Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Independent
Uploaded by
Koby Regalado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThe patient is experiencing fluid volume loss due to vomiting and diarrhea, as evidenced by poor skin turgor, sunken eyes, and a sodium level of 129.6. The nurse will monitor vital signs, urinary output, and skin signs over 6 hours and replenish fluids to maintain volume and resolve dehydration symptoms. Interventions include giving fluids orally or intravenously, monitoring input/output, weighing the patient daily, and preventing further fluid loss by stopping vomiting and diarrhea.
Original Description:
Ncpbshshaja
Original Title
NCP (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient is experiencing fluid volume loss due to vomiting and diarrhea, as evidenced by poor skin turgor, sunken eyes, and a sodium level of 129.6. The nurse will monitor vital signs, urinary output, and skin signs over 6 hours and replenish fluids to maintain volume and resolve dehydration symptoms. Interventions include giving fluids orally or intravenously, monitoring input/output, weighing the patient daily, and preventing further fluid loss by stopping vomiting and diarrhea.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesIndependent
Uploaded by
Koby RegaladoThe patient is experiencing fluid volume loss due to vomiting and diarrhea, as evidenced by poor skin turgor, sunken eyes, and a sodium level of 129.6. The nurse will monitor vital signs, urinary output, and skin signs over 6 hours and replenish fluids to maintain volume and resolve dehydration symptoms. Interventions include giving fluids orally or intravenously, monitoring input/output, weighing the patient daily, and preventing further fluid loss by stopping vomiting and diarrhea.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
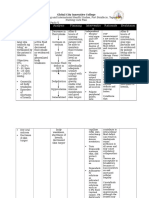
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Deficient Short Term: Independent Short Term:
Fluid At the end At the end of
Objective: Volume of 6 hours Assess vital signs, These changes 6 hours
- Poor related to Nursing noting low blood in vital signs are Nursing
skin active fluid Intervention pressure-severe associated with Interventions
turgor volume loss , the patient hypotension, fluid volume , the patient
- Sunken as will be able rapid heart beat, loss/ are able to:
eyeballs evidenced to: and thready hypovolemia.
- 3-4 by episodes peripheral
episode of loose • Maintain pulses. Replenished
s of stools and fluid volume (a number fluid loss,
loose vomiting at a Observe/ higher than 1.25 maintain
stools functional measure urinary is associated urine specific
- 5 Definition: level as output with gravity within
episode Deficient evidenced (hourly/24-hr dehydration normal
s of Fluid by totals)Note the with usual range range, no
vomitin Volume individually color (may be being 1.010- more
g adequate dark greenish 1.025). episodes of
- 129.6 (Diagnostic urinary brown because loose stools
sodium Division: output with of concentration) and
level Food/Fluid] normal and specific vomiting.
specific gravity
Definition: gravity,
Decreased stable vital Note complaints
intravascular signs, moist and physical
, interstitial, mucous signs associated
and/or membranes, with dehydration
intracellular good skin (e.g., scanty,
fluid, these turgor and concentrated
refers to prompt urine; lack of
dehydration, capillary tears when
water loss refill, crying [infant,
alone resolution child); dry, sticky
without a of edema. mucous
change in membranes: lack
sodium. of sweating;
delayed capillary
refill; poor skin
turgor;
confusion;
sleepiness;
lethargy; muscle
weakness;
dizziness or
headedness;
headache).
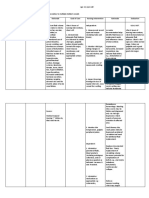
To reduce
pressure on
fragile skin and
Change position tissue
frequently
Bath every other
day; provide
optimal skin care To prevent
with emollients injury from
dryness
Provide frequent
oral as well as
eye care Too rapid a
correction of
Observe for fluid deficit may
sudden or compromise the
marked elevation cardiopulmonar
of blood y system,
pressure, causing fluid
restlessness, overload and
moist cough, edema,
dyspnea, basilar especially if
crackles, and colloids are used
frothy sputum. in initial fluid
resuscitation.
(dark urine
Instruct the equates with
client/SO(s) in concentration
how to monitor and
the color of urine dehydration) or
how to measure
and record I&O
(may include
weighing or
counting diapers
in
infant/toddler).
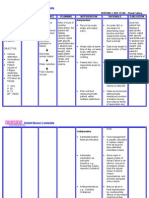
Dependent
Stop fluid loss
(e.g., administer
medication to
stop vomiting/
diarrhea, fever).
Administer fluids
and electrolytes
(e.g., blood,
isotonic so- dium
chloride solution,
lactated Ringer's
solution,
albumin,
fresh frozen
plasma, dextran,
and heptastich).
This prevents
Establish 24-hr peaks and
fluid valleys in fluid
replacement level.
needs and routes
to be used
Collaborative
Maintain
accurate input
and output (I&O)
and weigh daily
Monitor urine
specific gravity.
