Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PABROA
Uploaded by
lai cruzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PABROA
Uploaded by
lai cruzCopyright:
Available Formats
QUALITATIVE DISORDERS: PLATELETS &
VESSELS
BLEEDING
SUPERFICIAL bleeding- Associated with platelet defect or vascular
disorder
Petechiae – bleeding of small blood vessel
Gingival bleeding
Epistaxis
DEEP tissue bleeding- Associated with plasma clotting factor deficiencies
Hematoma or hemarthrosis
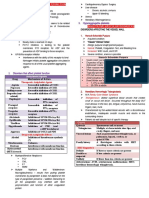
COAGULATION PLATELET/
DISORDER VASCULAR
DISORDER
SITE OF BLEEDING DEEP TISSUE SKIN, MUCOUS
MEMBRANES
PETECHIAE RARE COMMON
ECCHYMOSIS LARGE, DEEP SMALL, SUPERFICIAL
DEEP DISSECTING COMMON RARE
HEMATOMAS
HEMARTHROSIS COMMON RARE
DELAYED COMMON RARE
BLEEDING
BLEEDING AFTER YES NO
CUTS & SCRATCHES
BLEEDING AFTER IMMEDIATE, MILD DELAYED 1-2 DAYS,
SURGERY OR SEVERE
TRAUMA
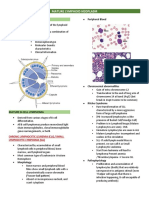
QUALITATIVE PLATELET DISORDER
A problem with the structure or function of the platelet
The disorder results in a poor “quality” of clotting
Common causes include
Missing or defective proteins on the surface of the platelet membrane
A deficiency or abnormality in the platelet granules or their contents
(also known as a “storage pool disorder”)
DISORDERS OF PLATELET SECRETION (RELEASE
REACTIONS)
STORAGE POOL DISEASE
DENSE GRANULES DEFICIENCIES
-Disorder arises from an inability to package the dense granule
content.
-Serotonin transport mechanism disorder
-Nucleotide transporter MRP4 (ABCC4) gene disorder
ALPHA GRANULE DEFICIENCIES
- Alpha granules are storage for proteins
- 50-80 alpha granule per platelet, responsible for the granular
appearance in PBS
THROMBOXANE PATHWAY DISORDERS
Aspirin like effects
DENSE GRANULE DEFICIENCIES
Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
Thrombocytopenia- Absent Radius (TAR) Syndrome
ALPHA GRANULE DEFICIENCY
Gray Platelet Syndrome
Hermansky - Pudlak syndrome (HPS)
Autosomal Recessive, HPS-1 gene (Chromosome 10q23)
HPS-1 gene – production and control of melanosome, dense granules,
lysosomes
Tyrosine (+)
Severe oculocutaneous albinism associated with photophobia, rotary
nystagmus, and loss of visual acuity
Excess accumulation of ceroid - like material in RE cell
Mild to moderate bleeding diathesis
Platelet Factor is the major cause of death
PT & APTT: Normal
Normal – Prolonged: bleeding time
Platelet Aggregation Standard: planted response in by basic course
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Autosomal Recessive (1q)
Partial albinism - caused by abnormal large melanosomes
Large intracytoplasmic granules in WBC and platelets
Immune dysfunction- poor mobilization of marrow leukocyte pool,
defective chemotaxis and bacterial degradation activity
May lead to overwhelming infection or lymphoproliferative disorders
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
X-linked recessive
Defective WASp- cytoskeletal reorganization
T cell reduces by age
LOW IgM, cell surface GP reduced
Inability to mound an IgM response to the capsular polysaccharide of
bacteria
Recurrent pyogenic infections, eczema and bleeding caused by
thrombocytopenia
Gene alterations interfere with migration of WBC to the inflammation site
Abnormal cell morphology & defective cytoskeleton dependent activation
signals
Abnormal cell to cell adhesion
IgA & IgE = elevated
IgG = normal
IgM = low
Decreased aggregation response to ATP epinephrine, & collagen
Low dense granules
TAR syndrome
Autosomal Recessive
Thrombocytopenia (absence or hypoplasia of megakaryocytes) that
presents in early infancy with bilateral radial anomalies.
