Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.4 The Science of My Toys
Uploaded by
NT ARTITISARIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.4 The Science of My Toys
Uploaded by
NT ARTITISARICopyright:
Available Formats
School Name : SPK PRIMARY GLOBAL INBYRA
Subject : SCIENCE
Teacher’s Name : NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Grade/ Semester : 1/1
Topic : Toy sorting
Date :
Period : 2 x 30 Minutes
Session :
Learning Objectives 1Cm.01 Identify, name, describe, sort and group common materials, including
wood, plastic, metal, glass, rock, paper and fabric.
1TWSc.01 Sort and group objects, materials and living things based on
observations of the similarities and differences between them.
1TWSc.05 Collect and record observations and/or measurements by annotating
images and completing simple tables.
Success Criteria
Prior Learning Learners would benefit from exposure to the broad range of vocabulary used for
describing properties of materials by hearing them used in everyday contexts.
Skills and Character Building
21 Century Skills
st
Pancasila Student Profile
The twelve 21st Century skills are: The Pancasila Student Profile consists of 6
1. Critical thinking competencies (dimensions) namely
2. Creativity 1. Faith, fear of God Almighty and noble
3. Collaboration character,
4. Communication 2. Global Diversity,
5. Information literacy 3. Mutual Cooperation (gotong royong),
6. Media literacy 4. Creativity,
7. Technology literacy 5. Critical thinking, and
8. Flexibility 6. Independent.
9. Leadership
10. Initiative
11. Productivity
12. Social skills
Learning Sequences
Lesson Activity Resources
Introduction Teacher greets, prays and checks the attendance of learners.
Teacher boosts the mood of the learners by doing warm up activity.
Main Activity Toy sorting Wide
selection
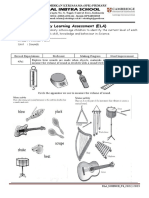
Gather a range of different kinds of toys for this activity, including metal, of toys
plastic and wooden toys; stuffed animals and toys that require batteries. Either made from
use a selection of toys at school or learners can bring in their own toys from a range of
home. materials
that are
Give learners the opportunity to share their toys with each other and talk about familiar to
their features. Then focus the discussion by asking them what materials they are learners.
made from and how they compare to those of their peers.
Is your toy made of more than one material?
Can you name any of the materials your toy is made of?
Is there anyone else who has a toy made of the same material?
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Next ask learners to stand with someone whose toy has a material in common
with theirs, then organise themselves into groups according to what materials
they are made of. Why have you chosen to stand with that person?
Are there any other groups you could join?
Which group has the most toys in?
Learners then record this learning by photographing sorted toys or drawing
pictures onto a simple chart.
This activity can be extended by asking learners to record their work on a Venn
diagram.
Closing Discussing Findings: Take feedback on the conclusions that learners made and
discuss if a conclusion can be made as a class.
Reflection
(Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions for your lesson.)
Next Plan :
(What will I teach next, based on learners’ understanding of this lesson?)
Support:
Give these learners planet Earth to research to increase their knowledge about something that they already
know some facts about
Extension:
Challenge these learners to find out the name of a famous scientist who discovered their planet or something
about it.
Tegal, 1 January 2023
Checked by Created by
JOEMER P.L., B.End NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Coordinator Science Teacher
Approved by
ERNA NUGRAHENING N, S.Pd.,MPd
Principal
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
School Name : SPK PRIMARY GLOBAL INBYRA
Subject : SCIENCE
Teacher’s Name : NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Grade/ Semester : 1/1
Topic : Designing a toy
Date :
Period : 2 x 30 Minutes
Session :
Learning Objectives 1Cp.01 Understand that all materials have a variety of properties
1TWSp.01 Ask questions about the world around us and talk about how to find
answers.
Success Criteria
Prior Learning Learners would benefit from exposure to the broad range of vocabulary used for
describing properties of materials by hearing them used in everyday contexts.
