Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSK CAT E1102m A116-125 PDF
NSK CAT E1102m A116-125 PDF
Uploaded by
ROANNIEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NSK CAT E1102m A116-125 PDF
NSK CAT E1102m A116-125 PDF
Uploaded by
ROANNIECopyright:
Available Formats
14.
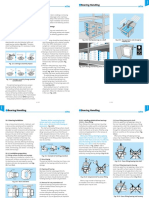
BEARING HANDLING
14.1 Precautions for Proper Handling of After the bearings are cleaned with filtered oil, they (2) Shrink Fits
Bearings should be protected to prevent corrosion. Since press fitting large bearings requires a large force,
Since rolling bearings are high precision machine Prelubricated bearings must be used without cleaning. a shrink fit is widely used. The bearings are first heated
parts, they must be handled accordingly. Even if high Bearing mounting methods depend on the bearing type in oil to expand them before mounting.
quality bearings are used, their expected performance and type of fit. As bearings are usually used on rotating This method prevents an excessive force from being
cannot be achieved if they are not handled properly. shafts, the inner rings require a tight fit. imposed on the bearings and allows mounting them in
The main precautions to be observed are as follows: Bearings with cylindrical bores are usually mounted a short time.
by pressing them on the shafts (press fit) or heating The expansion of the inner ring for various temperature
(1) Keep Bearings and Surrounding Area Clean them to expand their diameter (shrink fit). Bearings differences and bearing sizes is shown in Fig. 14.3.
with tapered bores can be mounted directly on tapered The precautions to follow when making shrink fits are
Dust and dirt, even if invisible to the naked eye, have shafts or cylindrical shafts using tapered sleeves.
harmful effects on bearings. It is necessary to prevent as follows:
Bearings are usually mounted in housings with a loose
the entry of dust and dirt by keeping the bearings and fit. However, in cases where the outer ring has an
their environment as clean as possible. (a) Do not heat bearings to more than 120˚C.
interference fit, a press may be used. Bearings can be (b) Put the bearings on a wire net or suspend them in
interference-fitted by cooling them before mounting an oil tank in order to prevent them from touching
(2) Careful Handling using dry ice. In this case, a rust preventive treatment Fig. 14.1 Press Fitting Inner Ring the tank's bottom directly.
Heavy shocks during handling may cause bearings to must be applied to the bearing because moisture in the (c) Heat the bearings to a temperature 20 to 30˚C
be scratched or otherwise damaged possibly resulting air condenses on its surface. higher than the lowest temperature required for
in their failure. Excessively strong impacts may cause mounting without interference since the inner ring
brinelling, breaking, or cracking. 14.2.1 Mounting of Bearings with Cylindrical Bores will cool a little during mounting.
(1) Press Fits (d) After mounting, the bearings will shrink in the
(3) Use Proper Tools axial direction as well as the radial direction while
Fitting with a press is widely used for small bearings.
Always use the proper equipment when handling A mounting tool is placed on the inner ring as shown cooling. Therefore, press the bearing firmly against
bearings and avoid general purpose tools. in Fig. 14.1 and the bearing is slowly pressed on the shaft shoulder using locating methods to avoid
the shaft with a press until the side of the inner ring a clearance between the bearing and shoulder.
(4) Prevent Corrosion rests against the shoulder of the shaft. The mounting
Since perspiration on the hands and various other tool must not be placed on the outer ring for press NSK Bearing Induction Heaters
contaminants may cause corrosion, keep the hands mounting, since the bearing may be damaged. Before Besides heating in oil, NSK Bearing Heaters, which
clean when handling bearings. Wear gloves if possible. mounting, applying oil to the fitted shaft surface is use electromagnetic induction to heat bearings, are
Pay attention to rust of bearing caused by corrosive recommended for smooth insertion. The mounting widely used. (Refer to Page C7.)
gasses. method using a hammer should only be used for small In NSK Bearing Heaters, electricity (AC) in a coil
ball bearings with minimally tight fits and when a press produces a magnetic field that induces a current inside
14.2 Mounting is not available. In the case of tight interference fits or the bearing that generates heat. Consequently, without
The method of mounting rolling bearings strongly for medium and large bearings, this method should not Fig. 14.2 Simultaneous Press Fitting of Inner and Outer Rings using flames or oil uniform heating in a short time is
affects their accuracy, life, and performance, so be used. Any time a hammer is used, a mounting tool possible, making bearing shrink fitting efficient and
their mounting deserves careful attention. Their must be placed on the inner ring. clean.
characteristics should first be thoroughly studied, and When both the inner and outer rings of non-separable In the case of relatively frequent mounting and
then they should be mounted in the proper manner. bearings, such as deep groove ball bearings, require dismounting such as cylindrical roller bearings for roll
It is recommended that the handling procedures for tight-fit, a mounting tool is placed on both rings as necks of rolling mills and for railway journal boxes,
bearings be fully investigated by the design engineers shown in Fig. 14.2, and both rings are fitted at the induction heating should be used for mounting and
μm
and that standards be established with respect to the same time using a screw or hydraulic press. Since the dismounting inner rings.
240
following items: outer ring of self-aligning ball bearings may deflect a
r6
7 0 °C
= 8 ence
mounting tool such as that shown in Fig. 14.2 should 220
60 °C
0
always be used for mounting them.
