Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Causes of Industrial Sickness
Uploaded by
Ankit RajOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Causes of Industrial Sickness
Uploaded by
Ankit RajCopyright:
Available Formats
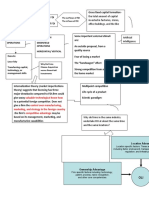
Cuuses of Sickness
A. Internal Causes
(1) Planning
(a) Technical feasibility
Inadequate technical know-how
Locational disadvantage
Outdated production process
Sickness in Small-Scale Industries Reasons and Remedies 705
() Economic viabili
High cost of inputs
Break-even point too high
Uneconomic size ot project
Under-estimation of financial requirements
Unduly large mvestent in fixed assets
Over-estimation of demand
(2) Implementation
Cost overmuns resultmg from delays in getting licences and sanctions etc.
Inadequate mobilisation of tinance.
(3) Production
(a) Pmduction management
Inappropriate product-mix
Poor quality contro
Poor capacity utilisation
High cost of production
P'oor inventory management
Inadequate maintenance and replacement
Lack of timely and adequate modernisation etc.
High wastage
(b) Labour management
Excessively high wvage structure
Inefficient handling of labour problems
Excessive manpover
Poor labour productivity
Poor labour relations
Lack of trained skilled labour or technically competent personnel
(c) Marketing management
Dependence on a single customer or a limited number of custorners/single or a limited nmber of prodiu
Poor sales realisation
Defective pricing policy
Booking of large orders at fixed prices in an inflationary market
Weak market organisation
Lack of market feedback and market research
Lack of knowledge of marketing techniques
Unscrupulous sales/purechase practices
(d) Financial management
The road to business is paved with bad financial decisions. More often, the entrepreneur's
mismanagement is responsible for a host of problems.
Poor resources management and financial planning
Faulty costing
Minimal capital
Liberal dividend policy
General financial indiscipline and application of fimds for unauthorised purposes
Poor liquidity
Deficiency of funds
Over-trading
Unfavourable gearing or keeping adverse debt-equity ratio
Inadequate working capital
Absence of cost conscousness
The Dynamics of Entreprerneurial Development and Management
706
Lack of ettective collection machiner
Poor cash control
No plan "B in sight
Throwing IT around
Delaying Debt
Borrowing Blind
Leaving lenders out
Thin reserves
Jnderestimation of
expenses like
import and
Excessive investment in
infrastructure transport costs
Ignoring the lender like SIDBI
Administratrve management
Over centralisation
Lack of professionalism
Lack of teedback to
Lack of controls management (Management Information System)
Lack of timely diversification
Excessive expenditure on R&D
Dividend 1oyaies wnere the same
management has interest in more than one unit, cases are knoWn
mited companies wo aiso Owm
private ownership firms tend to
wherePO
look after the interests of the latter, often at the cost ot tne
ormer).
Dissension within the
management
Incompetent management
Dishonest management
B. External Causes
(a) Infrastructural bottlenecks
Non-availability of
irregular supply of critical raw materials other
Chronic power shortage
or inputs
Transport bottlenecks
Financial bottlenecks
Non-availability of adequate finance
) Government controls and policies, etc.
Government price controls
Fiscal duties
Abrupt change in Government policies
Procedural delays on the part of the financial licensing other controlling or regulating authorities (Banks. Reserve Bank
India, financial institutions, Government departinents, ncensing autnorites, Monopolies and Restrictive
Trade Practices
Roard. etc.)
() Market constraints
Market saturation
advances rendering one s products obsolete
Revolutionary technological
(e) Extraneous factors
Natural calamities
well as international)
Political situation (domestic
as
War
Sympathetic strikes
labour unions.
