Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Types of Estimates Explained
Uploaded by
New Learners0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views26 pagesThe document describes 7 different types of estimates:
1. Preliminary estimates provide approximate costs quickly based on similar past projects.
2. Detailed estimates calculate exact quantities and costs of all items from drawings and specifications.
3. Revised estimates update original estimates when costs increase more than 5% due to rates or deviations.
4. Supplementary estimates cover additional works needed due to structural changes from original designs.
5. Annual maintenance estimates budget for regular repairs and replacements.
6. Extension estimates cover non-routine changes to old works.
7. Complete estimates incorporate all associated costs from land to supervision.
Original Description:
Estimation
Original Title
chapter 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes 7 different types of estimates:
1. Preliminary estimates provide approximate costs quickly based on similar past projects.
2. Detailed estimates calculate exact quantities and costs of all items from drawings and specifications.
3. Revised estimates update original estimates when costs increase more than 5% due to rates or deviations.
4. Supplementary estimates cover additional works needed due to structural changes from original designs.
5. Annual maintenance estimates budget for regular repairs and replacements.
6. Extension estimates cover non-routine changes to old works.
7. Complete estimates incorporate all associated costs from land to supervision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views26 pagesDifferent Types of Estimates Explained
Uploaded by
New LearnersThe document describes 7 different types of estimates:
1. Preliminary estimates provide approximate costs quickly based on similar past projects.
2. Detailed estimates calculate exact quantities and costs of all items from drawings and specifications.
3. Revised estimates update original estimates when costs increase more than 5% due to rates or deviations.
4. Supplementary estimates cover additional works needed due to structural changes from original designs.
5. Annual maintenance estimates budget for regular repairs and replacements.
6. Extension estimates cover non-routine changes to old works.
7. Complete estimates incorporate all associated costs from land to supervision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Chapter 3
Different Types of Estimates
Different Types of Estimates
1. Preliminary Estimate or Approximate
2. Detailed Estimate
3. Revised Estimate
4. Supplementary Estimate
5. Annual Maintenance Or Repair Estimate
6. Extension and Improvement of Estimates
7. Complete Estimate
1.Preliminary Estimate or Approximate
• This is an estimate to find out an approximate cost
in a short period of time
• The authority concerned to consider the financial
aspects of the scheme, for according sanction.
• Approximate estimate is calculate from a similar
construction already complete in the nearby area
• Preliminary estimate is required for studies of
various aspects of work
• For commercial projects, whether the net income
earned justifies the amount invested or not.
• The approximate estimate is prepared from the
practical knowledge and cost of similar works.
• A percentage 5 to 10% is allowed for contingencies.
Methods used for preparation of
approximate estimates
A) Unit base method.
• According to this method the cost of structure is
determined by multiplying the total number of
units with unit rate of each item.
• In case schools and colleges, the unit considered
to be as 'one student' and in case of hospital, the
unit is 'one bed'. the unit rate is calculated by
dividing the actual expenditure incurred or cost
of similar building in the nearby locality by the
number of units.
Methods used cont…
B) Plinth area method
• The cost of construction is determined by multiplying plinth
area with plinth area rate. The area is obtained by
multiplying length and breadth (outer dimensions of
building).
• In fixing the plinth area rate, careful observation and
necessary enquiries are made in respect of quality and
quantity
• Aspect of materials and labour, type of foundation, height
of building, roof, wood work, fixtures, number of storey's
etc.
• P/A=carpet area + area of wall+ circular area + area of
Kitchen and Bathroom
Methods used cont…
C) Cubical Contents Method:
• This method is generally used for multistoried buildings.
• It is more accurate that the other two methods viz., plinth
area method and unit base method.
• The cost of a structure is calculated approximately as the
total cubical contents (Volume of buildings) multiplied by
Local Cubic Rate.
• The volume of building is obtained by Length x breadth x
depth or height. The length and breadth are measured out
to out of walls excluding the plinth off set.
• The cost of building= volume of buildings x rate/ unit
volume.
Methods used cont…
D) Approximate Quantity Method:
• Quantities are worked out in linear
measurement,
• Foundation work (excavation, wall, concrete,
brick work) up to Plinth computed as per
running length
Example:1
Prepare an approximate estimate of building project
with total plinth area of all building is 800 sqm. and
from following given data.
i) Plinth area rate Rs. 6000 per sqm
ii) Cost of water supply @7%of cost of building.
iii) Cost of Sanitary and Electrical installations @ 10%
of cost of building.
iv) Cost of architectural features @1% of building cost.
v) Cost of roads and lawns @5% of building cost.
vi) Cost of Supervision and contingencies @4% of
building cost. Determine the total cost of building
project.
