Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 4 Computing The Variance of The Probability Distribution
Uploaded by
Raphael Kyle SayagoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 4 Computing The Variance of The Probability Distribution
Uploaded by
Raphael Kyle SayagoCopyright:
Available Formats
Polangui General Comprehensive High School
Polangui, Albay
Lesson: COMPUTING THE VARIANCE OF A DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
Lesson Objectives:
1.) Illustrate and calculate the variance of a discrete random variable;
2.) Interpret the variance of a discrete random variable; and
3.) Solve problems involving variance of probability distributions
Formula for the Variance and Standard Deviation of the Probability Distribution
The variance of a discrete probability distribution is given by the formula :
σ =∑ ( X−μ) ∙ P(X )
2 2
σ =∑ X ∙ P ( X ) −μ
2 2 2
Alternative formula:
The standard deviation of a discrete probability distribution is given by the formula :
√
σ = ∑ ( X−μ) ∙ P(X )
2
Alternative formula: σ =√∑ X 2 ∙ P ( X ) −μ 2
where:
X = value of the random variable X
P(X) = probability of the random variable X
μ = mean of the probability distribution
In-class Activity 1
Number of Cars Sold
The number of cars sold per day at a local car dealership, along with its corresponding
probabilities, is shown in the succeeding table. Compute the variance and the standard deviation of the
probability distribution by following the given steps.
Number of Cars Sold X Probability P(X)
0 1
10
1 2
10
2 3
10
3 2
10
4 2
10
Steps in Finding the Variance and Standard Deviation
1. Find the mean of the probability distribution.
2. Subtract the mean from each value of the random variable X.
3. Square the results obtained in Step 2.
4. Multiply the results obtained in Step 3 by the corresponding probability.
5. Get the sum of the results obtained in Step 4.
Solution:
Steps Solution
1. Find the mean of the probability Number of Probability X ∙P (X)
distribution using the formula Cars Sold X P(X)
0 1 0
μ=∑ X ∙ P ( X ) 10
1 2 2
10 10
2 3 6
10 10
3 2 6
10 10
4 2 8
10 10
22
μ=∑ X ∙ P ( X ) = =2.2
10
2. Subtract the mean from each Number of Probability X ∙ P (X ) X −μ
value of the random variable X. Cars Sold X P(X)
0 1 0 0 – 2.2 = -2.2
10
1 2 2 1 – 2.2 = -1.2
10 10
2 3 6 2 – 2.2 = -0.2
10 10
3 2 6 3 – 2.2 = 0.8
10 10
4 2 8 4 – 2.2 = 1.8
10 10
3. Square the results obtained in Number Probability X ∙ P (X ) X −μ ( X −μ)
2
Step 2. of Cars P(X)
Sold X
0 1 0 -2.2 4.84
10
1 2 2 -1.2 1.44
10 10
2 3 6 -0.2 0.04
10 10
3 2 6 0.8 0.64
10 10
4 2 8 1.8 3.24
10 10
4. Multiply the results obtained in Numbe Probability X ∙ P (X ) X −μ ( X −μ)2 ( X −μ)2 ∙ P (X )
Step 3 by the corresponding r of P(X)
probability. Cars
Sold X
0 1 0 -2.2 4.84 0.484
10
1 2 2 -1.2 1.44 0.288
10 10
2 3 6 -0.2 0.04 0.012
10 10
3 2 6 0.8 0.64 0.128
10 10
4 2 8 1.8 3.24 0.648
10 10
5. Get the sum of the results σ =∑ ( X−μ) ∙ P(X ) = 1.56
2 2
obtained in Step 4. The result is
the value of the variance. So, the
formula for the variance is :
σ =∑ ( X−μ) ∙ P(X ).
2 2
6. Get the square root of the The variance of the probability distribution is 1.56.
variance to get the standard The standard deviation is σ =√ 1.56=1.25 .
deviation.
In-class Activity 2
Number of Heads
When three coins are tossed, the probability distribution for the random variable X representing
the number of heads that occur is given below. Compute the variance and standard deviation of the
probability distribution.
Number of Heads X Probability P(X)