Skills and Character Building
21 Century Skills
st
Pancasila Student Profile
The twelve 21st Century skills are: The Pancasila Student Profile consists of 6
1. Critical thinking competencies (dimensions) namely
2. Creativity 1. Faith, fear of God Almighty and noble
3. Collaboration character,
4. Communication 2. Global Diversity,
5. Information literacy 3. Mutual Cooperation (gotong royong),
6. Media literacy 4. Creativity,
7. Technology literacy 5. Critical thinking, and
8. Flexibility 6. Independent.
9. Leadership
10. Initiative
11. Productivity
12. Social skills
Learning Sequences
Lesson Activity Resources
Introduction Teacher greets, prays and checks the attendance of learners.
Teacher boosts the mood of the learners by doing warm up activity.
Main Activity Designing a toy Selection
of toys for
Gather a range of different kinds of toys for this activity, including metal, babies or
plastic and wooden toys; stuffed animals and toys that require batteries. Either images of
use a selection of toys at school or learners can bring in their own toys from the same.
home.
Encourage learners to think of their own questions about the materials their toys
are made of.
Which materials were used for a lot of our toys?
Which materials are never used for toys?
Why do you think this is?
Show learners a selection of toys made for babies (or photographs of toys) and
ask them to discuss the materials used and why these have been chosen.
Why do you think plastic has been used?
What properties do baby toys need to have?
Support learners to come to the conclusion that toys for babies need to be sturdy
and easy to clean, or soft and smooth so as not to hurt them. Learners then
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
design their own toy for a baby, drawing it and labelling the materials used. Ask
them to explain why they have chosen these materials based on their properties.
Closing Discussing Findings: Take feedback on the conclusions that learners made and
discuss if a conclusion can be made as a class.
Reflection
(Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions for your lesson.)
Next Plan :
(What will I teach next, based on learners’ understanding of this lesson?)
Support:
Give these learners planet Earth to research to increase their knowledge about something that they already
know some facts about
Extension:
Challenge these learners to find out the name of a famous scientist who discovered their planet or something
about it.
Tegal, 1 January 2023
Checked by Created by
JOEMER P.L., B.End NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Coordinator Science Teacher
Approved by
ERNA NUGRAHENING N, S.Pd.,MPd
Principal
School Name : SPK PRIMARY GLOBAL INBYRA
Subject : SCIENCE
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Teacher’s Name : NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Grade/ Semester : 1/1
Topic : Searching for electrical objects
Date :
Period : 2 x 30 Minutes
Session :
Learning Objectives 1Pe.01 Identify things that require electricity to work.
1TWSc.05 Collect and record observations and/or measurements by annotating
images and completing simple tables.
Success Criteria
Prior Learning Learners would benefit from exposure to the broad range of vocabulary used for
describing properties of materials by hearing them used in everyday contexts.
Skills and Character Building
21 Century Skills
st
Pancasila Student Profile
The twelve 21st Century skills are: The Pancasila Student Profile consists of 6
1. Critical thinking competencies (dimensions) namely
2. Creativity 1. Faith, fear of God Almighty and noble
3. Collaboration character,
4. Communication 2. Global Diversity,
5. Information literacy 3. Mutual Cooperation (gotong royong),
6. Media literacy 4. Creativity,
7. Technology literacy 5. Critical thinking, and
8. Flexibility 6. Independent.
9. Leadership
10. Initiative
11. Productivity
12. Social skills
Learning Sequences
Lesson Activity Resources
Introduction Teacher greets, prays and checks the attendance of learners.
Teacher boosts the mood of the learners by doing warm up activity.
Main Activity Searching for electrical objects Selection
of toys,
With a selection of toys that can, again, be brought in from home or taken from including
those in school, ask learners to sort them into those that require electricity and some that
those that do not. Talk about, and explain that electricity can produce different are
effects, such as make the toys move, light up or make sounds. Then broaden the powered
discussion to objects in the classroom and learners’ homes that use electricity. by
What do you have in your bedroom that needs electricity? electricity.
What electrical objects have you used so far today?
Do all electrical things need to be plugged in?
