The CellsDocument7 pagesWeek 2 The Cells2F - MACAO, KHALILANo ratings yet
- Mdcat Bio W 2Document10 pagesMdcat Bio W 2Benzeen AromaticNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth & Life ScienceEHdz D. JameraNo ratings yet
- Systematic "A" Level Biology. Basic and Simplified Revision NotesDocument458 pagesSystematic "A" Level Biology. Basic and Simplified Revision NotesNelima Stella mercy100% (2)
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8Document15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8lavanya rajaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesScience 7 - Summative Test - Q2 - Week 1-Week 4 - SY 2021-2022Lenette AlagonNo ratings yet
- The main functions and structure of centrioles in cell divisionDocument2 pagesThe main functions and structure of centrioles in cell divisiontherese lamelaNo ratings yet
- Template DLP BioenergeticsDocument9 pagesTemplate DLP Bioenergeticsargie joy marie100% (1)
- Pro Vs EukDocument8 pagesPro Vs Eukapi-550959437No ratings yet
- Business Foundation: SAMI Academy of Excellence SAMI Academy of ExcellenceDocument31 pagesBusiness Foundation: SAMI Academy of Excellence SAMI Academy of ExcellenceTabish KhanNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology IDocument4 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology IGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio ReviewerCaptain YooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide ADocument3 pagesChapter 7 Bio Test Study Guide ARachel FrankenfieldNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis in Animal CellsDocument91 pagesStages of Mitosis in Animal CellsZakir KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsDocument16 pages1 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsBarnavo DasNo ratings yet
- Cabrera-Guiding Endosomal Maturation - 2010-CellDocument3 pagesCabrera-Guiding Endosomal Maturation - 2010-CellMargarita CabreraNo ratings yet