&T iffer
°C
(1) Cleaning the bearings and related parts. 200
D
(2) Checking the dimensions and finish of related In the case of separable bearings, such as cylindrical °C
ure
180
roller bearings and tapered roller bearings, the inner 50
rat
parts. 160 ° C p6
pe
and outer rings may be mounted separately. Assembly
Bore Expansion
(3) Mounting 40
(4) Inspection after mounting. of the inner and outer rings, which were previously 140 Tem °C n6
mounted separately, should be done carefully to align 30
(5) Supply of lubricants. 120
the inner and outer rings correctly. Careless or forced
20 °
100 C m5
Bearings should not be unpacked until immediately assembly may cause scratches on the rolling contact
k5
before mounting. When using ordinary grease surfaces. 80
lubrication, the grease should be packed in the 60 j5
bearings without first cleaning them. Even in the case 40
of ordinary oil lubrication, cleaning the bearings is not 20
required. However, bearings for instruments or for 80 120 180 250 315 400 500
mm
high speed operation must first be cleaned with clean Bore Diameter
filtered oil in order to remove the anti-corrosion agent. Fig. 14.3 Temperature and Thermal Expansion of Inner Ring
A 116 A 117
A100-125E.indd 116-117 11/20/13 4:52:27 PM
BEARING HANDLING
14.2.2 Mounting of Bearings with Tapered Bores become too tight and the true residual clearance may Table 14.1 Mounting of Spherical Roller Bearings with Tapered Bores
Bearings with tapered bores are mounted on tapered become too small. In this case, as shown in Fig. 14.9. Units : mm
shafts directly or on cylindrical shafts with adapters one half of the total clearance at points and b (which
or withdrawal sleeves (Figs. 14.4 and 14.5). Large are on a horizontal line passing through the Bearing Bore Reduction in Radial Push-in amount in axial direction Minimum Permissible
bearing center) and c (which is at the lowest position Diameter Clearance Residual Clearance
spherical roller bearings are often mounted using
hydraulic pressure. Fig. 14.6 shows a bearing of the bearing) may be used as the residual clearance. d Taper 1 : 12 Taper 1 : 30
mounting utilizing a sleeve and hydraulic nut. Fig. 14.7 When a self-aligning ball bearing is mounted on a shaft over incl. min. max. min. max. min. max. CN C3
shows another mounting method. Holes are drilled in with an adapter, be sure that the residual clearance
does not become too small. Sufficient clearance for 30 40 0.025 0.030 0.40 0.45 − − 0.010 0.025
the sleeve which are used to feed oil under pressure to 40 50 0.030 0.035 0.45 0.55 − − 0.015 0.030
the bearing seat. As the bearing expands radially, the easy alignment of the outer ring must be allowed. 50 65 0.030 0.035 0.45 0.55 − − 0.025 0.035
sleeve is inserted axially with adjusting bolts. 65 80 0.040 0.045 0.60 0.70 − − 0.030 0.040
Spherical roller bearings should be mounted while 14.3 Operation Inspection
80 100 0.045 0.055 0.70 0.85 1.75 2.15 0.035 0.050
checking their radial-clearance reduction and referring After the mounting has been completed, a running 100 120 0.050 0.060 0.75 0.90 1.9 2.25 0.045 0.065
to the push-in amounts listed in Table 14.1. The radial test should be conducted to determine if the bearing 120 140 0.060 0.070 0.90 1.1 2.25 2.75 0.055 0.080
clearance must be measured using clearance gauges. has been mounted correctly. Small machines may be
140 160 0.065 0.080 1.0 1.3 2.5 3.25 0.060 0.100
In this measurement, as shown in Fig. 14.8, the manually operated to assure that they rotate smoothly. 160 180 0.070 0.090 1.1 1.4 2.75 3.5 0.070 0.110
clearance for both rows of rollers must be measured Items to be checked include sticking due to foreign 180 200 0.080 0.100 1.3 1.6 3.25 4.0 0.070 0.110
simultaneously, and these two values should be kept matter or visible flaws, uneven torque caused by
roughly the same by adjusting the relative position of improper mounting or an improper mounting surface, 200 225 0.090 0.110 1.4 1.7 3.5 4.25 0.080 0.130
225 250 0.100 0.120 1.6 1.9 4.0 4.75 0.090 0.140
the outer and inner rings. and excessive torque caused by an inadequate 250 280 0.110 0.140 1.7 2.2 4.25 5.5 0.100 0.150
When a large bearing is mounted on a shaft, the outer clearance, mounting error, or seal friction. If there are
ring may be deformed into an oval shape by its own no abnormalities, powered operation may be started. 280 315 0.120 0.150 1.9 2.4 4.75 6.0 0.110 0.160
weight. If the clearance is measured at the lowest part 315 355 0.140 0.170 2.2 2.7 5.5 6.75 0.120 0.180
355 400 0.150 0.190 2.4 3.0 6.0 7.5 0.130 0.200
of the deformed bearing, the measured value may be
bigger than the true value. If an incorrect radial internal 400 450 0.170 0.210 2.7 3.3 6.75 8.25 0.140 0.220
clearance is obtained in this manner and the values in 450 500 0.190 0.240 3.0 3.7 7.5 9.25 0.160 0.240
Table 14.1 are used, then the interference fit may 500 560 0.210 0.270 3.4 4.3 8.5 11.0 0.170 0.270
560 630 0.230 0.300 3.7 4.8 9.25 12.0 0.200 0.310
630 710 0.260 0.330 4.2 5.3 10.5 13.0 0.220 0.330
710 800 0.280 0.370 4.5 5.9 11.5 15.0 0.240 0.390
800 900 0.310 0.410 5.0 6.6 12.5 16.5 0.280 0.430
900 1 000 0.340 0.460 5.5 7.4 14.0 18.5 0.310 0.470
1 000 1 120 0.370 0.500 5.9 8.0 15.0 20.0 0.360 0.530
Remarks The values for reduction in radial internal clearance are for bearings with CN clearance.