Multuplicity of
You might also like
- EM 19-17 Entry Mode ChoicesDocument26 pagesEM 19-17 Entry Mode ChoicesMikkel GramNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: International Strategic ManagementDocument35 pagesUnit-Iii: International Strategic ManagementShobanashree RNo ratings yet
- Blueprints 1.0-Round 2: Development of The Feasibility Study Team - #FinaticsDocument20 pagesBlueprints 1.0-Round 2: Development of The Feasibility Study Team - #FinaticsSomeoneNo ratings yet
- Finance Options For Infrastructure Juan Costain: South Asia Regional Workshop On Investment ClimateDocument10 pagesFinance Options For Infrastructure Juan Costain: South Asia Regional Workshop On Investment ClimatesajeevpallathNo ratings yet
- Export Transaction CostDocument5 pagesExport Transaction CostvinayNo ratings yet
- Icofr Trends Hot Topics KPMGDocument4 pagesIcofr Trends Hot Topics KPMGayesha arifNo ratings yet
- SWOT of India and ChinaDocument2 pagesSWOT of India and ChinaSatish KorabuNo ratings yet
- Challenges in International TradeDocument21 pagesChallenges in International TradeAnil BatraNo ratings yet
- The Global Ones Are Mainly High Tech Companies: Many Are Financial Institutions or Owned by Powerful PeopleDocument10 pagesThe Global Ones Are Mainly High Tech Companies: Many Are Financial Institutions or Owned by Powerful PeopleSergei DragunovNo ratings yet
- Liberalization of World Trade: Foreign Direct Investment (F.D.I)Document17 pagesLiberalization of World Trade: Foreign Direct Investment (F.D.I)Rubal SinghNo ratings yet
- 6Document1 page6Laskar REAZNo ratings yet
- 00 - End Term CombinedDocument409 pages00 - End Term Combinedrishabh tyagiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sickness CausesDocument4 pagesIndustrial Sickness CausesShilpa SadaphuleNo ratings yet
- Foundation of IBE (Unit 1&2)Document154 pagesFoundation of IBE (Unit 1&2)Mehak AhujaNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument11 pagesPerformance ManagementParvinbanu SirajudeenNo ratings yet
- L6 - Foreign Direct InvestmentDocument31 pagesL6 - Foreign Direct InvestmentSarnisha Murugeshwaran (Shazzisha)No ratings yet
- 12 - Slides - Tian - Asset Tokenization A Blockchain SolnDocument18 pages12 - Slides - Tian - Asset Tokenization A Blockchain SolnMuhammad ADNANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 FdiDocument19 pagesChapter 11 FdiArvilyn ArabellaNo ratings yet
- W20 8120 Ch07 - International Capital StructureDocument51 pagesW20 8120 Ch07 - International Capital StructureDehuan SiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document52 pagesChapter 14Pia SurilNo ratings yet
- Assorted FrameworksDocument30 pagesAssorted FrameworksPRASHANT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Asset Management IndustryDocument11 pagesAsset Management IndustrySaw Kyaw Kyaw NgweNo ratings yet
- 3rd TID Mr. Tanchis Presentation On Mass HousingDocument38 pages3rd TID Mr. Tanchis Presentation On Mass HousingCyril CartallaNo ratings yet
- The OLI Paradigm June 13Document15 pagesThe OLI Paradigm June 13ChandanNo ratings yet
- CH1 IfmDocument32 pagesCH1 IfmSaad RazaNo ratings yet
- Just-In-Time (Business) : Corporate Finance Just-In-Time (JIT) Is An Inventory Strategy That Strives To Improve ADocument1 pageJust-In-Time (Business) : Corporate Finance Just-In-Time (JIT) Is An Inventory Strategy That Strives To Improve Aarvan04No ratings yet
- Project Evaluation and Planning: I) What Do You Understand by Capital Investment? Its Importance and DifficultiesDocument5 pagesProject Evaluation and Planning: I) What Do You Understand by Capital Investment? Its Importance and DifficultiesGãurãv SãndhãlNo ratings yet
- Ihrm Sustaining International Business OperationsDocument47 pagesIhrm Sustaining International Business OperationsRabbir Rashedin TirnoNo ratings yet
- G CD Session 7 CoveredDocument33 pagesG CD Session 7 CoveredTushar Rawat H20118No ratings yet
- 14.5 Global Production and Supply-Chain Management: Strategic Choices: Export, Local Assembly, and Local ProductionDocument3 pages14.5 Global Production and Supply-Chain Management: Strategic Choices: Export, Local Assembly, and Local Productionabin kunjumonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Etext Exercises AnswerDocument54 pagesChapter 6 Etext Exercises AnswerMaryMarianaLingNo ratings yet
