Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Processes
Uploaded by
Gati LohiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Processes
Uploaded by
Gati LohiaCopyright:
Available Formats
LIFE PROCESSES
MOLECULAR MOVEMENT(Sign of LIVING) -No mov. In viruses-Considered dead
Living beings-well organised structures – These structures likely to break –Organism dead.So its imp-
Living beings must keep repairing,maintaining these structures
Since these structures – made of molecules-must be moving all the time
For a living being it is necessary to perform basic functions for proper body functioning. These
basic functions performed by organisms to maintain life are known as life processes.
Processes essential for maintaining life
1)NUTRITION –Energy needed for maintenance processes .This energy comes from outside of the
body of living organism .So the process to transfer the energy(food) from outside-inside the body is
called NUTRITION. CARBON-BASED MOLECULES
Food includes carbohydrates ,fats ,vitamins ,proteins.
CELLULOSE STARCH SUGAR
(CAN’T BE DIGESTED (DIGESTABLE)
BY HUMANS)
OUTSIDE RAW MATERIALS USED BY AN ORGANISM—food,water,sunlight,Oxygen( oxidise
food and release energy)
2)RESPIRATION-Energy must be broken down for use in the body.Oxidising-reducing reactions-
common chemical means to break down molecules..The process of acquiring oxygen from outside
the body and using it to breaking the food sources for cellular needs-RESPIRATION.
SINGLE-CELLED ORGANISM-No specific organs MULTI-CELLED ORGANISM-All cells may not be
Entire surface of organism is in Taking in food direct contact with the environmentSimple
contact with environment Exchanges of gases diffusion(gaeous movement from high to low
Removal of wastes concentration)will not meet requirements of all
Cells
3)TRANSPORTATION-Food and oxygen are taken up at only one place and all the body parts need
the foodProcess of carrying food and oxygen from one place in the body to another
TRANSPORATION(TRANSPORTS WASTE AWAYS FROM CELL TO EXCRETORY TISSUE)
4)EXCRETION- When chemical reactions uses food and O2 to generate energy, many by products are
created in the body that are not only useless but also harmful for the bodyNeeded to be removed
and discarded out from the body EXCRETION(TRANSPORTS OUT FROM THE BODY)
NUTRITION
AUTOTROPHIC HETEROTROPHIC
HIC
Organisms that prepare their Organisms that cannot prepare their own
own food through the process of food and depend upon autotrophs for
photosynthesis .Ex-Green plants nutrition
SYMBIOTIC PARASITIC SAPROTROPHIC HOLOZOIC
Two organisms live in Organism lives inside organisms feed Organism takes
close association to the host organism for on dead and food into the body
benefit each other nutrition decaying matter through mouth
EXAMPLES Of SYMBIOTIC-Lichens(algae and fungi)&corals and sponges
PARASITIC-Tapeworm,cuscuta,leeches
SAPROTRPHIC-Bacteria,fungi(yeast,mushrooms,bread moulds)-Convert dead
matter to compost(simpler sub.)
HOLOZOIC(Animal like)- Humans,amoeba
AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITION
Photosynthesis-Autotrophs take in substances from outside(CO2,H2O) and convert them
to forms of energy(Carbohydrates) in presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
Not used immediately are stored inSTARCH
(Serves as internal energy to be used as and when required)
For transportationSUCROSE
6CO2+12H2O C6H12O6+6CO2+6H2O
Sunlight &Chlorophyll (Glucose)
Comes from H 2O not CO2
Raw materials required for photosynthesis-
Sunlight(Keep it in dark room or cover one leaf with black paper)
Water-Taken up from soil by the roots(Stop giving it for days)
Carbon dioxide-Stomata(pl)/Stoma(s) are tiny pores present on the surface of leaves
Massive amounts of gaseous exchange takes place thrgh these pores
Since,large amt of water lost thrgh these pores,plant closes these pores when
not in need for CO2
Guard Cells-Kidney shaped cells that surround the stoma and responsible for
opening and closing of these pores.
They swell when water flows in thempore opens
Pore closesGuard cells shrink
Steps need not In DESERTS if stoma opens in daytime(water loss would be high-Sunlight)
take place one Stoma opens at night and exchange gases(Transpiration rate minimum) and
after the other
in morning traps sunlight and quickly prepares food
Necessity-Place two plants in sep. Glass plates.Put a watch glass containibng KOH in one .
(KOH will react with some CO2 present in glass and give K2CO3)No CO2 Die
Chlorophyll-Chloroplasts contains chlorophyll(green pigment) and responsible for
trapping solar energy from sun.