Example 1
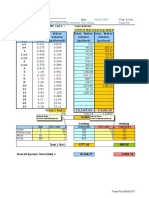
Soln:
• Given plinth area =800m2 and plinth area
rate=6000 per m2
• Building cost=800*6000=4,800,000
Cost of w/s and sanitation=7.5%
Preliminary estimation of building project =
Example:2
Prepare a preliminary estimate of a four storied office building having
total carpet area of 1500.sq.m for obtaining the administrative
approval of the government, given the following data.
i) 40% of the built up area will be taken up by corridors, verandah,
lavatories, staircase etc.
ii) Plinth area rate is Rs. 20,000/- per Esq. Extra for special
architectural treatment 0.5% of building cost.
iii) Extra due to deeper foundation at site 1% of building cost.
iv) Extra for water supply and sanitary installation 8% of building cost.
v) Extra for internal electrical installation 12.5% of building cost.
Vi) Extra for other services 5% of building cost.
Vii)Contingencies - 2.5%
Example 2 solution
Given ;
total Carpet area=1500sqm
40% of the built up area will be taken up by
corridors, verandah, lavatories, staircase etc.
Let, X=Plinth area of the building
We have , P/A=carpet area + area of wall+ circular
area + area of Kitchen and Bathroom
So, X =40%of X+1500sqm
X=0.4X+1500
X=(1500/0.6)sqm= qm= plinth area
Example:3
Prepare the rough estimate for a proposed commercial
complex for a municipal
Corporation for the following data.
• Plinth Area = 500m2/floor
• Ht of each storey = 3.5m
• No. of storey’s = G+2,
• Cubical content rate = Rs. 1500/m3
• Provided for a following as a percentage of structured cost
a) Water supply & Sanitary arrangement -15%
b) Contractors profit - 10%
c) supervision & contingencies - 3%
Given, PA=500m2, Cubical contain rate=1500m3
No of story= G+2=3
Building height=3.5m
Building cost=building volume X cubical rate
=(500x3x3.5)X1500=7,875,000.0
Now extra cost,
i)W/S=15%of building cost=15%7,875,000=1,181,250.0
ii)Contractor profit=10% of building cost=787,500.0
Total building cost=building cost(civil)+W/s+Con. Profit
=7,875,000.0+1,181,250.0+787,500.0
=9,843,750.0
Petty supervision & contingencies = 3% of total building cost
=3% X 9,843,750.0
Rough estimate for a proposed commercial complex for a municipal
=9,843,750.0+295,312.5= 10,139,062.50
Example:4
• Prepare the preliminary estimate for
administrative approval of a four storied building
having carpet area of 1 floor 250 sqm and floor
height 2.8m each. The area required for
circulation and wall is 32% of total area.
• If the cubic rate of the building for civil works
assumed to be Nrs: 8000 per cubic meter. The
masonry provision of electrification, water supply
and sanitation works is 20% of civil work.
contingencies – 2.5%
Given,
four storied building having carpet area of 250 sqm and floor height 2.8m each. The area
required for circulation and wall is 32% of total area
cubic rate of the building for civil works assumed to be Nrs: 8000 per cubic meter
The masonry provision of electrification, water supply and sanitation works is 20% of civil
work. contingencies – 2.5%
Now,
total plinth =X
X=250+32%of X
X=367.64m2
We know volume of building=Plinth area X building
height=367.64*(4*2.8)cum=4117.64m3
Building Civil cost = 32,941,176.47
Mansonary provision and Electric, W/s sanitary =20% of civil cost 6,588,235.29
Now total Building Cost = 39,529,411.76
Contingencies= 988,235.29
Now , Rough estimate of the four story Building = 40,517,647.06
2. Detailed Estimate:
• Most accurate estimate of any work
• Quantities of all items of work are calculated
from their respective dimensions on the drawings
on a measurement sheet.
• Abstract of cost is prepared by multiplying the
quantities of item by their rate.
• A detail estimate is accompanied by-
– Report
– Specifications.
– Detailed drawings showing plans and sections.
– Design data and calculations.
– Basis of rates adopted in the estimate.