For bearing with C3 Clearance,the maximum values listed should be used for the reduction
in radial internal clearance.
Fig. 14.4 Mounting with Adapter Fig. 14.5 Mounting with Withdrawal Sleeve
Oil
Large machines, which cannot be turned by hand,
can be started after examination with no load, and the
power immediately cutoff and the machine allowed to
coast to a stop. Confirm that there is no abnormality
such as vibration, noise, contact of rotating parts, etc.
Powered operation should be started slowly without
load and the operation should be observed carefully
until it is determined that no abnormalities exist, then
gradually increase the speed, load, etc. to their normal
levels. Items to be checked during the test operation
a b c include the existence of abnormal noise, excessive rise
C C c c
of bearing temperature, leakage and contamination of
lubricants, etc. If any abnormality is found during the
Fig. 14.6 Mounting with Fig. 14.7 Mounting with Special Sleeve Fig. 14.8 Clearance Measurement Fig. 14.9 Measuring Clearance in Large Spherical Roller test operation, it must be stopped immediately and the
Fig. 14.6 Hydraulic Nut Fig. 14.7 and Hydraulic Pressure Fig. 14.8 of Spherical Roller Bearing Fig. 14.9 Bearing machine should be inspected. If necessary, the bearing
should be dismounted for examination.
A 118 A 119
A100-125E.indd 118-119 11/20/13 4:52:28 PM
BEARING HANDLING
Although the bearing temperature can generally be mounting, or excessive friction of the seals. 14.4 Dismounting 14.4.2 Dismounting of Bearings with Cylindrical
estimated by the temperature of the outside surface of In the case of high speed operation, an incorrect A bearing may be removed for periodic inspection or Bores
the housing, it is more desirable to directly measure selection of bearing type or lubricating method may for other reasons. If the removed bearing is to be used If the mounting design allows space to press out the
the temperature of the outer ring using oil holes for also cause an abnormal temperature rise. again or it is removed only for inspection, it should be inner ring, this is an easy and fast method. In this
access. The sound of a bearing may be checked with a noise dismounted as carefully as when it was mounted. If the case, the withdrawal force should be imposed only on
The bearing temperature should rise gradually to locater or other instruments. Abnormal conditions are bearing has a tight fit, its removal may be difficult. The the inner ring (Fig. 14.12). Withdrawal tools like those
the steady state level within one to two hours after indicated by a loud metallic sound, or other irregular means for removal should be considered in the original shown in Figs. 14.13 and 14.14 are often used.
the operation starts. If the bearing or its mounting noise, and the possible cause may include incorrect design of the adjacent parts of the machine. When
is improper, the bearing temperature may increase lubrication, poor alignment of the shaft and housing, dismounting, the procedure and sequence of removal
rapidly and become abnormally high. The cause of this or the entry of foreign matter into the bearing. The should first be studied using the machine drawing Bolt
abnormal temperature may be an excessive amount possible causes and measures for irregularities are and considering the type of mounting fit in order to
of lubricant, insufficient bearing clearance, incorrect listed in Table 14.2. perform the operation properly.
Table 14. 2 Causes of and Measures for Operating Irregularities
14.4.1 Dismounting of Outer Rings
Irregularities Possible Causes Measures In order to remove an outer ring that is tightly fitted,
first place bolts in the push-out holes in the housing
Abnormal Load Improve the fit, internal clearance, preload, position of housing at several locations on its circumference as shown in
shoulder, etc. Fig. 14.10, and remove the outer ring by uniformly
Incorrect mounting Improve the machining accuracy and alignment of shaft and housing,
tightening the bolts. These bolt holes should always
Loud Metallic be fitted with blank plugs when not being used for Plug
accuracy of mounting method.
Sound (1)
dismounting. In the case of separable bearings, such
Insufficient or improper Lubricant Replenish the lubricant or select another lubricant. as tapered roller bearings, some notches should be Fig. 14.10 Removal of Outer Ring with Dismounting Bolts
Contact of rotating parts Modify the labyrinth seal, etc. made at several positions in the housing shoulder, as
shown in Fig. 14.11, so the outer ring may be pressed
Flaws,corrosion,or scratches on Replace or clean the bearing, improve the seals, and use clean out using a dismounting tool or by tapping it.
Noise raceways lubricant.
Loud Regular
Sound Brinelling Replace the bearing and use care when handling bearings.
Flaking on raceway Replace the bearing.
Excessive clearance Improve the fit, clearance and preload.