Skeletal abnormalities of the ulna, radius and lower extremities
Thumbs are present
Reduced number of platelets = hypomegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
Gray Platelet syndrome
Heterogenous disorder associated with abnormalities in alpha granule
formation and maturation
Autosomal recessive
Platelet inability to store alpha granule protein
Platelets appear gray on PBS
Mild thrombocytopenia, mild to moderate bleeding
Splenomegaly and fibrosis
Easy bruising, menorrhagia, excessive postpartum or postoperative
bleeding
Platelet: normal with variable morphology
Platelet Aggregation Standard: normal in primary wave BUT absence in
secondary wave when simulated with ADP, epinephrine, & arachidonic acid
Resistin Agglutination: Normal
Quebec Platelet defect
Autosomal dominant
Delayed bleeding
Deficiency of alpha granule multimerin leading to decreased content of
platelet Factor V
Abnormal proteolysis of alpha granule proteins due to increased levels of
platelet urinary type plasminogen activator
Normal or Slight thrombocytopenia
Reduced aggregation with epinephrine
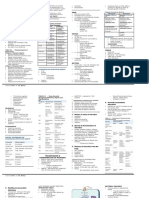
SUMMARY
Platelet Adhesion Disorder
Von Willebrand Disease
Bernard Soulier syndrome
Platelet Aggregation Disorder
Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Congenital afibrinogenemia
Disorder of Platelet Secretion & Abnormalities of Granules
Storage pool deficiency
Quebec platelet disorder
Disorder of Platelet Secretion & Signal Transduction
Defects in plt-agonist interaction
Cytoskeletal Regulation Defect
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
Membrane Phospholipid Defect
Scott syndrome
You might also like
- Qualitative Disorder (1) - 1Document27 pagesQualitative Disorder (1) - 1Christyl JoNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Disorders:: Primary HemostasisDocument58 pagesCoagulation Disorders:: Primary HemostasisFerji Rhenald Arditya100% (1)
- BoardReviewPart1A BenignHemePathDocument170 pagesBoardReviewPart1A BenignHemePathMaria Cristina Alarcon NietoNo ratings yet
- 1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersDocument9 pages1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersShiena ArchividoNo ratings yet
- Thalassaemia Hereditary Haem DisordersDocument12 pagesThalassaemia Hereditary Haem DisordersRawan HamzaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsIlyasHasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Thrombocytopenia and ThrombocytosisDocument6 pagesChapter 43 - Thrombocytopenia and ThrombocytosisNathaniel SimNo ratings yet
- Myelodysplasia (Definition/Incidence)Document10 pagesMyelodysplasia (Definition/Incidence)IlyasHasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Red Blood Cell and Bleeding DisordersDocument3 pagesChapter 14 - Red Blood Cell and Bleeding DisordersAgnieszka WisniewskaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis and Hereditary ElliptocytosisDocument40 pagesHereditary Spherocytosis and Hereditary ElliptocytosisJosh Matthew RosalesNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersDocument25 pagesHemostatic Disorders Quantitative and Qualitative DisordersKlein’s Gaming ChannelNo ratings yet
- HaematologyDocument62 pagesHaematologyManmeet SNo ratings yet
- Anemia TutoringDocument28 pagesAnemia TutoringngNo ratings yet
- AnemiasDocument2 pagesAnemiasdoktorcoop100% (2)
- HaematopathologyDocument253 pagesHaematopathologyamyNo ratings yet
- ANEMIIDocument34 pagesANEMIIAlin DragosNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia: Edwin S. Trinidad, M.D., FPCP, DPSHBTDocument39 pagesPancytopenia: Edwin S. Trinidad, M.D., FPCP, DPSHBTfachrie saputraNo ratings yet
- Clasification of Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) Dr. Malayana Nasutioan Mked - SPPKDocument46 pagesClasification of Anemia: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH) Dr. Malayana Nasutioan Mked - SPPKrubyniNo ratings yet
- Approach To Hemolytic AnemiaDocument63 pagesApproach To Hemolytic AnemiaSarath Menon R100% (2)
- Hemolytic AnaemiaDocument60 pagesHemolytic AnaemiaAthul GurudasNo ratings yet
- Secondary Clotting DisordersDocument34 pagesSecondary Clotting DisordersLyra Dennise LlidoNo ratings yet
- Approach To AnemiaDocument33 pagesApproach To AnemiaVaibhav KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Haemolytic Anaemia: DR Nurul Fahmiza Tumiran P109273Document55 pagesHaemolytic Anaemia: DR Nurul Fahmiza Tumiran P109273Nurul FahmizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Red Blood CellsDocument37 pagesChapter 14 Red Blood CellsCatherine LiuNo ratings yet
- Hematopoeitic and Lymphoid System Disorders: Red Cell Disorders A. AnemiaDocument12 pagesHematopoeitic and Lymphoid System Disorders: Red Cell Disorders A. Anemiaulfa mayasari100% (1)
- Week 5: Primary HemostasisDocument37 pagesWeek 5: Primary HemostasisRade GrbićNo ratings yet