Preparation of Detail Estimate:
– Details of measurement and calculation of
quantities
– Abstract of estimate cost
– Rate analysis (Material rate and labour rate)
Details of measurement and calculation of quantities
Item no Description/Particulars no L B H/D quantity unit remark
Abstract of estimate cost
Item no Description/Particulars quantity unit Rate Amount Remark
3. Revised Estimate:
• A revise estimate is the detail estimate or list of quantities
and rates of items of works originally provided in the
estimate without material deviations of a structural nature
from originally approved for a project
• It is required under any one of the following circumstances
– When the original approve estimate is exceed or likely exceed
by more than 5% either by in sufficient rate or any cause
– Even though the cost maybe made from the approve amount ,
there is material deviation from the initial detail estimate
– When the expenditure on the work exceed or likely exceed the
amount of administrative approve by more than 10% (for work
more than 5 lakhs)
• Also submit variation report.
4. Supplementary Estimate:
• While a work in progress, some changes or
additional works due to material deviation for
a structural nature from the design originally
approved may be thought necessary for
development of a project.
• Detail estimate of additional work in addition
to original estimate.
• It is required to get approval from the
concerned authority.
5. Annual Maintenance Or Repair
Estimate
• After completion of a work it is necessary to
maintain the same for its proper function
• The same and estimate is prepared for the
items which required renewal, replacement
and repairs.
• Example:- White washing, Color washing,
Painting of doors and windows etc
6. Extension and Improvement of
Estimates
• When some change and extension are
required to made the old work the cost of
which cannot be made out in Annual
Maintenance Or Repair Estimate
7. Complete estimate:
• Consist cost of all items including land cost to
supervision cost
(Consultant cost: Surveying, design , Drawing,
Estimation, tender document)
Split up of cost of building work:
General break-up of conventional buildings :
1. Labour component : 30 to 35% of total cost
2. Material component: 65 to 70% of total cost
Stagewise break-up of conventional buildings :
1. Foundation and beams upto plinth level : 10 to 15% of total cost
2. Construction above plinth level : 85 to 90% of total cost
Activitywise break-up of conventional buildings :
Foundation work : 17-18%
Brickwork/blockwork : 20%
Concreting and reinforcement steel : 15%
Doors,windows and ventilators : 12%
Roof water proofing and finishing with tiles: 5%
Plastering : 5-6%
Flooring : 5%
Painting : 2-3%
Water supply,electrification,sanitary works : 12-13%
Other works : 4-5%
This may vary slightly depending on the type of finishes/doors and
windows/sanitary fittings etc.
According to Materials:
Cost of Brick 22 to 25% Cost of steel bars 10 to 12%
Cost of Cement 12 to 15% Cost of timber 10 to 12%
if Any question?????
You might also like
- EstimationDocument71 pagesEstimationSONU71% (7)
- Catalogue Produits OnanDocument6 pagesCatalogue Produits OnanJohn LarsonNo ratings yet
- Types of EstimationDocument47 pagesTypes of EstimationNarendra Adapa100% (1)
- Convert HTML to PDF with Colors Using WkhtmltopdfDocument5 pagesConvert HTML to PDF with Colors Using WkhtmltopdfDJNo ratings yet
- Handbook on Construction Techniques: A Practical Field Review of Environmental Impacts in Power Transmission/Distribution, Run-of-River Hydropower and Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation ProjectsFrom EverandHandbook on Construction Techniques: A Practical Field Review of Environmental Impacts in Power Transmission/Distribution, Run-of-River Hydropower and Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation ProjectsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Project Cost Estimation and Valuation GuideDocument32 pagesProject Cost Estimation and Valuation GuideYohannes HabeshawiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instruments Magazine - January 2008Document68 pagesVirtual Instruments Magazine - January 2008Maria Tudosa100% (1)
- Career Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsFrom EverandCareer Change From Real Estate to Oil and Gas ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Simpson Rule PDFDocument29 pagesSimpson Rule PDFBrajesh Narayan100% (1)