0 1
8
1 3
8
2 3
8
3 1
8
Alternative Procedure in Finding the Variance and Standard Deviation
1. Find the mean of the probability distribution.
2. Multiply the square of the value of the random variable X by its corresponding probability.
3. Get the sum of the results obtained in Step 2.
4. Subtract the mean from the results obtained in Step 3.
Solution:
Steps Solution
1. Find the mean of the probability Number of Probability X ∙P (X)
distribution using the formula Heads X P(X)
0 1 0
μ=∑ X ∙ P ( X ) 8
1 3 3
8 8
2 3 6
8 8
3 1 3
8 8
12
μ=∑ X ∙ P ( X ) = =1.5
8
2. Multiply the square of the Number of Probability X ∙ P (X ) X 2 ∙ P (X )
value of the random Heads X P(X)
variable X by its 0 1 0 2 1
corresponding probability. 0 ∙ =0
8 8
1 3 3 2 3 3
1∙ =
8 8 8 8
2 3 6 2 3 12
2∙ =
8 8 8 8
3 1 3 2 1 9
3 ∙ =
8 8 8 8
3. Get the sum of the results 24
obtained in Step 2. ∑ X 2 ∙ P ( X )= 8 =3
4. Subtract the mean from the The variance is given by
results obtained in Step 3 to get σ =∑ X ∙ P ( X ) −μ
2 2 2
the variance. So, the formula for = 3 – (1.5)2
the variance of a probability
= 0.75
distribution is given by
σ =∑ X ∙ P ( X ) −μ
2 2 2
The standard deviation is σ =√ 0.75=0.87
The standard deviation is the
square root of the variance. Thus,
σ= √∑ X 2
∙ P ( X ) −μ 2
The variance is 0.75 and the standard deviation is 0.87.
Exercises!
A. Complete the table below and find the variance and the standard deviation of the following
probability distributions.
1.
X P(X) X ∙P (X ) X2 ∙ P (X )
1 1
7
6 2
7
11 1
7
16 1
7
21 2
7
2.
X P(X) X ∙P (X ) X2 ∙ P (X )
3 0.15
6 0.35
8 0.40
10 0.10
B. Solve the following problems.
1. The number of items sold per day at a retail store, with its corresponding probabilities, is
shown in the table. Find the variance and standard deviation of the probability
distribution.
Number of Items Sold X Probability P(X)
19 0.20
20 0.20
21 0.30
22 0.20
23 0.10
2.Find the variance and standard deviation of the probability distribution of the random
10 1
variable X, which can take only the values 1,2, and 3 given that P(1)= , P(2) =
33 33
12
and P(3) = .
33
-end-
mdsbalin’16-‘17
You might also like
- LR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 3 4Document5 pagesLR1 - Statistics and Probability - LESSON 3 4Leanne HernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Statistics and Probabilty - Module 2Document6 pagesGrade11 Statistics and Probabilty - Module 2Erickson SongcalNo ratings yet
- Math DemoDocument9 pagesMath DemoJohn PaulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3bonifacio gianga jr100% (1)
- Variance and Standard Deviation of A Discrete Random VariableDocument13 pagesVariance and Standard Deviation of A Discrete Random VariableVanessa Joyce Rivera100% (1)
- Stat Mod4 - Task 1Document12 pagesStat Mod4 - Task 1Mizzy DoroinNo ratings yet
- Unit - V Design of ExperimentsDocument9 pagesUnit - V Design of ExperimentsebenesarbNo ratings yet
- Allspect v5Document1 pageAllspect v5Alvaro Alex Osorio HernandezNo ratings yet
- OptimDocument23 pagesOptimMona AliNo ratings yet
- Math4052 2016Document6 pagesMath4052 2016John ChanNo ratings yet
- STAT4Document12 pagesSTAT4Marjuk RahibNo ratings yet
- Week2 StatisticsDocument7 pagesWeek2 StatisticsNancy LantinganNo ratings yet
- P and SDocument138 pagesP and Suxhihaitaxhi6No ratings yet
- Allspect v5Document1 pageAllspect v5Alvaro Alex Osorio HernandezNo ratings yet
- Stat Prob 11 q3 SLM Wk2Document10 pagesStat Prob 11 q3 SLM Wk2rico.odalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems Computing and Modeling 5th Edition Edwards Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems Computing and Modeling 5th Edition Edwards Solutions Manualhytrosbrandons2129100% (39)
- Gen MathDocument1 pageGen MathIanaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Virtual ClassDocument25 pagesStatistics and Probability: Virtual ClassFVicente, Vieyah Angela A.No ratings yet
- Solutions To The Exercises On Fisher Discriminant AnalysisDocument5 pagesSolutions To The Exercises On Fisher Discriminant Analysisyuyang zhangNo ratings yet
- 6 MulticolinearityDocument6 pages6 Multicolinearityhashinidharshikaso01No ratings yet
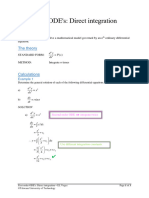
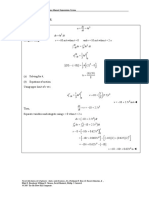
- 1 1 DirectIntegrationDocument3 pages1 1 DirectIntegrationMuavha MadembeNo ratings yet
- LPDocument4 pagesLPJerry Lim CangayaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- CompFin 2020 SS QF Sheet 09Document2 pagesCompFin 2020 SS QF Sheet 097 RODYNo ratings yet
- Physics - Numericals - APPLIED PHYSICS - ENGINEERING 1st YearDocument16 pagesPhysics - Numericals - APPLIED PHYSICS - ENGINEERING 1st YearManas Upadhyaya Telecommunication EngineeringNo ratings yet