After this, learners go on an electrical object hunt. Ideally, this will be
throughout school, enabling them to find more objects with different functions,
but it can be done within the classroom if necessary. Ask learners to record
what they find by completing a simple table.
Before setting off on the electrical object hunt, brief learners on the dangers of
plug sockets and tell them not to touch any sockets or plugs they may find.
Closing Discussing Findings: Take feedback on the conclusions that learners made and
discuss if a conclusion can be made as a class.
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Reflection
(Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions for your lesson.)
Next Plan :
(What will I teach next, based on learners’ understanding of this lesson?)
Support:
Give these learners planet Earth to research to increase their knowledge about something that they already
know some facts about
Extension:
Challenge these learners to find out the name of a famous scientist who discovered their planet or something
about it.
Tegal, 1 January 2023
Checked by Created by
JOEMER P.L., B.End NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Coordinator Science Teacher
Approved by
ERNA NUGRAHENING N, S.Pd.,MPd
Principal
School Name : SPK PRIMARY GLOBAL INBYRA
Subject : SCIENCE
Teacher’s Name : NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Grade/ Semester : 1/1
Topic : Pushes and pulls in the classroom
Date :
Period : 2 x 30 Minutes
Session :
Learning Objectives 1Pf.01 Explore, talk about and describe the movement of familiar objects.
1Pf.02 Describe pushes and pulls as forces.
1TWSc.01 Sort and group objects, materials and living things based on
observations of the similarities and differences between them.
Success Criteria
Prior Learning Learners would benefit from exposure to the broad range of vocabulary used for
describing properties of materials by hearing them used in everyday contexts.
Skills and Character Building
21 Century Skills
st
Pancasila Student Profile
The twelve 21st Century skills are: The Pancasila Student Profile consists of 6
1. Critical thinking competencies (dimensions) namely
2. Creativity 7. Faith, fear of God Almighty and noble
3. Collaboration character,
4. Communication 8. Global Diversity,
5. Information literacy 9. Mutual Cooperation (gotong royong),
6. Media literacy 10. Creativity,
7. Technology literacy 11. Critical thinking, and
8. Flexibility 12. Independent.
9. Leadership
10. Initiative
11. Productivity
12. Social skills
Learning Sequences
Lesson Activity Resources
Introduction Teacher greets, prays and checks the attendance of learners.
Teacher boosts the mood of the learners by doing warm up activity.
Main Activity Pushes and pulls in the classroom Selection
of toys
With a selection of toys that move or have moving parts (e.g. cars, dolls and that move,
toys with buttons), discuss with learners how they can be made to move, using set of
the language of push and pull throughout. ‘push’ and
What could you do to make your toy move? ‘pull’
What will happen if you push your toy? word cards
Does anyone have a toy that turns, spins or jumps? for each
learner or
From this, lead the discussion onto other familiar objects that move when pair of
pushed or pulled (e.g. doors, chairs, drawers). learners
(learners
Give learners cards that say ‘push’ and ‘pull’ and ask them to label objects in could
the classroom that can be pushed or pulled. After giving them a moment to find make
these objects, ask them to explain why they have placed their cards where they these
have done. themselve
How does that move when you push it? s).
Can your object be pushed as well as pulled?
Closing Discussing Findings: Take feedback on the conclusions that learners made and
discuss if a conclusion can be made as a class.
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Reflection
(Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions for your lesson.)
Next Plan :
(What will I teach next, based on learners’ understanding of this lesson?)
Support:
Give these learners planet Earth to research to increase their knowledge about something that they already
know some facts about
Extension:
Challenge these learners to find out the name of a famous scientist who discovered their planet or something
about it.
Tegal, 1 January 2023
Checked by Created by
JOEMER P.L., B.End NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Coordinator Science Teacher
Approved by
ERNA NUGRAHENING N, S.Pd.,MPd
Principal
School Name : SPK PRIMARY GLOBAL INBYRA
Subject : SCIENCE
Teacher’s Name : NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Grade/ Semester : 1/1
Topic : Exploring magnets
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
Date :
Period : 2 x 30 Minutes
Session :
Learning Objectives 1Pe.02 Explore, talk about and describe what happens when magnets approach
and touch different materials.
