Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abdominal Exam Guide
Uploaded by
Darawan MirzaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abdominal Exam Guide
Uploaded by
Darawan MirzaCopyright:
Available Formats
Abdominal Examination/Dr.
Abdulqadr
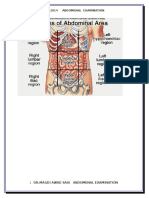
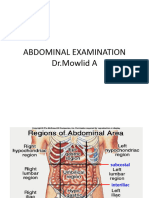
1/Inspection:
-From nipple to mid thigh,include genitalia.
-injuries in 4th intercostal may duo to liver injury.
-blood supply of testes the right one from aorta and left one
from abdominal aorta.
-paraaortic lymph node:located in left side of umbilical.
-Symmetric and borders of abdomen.
-Abdominal dissension:abdomen may distended or may
flat,by the ruler or something else from xiphoid to
symphysis pubic ,if touch all abdomen is flat,but if not
touched distended,and also we have abdominal
scaphoid,and there is gap.
-Hair distribution.
-Umbilical: invertd or everted.
-Also ask the patient cough we look to there is any hernia.
-Venous dilatation:three site for venous dilatation.
-Around umbilical.
-Costal margin.
-Flank.
visible in Inferior vena cava obstruction,duo to
And this venous dilatation called caput medusae,which is
dilation of veins,which occur in chronic liver disease,and
portal hypertension duo to that in normal person systemic
pressure more higher than portal pressure but in portal
hypertension portal pressure higher than systemic pressure.
Other sign of arteroivenous anastomoses left epigastric vein
and azygos vein around lower third of esophagus.
Third anorectal region,Fourth bare area of liver that not
covered by peritoneum,Five retro diaphragmatic.
Also for examination index finger over middle part of dilated
vein then empty the vein by to index finger remove blood
from vein and if see the vein no dilated from that mean
blood from umbilical to away .
If there is inferior vena cava obstruction from dawn to
umbilical.
In lateral aspects inguinal axillary from inguinal venous
plexus to axillary because by passing IVC and there’s
obstruction here.by passing upward.
-color:redness of abdomen may duo to cellulitis,which is
inflammation of subcutaneous tissue.
Or maybe yellow discoloration duo to jaundice,for different
between obstructive jaundice(surgical) and medical
jaundice(Hemolytic anemia)by Inspection:we look for
scratch,in surgical jaundice duo to disposition of bile
secretion(disposition of bilirubin),treatment for itching
Is cholesterol amine.
Which change bile salt to water soluble and secreted with
urine.tablespoon in glass of water.
-visible pulse:eye level to upper surface of abdomen.
We look to supraumbilical area,possibilities of pulsation
May duo to abdominal aortic aneurysm.
AA:mean Acute Abdomen.
AA:mean Acute Appendicitis.
AAA:Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.
AAAA:Anemia Asthenia Anorexia Group A blood is for
gastric cancer.
And blood group O mostly may has gastric ulcer.
Asthenia mean weakness and lack of energy.
And this visible pulse may duo to transmitted pulsation for
example abdominal aorta and there is mass sitting on
abdominal aorta.
And this mass could be retro peritoneal mass,or CA
pancreases,or CA stomach,or hydrated cysts of the retro
peritoneal area.
How we can differentiate between AAA and transmitted
pulsation?both index finger on it and two movements for
aortic aneurysm,wider separation and elevation of finger.
But in transmitted pulsation only elevation no expansion.
-Scar:site of Scar:midline,right paramedian,left paramedian,
Subcostal margin,right subcostal margin called koxer
incision for cholecystectomy,and left subcostal margin.
Cadaveric incision form xiphoid sternum to suprapubic use
for bomb injuries(shell injury).
-huge mass if present.
-Movement with respiration:if no movement with respiration
is indicate pain,or paralysis of all intestine and generalized
peritonitis.
-Peristalsis:movements of intestine,if you check from left to
right in upper part of abdomen,usually occur in midday
called hunger peristalsis.and audible peristalsis called
Borborigmi.and diagnosis of it gastric outlet obstruction.
