Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4C
Uploaded by
Orlando Villanueva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views1 pageOriginal Title
Risk-NCP_PESCADERO-4C.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4C
Uploaded by
Orlando VillanuevaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
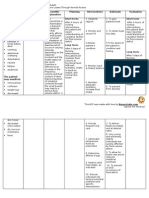
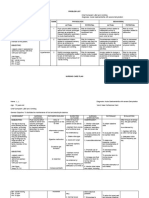
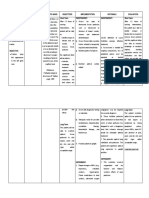
Assessment Nursing (Rationale) Desired Nursing Intervention Justification Evaluation
Cues Diagnosis Pathophysiologic / Outcome
Name of Student: Mary Claire Joy Pescadero Schematic Diagram
Subjective: Risk for fluid Predisposing Factor: NURSING
After 8 hours ofCARE PLANInterventions:
Independent After 8 hours of
Patient verbalized, volume deficit Age: 45 years old Nursing Intervention, 1. Assess and document 1. This will serve as baseline Nursing
“sagay lang ko suka related to Gender: Male the patient and vital signs and weight of the data for assessment. Intervention, the
Section andnurse
nga suka Group number: 4C Group
excessive 5
fluid significant other will patient. patient and
asta sa gapangluya losses secondary Precipitating Factor: be able to: significant other was
Name of CI: Myka Billones Canlas RN, MN 2. Weight changes are an
nako” to nausea, Environmental stressors 2. Ensure that daily able to:
vomiting and Lifestyle Short Term Goal: weights are taken at the effective indicator of fluid
Area of Exposure: TDHI Medical Surgical volume.
diarrhea Suffered a cervical spine A. Establish fluid same time each day A. The patient was
fracture and phrenic nerve balance within the able to establish
injury 7 years ago. normal range 3. Ensure fluid intake 3. This helps ensure that fluid balance within
Objective: Definition: within the recommended the patient receives the normal range by
Restlesness At risk for Systemic immune response volume. appropriate amounts of having adequate
Guarding sign experiencing primarily against the GI tract fluids, keeping him properly fluid intake by 1 liter
Facial grimace vascular, cellular (unclear mechanism, hydrated and eliminating per day. Goal Met.
Tenderness over or intracellular mediated by cytokine release the risk for excessive fluid
McBurney's point dehydration B. Adhere to intake which may cause B. The patient was
and neutrophil inflammation)
is elicited, as is interventions aimed congestion later on able to follow
rebound Inflammation of the GI tract to help maintain interventions given
tenderness in the acceptable fluid 4. Maintain oral 4. Colon is placed at rest for by the nurse such as
right lower Source/Reference balance restrictions, bed rest; avoid healing and to decrease
Inflammatory cytokines drinking fluids. Goal
quadrant. Nurse’s Pocket exertion. intestinal fluid losses.
destroy the mucosa epithelial Met
Guide. Edition 11 cells of the GI tract wall
MIO of: by Marilynn Long Term Goal: Dependent Interventions:
causing apoptosis and
Intake: Doenges, Mary C. Display intake and 1. Administer parenteral 1. Maintenance of bowel
ulceration. C. The patient was
Parenteral: 2500 cc Frances output near balance, fluids as indicated. rest requires alternative able to able to
Output: 1200 cc Moorhouse and Transporter proteins good skin turgor, fluid replacement to correct display intake and
Alice Murr responsible for Na+ moist mucous losses and anemia. Note: output near balance
V/s: reabsorption gradually membranes, palpable Fluids containing sodium which is 30 cc per
T- 36.0 ‘C disappear from the peripheral pulses, may be restricted in hour, has stable
P- 75 bpm epithelium. stable weight and presence of regional weight. Goal Met.
R- 20 cpm vital signs, and enteritis.
BP- 145/80 mmHg More sodium (and thus electrolytes within
water) is retained in the GI normal range.
tract lumen. 2. Administer prescribed 2. Anti-inflammatory drugs,
medications. including corticosteroids
Strength : Diarrhea and oral 5 aminosalicylates
Good family — initially used to reduce
support S/S: the inflammation such as
Willing to adhere Methylprednisolone and
You might also like
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscanteNo ratings yet
- Role Gastrointestinal Tract Nutrient Delivery: The Role of the Gastrointestinal Tract in Nutrient DeliveryFrom EverandRole Gastrointestinal Tract Nutrient Delivery: The Role of the Gastrointestinal Tract in Nutrient DeliveryNo ratings yet
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Human Brain Evolution: The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food ResourcesFrom EverandHuman Brain Evolution: The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food ResourcesStephen CunnaneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition in Chronic Diet-Associated Infantile Diarrhea: Diagnosis and ManagementFrom EverandMalnutrition in Chronic Diet-Associated Infantile Diarrhea: Diagnosis and ManagementCarlos H. LifschitzRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- NCP Fdar Fin.Document8 pagesNCP Fdar Fin.Bissette DomingoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaDocument3 pagesAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for GastroenteritisgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- Nursing Intervention for Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesNursing Intervention for Intestinal ObstructionOPssslNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosi S Analysis GOAL and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Duty RequirementsDocument13 pagesDuty RequirementsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- NCP PediatricDocument5 pagesNCP PediatricSL Hanna NebridaNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Pregnant Patient with Asthma and Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Pregnant Patient with Asthma and Hyperemesis GravidarumRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 pagesNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPyamie sulongNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (AGE)Document2 pagesDiarrhea (AGE)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for AmebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for AmebiasiskristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Assessing and Treating Acute Gastroenteritis and DehydrationDocument2 pagesAssessing and Treating Acute Gastroenteritis and DehydrationvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- NCP Assessment Fluid DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Assessment Fluid DeficitBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDan MandigNo ratings yet
- Baby Carla Bajih Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesBaby Carla Bajih Nursing Care PlanR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Short TermLorie May GuillangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Managing Overweight through Diet and ExerciseDocument17 pagesManaging Overweight through Diet and ExerciseMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Specific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaDocument7 pagesSpecific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaLeni YulisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Basema HashhashNo ratings yet
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 pagesNCP Post PartumsteffiNo ratings yet
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDocument5 pagesNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: AB: Henriette Jane de Leon Bn3A January 21, 2021Document5 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: AB: Henriette Jane de Leon Bn3A January 21, 2021Sbs Nhanxzkie Jountey MushroomxzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goals Intervention Rationale EvaluationLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentDocument10 pagesCase Study: Subjective: Objective: General Objective: Independent IndependentChristine EmanNo ratings yet
- Brunswick Lens ModelDocument3 pagesBrunswick Lens ModelBelen ToledoNo ratings yet
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- NCP-SUGATON-HYPERTHERMIA IndivdualDocument2 pagesNCP-SUGATON-HYPERTHERMIA IndivdualPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- Group-5 NCM-107 NCPDocument4 pagesGroup-5 NCM-107 NCPbulok netflakes100% (1)
- Case Study - Hematology 1 PDFDocument21 pagesCase Study - Hematology 1 PDFMaria Lyn Ocariza ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Vomiting and LBMDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan for Vomiting and LBMKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario 2 NCP RevisedDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 2 NCP RevisedkdfhjfhfNo ratings yet