1TWSp.02 Make predictions about what they think will happen.
Success Criteria
Prior Learning Learners would benefit from exposure to the broad range of vocabulary used for
describing properties of materials by hearing them used in everyday contexts.
Skills and Character Building
21st Century Skills Pancasila Student Profile
The twelve 21st Century skills are: The Pancasila Student Profile consists of 6
1. Critical thinking competencies (dimensions) namely
2. Creativity 1. Faith, fear of God Almighty and noble
3. Collaboration character,
4. Communication 2. Global Diversity,
5. Information literacy 3. Mutual Cooperation (gotong royong),
6. Media literacy 4. Creativity,
7. Technology literacy 5. Critical thinking, and
8. Flexibility 6. Independent.
9. Leadership
10. Initiative
11. Productivity
12. Social skills
Learning Sequences
Lesson Activity Resources
Introduction Teacher greets, prays and checks the attendance of learners.
Teacher boosts the mood of the learners by doing warm up activity.
Main Activity Exploring magnets Selection
of
Allow learners to freely explore a range of differently-shaped magnets and differently
magnetic toys (e.g. magnetic letters, train carriages that join with magnets). -sized
Discuss with them what they can see happening while they play. magnets
What happens when one magnet goes near another magnet? and
Can you make a magnet move without touching it? magnetic
Can you push these two magnets together? toys,
selection
Bring learners back together as a class to share their observations with one of small
another. magnetic
Have they noticed any patterns in the materials that magnetic toys are made of? and
non-magn
Introduce learners to the terms ‘attract’ and ‘repel’ and demonstrate each clearly etic
with the magnets. Then show learners a small, magnetic object such as a coin objects
(or paper clip and ask them to predict what will happen when a magnet (include
approaches it. Model moving the magnet slowly towards the object until it is some
attracted to and moves towards the magnet. Repeat this with a non-magnetic metal
object asking learners to first make a prediction and then move the magnet objects
towards the object until they are touching. that are
not
Learners then repeat this themselves with small objects made of a range of magnetic).
different, familiar materials. Learners, using a pre-made table, record their
simple predictions about what they think will happen. They then test each
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
object. As they work, talk to them about what they have seen, and whether or
not their predictions were correct.
What happened when you tested the marble?
What materials are the magnetic objects made from?
Were all the metal objects attracted to the magnet?
Reinforce with the learners that magnets do not stick to anything. Instead, an
invisible force from the magnet can attract or repel materials. Learners will also
discover that a magnet does not affect some materials.
Closing Discussing Findings: Take feedback on the conclusions that learners made and
discuss if a conclusion can be made as a class.
Reflection
(Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most relevant questions for your lesson.)
Next Plan :
(What will I teach next, based on learners’ understanding of this lesson?)
Support:
Give these learners planet Earth to research to increase their knowledge about something that they already
know some facts about
Extension:
Challenge these learners to find out the name of a famous scientist who discovered their planet or something
about it.
Tegal, 1 January 2023
Checked by Created by
JOEMER P.L., B.End NT ARTITISARI, S.S., M.Pd.