- Modes of Entering IBDocument43 pagesModes of Entering IBDhruv SardanaNo ratings yet
- Global Sourcing - A Strategic Business ActivityDocument65 pagesGlobal Sourcing - A Strategic Business ActivityamohuidromNo ratings yet
- LECTURE5Document27 pagesLECTURE5Marwan wallyNo ratings yet
- Sectoral Issues in IndustryDocument18 pagesSectoral Issues in IndustryMayank AllawadhiNo ratings yet
- Foreign Investment: The Motives Organisation and StaffingDocument2 pagesForeign Investment: The Motives Organisation and StaffingJessy SeptalistaNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument13 pagesManagerial Economics20me23No ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 India's Stalled RiseDocument3 pagesUnit 1.1 India's Stalled RiseKushagra AroraNo ratings yet
- IT and ITeS June 2017Document54 pagesIT and ITeS June 2017Urja ManderaNo ratings yet
- Infosys Strategic AnalysisDocument39 pagesInfosys Strategic Analysisshahidnmims100% (29)
- Bharti Airtel 3 ASTAMIADocument7 pagesBharti Airtel 3 ASTAMIAtanusharma.mba23No ratings yet
- India Vs China Nov201Document33 pagesIndia Vs China Nov201pawangguptaNo ratings yet
- Direct Foreign Investment: Restrictions On ImportsDocument5 pagesDirect Foreign Investment: Restrictions On ImportsVenus Gavino ManaoisNo ratings yet
- GIFEB Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesGIFEB Finals ReviewerFire burnNo ratings yet
- Proposal - Digital Transformation - Banking and Capital MarketsDocument52 pagesProposal - Digital Transformation - Banking and Capital MarketsAnkit CapoorNo ratings yet
- Anchal - Gauri - Ghazal - Mohit - Pulokesh: The Consulting and Strategy Interest Group, IIM KozhikodeDocument13 pagesAnchal - Gauri - Ghazal - Mohit - Pulokesh: The Consulting and Strategy Interest Group, IIM KozhikodeNikhil ChipadeNo ratings yet
- Liberalisation, Privatisation and GlobalisationDocument14 pagesLiberalisation, Privatisation and GlobalisationDevshree DawarNo ratings yet
- Fdi Knoweldge Manaagement DiagramDocument1 pageFdi Knoweldge Manaagement DiagramHashaam MeharNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignments Section A - Short Answer Questions: 1) Summarize The Five Main Motives That Drive The Decision To Initiate FDIDocument15 pagesIndividual Assignments Section A - Short Answer Questions: 1) Summarize The Five Main Motives That Drive The Decision To Initiate FDIRogerchua5901No ratings yet
- Strategies For International Competition - GlobalOperationsDocument37 pagesStrategies For International Competition - GlobalOperationsDeepa ChandirrasekarNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting IBDocument26 pagesSamenvatting IBA.L.E.K. Wit, deNo ratings yet
- Fintech Landscape: Ashish Fafadia Kartikeya Shekhar Sujay ChoubeyDocument27 pagesFintech Landscape: Ashish Fafadia Kartikeya Shekhar Sujay Choubeydevang bohraNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two Airlines in The Information AgeDocument14 pagesA Tale of Two Airlines in The Information AgeRabya AmjadNo ratings yet
- Maersk Europe Customs Optimisation Blueprint EbookDocument18 pagesMaersk Europe Customs Optimisation Blueprint EbookArnaud DolyNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint® Lecture Presentation: To Accompany International Financial Management Zaima AhmedDocument33 pagesPowerpoint® Lecture Presentation: To Accompany International Financial Management Zaima AhmedSumaiya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Making Foreign Direct Investment Work for Sub-Saharan AfricaFrom EverandMaking Foreign Direct Investment Work for Sub-Saharan AfricaNo ratings yet
- International Business Control, Reporting and Corporate Governance: Global business best practice across cultures, countries and organisationsFrom EverandInternational Business Control, Reporting and Corporate Governance: Global business best practice across cultures, countries and organisationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthFrom EverandThe Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm SystemDocument5 pagesFire Alarm SystemAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm SystemDocument5 pagesFire Alarm SystemAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm SystemDocument8 pagesFire Alarm SystemAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Number TheoryDocument82 pagesNumber TheoryAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Public