Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Islam PDF
Islam PDF
Uploaded by
Buhle M.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Islam (1).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesIslam PDF
Islam PDF
Uploaded by
Buhle M.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
aia ISLAM
‘Mobainimed was born in 570 AD in Mecca in Arabia. He was a poor camel-driver whe became wealthy.
‘He was very religious and often used to pray in a cave in Mecca. There the angel Gabriel is said to have
appeared to him, The angel instructed him to preach anew religion and to write down its tenets in a book
which was later called the Koran. Mohammed's teaching caused him to make many enemies, and in 622
AD he had to make a joumey from Mecca to Medina ta escapé his enemies. From this date the Islamic
calendar begins. Vaton Ye died in 632, it-wes-belicued that-he-was-taken.up to heaves, His followers were
known as Muslims, which means “trae believers” and thé religion spread very fast indeed.
Tthad a strict code of conduct, Muslims were not allowed to drink alcoholic drinks and they were to give
to the poor, They were to pray five times a day, and must face Mecca when doing 60. The religion came.
with a set of laws and moral teachings. Muslims believed that Jesus was a prophet but that he was not the
son of God. The central teaching of Islamn was: “There is no God but Allah and Mohammed is his
Prophet.” Islam and Christianity therefore disagreed on a fundamental point even though they had come
from the same root. - A
By the time Mohammed died, most Arabians had become Muslims. Then the religion spread into Affica
and along its whole north coast. Then the Muslims captured Spain, but were unable to take France
because Charles Martel, the father of Charlemagne, defeated them and prevented them from taking any
more’ of Europe. Palestine, Syria and Asia Minor soon belonged to Islam.
‘The Arabian people preserved mich of the learning of Classical Greece and Rome, They were excellent
astronomers and mathematicians. It is from them that most of the world takes its system of counting,
Charlemagne was later crowned Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope, because he had spread the Christian
religion, had restored the order that had prevailed during the Romian Empire, and had conquered land in
Germany and Italy.
THE CRUSADES ‘
~The word comes from the Latin crux, meaning cross.
‘The Muslims took Jerusalem in 637 AD but only in 1078 did they begin to prevent the Christians from
visiting the Holy Sepulchre and other religious sites in Jerusalem, This wes when the Seljuk Turks or
‘Saracens took control of the armies in that area and Jews and Christians were no longer allowed to make
pilgrimages to Jerusalem. If they did they risked being killed ar totured,
‘The Roman Emperor in Constantinople appealed to the Pope for assistance and Pope Urban II made an
appeal in 1095 to all Christians urging them to reconquer Jerusalem. He added that any Christian who
died on any crusade’ would go straight to Heaven.
Why did people go on the Crusades?
% ‘They were religious and wanted to fight for thei faith, :
% They wanted to do penance (punishment) for their sins.
% They wished to leave home for other reasons (such as debt, crimes they had committed, etc).
4 They hoped to find a better life (some of them had been very poor).
They hoped they might find new land and wealth when they conquered the Holy Land.
+ They were merely seeking adventure,
‘The Crusade of Peter the Hermit
Peter was a French monk who gathered peasants together in France and Germany and made for the East.
He himself was a rather dirty long-haired man who rode on a donkey. These crusaders were ill-prepared
and untrained in militéry arts. They had no supplies so they robbed and murdered the inhabitants of all the
areas through which they passed. Many of them were murdered too because they were a nuisance. At
Constantinople the Emperor, shocked at the peculiar crowd that arrived with Peter, immediately sent them
to Asia Minor where most of them were slaughtered by the Saracens. Peter himself narrowly escaped with
his life.
The First Crusade (1096-1099 AD)
This was led by a group of nobles and knights, :
Foroes marched to Constantinople where they argived with the Emperor. The dispute concernitig authority
‘was sorted out but there was much distrust. uy a
1097 militery operations began, 100 000 men'laid siege to Nicaea, Victory was obtained over the
Muslims, and Antioch war taken after a siege of 7 months.
15 July 1099 an army of 20 000 crusaders took Jerusalem and brutally slaughtered the Jewish inhabitants.
To defend the new Christian Jerusalem two new orders of knights were formed:
Kaights of the Ts ats) to protect the Christian pilgrims
Knights of St John (Hospitallers) to heal the sick.