- Approximate Estimates MethodsDocument20 pagesApproximate Estimates Methodsऋषिकेश कोल्हे पाटिलNo ratings yet
- Estimationpart 1Document42 pagesEstimationpart 1Bia MughalNo ratings yet
- Estimation and CostingDocument44 pagesEstimation and CostingSuhasini Pranay100% (2)
- Chapter4 Transceiver ArchitecturesDocument137 pagesChapter4 Transceiver ArchitecturesNikunj Shah100% (1)
- Methods of Approximate Construction Cost Estimation PreparationDocument5 pagesMethods of Approximate Construction Cost Estimation PreparationcivilNo ratings yet
- Expansion Tank SizingDocument36 pagesExpansion Tank SizingEngFaisal AlraiNo ratings yet
- 65° Panel Antenna 1710-2200 MHz X-polarized Adjustable Electrical DowntiltDocument2 pages65° Panel Antenna 1710-2200 MHz X-polarized Adjustable Electrical DowntiltKhawar WaheedNo ratings yet
- Estimation Types & PurposesDocument19 pagesEstimation Types & PurposesVenkat Ravichandran100% (1)
- Estimation 8th 110215Document19 pagesEstimation 8th 110215Hammad Bashir GondalNo ratings yet
- Estimation Techniques for Construction ProjectsDocument20 pagesEstimation Techniques for Construction ProjectsSaurav Gautam100% (1)
- Methods of EstimateDocument23 pagesMethods of Estimatesiddhi gangwalNo ratings yet
- Estimation and EstimatesDocument61 pagesEstimation and EstimatesShaheryar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design of Tank and Tubes - TransformersDocument6 pagesDesign of Tank and Tubes - TransformersAJAY KOSHY PS 18-20No ratings yet
- Estimating and Costing EngineeringDocument71 pagesEstimating and Costing EngineeringPURUSHOTTAMNo ratings yet
- Types of Estimates and Methods ExplainedDocument14 pagesTypes of Estimates and Methods ExplainedEvan SantoshNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of EstimatesDocument6 pages3 Types of EstimatesRight TurnNo ratings yet
- Estimating and Costing I Chapter 2Document27 pagesEstimating and Costing I Chapter 2milan nepaliNo ratings yet
- Rough Cost Estimate for Multi-Storey Residential Building ProjectDocument31 pagesRough Cost Estimate for Multi-Storey Residential Building ProjectRajan Ranjan100% (2)
- Lec 5Document27 pagesLec 5AHMAD AHMADNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document5 pagesUnit 2Amit RoyNo ratings yet
- Types of Construction EstimatesDocument17 pagesTypes of Construction EstimatesBharat AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Types of EstimateDocument45 pagesTypes of EstimateAkhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Estimating and Cost Engineering IntroductionDocument69 pagesEstimating and Cost Engineering IntroductionVennela ReddyNo ratings yet
- Estimation 1Document35 pagesEstimation 1MdNo ratings yet
- ESC1Document43 pagesESC1uditmodi4No ratings yet
- EAC MicroprojetDocument20 pagesEAC MicroprojetSohail ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Quantity SurveyingDocument33 pagesQuantity SurveyingFretzelle John BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Estimates - The Essential GuideDocument12 pagesEstimates - The Essential GuideDILEEP KUMAR SAMADHIYANo ratings yet
- Estimating, Costing & Building SpecificationsDocument22 pagesEstimating, Costing & Building SpecificationsSakshi RawatNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying and Contract Management NotesDocument83 pagesQuantity Surveying and Contract Management NotesMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- EstimateDocument4 pagesEstimateOgbuka ChibuzoNo ratings yet
- EstimateDocument6 pagesEstimateSansar PanchalNo ratings yet
- Fuw5fomwrucbh1ojdlxe Signature Poli 201005073934 PDFDocument24 pagesFuw5fomwrucbh1ojdlxe Signature Poli 201005073934 PDFDeepakNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument31 pagesUnit 1 NotesAniket HireNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying and Estimation GuideDocument11 pagesQuantity Surveying and Estimation Guideparul vyasNo ratings yet
- Professional Practices: Estimation MethodsDocument31 pagesProfessional Practices: Estimation Methodsgargie20No ratings yet
- Estimationpart 1Document42 pagesEstimationpart 1kajale_shrikant2325No ratings yet
- Quantity SurveyingDocument8 pagesQuantity Surveyingshahid aliNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Lecture - 1Document17 pagesDefinition:: Lecture - 1ecba2b8cdeNo ratings yet
- Asha Chuhan EAC MICRO-PROJECTDocument17 pagesAsha Chuhan EAC MICRO-PROJECTAsha ChuhanNo ratings yet
- BT4-PP-LECTURE-ESTIMATEDocument64 pagesBT4-PP-LECTURE-ESTIMATElucky dolphinNo ratings yet
- Estimation and CostingDocument19 pagesEstimation and CostingAditi ShahNo ratings yet