You might also like
- NCP - Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP - Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancePaolo Belleza78% (9)
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention-Rationale Evaluation Fluid Volume Excess Related ToJen BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume Deficitnj_pink08179456% (9)
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMr. whiteNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Insipidus: Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesDiabetes Insipidus: Nursing Care PlansSewyel GarburiNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceVitha100% (1)
- Maintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientDocument9 pagesMaintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 1Document5 pagesNursing Diagnosis 1Kim TangoNo ratings yet
- Managing Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances in Older AdultsDocument3 pagesManaging Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances in Older AdultsLacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- NURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusYsun Espino100% (1)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Fluid Volume Deficit: Causes, Signs, Assessment, TreatmentDocument2 pagesNCM 112 Fluid Volume Deficit: Causes, Signs, Assessment, TreatmentAngeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Management DeshidratationDocument15 pagesManagement DeshidratationDani G CeñalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- KimPhan PediatricDocument4 pagesKimPhan PediatricStephen Leeper100% (2)
- Ncp. Pedia.Document2 pagesNcp. Pedia.Czarina MayoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitusinagasi83% (12)
- Dehydration: DR Nadeem ZubairiDocument78 pagesDehydration: DR Nadeem ZubairiDhitaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Dehydration in ChildrenDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Dehydration in ChildrenzikraalfaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Assessment and ManagementKhalid KhanNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument4 pagesNursing Diagnosis and InterventionsChe SalveronNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument6 pagesAbruptio PlacentaBb RabbitNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- Kuliah S2 AirDocument23 pagesKuliah S2 AirViany RehansyahNo ratings yet
- Managing Fluid and Nutrition Deficits in Diabetes Type 1Document3 pagesManaging Fluid and Nutrition Deficits in Diabetes Type 1Kartika MilaningrumNo ratings yet
- Master's Nursing Program Analyzes Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument7 pagesMaster's Nursing Program Analyzes Electrolyte Imbalanceslovely roan riolaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Elec ImbalancesDocument19 pagesFluid and Elec ImbalancesswethashakiNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNo ratings yet
- Prio NCP NG Dka ByeDocument5 pagesPrio NCP NG Dka ByeMARIA HILARY TABLANTENo ratings yet
- NCP ShockDocument5 pagesNCP ShockJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- Final NCP1 2Document2 pagesFinal NCP1 2hahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- 1-Gastroenteritis and DehydrationDocument29 pages1-Gastroenteritis and Dehydrationabdalmajeed alshammaryNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongDocument47 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation Case: Amoebiasis Subjective:" Madalas Po AkongNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Managing Fluid Volume for Renal FailureDocument2 pagesManaging Fluid Volume for Renal FailureMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentThomas FarrishNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Renal Failurederic87% (31)
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisHanz AlecNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science And: O V A ADocument9 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science And: O V A ALeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis & Interventions for DehydrationDocument6 pagesNursing Diagnosis & Interventions for DehydrationKRISTINE BULACANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan TemplateTricia LiporadaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- Sakha DictionaryDocument14 pagesSakha DictionarySojeong MinNo ratings yet
- Spraying TechniquesDocument12 pagesSpraying TechniquesX800XLNo ratings yet
- PPF Pumps CatalogDocument112 pagesPPF Pumps Catalogesau hernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument36 pagesChapter Onepretoria agreement21No ratings yet
- Silent Spring: What's InsideDocument22 pagesSilent Spring: What's InsideDelina TedrosNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Ds&BdalDocument100 pagesLab Manual Ds&BdalSEA110 Kshitij BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Company Profile ASIA ONE - 2022Document15 pagesCompany Profile ASIA ONE - 2022Nur SiswantoNo ratings yet
- The Metacentric Height EX3Document3 pagesThe Metacentric Height EX3Edrees JamalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Positive Psychology 4th Edition Lopez PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Positive Psychology 4th Edition Lopez PDF Full Chaptershaps.tortillayf3th100% (21)
- PP 1Document33 pagesPP 1Vishnu IngleNo ratings yet
- BukuDocument39 pagesBukusimon sembiringNo ratings yet
- ZEOLITEDocument13 pagesZEOLITEShubham Yele100% (1)
- BearingsDocument26 pagesBearingstmscorreiaNo ratings yet
- LAC Intraregional IRF GuideDocument81 pagesLAC Intraregional IRF GuideMario Cortez EscárateNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature Quarter 2 Week 7Document5 pages21st Century Literature Quarter 2 Week 7SHERRY MAE MINGONo ratings yet
- ENGG378 - 948 HydroPower-Lecture - 1 - 2019 PDFDocument34 pagesENGG378 - 948 HydroPower-Lecture - 1 - 2019 PDFJ CNo ratings yet
- Spread footing design calculationDocument6 pagesSpread footing design calculationFrancklinMeunierM'ondoNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts, Cost Analysis, and Cost EstimationDocument2 pagesCost Concepts, Cost Analysis, and Cost EstimationGêmTürÏngånÖNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and Student Relationship of Haydn and BeethovenDocument10 pagesThe Teacher and Student Relationship of Haydn and BeethovenVinny MuscarellaNo ratings yet
- Rossetto Et AlDocument21 pagesRossetto Et AlEunice FiecasNo ratings yet
- Drill Pipe Performance DataDocument35 pagesDrill Pipe Performance DatasnatajNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Financial Analysis Technoques PresentationDocument44 pagesCH 2 Financial Analysis Technoques PresentationHamza AsifNo ratings yet
- HER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDocument3 pagesHER201 Flex Tiles Set 01 - VehiclesDouglas Mears100% (2)
- Troubleshooting Guide: Multifunctional Digital SystemsDocument132 pagesTroubleshooting Guide: Multifunctional Digital SystemsnguyenhieuproNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument26 pagesHypertensionAbdalrhman Zaqqa100% (1)
- 1ST Quarter Exam Mapeh 8Document7 pages1ST Quarter Exam Mapeh 8John Rey Manolo BaylosisNo ratings yet
- GPSForex Robot V2 User GuideDocument40 pagesGPSForex Robot V2 User GuideMiguel Angel PerezNo ratings yet
- Advertisement AnalysisDocument15 pagesAdvertisement AnalysisDaipayan DuttaNo ratings yet
- Labview ProgrammingDocument20 pagesLabview ProgrammingJames WoodNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Is A Leadership TrickDocument10 pagesEmpowerment Is A Leadership TrickAura Carla TolentinoNo ratings yet