The Second Crusade (1147-1148)
The Saracens had begun gaining ground and were again likely to threaten Jerusalem. People were,
promised special privileges for fighting in the Crusade. Their sins-would be forgiven including any sins.
they might commit during the Crusade. Debts were cancelled. :
Ce of. (Holy Roman ror) and Louis VIL of France led this Crusade. They set out in
April 1147. The German army was nearly annihilated in Asia Minor but what was left of them joined the
French army to try to take Damascus, where they were defeated by the Saracens. The Crusade was later
abandoned and the last surviving crusaders arrived home in 1149,
The Third Crusade (1189-1192)
Pope Gregory VIII encouraged further Crusades since the new: Saracen leader Saladin had captured
Jerusalem in 1187. This Crusade was led By Frederick [ Richard I (the Lis
of lip I 2. The only-military victory was the conquest of Acre in 1191, Frederick
‘had drowned in a river on the way and his leaderless army had gone home. Philip and Richard had serious
disagreements and Philip went home with his men, leaving Richard to continue alone. He did not have
, enough forces to attack Jerusalem, and itis said that when he neared it he covered his eyes rather than
look at it, Richard received news that his brother John was conspiring against him in England so he had to
~ “Go home, He therefore made a treaty with Saladin stating that though Saladin was ruler of Jerusalem
Christians would have the right to make pilgrimages to the city unmolested
There were other crasades inchiding the disastrous Children's’ Crusade in 1212, during which 50 000
children from France and Germany journeyed East. Many died on the journey and many were enslaved.
‘During the later Crusades Jerusalem was captured but the Crusaders failed to keep control of it
Results of the Crusades
© People were exposed to a different lifestyle. They had seen the plush courts and grand cities of the
‘Muslim rulers, and the beautiful fabrics and exciting spices they used.
*& The exposure of Christians to another religion and another perception of reality made them curious,
and this later helped them to shake off their fear and superstition and ask questions about all aspects
#-_ offlfe. This led eventually to the Renaissance. :
* Trade by sea grew and cities that had been important for those travelling, on Crusades became
Prosperous trading cities. Commerce between East and West also gave rise to contact between people
of differing ideas, and this also helped to end ignorance and to stimulate curiosity. From the Eastern
+ peoples they learned about mathematics and medicine. They became inclined to think for themselves
% The Church also gained wealth during the Crusades, which may have led to its later.corruption.
% The Church became divided into three: The Western Church with its Pope in Rome
The Greek (Orthodox) Church with its Patriarch in
Constantinople
~The Coptic Church (with members in the Middle East and
Africa) under the Patriarch of Alexandria.
1. Reasons for the crusades
‘* The pope wanted to rescue the Holy Places from the hands of the Saracens and
make them safe for pilgrims.
‘2 By helping the Emperor in the East to defeat the Saracens, the Pope hoped to
* secure better relations between the church of Constantinople and the church
of Ro.ue.
* The Pope hoped that if the nobles of Western Europe could be united in a
common cause, they would stop waging wars against each other:
The first crusade
The First Crusade was an attempt to re-capture Jerusalem, After the capture of Jerusalem by
the Muslims in.1076, any Christian who wanted to pay a pilgrimage to the city faced a very
hard time. Muslim soldiers made life very difficult for the Christians and trying to get to
Jerusalem was filled with danger for a Christian, This greatly angered all Christians. Alexius.
Lof Constantinople - feared that his country might also fall to the Muslims as it was very
close to the territory captured by the Muslims. Constantinople is in modern day Turkey,
Alexius called on the pope - Urban IT to give him help.
In 1095, Urban spoke to a great crowd at Clermont in France. He called for a war against the
Muslims so that Jerusalem was regained for the Christian faith. Those who volunteered to go
+o fight the Muslims cut out red crosses and sewed them on their tunics. The French word
“croix” means cross.and the word changed to "eroisades" or crusades, The fight against the
‘Muslims became a Holy War.
Many people did volunteer to fight on the First Crusade.