Coordinator Science Teacher
Approved by
ERNA NUGRAHENING N, S.Pd.,MPd
Principal
SC IENCE1 - NT ARTI TISAR I, S.S. , M .Pd. Page 10
You might also like
- Lesson Plan in Science 5 - FinalDocument207 pagesLesson Plan in Science 5 - FinalMaida Macabantog100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science Grade 4Document194 pagesLesson Plan in Science Grade 4hasnifa100% (44)
- Warm and Toasty Newsletter - Issue 14 - December 2021Document12 pagesWarm and Toasty Newsletter - Issue 14 - December 2021Johnno CassonNo ratings yet
- Regional Test Item Bank Filipino Grade 8: Department of EducationDocument1 pageRegional Test Item Bank Filipino Grade 8: Department of EducationManolet PinedaNo ratings yet
- Respect is Important for All AgesDocument2 pagesRespect is Important for All AgesMoriahbbc StaTeresitaNo ratings yet
- District SchoolID SchLibProfileDocument6 pagesDistrict SchoolID SchLibProfileMinorka Riego LarañoNo ratings yet
- The Strongest One: Author: Ilustrator:. Genre: Setting: Main Characters: Beginning MiddleDocument1 pageThe Strongest One: Author: Ilustrator:. Genre: Setting: Main Characters: Beginning MiddleKarina AyalaNo ratings yet
- Bones Protect OrgansDocument349 pagesBones Protect OrgansGolden Sunrise100% (1)
- COT DLP in Science 4Document2 pagesCOT DLP in Science 4Ronnie Tienzo Villanueva Jr.0% (1)
- Erosion Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesErosion Lesson Plan3kara_nance7069No ratings yet
- 1Cm.01 1Twsc.01: How Does It Feel? Have You Seen This Material Before?Document16 pages1Cm.01 1Twsc.01: How Does It Feel? Have You Seen This Material Before?NT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- 1.5 Staying AliveDocument9 pages1.5 Staying AliveNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- 1.3 Growing StrongDocument10 pages1.3 Growing StrongNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- Name: Sydney Bull Grade: Kindergarten/ Grade 1 Draft Unit Planning TemplateDocument6 pagesName: Sydney Bull Grade: Kindergarten/ Grade 1 Draft Unit Planning Templateapi-339858952No ratings yet
- Naming and Describing Body Parts in HumansDocument17 pagesNaming and Describing Body Parts in HumansNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- ExplainDocument3 pagesExplainapi-409531048No ratings yet
- Fundamentals Unitplan Science Grade1Document15 pagesFundamentals Unitplan Science Grade1api-616056306No ratings yet
- My approach to teaching for effective placesDocument12 pagesMy approach to teaching for effective placesLauren JacksonNo ratings yet
- G U3 W3 Read Aloud 3.2 Homes Around The WorldDocument4 pagesG U3 W3 Read Aloud 3.2 Homes Around The WorldSherif MohamedNo ratings yet
- Creative Plant LessonDocument3 pagesCreative Plant Lessonapi-469160289No ratings yet
- Curricular Connections Big Ideas Essential QuestionsDocument6 pagesCurricular Connections Big Ideas Essential Questionsapi-520314380No ratings yet
- Final Light and Shadow Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesFinal Light and Shadow Lesson Planapi-527907054No ratings yet
- Конспект урока по английскому языку для 8 класса - Tamgaly petroglyphs -Document3 pagesКонспект урока по английскому языку для 8 класса - Tamgaly petroglyphs -Yessenali AmetovNo ratings yet
- Ece Planning DocumentDocument16 pagesEce Planning Documentapi-357305515No ratings yet
- Lesson Three FPDDocument3 pagesLesson Three FPDapi-350044445No ratings yet
- General Plan Academic Content Standard/s: History and Social Studies Grade 2Document5 pagesGeneral Plan Academic Content Standard/s: History and Social Studies Grade 2api-542904320No ratings yet
- Reflection Planner Uoi 3 Pre K BDocument4 pagesReflection Planner Uoi 3 Pre K Bapi-281133792No ratings yet
- ED508-5E Lesson Plan #1 Writing & ScienceDocument3 pagesED508-5E Lesson Plan #1 Writing & ScienceBethony JohnsonNo ratings yet
- DaniellaDocument2 pagesDaniellaapi-618921058No ratings yet
- General Plan Academic Content Standard/s: History and Social Studies Grade 2Document5 pagesGeneral Plan Academic Content Standard/s: History and Social Studies Grade 2api-542904320No ratings yet