Petechiae:small subcutaneous bleeding,occur in ITP
Hematoma:large size.
-spider nevi :is composed of central arterial surrounded by
capillaries.by the pin press if spider nevi remove but if
ordenari nevi not removed.also we cam difference between
them by magnifying glass.
In liver cirrhosis patient has jaundice+spider nevi+dilated
vein around umbilical.
We should say Acute appendicitis or its chronic.
Check for Acute appendicitis:
McBurney line. we draw imaginary line between
supraanterioilliacspine and umbilical,junction of medial two
third and lateral third called mcburnery .
Test for Acute appendicitis:
1.Pointing test:ask patient to cough where site of pain.
2.McBurney test:Press to medial two third and lateral third
and look to face of patient.
How we know it’s right iliac fossa?
Two vertical line two horizontal line,vertical line mid clavicle
line to midinguinal point.
We have two term midinguinal ligament and point.
Midinguinal ligament is the ligament that join pubic tubercle
to anterior iliac spine,but midinguinal point extend from
anterior iliac spine to symphysis pubis.
Two horizontal line upper from subcostal.
We can’t touch ten rib,and its nine and ten comes to touch
nine above this line.
11 and 12 called floating rib.
Lower horizontal:transtubercle.
DDH/development dislocation of hip.
From lower why not from anterior iliac spine?
Duo to limping leg In DDH if stand is not horizontal line is
oblique line.
How you can find iliac crest?
Find anterior iliac spine then follow anterior iliac spine the
second most prominent iliac crest.
3.Most important test is localized tenderness.
4.rebound tenderness mechanism of pain:
Visceral peritoneum and parietal peritoneum,visceral nerve
supplied by Autonomic nervous system but parietal by
lower six intercostal nerve,when press on it you are
touching parietal peritoneum lowering down when you
move your hand upward suddenly cause irritation of parietal
peritoneum by acute appendix causing pain.
5.rolfzen test:press over left iliac fossa,pressings on
sigmoid colon Other name called pelvic colon By this
mechanism feeling severe pain in right side of abdomen,the
mechanism is increasing pressure,gas inside colonic lumen
will be reflected backward,increasing pressure in cecal area
appendix attached to cecum increase intralumen pressure
cause severe pain in acute appendicitis,mechanism number
two most of small bowel presents in left side.and cause
pressure.
6.obturator test:.90 degrees Reflexion of hip joint and 90
degree reflexion of hip joint then internal rotation feel severe
pain in right iliac fossa.obturator muscle attached to inner
aspect of upper head of femur cause contraction touched
to infected appendix and cause severe pain .
7.Sous test :palm of left hand over hip joint take all lower
limb by right hand and has pain duo to contraction of sous
muscle.
8.sheren test:there is triangle umbilical and anterior iliac
spin and pubic symphysis bring something not sharp press
over skin there is nothing when you reach right side patient
shout duo to severe pain,mechanism of test Hyperesthesia
by dermatome.
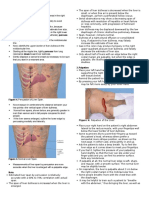
Palpation of kidney:bimanual examination:left hand below
costal margin below last rib never mention number lateral to
paraspinal muscle,right hand over lumbar region,pushing by
left hand and detecting by right hand.anterior hand called
watching hand posterior hand called depressing hand.
Renal angle tenderness:lower border of last rib,the angle
that located between horizontal line of last rib and
paraspinatous muscle called renal angle.
Two test by local pressure on renal angle and percussion,
And third one by hitting for very obese patient.
Second lecture abdominal examination:
Best way to relax muscle take breath from mouth.
In history taking say right upper abdomen and.....no right
iliac fossa we say right iliac fossa in Examination.
-Aim of superficial palpation: locate site of pathology.
-Aim of deep palpitation:details os superficial pathology.
-Temperature.
Rectus Abdominal joined by linea alba.
-Spleen palpation:for splenomegaly,why we start from right
iliac fossa?duo to direction of spleen enlargement is right
iliac fossa.
Say to patient to breath.why?because during respiration
spleen intraperitoneal organ and move with respiration,and
move dawn.