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDocument30 pagesDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNo ratings yet
- DR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDocument30 pagesDR Vishu P Bhasin DCP Resident, Santosh Medical CollegeDabogski FranceNo ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument28 pagesAnaemiaAnhad SinghNo ratings yet
- Anemia PTGDocument33 pagesAnemia PTGPurple basketNo ratings yet
- Spleen Outline For FacultyDocument9 pagesSpleen Outline For Facultygaulep3164valNo ratings yet
- SBRC General PrinciplesDocument51 pagesSBRC General Principlesdalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Board Review Course Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: Kusum Viswanathan, MDDocument126 pagesPediatric Board Review Course Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: Kusum Viswanathan, MDIbrahem AlNo ratings yet
- Anaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsDocument33 pagesAnaemia: by Swaathi R Final Year MbbsGopi NathNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument99 pagesHemolytic AnemiaSagar Chandrakant Mhetre100% (3)
- PLT DisordersDocument3 pagesPLT DisordersAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Bleeding DisordersDocument137 pagesBleeding DisordersJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- 4) Inherited Hemolytic Anemia - Intraerythocytic With Defects of Haemoglobin Synthesis. Hemoglobinopathies and Thalassemia.Document2 pages4) Inherited Hemolytic Anemia - Intraerythocytic With Defects of Haemoglobin Synthesis. Hemoglobinopathies and Thalassemia.Lefteris ChatzidoukasNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis ChartDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis Chartaxmedfare138No ratings yet
- roDAKS Chapter 37Document3 pagesroDAKS Chapter 37John DavidNo ratings yet
- QPD Reporting Hema 2Document27 pagesQPD Reporting Hema 2Edmarie GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Anemias: Disorders of The Red Blood CellsDocument32 pagesAnemias: Disorders of The Red Blood CellsDthird Mendoza ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Subject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyDocument30 pagesSubject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyCristina Teodora BerbecaruNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Anemia 1Document24 pagesTopic 6 - Anemia 1Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument29 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationAnju RadhikaNo ratings yet
- RBC Disorders: Decreased Production of RBCDocument29 pagesRBC Disorders: Decreased Production of RBCJayanti Chairina SariNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Copy FINAL EDITEDDocument42 pagesCirrhosis Copy FINAL EDITEDpraisidNo ratings yet
- DR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDocument68 pagesDR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2024Document50 pagesAnemia 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Tambahan AnemiaDocument20 pagesTambahan AnemiaArnettaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Spherocytosis: DR Naing Naing Oo Senior LecturerDocument9 pagesHereditary Spherocytosis: DR Naing Naing Oo Senior LecturerAbdulrahman NajiNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument5 pagesAnemia SGps PandetteNo ratings yet
- הרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהDocument87 pagesהרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהliatfurmanNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Iin Novita Nurhidayati Mahmuda FK Ums Rs Pku Muhammadiyah SurakartaDocument55 pagesAnemia: Iin Novita Nurhidayati Mahmuda FK Ums Rs Pku Muhammadiyah Surakartafenti nurul khafifahNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument106 pagesCirrhosis of LiveraahadNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia Inherited: Hematologi-Onkologi Division Child Departement - Fkusu/RshamDocument56 pagesHemolytic Anemia Inherited: Hematologi-Onkologi Division Child Departement - Fkusu/RshamMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- Platelet: Muhammad Nazarudin, S.STDocument15 pagesPlatelet: Muhammad Nazarudin, S.STFafha FafhaNo ratings yet
- SBRC HematologyOncology 1Document80 pagesSBRC HematologyOncology 1dalia khamoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDocument24 pagesClinical Approach To Anemia: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Prima IndonesiaDzil FikriNo ratings yet
- Principles in Medical Laboratory Science 2Document2 pagesPrinciples in Medical Laboratory Science 2lai cruzNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document2 pagesDocument 6lai cruzNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument125 pagesUntitledlai cruzNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOSERO Group 4Document22 pagesIMMUNOSERO Group 4lai cruzNo ratings yet