- Learning Task 5 PortfolioDocument6 pagesLearning Task 5 PortfolioRamo, Shajani Klare J.No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template Birds JournalDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Template Birds Journalapi-613934482No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4Document4 pagesLesson Plan 4api-307141452No ratings yet
- MS SCI 102-Lesson 4Document3 pagesMS SCI 102-Lesson 4Jervyn Guianan100% (2)
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan TemplateDocument7 pagesUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan Templateapi-403531466No ratings yet
- Curriculum - Science Stage 4 - Lesson PlansDocument28 pagesCurriculum - Science Stage 4 - Lesson Plansapi-435765102No ratings yet
- Learning Plan On Science 5: Preliminary PartDocument2 pagesLearning Plan On Science 5: Preliminary PartDevin Joshua WintersNo ratings yet
- Scsu Coeld Edtpa Lesson Plan Template 1Document4 pagesScsu Coeld Edtpa Lesson Plan Template 1api-644630867No ratings yet
- Model: Universal Design For Learning PlanDocument7 pagesModel: Universal Design For Learning Planapi-561007976No ratings yet
- Legends From KazakhstanDocument4 pagesLegends From KazakhstanАли ПралиевNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BurningDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Burningapi-310800145No ratings yet
- Bismillah Presentasi 1 KD 3.8&4.8Document11 pagesBismillah Presentasi 1 KD 3.8&4.8Frisca AyuNo ratings yet
- Unit PlanDocument8 pagesUnit Planapi-469160289No ratings yet
- R-LSK 211Document9 pagesR-LSK 211neomakabe14No ratings yet
- Aboriginal Ped 102085 Lesson Plan Assignment 2Document12 pagesAboriginal Ped 102085 Lesson Plan Assignment 2api-321469415No ratings yet
- Kindergarten Intro Lesson Science SeasonsDocument2 pagesKindergarten Intro Lesson Science Seasonsapi-533726217No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Bryan Vazquez and Julianne LudlowDocument9 pagesLesson Plan - Bryan Vazquez and Julianne Ludlowapi-708336557No ratings yet
- Activity Plan Ms CreeDocument3 pagesActivity Plan Ms Creeapi-539087810No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8 WaysDocument6 pagesLesson Plan 8 Waysapi-428550300No ratings yet
- Forces Causing Movement CompletelessonDocument28 pagesForces Causing Movement Completelessonapi-616056306No ratings yet
- CO2 Lesson Plan - AlonaDocument7 pagesCO2 Lesson Plan - AlonaAlona BetitaNo ratings yet
- Geography 2Document5 pagesGeography 2api-561111966No ratings yet
- Walker of Sample Two Day Lesson Plan - First Days of ClassDocument3 pagesWalker of Sample Two Day Lesson Plan - First Days of Classapi-680455287No ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-Template 1Document4 pagesLesson-Plan-Template 1api-360143529100% (1)
- Unit 2-kdg 2018-2019 PBL TemplateDocument8 pagesUnit 2-kdg 2018-2019 PBL Templateapi-438888114No ratings yet
- Potential Artefact 3 2Document7 pagesPotential Artefact 3 2api-357641767No ratings yet
- Constructivist Theory in Teaching Science: Lesson 4 ActivitiesDocument4 pagesConstructivist Theory in Teaching Science: Lesson 4 ActivitiesSHARWIN BORDARAISNo ratings yet
- Y4 English LP104 (Reading 20)Document14 pagesY4 English LP104 (Reading 20)TESL2-0620 Jocelyn Marianne Anak JunnyNo ratings yet
- Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template - Lesson 1Document3 pagesEd508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template - Lesson 1api-479456611No ratings yet
- Matter and Energy - 4th Grade by SlidesgoDocument40 pagesMatter and Energy - 4th Grade by SlidesgoManuel MoralesNo ratings yet
- 1Cm.01 1Twsc.01: How Does It Feel? Have You Seen This Material Before?Document16 pages1Cm.01 1Twsc.01: How Does It Feel? Have You Seen This Material Before?NT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- 1.5 Staying AliveDocument9 pages1.5 Staying AliveNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- Naming and Describing Body Parts in HumansDocument17 pagesNaming and Describing Body Parts in HumansNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- 1.3 Growing StrongDocument10 pages1.3 Growing StrongNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- Learning Objective Key Vocabulary Possible Misconceptions LB WBDocument9 pagesLearning Objective Key Vocabulary Possible Misconceptions LB WBNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- Measuring Sound Levels with a Decibel MeterDocument5 pagesMeasuring Sound Levels with a Decibel MeterNT ARTITISARINo ratings yet