- UMS Maths - 14 - Binary Number System - 6A3Document3 pagesUMS Maths - 14 - Binary Number System - 6A3Minh NguyễnNo ratings yet
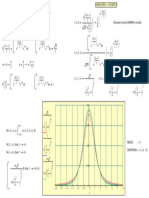
- 0 (Four) Most Common Hypothesis Tests: An Ap Plied ReviewDocument6 pages0 (Four) Most Common Hypothesis Tests: An Ap Plied ReviewVedantaNo ratings yet
- 2906 Physics Paper With Solution EveningDocument8 pages2906 Physics Paper With Solution EveningTimothy SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Data Managmnt Lesson 3 Measures of DispersionDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Data Managmnt Lesson 3 Measures of DispersionChristine CagaraNo ratings yet
- Random Binomial Poisson DistributionsDocument8 pagesRandom Binomial Poisson DistributionsKarthik BingiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Integral CalculusDocument81 pagesChapter 3 - Integral Calculuskit199411No ratings yet
- Problems Convolutional Codes PDFDocument12 pagesProblems Convolutional Codes PDFprbNo ratings yet
- UNIT II Probability SolutionsDocument21 pagesUNIT II Probability SolutionsJohnnyNo ratings yet
- Calculus AngelDocument6 pagesCalculus AngelEzekiel A. NavarroNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET - 1 (On Convex Set) .Document10 pagesWORKSHEET - 1 (On Convex Set) .Gudeta nNo ratings yet
- Steps in Finding The Mean Variance and Standard Deviation of The Probability Distribution of The Discrete Random VariableDocument11 pagesSteps in Finding The Mean Variance and Standard Deviation of The Probability Distribution of The Discrete Random VariableSiestaNo ratings yet
- 0 and Plot The Result For at Least Two Periods For The CaseDocument2 pages0 and Plot The Result For at Least Two Periods For The CaseDinesh JangraNo ratings yet
- 2 Integrals Yielding To Trigo Inv Trigo FNDocument6 pages2 Integrals Yielding To Trigo Inv Trigo FNRosewill AlcaideNo ratings yet
- Solve Each Equation. Remember To Check For Extraneous SolutionsDocument4 pagesSolve Each Equation. Remember To Check For Extraneous SolutionsAron AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - StudentDocument1 pageMathcad - Studentmatei_costin_1No ratings yet
- Enrichment Activities-Mean Variance and Standard DeviationDocument1 pageEnrichment Activities-Mean Variance and Standard DeviationRandolf DinerosNo ratings yet
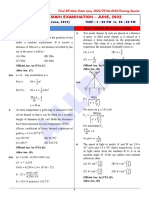
- Homework #2 - Solution Coverage: Chapter 3-4 Due Date: 15 April, 2021Document4 pagesHomework #2 - Solution Coverage: Chapter 3-4 Due Date: 15 April, 2021estymrtunNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Book 2.5Document3 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamics Book 2.5David Clark100% (3)
- Las NelvieDocument5 pagesLas NelvieNancy OliverioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Robust and Optimal ControlDocument7 pagesLecture 1 Robust and Optimal ControlRoger BertranNo ratings yet
- Foerign MathematicsDocument37 pagesFoerign MathematicsDivya VatsaNo ratings yet
- Set 3 AnswersDocument2 pagesSet 3 AnswersPrince VegetaNo ratings yet
- STERLIDocument13 pagesSTERLIsuar90No ratings yet
- Task 7Document9 pagesTask 7JosephNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Substitution: Jzfa20Document12 pagesTrigonometric Substitution: Jzfa20Samuel SmallmanNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Multivariate Probability Distributions: Joint Probability Distribution (Density) FunctionDocument8 pages2.2. Multivariate Probability Distributions: Joint Probability Distribution (Density) Functionjkleinhans.jkNo ratings yet
- Mountain Passes and Saddle PointsDocument19 pagesMountain Passes and Saddle PointsАйкын ЕргенNo ratings yet
- 04 Differential Equations Elementary Applications of ODE PDFDocument45 pages04 Differential Equations Elementary Applications of ODE PDFMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document89 pagesCH 10Mhmd AlKhreisat100% (1)
- 4.2 Expected Value and Variance of Continuous Random VariablesDocument2 pages4.2 Expected Value and Variance of Continuous Random VariablesJoséBorjNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations Practice WorksheetsDocument12 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations Practice WorksheetsNyameye DanquahNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems Computing and Modeling 5th Edition by Edwards ISBN 0321796985 9780321796981Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems Computing and Modeling 5th Edition by Edwards ISBN 0321796985 9780321796981shannonvazquezrkycbwmdit100% (30)
- Homework 1: This Is Problem 9.2 in Mor Harchol-Balter's BookDocument3 pagesHomework 1: This Is Problem 9.2 in Mor Harchol-Balter's BookParas BodkeNo ratings yet