Key-Crypto SystemDocument44 pagesPublic Key-Crypto SystemAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Intro Duction To Number TheoryDocument89 pagesIntro Duction To Number TheoryAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Diffle HuffmanDocument29 pagesDiffle HuffmanAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Using Predicate LogicDocument86 pagesUsing Predicate LogicAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Ai HandoutDocument74 pagesAi HandoutAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- AI Handout 2Document50 pagesAI Handout 2Ankit RajNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Representation IssueDocument18 pagesKnowledge Representation IssueAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Representation IssueDocument18 pagesKnowledge Representation IssueAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuits Anand KumarDocument341 pagesDigital Circuits Anand Kumarsubhadarshini dasNo ratings yet
- V13 D03 1 PDFDocument45 pagesV13 D03 1 PDFFredy Camayo De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Linux and The Unix PhilosophyDocument182 pagesLinux and The Unix PhilosophyTran Nam100% (1)
- School Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolDocument2 pagesSchool Activity Calendar - Millsberry SchoolSushil DahalNo ratings yet
- BLG311 Cell Biology: Course Outline (Fall 2020)Document11 pagesBLG311 Cell Biology: Course Outline (Fall 2020)Emilija BjelajacNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Migraine and HomoeopathyDocument17 pagesAbdominal Migraine and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- 全新全真题库一 PDFDocument36 pages全新全真题库一 PDFTzarlene100% (1)
- Very Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsDocument5 pagesVery Hungry Caterpillar Clip CardsARTGRAVETO ARTNo ratings yet
- (Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesDocument196 pages(Bruno Bettelheim) Symbolic Wounds Puberty RitesAmbrose66No ratings yet
- Student Research Project Science ReportDocument8 pagesStudent Research Project Science Reportapi-617553177No ratings yet
- Eng03 Module Co4Document14 pagesEng03 Module Co4Karl Gabriel ValdezNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Syllabus PDFDocument23 pages2023 2024 Syllabus PDFRika DianaNo ratings yet
- Ass AsDocument23 pagesAss AsMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- Using Your Digital Assets On Q-GlobalDocument3 pagesUsing Your Digital Assets On Q-GlobalRemik BuczekNo ratings yet
- KM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)Document4 pagesKM170, KM171, KM172, F3A21, F3A22: 3 SPEED FWD (Lock Up & Non Lock Up)krzysiek1975No ratings yet
- Uniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFDocument64 pagesUniden PowerMax 5.8Ghz-DSS5865 - 5855 User Manual PDFtradosevic4091No ratings yet
- M.SC Food NutritionDocument44 pagesM.SC Food Nutritionasu reddyNo ratings yet
- The Handmaid's TaleDocument40 pagesThe Handmaid's Taleleher shahNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument20 pagesMidterm ReviewerJonnafe IgnacioNo ratings yet
- GST RATE LIST - pdf-3Document6 pagesGST RATE LIST - pdf-3Niteesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaDocument48 pages03 IGT-Influence of Codes Guidelines and Other Regulations On The Tunnel Design in AustriaSudarshan GadalkarNo ratings yet
- Do Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectDocument18 pagesDo Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectJO ANTHONY ALIGORANo ratings yet
- ANTINEOPLASTICSDocument21 pagesANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- 1en 02 PDFDocument96 pages1en 02 PDFAndrey100% (2)
- Storage-Tanks Titik Berat PDFDocument72 pagesStorage-Tanks Titik Berat PDF'viki Art100% (1)
- Product Handbook Arendal 1961 Series SubwoofersDocument44 pagesProduct Handbook Arendal 1961 Series SubwoofersDomagoj KovacevicNo ratings yet
- Oracle SOA Suite Oracle Containers For J2EE Feature Overview OC4JDocument10 pagesOracle SOA Suite Oracle Containers For J2EE Feature Overview OC4JLuis YañezNo ratings yet
- Kingroon ConfiguracoesDocument3 pagesKingroon ConfiguracoesanafrancaNo ratings yet
- Unilever PakistanDocument26 pagesUnilever PakistanElie Mints100% (3)
- CrimDocument29 pagesCrimkeziahmae.bagacinaNo ratings yet
- Wiska Varitain - 0912Document18 pagesWiska Varitain - 0912Anonymous hHWOMl4FvNo ratings yet