Sometimes there is resistance and can’t relax abdomen
such in perforated vesicous For this hand over hand .
How we know I know this is spleen?
.Notch.
.sharp edge.
.direction enlargement.
.can not get above it.
.in percussion dull.
Kidney resonant duo to lobes of bowel between kidney and
anterior abdominal wall.
Spleen should be 2.5 enlarged then palpable.
.spleen is mobile kidney is not mobile.
Bimanual palpation of spleen(just palpable):lateral right
position put one hand support other hand above.
Liver palpation:say to patient to breath also liver move duo
to its intraperitonum.
Also measure how many cm below costal margin.
If it’s nodules,may has cirrhosis or mitastaic.also for
tenderness.
Test for Acute cholistaytis?
1.Murphy sign:say to patient breath mid clavicular below
costal margin put your hand here position of hand funds of
gallbladder then deep deep breath during one of breath
press patient stop from respiration then that mean murphy
sign positive.
Or palm of hand parallel to costal margin and thumb below
costal margin in mid clavicular line ask patient deep breath
during one inspirations press and patient stop from
inspiration.
Auscultation:
Bowel sound:for bowel sound stethoscope in right iliac
fossa because sound pass from iliac to cecum here and
sound pass from narrow lumen to wider lumen there’s
amplification of sound.and wait for one minute.
1.No bowel sound/called ileus.
2.sluggish bowel sound/less than 3 in one minute.
3.normal bowel sound.
4.exaggerated bowel sound.More than 3 in 1 minuetIn
intestinal obstruction for two day but then became
paralysis.
Also auscultation for AAA.
Also for renal artery stenosis.
Also when we have pulsation in epigastric region.
Also we should do back Examination.
Also we should do rectal examination.
For rectal examination lateral position,but best one is knee
elbow position,very tiered patient in same position.
First inspection:
For swelling,thrombosis,abscess,strangulated pay.
Contraindication for PR examination:
-Acute painful fissure
-Thrombosed pile
-perianal abscess/sub mucus abscess.
-thrombitis of pile. /infection of pile.
Index finger put over annul pressure then after few second
become relaxation.
Put your brain on tip of finger.
Any palpable mass,foreign body,hard feces,palpable ulcers,
Prostate benign or malignancy in benign mobile but in
malignancy fixed.and normally there is groove between
right and left lobe but in malignancy this groove not remain.
Also we have shifting dullness in Abdominal Examination:
In huge a cities assistant hand? other hand opposite side
and tap there is impulse hitting hand.also transmission is
positive.
In huge acitis can’t exam spleen and liver so push spleen
down hitting your hand when come back.
In percussion is dull but when patient move lateral upper
part become resonant because fluid go dawn.
Also we should palpate left supraclavicular Lymph node
Varicose Lymph node and sign called trozas sign.
Why left side?
Because cictema chyli start in portal hepatic then move to
right side but at level of maniburnum sterni pass to left
side .