- Manley CH 3 Part 1Document12 pagesManley CH 3 Part 145. Phùng Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Technique ExplainedDocument5 pagesMind Mapping Technique Explainedviraaj pawarNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology in OrthodonticsDocument69 pagesChild Psychology in OrthodonticsShristi ChahalNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGY & THE SELF: KEY THEORIES OF THE I-SELF AND ME-SELFDocument33 pagesPSYCHOLOGY & THE SELF: KEY THEORIES OF THE I-SELF AND ME-SELFJeremy DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Tyrone Tumale - Iphp Assessment (Module 1)Document1 pageTyrone Tumale - Iphp Assessment (Module 1)Tyrone TumaleNo ratings yet
- Writing A Short Story Lesson Plan 11BDocument3 pagesWriting A Short Story Lesson Plan 11Banca alexaNo ratings yet
- Why Trust Your IntuitionDocument6 pagesWhy Trust Your IntuitionitachiiNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 8Document3 pagesLearning Episode 8Anny May GusiNo ratings yet
- LP Lesson Plan EN2Document11 pagesLP Lesson Plan EN2Shanine Melendres Pastrana100% (1)
- The Little Voices in Your HeadDocument12 pagesThe Little Voices in Your Headmuralimohanrao rojukurthiNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism AnswerDocument3 pagesBehaviorism AnswerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- PEAC Classroom Observation FormDocument2 pagesPEAC Classroom Observation FormMiles SantosNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesConstructing A Lesson PlanSara AssiriNo ratings yet
- 22 Supremely Powerful Tips For Highly Impressive Communication SkillsDocument7 pages22 Supremely Powerful Tips For Highly Impressive Communication SkillsGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- Group1 - BSED-ENGLISH4 Full Blown Manuscript - Reading Comprehension of The Students in Grade 7Document67 pagesGroup1 - BSED-ENGLISH4 Full Blown Manuscript - Reading Comprehension of The Students in Grade 7Renz MatiasNo ratings yet
- How Do Children Learn Math and How Do We Teach and Assess MathDocument32 pagesHow Do Children Learn Math and How Do We Teach and Assess MathJenny AsneNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent LearnersDocument179 pagesThe Child and Adolescent LearnersMyla Guab100% (1)
- Students Perceptions About The Use of SoDocument13 pagesStudents Perceptions About The Use of SoAngel SicatNo ratings yet
- 10 Benefits of Painting for Your Health and HappinessDocument4 pages10 Benefits of Painting for Your Health and HappinessKarthick PanduranganNo ratings yet
- Radical Candor: 1-Page SummaryDocument66 pagesRadical Candor: 1-Page SummarynachoNo ratings yet
- Human Relation Activity SampleDocument3 pagesHuman Relation Activity Samplearis apridNo ratings yet
- English 8 Q3 Week 3Document10 pagesEnglish 8 Q3 Week 3JillianNo ratings yet
- E 0034654315626801Document35 pagesE 0034654315626801ThomasNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1Apple Jane NicolasNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Human Communication: Ninth EditionDocument37 pagesEssentials of Human Communication: Ninth EditionAlish DhamaniNo ratings yet
- Objective Personality ENG PDFDocument14 pagesObjective Personality ENG PDFLuana MestreNo ratings yet
- Mental Health WSS A Survey NewDocument154 pagesMental Health WSS A Survey NewpoemNo ratings yet
- Communicative Styles for Various SituationsDocument16 pagesCommunicative Styles for Various SituationsMaryjane Janiola Tulayan100% (1)
- Summary SlaDocument36 pagesSummary SlaNatalia OliveraNo ratings yet
- PhilosophyDocument11 pagesPhilosophyMaxpein MoonNo ratings yet