- Group1 Hematology Prelim Learning SummaryDocument22 pagesGroup1 Hematology Prelim Learning Summarylai cruzNo ratings yet
- Mature B Cell Lymphoma CLL PLL HCLDocument4 pagesMature B Cell Lymphoma CLL PLL HCLlai cruzNo ratings yet
- Hema2 Lec PrefinalDocument9 pagesHema2 Lec Prefinallai cruzNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever in ChildrenDocument3 pagesCase Report: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever in ChildrenVhievien ChiaNo ratings yet
- Monospot LatexDocument12 pagesMonospot Latexlai cruzNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Defects: 1. Henoch-Schonlein PurpuraDocument3 pagesDrug-Induced Defects: 1. Henoch-Schonlein Purpuralai cruzNo ratings yet
- Jurkat, Clone E6 1 (ATCC TIB 152) : Product SheetDocument3 pagesJurkat, Clone E6 1 (ATCC TIB 152) : Product Sheetabdul88fNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Carbon Nanotubes: Applications in Pharmacy and MedicineDocument13 pagesReview Article: Carbon Nanotubes: Applications in Pharmacy and MedicineShrinivas KatkamwarNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument18 pagesTraumatic Brain InjuryPenvampyreNo ratings yet
- NCERT Books For Class 11 BiotechnologyDocument336 pagesNCERT Books For Class 11 BiotechnologyPiyush MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Neonatal AnemiaDocument22 pagesNeonatal AnemiaFebrina Utami Putri100% (4)
- The RH Negative Factor BookDocument117 pagesThe RH Negative Factor BookRoberta Ruth Hill67% (3)
- Lesson 4 Infancy by HurlockDocument44 pagesLesson 4 Infancy by HurlockJessica Recaido100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFRitz Celso100% (1)
- Leprosy: Pathogenesis Updated: ReviewDocument15 pagesLeprosy: Pathogenesis Updated: ReviewagneselimNo ratings yet
- Basic Science JSS 3 1STDocument58 pagesBasic Science JSS 3 1STAdeoye OlufunkeNo ratings yet
- K - 1 Perspective and The Future of OncologyDocument36 pagesK - 1 Perspective and The Future of OncologyPRAGAATHYRAJANNo ratings yet
- Chap 79Document5 pagesChap 79Ma.Nicole SubongNo ratings yet
- Cronologia de La Erupcion Dentaria Permanente en Pacientes Con Sindrome de DownDocument7 pagesCronologia de La Erupcion Dentaria Permanente en Pacientes Con Sindrome de DownArturoGrizNo ratings yet
- Biology 1010 General ObjectivesDocument2 pagesBiology 1010 General Objectivesapi-241247043No ratings yet
- Focal Adhesion Dynamics in Cellular Function and DiseaseDocument19 pagesFocal Adhesion Dynamics in Cellular Function and DiseaseEly Huaman PorrasNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation: En. Mohd Fahmi B Mohd YusofDocument45 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing Radiation: En. Mohd Fahmi B Mohd YusofFahmi BestNo ratings yet
- EFFECT of TemperatureDocument3 pagesEFFECT of Temperatureswati sharmaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Blood Transfusion 2Document15 pagesExchange Blood Transfusion 2Sarah100% (1)
- Alzheimer's Disease: 2017 Facts and FiguresDocument88 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: 2017 Facts and FiguresGina SmithNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic ShockDocument29 pagesAnaphylactic ShockHIND100% (7)
- Addiction AND Upregulation BUISSON 2002Document7 pagesAddiction AND Upregulation BUISSON 2002Andra SilvaNo ratings yet
- ASNC AND EANM Amyloidosis Practice Points WEBDocument12 pagesASNC AND EANM Amyloidosis Practice Points WEBElena FlorentinaNo ratings yet
- ACVIM Consensus Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease in Dogs.Document14 pagesACVIM Consensus Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease in Dogs.Evaldo MamedesNo ratings yet
- Lymphomas: Varun. M M-Pharm (Pharmacology) IyriisemDocument32 pagesLymphomas: Varun. M M-Pharm (Pharmacology) IyriisemPintoo Pintu100% (2)
- PANCYTOPENIADocument51 pagesPANCYTOPENIAResmyNo ratings yet
- Aplastic Hemolitic 2021 OlgaDocument43 pagesAplastic Hemolitic 2021 OlgalaibaNo ratings yet
- Managing Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases - Past, Present and FutureDocument6 pagesManaging Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases - Past, Present and FutureNICOLASNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Basics of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic ScienceDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Basics of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic SciencevivekNo ratings yet
- Advanced Prostate Cancer: Treatment Advances and Future DirectionsDocument14 pagesAdvanced Prostate Cancer: Treatment Advances and Future DirectionsMishel Rodriguez GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Frog OrgansDocument25 pagesFrog OrgansKen RubioNo ratings yet
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)