0% found this document useful (0 votes)
769 views26 pagesLecture - 6 - Sockets & Switch Board Desing
This document discusses electrical sockets and switchboard design. It describes different types of sockets, including normal, power, UPS, and weatherproof sockets. It outlines requirements for sockets mounting and wiring. The document then covers switchboard components, functions, required instruments and devices, design requirements, construction, types including lighting and power distribution boards, panel balancing, and circuit subdivision standards. An example is provided to calculate circuit current and balance loads across phases.
Uploaded by
xx amjaddCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
769 views26 pagesLecture - 6 - Sockets & Switch Board Desing
This document discusses electrical sockets and switchboard design. It describes different types of sockets, including normal, power, UPS, and weatherproof sockets. It outlines requirements for sockets mounting and wiring. The document then covers switchboard components, functions, required instruments and devices, design requirements, construction, types including lighting and power distribution boards, panel balancing, and circuit subdivision standards. An example is provided to calculate circuit current and balance loads across phases.
Uploaded by
xx amjaddCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Sockets Design
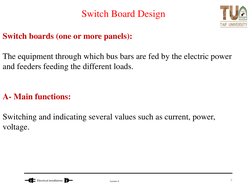
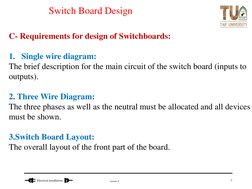
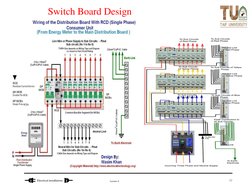
- Switch Board Design