N2,Phosphorus,Mg,Fe-Taken up frm soil.N2 Synthesis of proteins.Taken up in form
of inorganic nitrates/organic compounds prepared by bacteria from atmospheric
nitrogen
EVENTS OCCURING DURING THE PROCESS OF PHOTOYNTHESIS
1)Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
2)Conversion of light energychemical energy splitting water moleculesH2 and O2
3)Reduction of CO2 CH2(Oxygen removed+Hydrogen added)
HETEROTROPHS-Consume complex substances broken down into simpler ones upkeep
and growth of body bio-catalysts(enzymes)
PROCESS FOR NUTRITION IN AMOEBA
ASSIMILIATION EGESTION
INGESTION DIGESTION ABSORPTION
The absorbed food is The remaining
Pseudopodia(temporary Inside the food small molecules
further assimilated by undigested
finger like projections) vacuole , then absorbed
amoeba to use energy for material is moved
engulfs the food that complex food is by cytoplasm growth to the surface of
comes in contact with broken down cell and thrown
its cell surface and
into simpler out.
forms food vacuole
PROCESS OF NUTRITION IN PARAMOECIUM(unicellular org.)
1)Cell has a definite shape and food is taken in at a specific spot
2)Food is moved to this spot by movement of cilia which cover the entire surface of cell.
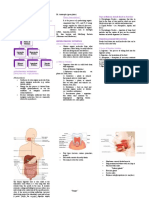
PROCESS OF NUTRITION IN HUMANS
ALIMENTARY CANAL-Long tube extending from mouthanus
Food has to be processed to 1)Ingestion-It means taking in food into
generate particlessmall,same mouth or buccal cavity . As the food enters
texturecrushing food with teeth the mouth ft is moistened by saliva (lining of
canal is soft)-fluid secretedsalivary gland
Food
MouthStomac As food is complex in nature,so it is
oesophagus converted into its simpler form by the
action of biological catalyst called enzymes.
S.I.-Longest part of canal 2) Digestion-Breaking down of large organic
fitted in a compact molecules ( like carbohydrates to small
space becoz of extensive molecules (like simple sugar) .
coiling-more time for
absorption.Site of Large organ that expands
complete digestion when food enters it
4)Assimiliation- The villi in small 3)Absorption-Inner lining of s.i. has
Intestine are richly supplied with numerous finger like projections
blood vessels which take the called villi which increase the surface
absorbed food to each cell of
area for absorption of digested food.
body to building new cells or
repair of old ones
L.I.-Unabsorbed food sent to 5)Excretion-Rest of material
l.i. where its wall aborbs more removed from body via anus
water from this material
Paristaltic movement(Wave like mov.)-Contraction and expansion of muscles of the Oesophagus to
push the food forward . Food move in a regulated manner and process properly in each part.
GLAND SECRETION SITE FUNCTIONS
FUNCTION
1)Salivary Gland Saliva(salivary Buccal The enzyme(salivary amylase)breaks down starch to
amylase) Cavity maltose then to glucose
2)Gastric Gland Hydrochloric acid Creates an acidic environment for Enzyme pepsin to action
Stomach Kills harmful microbes present in stomach
Pepsin ProteinAmino acids
Mucus Protects the inner lining of stomach from the action of acid
3)Liver(Largest gland) Bile juice Food coming from stomach-acidic .To make it alkaline for
Gall Bladder(storage) S.I pancreatic enzymes to act
Bile Salt Fats- large globules in intestine-difficult for enzymes to act.
Breaks down into small globules-Incr. in efficiency of enzy.
Known as EMULSIFICATION
4)Pancreas(second Amaylse Starch/GlucoseSugar
largest gland) Trypsin S.I ProteinAmino Acids
Lipase FatsFatty Acids+ Glycerol(energy stored)
5)Small Intestine Intestinal Juice S.I. Starch/GlucoseSugar
ProteinAmino Acids
FatsFatty Acids+ Glycerol(energy stored)
You might also like
- 6 Life Processes NotesDocument7 pages6 Life Processes NotesBurhaan MalikNo ratings yet
- STM008 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSTM008 ReviewerCatherine Sanchez RosarioNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Processes in Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesNutrition Processes in Living OrganismsRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdDocument8 pagesAdobe Scan Sep 05, 2021iytzitst88txdKumari KNo ratings yet
- Living Processes in Unicellular OrganismsDocument2 pagesLiving Processes in Unicellular Organismsalya yNo ratings yet
- Pee Notes - 085321Document8 pagesPee Notes - 085321Kathlyn LopeñaNo ratings yet
- The Formation of Life on Earth: A Quick ReviewDocument29 pagesThe Formation of Life on Earth: A Quick ReviewVincent Emilio L. ChanNo ratings yet
- Organismal Biology and Genetics GuideDocument33 pagesOrganismal Biology and Genetics GuideNeera ManalangNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDocument10 pages7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- What Is Life Process?Document48 pagesWhat Is Life Process?Sujan BansodNo ratings yet
- HSB Section ADocument12 pagesHSB Section AAshford Thom100% (1)
- Life Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESDocument10 pagesLife Processes - BIO - CLASS 10 - NOTESvaarunisaxenaNo ratings yet
