Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER 4-Elasticity
Uploaded by
Akira MaharajOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 4-Elasticity
Uploaded by
Akira MaharajCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 4: ELASTICITY
Elasticity of demand
A measure of how sensitive QD is to the change in the price.
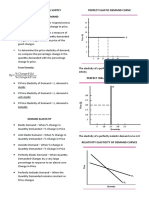
PRICE ELASTICITIES OF DEMAND
PERFECTLY Smallest possible increase in price is
ELASTIC ∞ equal to in a decrease in QD
ELASTIC A percentage decrease in QD is more
(SENSITIVE) >1 than the percentage increase in price
UNIT A percentage decrease in QD is equal
ELASTIC 1 to a percentage increase in price
INELASTIC <1 AND A percentage decrease in QD is less
(INSENSITIVE) than the percentage increase in price
>0
PERFECTLY QD is the same at all prices
INELASTIC 0
CALCULATION (STEPS):
1. Percentage change in Quantity:
CHANGE IN QUANTITY
AVERAGE X 100 = % CHANGE IN QUANTITY
2. Percentage change in Price:
CHANGE IN PRICE
AVERAGE X 100 = % CHANGE IN PRICE
3. Price of Elasticity:
% CHANGE IN QUANTITY
% CHANGE IN PRICE
TOTAL REVENUE ELASTICITY:
TR TEST – A method of estimating the POED by observing the change in TR as a result of a change in
price.
INELASTIC ELASTIC
Price increases = Total Revenue Price increases = Total Revenue
increases decreases
Price decreases = Total Revenue Price decreases = Total Revenue
decreases increases
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
PROPORTION OF INCOME
SPENT ON A GOOD:
Greater proportion-elastic,
And vice versa….
FACTORS THAT
INFLUENCE ELASTICITY
OF DEMAND CLOSENESS TO SUBSTITUTES:
TIME ELAPSED SINCE PRICE The closer to substitutes-
CHANGE: elastic,
The longer the time-elastic, And vice versa…
And vice versa...
INCOME ELASTICITIES OF DEMAND:
Measure of how sensitive the demand is to a change in income.
INCOME Percentage increase in QD is greater Income
ELASTIC >1 than percentage increase in come spent (+)
(NORMAL Income (+)
GOOD)
INCOME <1 AND Percentage increase in QD is greater Income
INELASTIC than 0 BUT less than the percentage spent (-)
(NORMAL >0 increase income (savings) Income (+)
GOOD)
NEGATIVE Income increases and QD decreases Income
(INFERIOR <0 spent (-)
GOOD) Income (+)
CALCULATION: (same as the 1st and 2nd steps in POED)
3. Income elasticity of demand:
% CHANGE IN QUANTITY
% CHANGE IN INCOME
CROSS ELASTICITIES OF DEMAND:
Measure of how sensitive the demand is to the change of price of substitutes/complements.
CLOSE Large Small possible increase in one good is
SUBSTITUTES/ Value equal to large increase/decrease in ⅍
COMPLEMENTS of another good
SUBSTITUTES Positive Price of one good increase is equal to
Value QD of another good increase
UNRELATED Zero Price of one good increase is equal to
GOODS QD of another good remains the same
COMPLEMENTARY NEGATIVE Price of one good increase is equal to
VALUE QD of another good increase
CALCULATION: (same as the 1st and 2nd steps in POED)
4. Cross elasticity:
% CHANGE IN QUANTITY
% CHANGE IN PRICE OF COMPLEMENTARY/SUBS.
Elasticity of supply
A measure of how sensitive quantity supplied is to a change.
PERFECTLY Smallest possible increase in price is
ELASTIC ∞ equal to in a large increase in QS
ELASTIC A percentage increase in QS is more
(SENSITIVE) <∞ than the percentage increase in price
AND >1
UNIT A percentage increase in QS is equal to
ELASTIC 1 a percentage increase in price
INELASTIC >0 AND A percentage increase in QS is less than
(INSENSITIVE) the percentage increase in price
<1
PERFECTLY QS is the same at all prices
INELASTIC 0
CALCULATION: (same as the 1st and 2nd steps in POED)
5. Income elasticity of supply:
% CHANGE IN QUANTITY
% CHANGE IN PRICE
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
TIME FRAME FOR SUPPLY
DECISIONS:
Momentary supply –
(Immediate response after
the price changes) In
FACTORS THAT advance decisions-Inelastic
INFLUENCE ELASTICITY
OF SUPPLY Short-Run supply –
RESOURCE SUBSTITUTION (Response of QS to price
POSSIBILITIES: change only when some
Unique/rare goods – Low adjustments in production is
elasticity made) Inelastic.
And vice versa… Long-Run supply –
(Response of QS to price
change when all
technological ways of
adjusting supply is
exploited) Elastic.