Irregular Penetration of foreign particles Replace or clean the bearing, improve the seals, and use clean
Sound lubricant.
Flaws or flaking on balls Replace the bearing.
Fig. 14.11 Removal Notches
Excessive amount of lubricant Reduce amount of lubricant, select stiffer grease.
Insufficient or improper lubricant Replenish lubricant or select a better one.
Abnormal load Improve the fit, internal clearance, preload, position of housing
Abnormal Temperature shoulder.
Rise
Incorrect mounting Improve the machining accuracy and alignment of shaft and housing,
accuracy of mounting, or mounting method.
Creep on fitted surface, excessive seal Correct the seals, replace the bearing, correct the fitting or mounting.
friction
Brinelling Replace the bearing and use care when handling bearings.
Flaking Replace the bearing.
Vibration
(Axial runout) Incorrect mounting Correct the squareness between the shaft and housing shoulder or side
of spacer.
Penetration of foreign particles Replace or clean the bearing, improve the seals.
Leakage or
Too much lubricant, Penetration by Reduce the amount of lubricant, select a stiffer grease. Replace the Fig. 14.12 Removal of Inner Fig. 14.13 Removal of Inner Ring Using Fig. 14.14 Removal of Inner Ring Using
Discoloration of
foreign matter or abrasion chips bearing or lubricant. Clean the housing and adjacent parts. Fig. 14.1 2 Ring Using a Press Fig. 14.13 Withdrawal Tool (1) Fig. 14.14 Withdrawal Tool (2)
Lubricant
Note (1) Intermittent squeal or high-pitch noise may be heard in medium- to large-sized cylindrical roller bearings or ball
bearings that are operating under grease lubrication in low-temperature environments. Under such low-temperature
conditions, bearing temperature will not rise resulting in fatigue nor is grease performance affected. Although
intermittent squeal or high-pitch noise may occur under these conditions, the bearing is fully functional and can
continue to be used. In the event that greater noise reduction or quieter running properties are needed, please contact
your nearest NSK branch office.
A 120 A 121
A100-125E.indd 120-121 11/20/13 4:52:29 PM
BEARING HANDLING
In both cases, the claws of the tools must substantially 14.4.3 Dismounting of Bearings with Tapered Bores 14.5 Inspection of Bearings 14.5.2 Inspection and Evaluation of Bearings
engage the face of the inner ring; therefore, it is When dismounting relatively small bearings with 14.5.1 Bearing Cleaning After being thoroughly cleaned, bearings should be
advisable to consider the size of the shaft shoulder adapters, the inner ring is held by a stop fastened to examined for the condition of their raceways and
or to cut grooves in the shoulder to accommodate the When bearings are inspected, the appearance of the
the shaft and the nut is loosened several turns. This is bearings should first be recorded and the amount and external surfaces, the amount of cage wear, the
withdrawal tools (Fig. 14.14). followed by hammering on the sleeve using a suitable increase in internal clearance, and degradation of
The oil injection method is usually used for the condition of the residual lubricant should be checked.
tool as shown in Fig. 14.18. Fig. 14.16 shows one After the lubricant has been sampled for examination, tolerances. These should be carefully checked, in
withdrawal of large bearings. The withdrawal procedure for dismounting a withdrawal sleeve by addition to examination for possible damage or other
is achieved easily by mean of oil pressure applied the bearings should be cleaned. In general, light oil or
tightening the removal nut. If this procedure is difficult, kerosene may be used as a cleaning solution. abnormalities, in order to determine the possibility for
through holes in the shaft. In the case of extra wide it may be possible to drill and tap bolt holes in the nut its reuse.
bearings, the oil injection method is used together with Dismounted bearings should first be given a
and withdraw the sleeve by tightening the bolts as preliminary cleaning followed by a finishing rinse. Each In the case of small non-separable ball bearings, hold
a withdrawal tool. shown in Fig. 14.17. the bearing horizontally in one hand, and then rotate
Induction heating is used to remove the inner rings bath should be provided with a metal net to support
Large bearings may be withdrawn easily using oil the bearings in the oil without touching the sides or the outer ring to confirm that it turns smoothly.
of NU and NJ types of cylindrical roller bearings. The pressure. Fig. 14.19 illustrates the removal of a Separable bearings such as tapered roller bearings
inner rings are expanded by brief local heating, and bottom of the tank. If the bearings are rotated with
bearing by forcing oil under pressure through a hole foreign matter in them during preliminary cleaning, the may be checked by individually examining their rolling
then withdrawn (Fig. 14.15). Induction heating is also and groove in a tapered shaft to expand the inner elements and the outer ring raceway.
used to mount several bearings of these types on a raceways may be damaged. The lubricant and other
ring. The bearing may suddenly move axially when the deposits should be removed in the oil bath during the Large bearings cannot be rotated manually; however,
shaft. interference is relieved during this procedure so a stop the rolling elements, raceway surfaces, cages,
initial rough cleaning with a brush or other means.
nut is recommended for protection. Fig. 14.20 shows a After the bearing is relatively clean, it is given the and contact surface of the ribs should be carefully
withdrawal using a hydraulic nut. finishing rinse. The finishing rinse should be done examined visually. The more important a bearing is,
carefully with the bearing being rotated while immersed the more carefully it should be inspected.
in the rinsing oil. It is necessary to always keep the The determination to reuse a bearing should be made
rinsing oil clean. only after considering the degree of bearing wear,
the function of the machine, the importance of the
bearings in the machine, operating conditions, and
the time until the next inspection. However, if any of
the following defects exist, reuse is impossible and
Oil
replacement is necessary.