- 472 - Bio 103 WeboDocument8 pages472 - Bio 103 Weboabiolaelizabeth255No ratings yet
- Arvind Academy: Mode of NutritionDocument20 pagesArvind Academy: Mode of Nutritionrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes (Yashvi Modi)Document15 pagesLife Processes Notes (Yashvi Modi)YASHVI MODI60% (5)
- Cell Specialization in Multicellular OrganismsDocument2 pagesCell Specialization in Multicellular OrganismsNITIASSWARENo ratings yet
- bio -4.1Document4 pagesbio -4.1Alecel May PacardoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Theory Class 10Document11 pagesNutrition Theory Class 10TarunNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyRizzuya UrakuwaNo ratings yet
- Biological Science EssentialsDocument35 pagesBiological Science EssentialsJYOTHI DNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology (NCERT)Document65 pages10th Biology (NCERT)abbasahamed124No ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture: Transcript + NotesDocument35 pagesZoology Lecture: Transcript + NotesCharles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- E&L Science 8-22-19Document2 pagesE&L Science 8-22-19Borbe ClauNo ratings yet
- Biology 1-3 Class 10Document3 pagesBiology 1-3 Class 10Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- Additional Science B2 (Biology) SpecificationDocument6 pagesAdditional Science B2 (Biology) Specificationgunslinger78No ratings yet
- Life ProcessDocument21 pagesLife ProcessthankschinmayNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 1Document49 pagesLife Process Part 1Jyoti AsatiNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter-1-Characteristics of Living Things & Branches of BiologyDocument36 pagesBiology Chapter-1-Characteristics of Living Things & Branches of BiologyJACKSONNo ratings yet
- Life Process: Summary of 6.1 & 6.2Document4 pagesLife Process: Summary of 6.1 & 6.2Vanavarajan R TPSNGLNo ratings yet
- A Self-Regulated Learning 1Document5 pagesA Self-Regulated Learning 1JoanNo ratings yet
- Biology Short Notes - Term IiDocument1 pageBiology Short Notes - Term IiMasuma M RemtullaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - 1ST Sem Week 1&2 ActivitiesDocument12 pagesGrade 12 - 1ST Sem Week 1&2 ActivitiesWolf DmitriNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life and Earth ScienceDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Life and Earth ScienceRalph Francis GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Nutritive RequirementsDocument7 pagesNutrition: Nutritive RequirementsMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- LifeDocument21 pagesLifeDheer AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cell EnergyDocument29 pagesCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNo ratings yet
- Chem 2212Document2 pagesChem 2212Marg'riette PascuaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Intro BiosciDocument57 pagesLec 1 - Intro BiosciKristine VailNo ratings yet
- Intro To BotanyDocument11 pagesIntro To BotanyALTHE NICOLE ALVIOLANo ratings yet
- Life Processes 2Document21 pagesLife Processes 2jeena raNo ratings yet
- Science ProjectDocument47 pagesScience ProjectArnav KadamNo ratings yet
- Honey Cambridge PDFDocument10 pagesHoney Cambridge PDFTanvi BujalaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Kithmini100% (1)
- Life Processes NotesDocument87 pagesLife Processes Notesashtosh1418No ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument21 pagesLife ProcessesMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Ii - 2ND Sem PrelimsDocument4 pagesGen Bio Ii - 2ND Sem PrelimsRomeia Rhayne Olivar MagaoayNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesDocument54 pagesDelhi Public School, Harni: Subject - Biology (Science) Class - X Chapter-6 Life ProcessesAnin BertNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerDapflean Centeno MusniNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument14 pagesBiology NotesZuZZi PlayNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Nutrition in PlantsDocument15 pagesClass 7 - Nutrition in PlantsSMKNo ratings yet
- 02 Energy Flow in EcosystemsDocument21 pages02 Energy Flow in EcosystemsARIELLE DESAMITONo ratings yet
- Nutrition: General Biology 2Document5 pagesNutrition: General Biology 2Thea DegraciaNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food Web PDFDocument6 pagesFood Chain and Food Web PDFA. ZNo ratings yet
- Final Life ProcessDocument50 pagesFinal Life Processdivyanshikeshari546No ratings yet
- 3 Year Biology Course for Class 10 Covers Key Life ProcessesDocument120 pages3 Year Biology Course for Class 10 Covers Key Life ProcessesNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Life Processes TutionDocument37 pagesLife Processes Tutionmanpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Kingdom EubacteriaDocument47 pagesKingdom EubacteriafarhanxxNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER-Gen Bio-Q4Document8 pagesREVIEWER-Gen Bio-Q4Pauline Jean Cueto BundaNo ratings yet