You might also like
- Structural Notes and Specifications for ConcreteDocument1 pageStructural Notes and Specifications for Concreteroger100% (2)
- Stanley - Your Voice (1957) PDFDocument396 pagesStanley - Your Voice (1957) PDFŠašavi Sam MajmunNo ratings yet
- Unipack II ManualDocument30 pagesUnipack II ManualMarijaŽaper67% (3)
- AbdomenDocument7 pagesAbdomenShayne Lyrrie Pajela100% (1)
- LWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALDocument6 pagesLWW BATES 13 Abdomen Transcript FINALmuhammad Babar50% (2)
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Document4 pagesOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument39 pagesAcute Appendicitis Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentVishva Lalitbhai HirparaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Caterpillar C 27Document594 pagesManual de Partes Caterpillar C 27LuisPupiales100% (1)
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument91 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenEndah Cahaya SufianyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam GuideDocument5 pagesAbdominal Exam GuideNesma AdelNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment of Abdomen and RectumDocument41 pagesPhysical Assessment of Abdomen and RectumLeonilyn Dagoplo RN100% (1)
- Notes On Physical Examination of AbdomenDocument6 pagesNotes On Physical Examination of AbdomenMarwa Al-AzzawiNo ratings yet
- H.A Abd SPLEENDocument36 pagesH.A Abd SPLEENromaaNo ratings yet
- Abdomenal Exam HandoutDocument4 pagesAbdomenal Exam HandoutAjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Assessing the Abdomen: 4 Quadrants and 9 RegionsDocument54 pagesAssessing the Abdomen: 4 Quadrants and 9 RegionsWilma Acorin OrillinedaNo ratings yet
- LI - Physical Examination - AbdomenDocument6 pagesLI - Physical Examination - AbdomenTravis DonohoNo ratings yet
- Examination of Gastrointestinal SystemDocument37 pagesExamination of Gastrointestinal SystemayushiNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: Temperature: Respiratory Rate: PulseDocument55 pagesVital Signs: Temperature: Respiratory Rate: PulsemiraNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument46 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenPrystia_RNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1Document33 pagesAbdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1myarjddbzNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam GuideDocument22 pagesAbdominal Exam GuideSamuel Sebastian SirapanjiNo ratings yet
- PACES 3 - AbdomenDocument14 pagesPACES 3 - AbdomenDrShamshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Checklist Reticuloendothelial System ExaminationDocument5 pagesChecklist Reticuloendothelial System Examinationmohammed alrubaiaanNo ratings yet
- Bates Physical Exam Video NotesDocument3 pagesBates Physical Exam Video Notesdulcedeleche12359No ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam StepsDocument4 pagesAbdominal Exam StepsRonaldoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination ProcedureDocument5 pagesAbdominal Examination ProcedureAnamul hossainNo ratings yet
- Safawr 353264364562Document5 pagesSafawr 353264364562non_zenseNo ratings yet
- Session 6 - Performing Abdominal ExaminationDocument33 pagesSession 6 - Performing Abdominal ExaminationOtsward OwdenNo ratings yet
- Incarcerated Hernia: Case Studies Sushila Ladumor, MDDocument11 pagesIncarcerated Hernia: Case Studies Sushila Ladumor, MDbeautifulbeastNo ratings yet
- Abdomen PE ChecklistDocument6 pagesAbdomen PE ChecklistJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IDocument4 pagesSemester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IFlowerNo ratings yet
- Abdomen exam guide under 40 charsDocument5 pagesAbdomen exam guide under 40 charsdidutza91No ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination: Before Examining The PatientDocument4 pagesAbdominal Examination: Before Examining The PatientrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Basic Abdominal ExaminationDocument3 pagesBasic Abdominal Examinationcpradheep100% (1)
- No. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Document3 pagesNo. Description of Actions To Be Done Score 0 1 2Adiprayogo LiemenaNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument28 pagesAbdomenCindi EricaNo ratings yet
- PE of The LiverDocument2 pagesPE of The LiverJules DiwasNo ratings yet
- DR - Serwan HX - ExDocument3 pagesDR - Serwan HX - ExDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Hernia Scrotalis FIxDocument56 pagesHernia Scrotalis FIxivaniNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument9 pagesAbdominal Examinationthunderlike30No ratings yet
- GI Exam TechniquesDocument6 pagesGI Exam TechniquesTommy LeNo ratings yet
- HemorrhoidsDocument6 pagesHemorrhoidsRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Hepatitis CDocument2 pagesSymptoms of Hepatitis CStay OptimisticNo ratings yet