Inner Ring
(a) When there are cracks in the inner or outer rings,
rolling elements, or cage.
(b) When there is flaking of the raceway or rolling
elements.
Withdrawal Claw (c) When there is significant smearing of the raceway
surfaces, ribs, or rolling elements.
Fig. 14.16 Removal of Withdrawal Fig. 14.17 Removal of Withdrawal (d) When the cage is significantly worn or rivets are
Fig. 14.15 Removal of Inner Ring Using Fig. 14 .16 Sleeve Using Withdrawal Nut (1) Fig. 14.17 Sleeve Using Withdrawal Nut (2) loose.
Fig. 14. 15 Induction Heater (e) When there is rust or scoring on the raceway
surfaces or rolling elements.
(f) When there are any significant impact or brinell
traces on the raceway surfaces or rolling elements.
(g) When there is significant evidence of creep on the
bore or the periphery of the outer ring.
(h) When discoloration by heat is evident.
( i ) When significant damage to the seals or shields of
Fig. 14.20 Removal Using Hydraulic Nut grease sealed bearings has occurred.
Fig. 14.18 Removal of Adapter with Stop and Axial Pressure Fig. 14.19 Removal Using Oil Injection Hydraulic Pump
A 122 A 123
A100-125E.indd 122-123 11/20/13 4:52:29 PM
BEARING HANDLING
14.6 Maintenance and Inspection 14.6.2 Bearing Failures and Measures
14.6.1 Detecting and Correcting Irregularities In general, if rolling bearings are used correctly they Type of Failure Probable Causes Measures
In order to maintain the original performance of a will survive to their predicted fatigue life. However, they
bearing for as long as possible, proper maintenance often fail prematurely due to avoidable mistakes. Scoring
and inspection should be performed. If proper In contrast to fatigue life, this premature failure is Scoring or smearing between raceway Inadequate initial lubrication, excessively Use a softer grease and avoid rapid
procedures are used, many bearing problems can be caused by improper mounting, handling, or lubrication, and rolling surfaces. hard grease and high acceleration when acceleration.
avoided and the reliability, productivity, and operating entry of foreign matter, or abnormal heat generation. starting.
costs of the equipment containing the bearings are all For instance, the causes of rib scoring, as one
example of premature failure, may include insufficient Spiral scoring or smearing of raceway Raceway rings are not parallel and Correct the mounting, apply a preload, or
improved. It is suggested that periodic maintenance surface of thrust ball bearing. excessive speed. select another bearing type.
be done following the procedure specified. This lubrication, use of improper lubricant, faulty lubrication
periodic maintenance encompasses the supervision system, entry of foreign matter, bearing mounting
Scoring or smearing between the end face Inadequate lubrication, incorrect mounting Select proper lubricant and modify the
of operating conditions, the supply or replacement of error, excessive deflection of the shaft, or any of the rollers and guide rib. and large axial load. mounting.
lubricants, and regular periodic inspection. Items that combination of these. Thus, it is difficult to determine
should be regularly checked during operation include the real cause of some premature failures. Cracks
bearing noise, vibration, temperature, and lubrication. If all the conditions at the time of failure and previous to Crack in outer or inner ring. Excessive shock load, excessive Examine the loading conditions, modify the
If an irregularity is found during operation, the cause the time of failure are known, including the application, interference in fitting, poor surface fit of bearing and sleeve. The fillet radius
should be determined and the proper corrective actions the operating conditions, and environment; then by cylindricality, improper sleeve taper, large must be smaller than the bearing chamfer.
studying the nature of the failure and its probable fillet radius, development of thermal
should be taken after referring to Table 14.2. cracks and advancement of flaking.
If necessary, the bearing should be dismounted causes, the possibility of similar future failures can be
and examined in detail. As for the procedure for reduced. The most frequent types of bearing failure,
Crack in rolling element. Advancement of flaking, shock applied to Be carefull in handling and mounting.
dismounting and inspection, refer to Section 14.5, along with their causes and corrective actions, are Broken rib. the rib during mounting or dropped during
Inspection of Bearings. listed in Table 14.3. handling.
Fractured cage. Abnormal loading of cage due to incorrect Reduce the mounting error and review the
NSK BEARING MONITOR (Bearing Abnormality mounting and improper lubrication. lubricating method and lubricant.
Detector)
It is important during operation to detect signs of Indentations
irregularities early before damage becomes severe. Indentations in raceway in same pattern Shock load during mounting or excessive Use care in handling.
The NSK Bearing Monitor (see Page C5) is an as rolling elements. load when not rotating.
instrument that checks the condition of bearings
and gives a warning of any abnormality, or it stops Indentations in raceway and rolling Foreign matter such as metallic chips Clean the housing, improve the seals, and
elements. or sand. use a clean lubricant.
a machine automatically in order to prevent serious
trouble. In addition, it helps to improve maintenance Abnormal Wear
and reduce its cost. False brinelling (phenomenon similar to Vibration of the bearing without rotation Secure the shaft and housing, use oil as a
brinelling) during shipment or rocking motion of lubricant and reduce vibration by applying
small amplitude. a preload.