NOTES:
ELASTIC – demand/supply responds to changes in price
INELASTIC – demand/supply remains the same
The steeper the slope, the less elastic
You might also like
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chapter-3 Elasticities (Economics)Document14 pagesChapter-3 Elasticities (Economics)tychrNo ratings yet
- 2.2 2.3 Price Elasticity, Income Elasticity and Cross ElasticityDocument41 pages2.2 2.3 Price Elasticity, Income Elasticity and Cross Elasticityhao ruiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 MEDocument21 pagesUnit 3 MEshadabrafiNo ratings yet
- 3.elasticity of DemandDocument18 pages3.elasticity of DemandCharlesNo ratings yet
- CH 4 ElasticityDocument31 pagesCH 4 Elasticityshaheduzaman ShahedNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument69 pagesElasticityAmit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Econs Unit 2 Chap 8-9-11Document72 pagesEcons Unit 2 Chap 8-9-11b972xmny46No ratings yet
- T4 Applications of Supply and Demand SummaryDocument4 pagesT4 Applications of Supply and Demand Summarycassandra evangelistaNo ratings yet
- CECN 104 CH 6Document7 pagesCECN 104 CH 6ariannaNo ratings yet
- G10 Market EquilibriumDocument18 pagesG10 Market EquilibriumAprilia RumahorboNo ratings yet
- IB Econ Notes Chapter 3Document13 pagesIB Econ Notes Chapter 3Yiyun HanNo ratings yet
- IOA Personal NotesDocument9 pagesIOA Personal NotesmadsNo ratings yet
- Application of Elasticity PDFDocument26 pagesApplication of Elasticity PDFvibhuNo ratings yet
- Ayaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1Document12 pagesAyaz Nujuraully - 59376351 1AzharNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Application and ElasticityDocument40 pagesDemand and Supply Application and ElasticityRavi Teja BhagiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument26 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyS522 DAKSHAYININo ratings yet
- ElascticityDocument43 pagesElascticityAbhishek DuttaNo ratings yet
- Application of PedDocument11 pagesApplication of PedmohdportmanNo ratings yet
- Application of PedDocument11 pagesApplication of PedmohdportmanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterDocument29 pagesCh. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterSpencer AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic - CH2Document31 pagesBasic Economic - CH2aunizakaria8No ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesElasticity of DemandRonan FerrerNo ratings yet
- ECO101 Lec 9Document14 pagesECO101 Lec 9HHGV JGYGUNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply - 2021Document51 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply - 2021nitin heart hakerNo ratings yet
- PPT2.4 - Elasticity of DemandDocument37 pagesPPT2.4 - Elasticity of DemandANOUSHKANo ratings yet
- Demand Notes1Document25 pagesDemand Notes1Jada CallisteNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument26 pagesElasticity of DemandatulmirNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Report DEMANDDocument22 pagesGroup 8 Report DEMANDMa'am Roma GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Priscilla T Baffour, PHDDocument47 pagesElasticity of Demand: Priscilla T Baffour, PHDDavidNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument28 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityGurJot SandhuNo ratings yet
- ECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 8Document24 pagesECO2011 Basic Microeconomics - Lecture 81194390705No ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its ApplicationsDocument22 pagesElasticity and Its ApplicationsChaseNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 4Document14 pagesEconomics Chapter 4Sharif HassanNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument8 pagesElasticityadilnewaz75No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Eco 101Document40 pagesChapter 5 - Eco 101Francine De veraNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply - 2nd PartDocument56 pagesDemand and Supply - 2nd PartsuryaabhimaniNo ratings yet
- The Elasticity of DemandDocument53 pagesThe Elasticity of DemandShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis: MicroeconomicsDocument26 pagesEconomic Analysis: MicroeconomicsCarlo QuinlogNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Demand Forecasting Final1Document86 pagesElasticity of Demand and Demand Forecasting Final1mahantymunni3131No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand SupplyDocument65 pagesElasticity of Demand SupplyAkarsh BhattNo ratings yet
- Degrees of ElasticityDocument9 pagesDegrees of ElasticityFiona UsherNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument16 pagesElasticity of DemandHumayun95% (20)
- Webinar 5 Economics 1A 29 April 2023Document28 pagesWebinar 5 Economics 1A 29 April 2023TarynNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument21 pagesElasticityBob MarshellNo ratings yet
- Blen EconDocument35 pagesBlen EconheldanaNo ratings yet
- 专题1 7讲解版Document80 pages专题1 7讲解版bbbbdxNo ratings yet
- Cfa Notes IftDocument15 pagesCfa Notes IftShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Demand and Supply: Equilibrium Quantity (5 Points Each)Document32 pagesQuiz Demand and Supply: Equilibrium Quantity (5 Points Each)Willy DemdamNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - . .: Is A Measure of How Much Buyers and Sellers Respond To Changes in Market ConditionsDocument52 pagesElasticity - . .: Is A Measure of How Much Buyers and Sellers Respond To Changes in Market ConditionsCassandra BoduchNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand (E) Elasticity Measures The Extent To Which Demand Will ChangeDocument17 pagesElasticity of Demand (E) Elasticity Measures The Extent To Which Demand Will ChangeHimanshu PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Econ MidtermsDocument2 pagesEcon Midtermsdiumpmae andalNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Responsiveness/sensitiveness Elasticity of DemandDocument25 pagesElasticity Responsiveness/sensitiveness Elasticity of DemandyasmeenNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument38 pagesElasticity of Demandhitesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Cheat Sheet - CompressDocument2 pagesTest 1 Cheat Sheet - CompressThe TwitterNo ratings yet
- Demand Theory: Dr. Smita ShuklaDocument46 pagesDemand Theory: Dr. Smita ShuklaAmey HamandNo ratings yet
- Elasticities: Gce A-Level & Ib EconomicsDocument37 pagesElasticities: Gce A-Level & Ib EconomicsingeNo ratings yet
- M2 ElasticityDocument28 pagesM2 ElasticityYASHAS MOHAN 2150240No ratings yet
- 2.5 - Elasticity 2Document34 pages2.5 - Elasticity 2Brady HamrickNo ratings yet
- Utility and Elasticity SummaryDocument2 pagesUtility and Elasticity Summaryshafa anisa ramadhaniNo ratings yet