- Ce1401 Eqs 1 - 2Document12 pagesCe1401 Eqs 1 - 2Alex ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Estimate TypesDocument15 pagesEstimate TypesSugam SehgalNo ratings yet
- Q&e TheoryDocument9 pagesQ&e TheorySansar PanchalNo ratings yet
- Notes On Detailed & Approximate EstimatesDocument4 pagesNotes On Detailed & Approximate EstimatesNidhi Mehta100% (1)
- Project Cost Estimation, Quality Management and TimelinesDocument14 pagesProject Cost Estimation, Quality Management and TimelinesDheeraj TkNo ratings yet
- Types of EstimatesDocument4 pagesTypes of Estimateskisansah145No ratings yet
- Ce702 Estimation PDFDocument71 pagesCe702 Estimation PDFDanish BhatNo ratings yet
- Acm ReportDocument29 pagesAcm ReportKayne Valerie PadojinogNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying - Approximate EstimationDocument6 pagesQuantity Surveying - Approximate EstimationAhmed AmediNo ratings yet
- Final Doc QS Project 16.08.2018Document54 pagesFinal Doc QS Project 16.08.2018srinivasNo ratings yet
- Cost Modelling - ASB - Part 2 For StudentsDocument30 pagesCost Modelling - ASB - Part 2 For StudentsGloria DanielNo ratings yet
- Approximate EstimateDocument20 pagesApproximate EstimateGroot AvengerNo ratings yet
- Estimating CostingDocument15 pagesEstimating CostingAarush MauryaNo ratings yet
- Introduction QSEDocument21 pagesIntroduction QSEsiddhi gangwalNo ratings yet
- Model 3410: Shear Beam Load CellsDocument4 pagesModel 3410: Shear Beam Load CellsIvanMilovanovicNo ratings yet
- Ge Stator Earth FaultDocument7 pagesGe Stator Earth FaultMarioNo ratings yet
- The Tower Undergraduate Research Journal Volume VI, Issue IDocument92 pagesThe Tower Undergraduate Research Journal Volume VI, Issue IThe Tower Undergraduate Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Part 4 (Titration Curves) EdexcelDocument5 pagesAcids and Bases Part 4 (Titration Curves) EdexcelKevin The Chemistry Tutor50% (2)
- MEPLDocument35 pagesMEPLMegamet Engineers Pvt. Ltd.No ratings yet
- Advantages of SSHS For Construction Extract TDG20Document5 pagesAdvantages of SSHS For Construction Extract TDG20skooba84No ratings yet
- Falcon 1600Document45 pagesFalcon 1600manohar kumar100% (1)
- Concrete Bridges in GermanyDocument12 pagesConcrete Bridges in GermanydelujaNo ratings yet
- Cellular manufacturing: a lean system for grouping similar machinesDocument4 pagesCellular manufacturing: a lean system for grouping similar machinesPrashant AroraNo ratings yet
- RISK ASSESSMENT White Paper: A Harmonious ApproachDocument8 pagesRISK ASSESSMENT White Paper: A Harmonious ApproachMaduroNo ratings yet
- Medium and Long-Term Strategic Skills List (MLTSSL) : So Who Is Bravo Migration?Document1 pageMedium and Long-Term Strategic Skills List (MLTSSL) : So Who Is Bravo Migration?OsniSoiNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Derajat Merokok Dengan Nilai Arus Puncak Ekspirasi Pada Pria Dewasa Awal (20-40 Tahun) Di Desa Tampaksiring, Kecamatan TampaksiringDocument8 pagesHubungan Derajat Merokok Dengan Nilai Arus Puncak Ekspirasi Pada Pria Dewasa Awal (20-40 Tahun) Di Desa Tampaksiring, Kecamatan TampaksiringBima SorayaNo ratings yet
- Basilica of TrajanDocument9 pagesBasilica of TrajanKavya Eranagoudar MallanagoudarNo ratings yet
- R001-358-V1.2 Sensr GP2-X User ManualDocument12 pagesR001-358-V1.2 Sensr GP2-X User ManualJosé Francisco AnunciaçãoNo ratings yet
- Replace fan kit for hp Model 211A Square Wave GeneratorDocument1 pageReplace fan kit for hp Model 211A Square Wave GeneratorxibmNo ratings yet
- SCIADocument39 pagesSCIASudhakar KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Drilling and Tapping MachineDocument4 pagesAutomatic Drilling and Tapping MachineSHUSHEELNo ratings yet
- Technical Guidline On Migration TestingDocument30 pagesTechnical Guidline On Migration Testingchemikas8389No ratings yet
- Transformer Protection Relay GRE160 Brochure 12027-1 0Document22 pagesTransformer Protection Relay GRE160 Brochure 12027-1 0tanujaayerNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Seaweed Waste Gracilaria SP and eDocument10 pagesThe Potential of Seaweed Waste Gracilaria SP and eAngelica Riviera Brery GirsangNo ratings yet
- 1.blowers Air Supply Silencer PDFDocument8 pages1.blowers Air Supply Silencer PDFYendry Huezo RosalesNo ratings yet
- Présentation - Cnes - Icam - Materiaux - Structuraux - 2021 PDFDocument62 pagesPrésentation - Cnes - Icam - Materiaux - Structuraux - 2021 PDFJoshua VUITTENEZNo ratings yet