Table 14.3 Causes and Measures for Bearing Failures
Fretting Slight wear of the fitting surface. Increase interference and apply oil.
Type of Failure Probable Causes Measures
Wearing of raceway, rolling elements, rib, Penentration by foreign matter, incorrect Improve the seals, clean the housing, and
Flaking and cage. lubrication, and rust. use a clean lubricant.
Flaking of one-side of the raceway of Abnomal axial load. A loose fit should be used when mounting
Creep Insufficient interference or insufficient Modify the fit or tighten the sleeve
radial bearing. the outer ring of free-end bearings to allow
tightening of sleeve.
axial expansion of the shaft.
Seizure
Flaking of the raceway in symmetrical Out-of-roundness of the housing bore. Correct the faulty housing.
patterm. Discoloration and melting of raceway, Insufficient clearance, incorrect Review the internal clearance and bearing
rolling elements, and ribs. lubrication, or improper mounting. fit, supply an adequate amount of the
proper lubricant and improve the mounting
Flaking pattern inclined relative to the Improper muonting, deflection of shaft, Use care in mounting and centering, select
method and related parts.
raceway in radial ball bearings. Flaking inadequate tolerances for shaft and a bearing with a large clearance, and
near the edge of the raceway and rolling housing. correct the shaft and housing shoulder.
Electric Burng
surfaces in roller bearings.
Fluting or corrugations. Melting due to electric arcing. Install a ground wire to stop the flow of
Flaking of raceway with same spacing as Large shock load during mounting, rusting Use care in mounting and apply a rust electricity or insulate the beaning.
rolling elements. while bearing is out of operation for preventive when machine operation is
prolonged period. suspended for a long time. Corrosion & Rust
Rust and corrosion of fitting surfaces and Condensation of water from the air, or Use care in storing and avoid high
Premature flaking of raceway and rolling Insufficient clearance, excessive load, Select proper fit, bearing clearance, and bearing interior. fretting. temperature and high humidity, treatment
elements. improper lubrication, rust, etc. lubricant. Penetration by corrosive for rust prevention is necessary when
substance(especially varnish-gas, etc). operation is stopped for long time.
Premature flaking of duplex bearings. Excessive preload. Adjust the preload. Selection of varnish and grease.
A 124 A 125
A100-125E.indd 124-125 11/20/13 4:52:30 PM
You might also like
- Astm D4239 18 SulphurDocument8 pagesAstm D4239 18 SulphurMd Naseem Javed100% (4)
- BR3 001 - Rex 2000,3000,5000,9000 Series Roller BearDocument5 pagesBR3 001 - Rex 2000,3000,5000,9000 Series Roller BearRodrigo Jechéla BarriosNo ratings yet
- Mini-Project Mounting and Dismounting Technology of Rolling BearingsDocument8 pagesMini-Project Mounting and Dismounting Technology of Rolling BearingshouriaNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Tapered Roller BearingsDocument20 pagesTechniques For Tapered Roller BearingsJackson PhinniNo ratings yet
- Bearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesBearings With Replaceable Split Bronze Bushings: Instruction ManualCAT CYLINDERNo ratings yet
- Rolling Bearings: Bearing HandlingDocument6 pagesRolling Bearings: Bearing HandlingSreenivasNo ratings yet
- Proper Handling Practice of BearingsDocument16 pagesProper Handling Practice of Bearingszakizaki100% (1)
- Hyatt BFA Bearing Failure AnalysisDocument16 pagesHyatt BFA Bearing Failure AnalysisRodrigo Jechéla BarriosNo ratings yet
- NSK Bearing DoctorDocument40 pagesNSK Bearing DoctorforoNo ratings yet
- Crusher Bearings Technical White PaperDocument6 pagesCrusher Bearings Technical White PaperApna BharatNo ratings yet
- NSK PreventingCreepOnSubmersiblePumpBearings PDFDocument2 pagesNSK PreventingCreepOnSubmersiblePumpBearings PDFSaikat PurkaitNo ratings yet
- Bearing - Handling - 1654983393 2022-06-11 21 - 36 - 40Document10 pagesBearing - Handling - 1654983393 2022-06-11 21 - 36 - 40satya krishna chagantiNo ratings yet
- BR3 007 ManualDocument5 pagesBR3 007 ManualRodrigo Jechéla BarriosNo ratings yet
- NSK Bearing Maintenance GuideDocument40 pagesNSK Bearing Maintenance Guideexodia92alphaNo ratings yet
- Ball Transfer Units PDFDocument40 pagesBall Transfer Units PDFHyundianto AgNo ratings yet
- HDBIDocument5 pagesHDBIkevlar315No ratings yet
- H - SG NSK Handling & StorageHO 6Document3 pagesH - SG NSK Handling & StorageHO 6mohamed bakryNo ratings yet