- Examination of Gastrointestinal System: I.InspectionDocument7 pagesExamination of Gastrointestinal System: I.Inspectionvonon35132No ratings yet
- Respiratory Examination: The Position of The PatientDocument24 pagesRespiratory Examination: The Position of The PatientMuhammed Barznji100% (1)
- 3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamDocument15 pages3 Session 3 - AbdominalExamjhk0428No ratings yet
- Stagiaire's Guide To General Surgery OSCEsDocument36 pagesStagiaire's Guide To General Surgery OSCEsMawNo ratings yet
- Examining the Hips: A Guide to Palpation and Mobility TestsDocument2 pagesExamining the Hips: A Guide to Palpation and Mobility TestsReham QueNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Palpation: Dupuytren's ContractureDocument6 pagesAbdominal Palpation: Dupuytren's ContractureshaifNo ratings yet
- Retdem Checklist: Abdomen Lopez, Marjorie Joy C.: Refer To Picture inDocument4 pagesRetdem Checklist: Abdomen Lopez, Marjorie Joy C.: Refer To Picture inAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Performance Evaluation Checklist On The Assessment of The AbdomenDocument5 pagesCollege of Health Sciences Department of Nursing Performance Evaluation Checklist On The Assessment of The AbdomenTangonan DarrelNo ratings yet
- Abdomen AssessmentDocument7 pagesAbdomen Assessmentbi santiagoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam: Step-by-Step GuideDocument14 pagesAbdominal Exam: Step-by-Step GuideAffan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen 1Document20 pagesAssessing The Abdomen 1srslytrdNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination Guide for Medical StudentsDocument9 pagesAbdominal Examination Guide for Medical StudentsAnonymous 278KLXQgI3No ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument107 pagesAbdominal Examinationaxmedfare138No ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesClinical Examination of Respiratory SystemDipienshu BhatNo ratings yet
- GGGGHHDocument7 pagesGGGGHHนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment VideoDocument4 pagesAbdominal Assessment VideoAmber Nicole HubbardNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination - 2 - 1Document16 pagesAbdominal Examination - 2 - 1Zeinab AmerNo ratings yet
- Abdomen quadrants organs assessment pain tendernessDocument3 pagesAbdomen quadrants organs assessment pain tendernessDessytha NathaniaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument14 pagesAbdominal ExaminationValeria Guerra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesClinical Examination of Respiratory SystemAmit PandyaNo ratings yet
- URTI (DR Hemin Khalid)Document21 pagesURTI (DR Hemin Khalid)Darawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Hemoptysis - CA Bronchus PDFDocument49 pagesHemoptysis - CA Bronchus PDFDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- URTI (DR Omer Surchi)Document45 pagesURTI (DR Omer Surchi)Darawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Pleural DiseasesDocument33 pagesPleural DiseasesDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Copd PDFDocument28 pagesCopd PDFDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Esoph CA DavidsonDocument2 pagesEsoph CA DavidsonDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Chest PainDocument17 pagesApproach To Patient With Chest PainDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Bradycardia: Causes, Types and ManagementDocument35 pagesBradycardia: Causes, Types and ManagementDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- SGL14 Epigastric Pain and Weight LossDocument23 pagesSGL14 Epigastric Pain and Weight LossDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- GIT History TakingDocument7 pagesGIT History TakingDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Stable IHDDocument16 pagesStable IHDDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Gastric CA DavidsonDocument3 pagesGastric CA DavidsonDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- DR - Serwan HX - ExDocument3 pagesDR - Serwan HX - ExDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Approach To PalpitationsDocument74 pagesApproach To PalpitationsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine and Behavioural Sciences MCQsDocument29 pagesCommunity Medicine and Behavioural Sciences MCQsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument4 pagesHistory TakingDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Review of PhysiologyDocument24 pagesReview of PhysiologyDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Group B Surgery QuestionsDocument4 pagesGroup B Surgery QuestionsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- DR - Niyan HerniaDocument7 pagesDR - Niyan HerniaDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- DR - Abdulqadir HXDocument2 pagesDR - Abdulqadir HXDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- GUTDocument4 pagesGUTDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia: Dr. Sameeah A. Rashid MBCHB, DMRD, Fibms College of Medicine, Hawler Medical UniversityDocument35 pagesDysphagia: Dr. Sameeah A. Rashid MBCHB, DMRD, Fibms College of Medicine, Hawler Medical UniversityDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- GITDocument4 pagesGITDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral arterial disease clinical manifestationsDocument4 pagesPeripheral arterial disease clinical manifestationsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- SGL1 - Breast ImagingDocument93 pagesSGL1 - Breast ImagingDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Group D Surgery QuestionsDocument3 pagesGroup D Surgery QuestionsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDocument103 pagesApproach To The Patient With A Heart MurmurDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- SGL6 - CoughDocument63 pagesSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Review of Physiology of Respiratory System Cardiovascular System Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesReview of Physiology of Respiratory System Cardiovascular System Digestive SystemDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Laporan FaalDocument25 pagesLaporan FaalAgnes NathaniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter III Pharmacokinetics: Durge Raj GhalanDocument64 pagesChapter III Pharmacokinetics: Durge Raj GhalanDurge Raj Ghalan100% (3)
- Chapter 43 - Lead - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsDocument57 pagesChapter 43 - Lead - 2015 - Handbook On The Toxicology of MetalsChanWingSanNo ratings yet
- Constance Carroll Cosmetics) Final.1Document4 pagesConstance Carroll Cosmetics) Final.1api-26027438100% (1)
- Uganda National Urban ProfileDocument74 pagesUganda National Urban ProfileUnited Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-HABITAT)No ratings yet
- Wörterbuch Der Humanbiologie - Dictionary of Human Biology - Deutsch - Englisch - Englisch - Deutsch. English - German - German - English (PDFDrive)Document1,002 pagesWörterbuch Der Humanbiologie - Dictionary of Human Biology - Deutsch - Englisch - Englisch - Deutsch. English - German - German - English (PDFDrive)MilaNo ratings yet
- SpaceX ProposalDocument6 pagesSpaceX ProposalTexas WatchdogNo ratings yet
- Diseases That Cause HypoproteinemiaDocument12 pagesDiseases That Cause HypoproteinemiaRachel Marie M. GaniaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Skull Bones - English - Student - Fill inDocument6 pagesLab Manual - Skull Bones - English - Student - Fill inthejaskumar2026No ratings yet
- The Life and Works of Dr. Jose P. Rizal: Rizal As A DoctorDocument14 pagesThe Life and Works of Dr. Jose P. Rizal: Rizal As A DoctorPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Non-Digestible Oligosaccharides: A Review: Solange I. Mussatto, Ismael M. MancilhaDocument11 pagesNon-Digestible Oligosaccharides: A Review: Solange I. Mussatto, Ismael M. MancilhaPatrícia Felix ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- Aftercooler - Test: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument7 pagesAftercooler - Test: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenKeron Trotz100% (1)
- NASA Water Filtration System GuideDocument54 pagesNASA Water Filtration System GuideBoey Soo Yin100% (1)
- EXERCISE - (JEE Main) Chemical Equilibrium - CombinedDocument24 pagesEXERCISE - (JEE Main) Chemical Equilibrium - CombinedKeerthana Reddy DomaNo ratings yet
- RS9923 - Grade 12 Compulsory Subjects - Test Specification Chart and Model Questions - FinalDocument32 pagesRS9923 - Grade 12 Compulsory Subjects - Test Specification Chart and Model Questions - FinalPrince JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Dapsone 2Document2 pagesDapsone 2JeanMENo ratings yet
- Payroll Accounting 2015 1st Edition Landin Test Bank 1Document106 pagesPayroll Accounting 2015 1st Edition Landin Test Bank 1dorothy100% (47)
- Work Immersion PortfolioDocument15 pagesWork Immersion PortfolioKaye Irish RosauroNo ratings yet
- DCM601A51 - Technical DataDocument405 pagesDCM601A51 - Technical Datathanhthuan100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Melissa NagyNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Reviewer: Surgical Handwashing QuizDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam Reviewer: Surgical Handwashing QuizOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- 4140DE Data SheetDocument1 page4140DE Data SheetNabeel AmeerNo ratings yet
- Subway 2009Document12 pagesSubway 2009sparklers_mNo ratings yet
- Wazaif Totaky Home Remedies Receiver Software Powervu Key-1Document18 pagesWazaif Totaky Home Remedies Receiver Software Powervu Key-1Habib MohammedNo ratings yet
- Topic - 2015 Quality MethotdDocument12 pagesTopic - 2015 Quality MethotdclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Health Behaviour: Current Issues and ChallengesDocument13 pagesHealth Behaviour: Current Issues and ChallengesK.A.No ratings yet