- Fan Bearing Selection Fe 1200Document4 pagesFan Bearing Selection Fe 1200Rinsitha FahadNo ratings yet
- 6255 - Full-Circle Casing ScraperDocument8 pages6255 - Full-Circle Casing Scrapermaulana hapidNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operations & Maintenance Manual: Subject: Assembly and Disassembly With Thrust BearingDocument1 pageInstallation, Operations & Maintenance Manual: Subject: Assembly and Disassembly With Thrust Bearingdave fowlerNo ratings yet
- Full-Circle Casing Scraper: Instruction Manual 6255Document6 pagesFull-Circle Casing Scraper: Instruction Manual 6255Jubin JacobNo ratings yet
- BearingDocument423 pagesBearingaubd100% (2)
- 06 PDFDocument12 pages06 PDFBouzidnoui NouiNo ratings yet
- Care and MaintenanceDocument15 pagesCare and MaintenanceJeff LeeNo ratings yet
- NTN CatalogDocument50 pagesNTN CatalogThiên VõNo ratings yet
- Bearing Specs With Weardown LimitsDocument17 pagesBearing Specs With Weardown LimitsAkhtar QuddusNo ratings yet
- Nord Shaft Fixing Kit Bim1002 - UsDocument2 pagesNord Shaft Fixing Kit Bim1002 - UsBrad BorgesNo ratings yet
- Vasim 2Document17 pagesVasim 2Vasim shaikhNo ratings yet
- Craftsman 4.5-In. Angle Grinder 927726 Model 900.277230 Instruction Manual (MAY95-CD8) - 1006464LDocument8 pagesCraftsman 4.5-In. Angle Grinder 927726 Model 900.277230 Instruction Manual (MAY95-CD8) - 1006464LboomissyNo ratings yet
- TimkenTT en Vol1 Iss3Document2 pagesTimkenTT en Vol1 Iss3grupa2904No ratings yet
- The Importance of Properly Mounting Thin Section Bearings: An SKF Group BrandDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Properly Mounting Thin Section Bearings: An SKF Group BrandTony CasillaNo ratings yet
- 7 ReductorDocument9 pages7 ReductorArielNo ratings yet
- Fan Bearing Selection Fe 1200Document4 pagesFan Bearing Selection Fe 1200phineasphineNo ratings yet
- Uso, Instalación de CardanDocument14 pagesUso, Instalación de Cardansemagor100% (1)
- Timken ADAPT Bearing Installation GuideDocument16 pagesTimken ADAPT Bearing Installation GuideAlvaroNo ratings yet
- FE 1200 Fan Bearing SelectionDocument4 pagesFE 1200 Fan Bearing SelectionAvery OppegardNo ratings yet
- Dodge ALL-STEEL Pillow Blocks: Instruction Manual ForDocument2 pagesDodge ALL-STEEL Pillow Blocks: Instruction Manual ForWisnu BharataNo ratings yet
- FD Series IomDocument7 pagesFD Series IomdasdaNo ratings yet
- Installation: Sandvik SRP AB SE-233 81 Svedala, SwedenDocument18 pagesInstallation: Sandvik SRP AB SE-233 81 Svedala, SwedenWilliam Villamizar100% (1)
- Cylindrical Roller BeaDocument6 pagesCylindrical Roller Beasatish kumar reddyNo ratings yet
- Shrink Disc Type HSD: Mounting and Removal Instructions ForDocument1 pageShrink Disc Type HSD: Mounting and Removal Instructions ForGuang ChenzNo ratings yet
- Bearing Maintenance PracticesDocument19 pagesBearing Maintenance PracticesAbigor45No ratings yet
- BEARINGDocument13 pagesBEARINGhariprasad.mmechregd1No ratings yet
- Bearing FailDocument5 pagesBearing FailAmar NatourNo ratings yet
- DODGE ISNX Bearings Hydraulic Mount: Instruction and Lubrication ManualDocument4 pagesDODGE ISNX Bearings Hydraulic Mount: Instruction and Lubrication ManualRodrigo Jechéla BarriosNo ratings yet
- Angular Contact Ball BearingsDocument3 pagesAngular Contact Ball BearingsDannyschNo ratings yet
- Bearing: Service Manual MaintenanceDocument9 pagesBearing: Service Manual MaintenanceNazira NassNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Installation of The ULTRX HP (DD) Rupture Disc / ULTRX Double Disc Holder AssemblyDocument6 pagesPreparation and Installation of The ULTRX HP (DD) Rupture Disc / ULTRX Double Disc Holder AssemblyPaul LauNo ratings yet
- MN3085 - 0222 (W)Document12 pagesMN3085 - 0222 (W)mariamalloney1730No ratings yet
- DEH 3100SD Installation Manual PDFDocument7 pagesDEH 3100SD Installation Manual PDFAdriaono Gonzaga RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Disc Bearings 0Document9 pagesDisc Bearings 0aapennsylvaniaNo ratings yet
- Angular Co Installation GuideDocument2 pagesAngular Co Installation GuideGabrielNo ratings yet
- Proper and Efficient Work Procedures: 1. RemovalDocument5 pagesProper and Efficient Work Procedures: 1. RemovalMilton Poma CabasNo ratings yet
- Recommended Frame Shoring Erection ProceduresDocument2 pagesRecommended Frame Shoring Erection ProceduresDak KaizNo ratings yet
- 3DD029-A06-IOM-Gate Globe and Check ValvesDocument6 pages3DD029-A06-IOM-Gate Globe and Check ValvesgabrielNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry Fans - TCM - 12-113803Document7 pagesCement Industry Fans - TCM - 12-113803Anonymous H3I29yjNo ratings yet
- Kapitel 07 DINO Techn TeilDocument5 pagesKapitel 07 DINO Techn Teilalecandro_90No ratings yet
- Planetary Gearboxes Mounting Instruction V1.5 EngDocument2 pagesPlanetary Gearboxes Mounting Instruction V1.5 EngRee-anne SabanalNo ratings yet
- General Introduction: Chapter Four ExtractionDocument19 pagesGeneral Introduction: Chapter Four ExtractionMujahid HaddadNo ratings yet
- MIPI/DSI Receiver With HDMI Transmitter: Data SheetDocument12 pagesMIPI/DSI Receiver With HDMI Transmitter: Data SheetRobert GrabekNo ratings yet
- Black Berry Technology Seminar REportDocument24 pagesBlack Berry Technology Seminar REportparzpinku100% (1)
- Đề Số 9 Section B: Phonetics (5 Pts) : - - - - - - - I am leavingDocument6 pagesĐề Số 9 Section B: Phonetics (5 Pts) : - - - - - - - I am leavingĐỗ LinhNo ratings yet
- CV - Victor Bodero - EstructurasDocument4 pagesCV - Victor Bodero - EstructurasLeonid SolisNo ratings yet
- MicrowaveDocument48 pagesMicrowaverussel enriquezNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Veritas Cluster Server VCS Interview QuestionsDocument19 pagesThe Ultimate Veritas Cluster Server VCS Interview QuestionsBharanitharan SundaramNo ratings yet
- Front Drive AxleDocument19 pagesFront Drive AxleGeraldo Pozos VazquezNo ratings yet
- Is JIT Manufacturing The Right PrescriptionDocument1 pageIs JIT Manufacturing The Right PrescriptionjoannakamNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3-Theory of ModernisationDocument39 pagesTOPIC 3-Theory of Modernisationhartanahlot1421No ratings yet
- Prediction of Mineral Scale Formation in Wet Gas Condensate Pipelines and in MEG Regeneration PlantsDocument209 pagesPrediction of Mineral Scale Formation in Wet Gas Condensate Pipelines and in MEG Regeneration PlantsNasser GhorbaniNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid As PassivationDocument175 pagesCitric Acid As Passivationluthfi machmudi100% (1)
- Latihan Sas 1 Kelas 5 Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesLatihan Sas 1 Kelas 5 Bahasa InggrisLaila Purnamasari100% (1)
- Normal Calculus On Moving Surfaces - Keith C. AfasDocument29 pagesNormal Calculus On Moving Surfaces - Keith C. AfasAndres GranadosNo ratings yet
- Imm Toacs Feb 2023Document57 pagesImm Toacs Feb 2023rehan hayderNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Managing Safety With Basic ControllersDocument39 pagesBest Practices For Managing Safety With Basic ControllersWellington Silva TomNo ratings yet
- A Quantitative Approach To Selecting Nozzle Flow Rate and StreamDocument25 pagesA Quantitative Approach To Selecting Nozzle Flow Rate and StreamLeo MeliNo ratings yet
- A Novel Triple-Band Microstrip Branch-Line Coupler With Arbitrary Operating FrequenciesDocument3 pagesA Novel Triple-Band Microstrip Branch-Line Coupler With Arbitrary Operating FrequenciesPECMURUGANNo ratings yet
- General Psychology - An Introduction - Instructor Manual PDFDocument426 pagesGeneral Psychology - An Introduction - Instructor Manual PDFenoquemibey100% (1)
- Principles For Layout Plans and Sectioning Diagrams For 25 KV Ac TractionDocument4 pagesPrinciples For Layout Plans and Sectioning Diagrams For 25 KV Ac TractionPragati SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lo KendraDocument76 pagesLo Kendrasagar19sNo ratings yet
- Math 8-Third Quarter ExaminationDocument4 pagesMath 8-Third Quarter ExaminationJoeyGansan80% (5)
- Tourism Code San Andres, CatanduanesDocument42 pagesTourism Code San Andres, Catanduanesraniboi100% (2)
- Draft Ordinance For Bike Lanes in Q.CDocument4 pagesDraft Ordinance For Bike Lanes in Q.CRosé AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual - Series 70CV2000 Chloromatic Valve Used With Series 70-4400 & FX4400 Gas Dispensing SystemsDocument6 pagesInstruction Manual - Series 70CV2000 Chloromatic Valve Used With Series 70-4400 & FX4400 Gas Dispensing SystemsSỹ TháiNo ratings yet
- CV3B EW1 Group5 Experiment2&3Document6 pagesCV3B EW1 Group5 Experiment2&3jml aguilarNo ratings yet
- Lease Telecom Sprint MD3147 CityCollegeDocument23 pagesLease Telecom Sprint MD3147 CityCollegeParents' Coalition of Montgomery County, Maryland100% (1)
- Mag Instrument Product CatalogDocument14 pagesMag Instrument Product Cataloglutkica11No ratings yet
- Misamis Oriental: BMPS-TS-0818-01Document8 pagesMisamis Oriental: BMPS-TS-0818-01James Clerk LugtuNo ratings yet