‘There were true Christians who wanted to reclaitn Jerusalem for their belief and get the
Muslims out of the city. There were those who knew they had committed sin and that by
going on the Crusade they might be forgiven by God. They had also been told by the pope
that if they were killed, they would automatically go to heaven as they were fighting for God.
By 1097, nearly 10,000 people had gathered at Constantinople ready for the journey to the
Holy Land. There was no one person in charge of the First Crusade, The first target of the
Crusaders was the important fortress city of Nicea. This city was taken by the Crusaders
without too much trouble as the man in charge of it was away fighting!
‘The next target for the Crusaders was Antioch - a strongly protected Turkish city. It took a
seven month siege before the city fell. The next target was Jerusalem.
‘The ettack and capture of Jerusalom started in the summer of 1099 Jerusalem was
well defended with high walls around it. The first attacks on the city were not successful as
the Crusaders were short of materials for building siege machines. Once logs had arrived, two
siege machines were built.
After the success of the Crusaders, the Kingdom of Jerusalem was created and its first king
‘was Godftey of Bouillon who was elected by other crusaders. He died in 1100 and was
succeeded by his brother Baldwin of Boulogne.
2
‘The capture of Jerusalem did not end the Crusades as the Crusaders wanted to get rid of the
‘Muslims from the whole region and not just Jerusalem, This desire led to the other crusades.
Benefits of the crusades
pe
‘The Crusades -ontributed to increase the wealth of the Church and the power of
the Papacy, Thus the prominent part which the Popes took in the enterprises
naturally fostered their authority and influence; by placing in their hands, the
armies and resources of Christendom, and accustoming the people to look fo
them as guides and leaders.
One of the most important effects of the crusades was on commerce. They
created a constant demand for the transportation of men.and supplies,
encouraged ship-building, and extended the market for eastern wares in Europe.
They helped {o undermine feudalism, Thousands of barons and knights
mortgaged or sold their lands in order to raise money for a crusading expedition.
they helped to break down the power of the feudal aristocracy.
‘The Crusades afforded an opportunity for tomantic adventure. The Crusades
were therefore one of the principal fostering influences of Chivalry,
_The crusaders returned with finer tastes, broader ideas, and wider sympathies.
‘The crusades opened up a new world, Furthermore, the knowledge of the science
and learning of the East gained by the crusaders through their expeditions,
greatly stimulated the Latin intellect, and helped to awaken in Western Europe
that mental activity which resulted finally in the great intellectual outbarst
known as the Revival of Learning and the period of the Renaissance.
‘Various arts, manufactures, and inventions before unknown in Europe, were
introduced from Asia.
‘The incentive given to geographical discovery led various travellers, such as the
celebrated Italian, Marco Polo, and the scarcely less noted Englishman, Sir John
Mandeville, to explore the most remote countries of Asia, Even that spirit of
maritime enterprise and adventure which rendeyed illustrious the fifteenth
century, inspiring the voyages of Columbus, Vasco de Gama, and Magellan, may
be traced back to that lively interest in geographical matters awakened by the
expeditions of the crusaders,
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
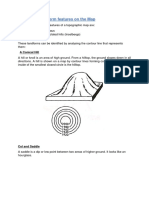
- Mapwork Pt9 - Identifying Landform Features On The Map PDFDocument5 pagesMapwork Pt9 - Identifying Landform Features On The Map PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Mapwork Pt8 - Contour Lines and Calculating Height PDFDocument4 pagesMapwork Pt8 - Contour Lines and Calculating Height PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Primary Triad Handout PDFDocument4 pagesPrimary Triad Handout PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Mapwork Pt10 - Drawing A Cross Section PDFDocument4 pagesMapwork Pt10 - Drawing A Cross Section PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- HistoryReview24 1 English ReformationDocument18 pagesHistoryReview24 1 English ReformationBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Rivers Pt2 River Processes PDFDocument8 pagesRivers Pt2 River Processes PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Thursday 26 September 2019 Test 2: Trace EDocument2 pagesThursday 26 September 2019 Test 2: Trace EBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Zibusiso M NdlovuDocument1 pageZibusiso M NdlovuBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Bliss Makanza - Caregiver PDFDocument2 pagesBliss Makanza - Caregiver PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Form 2 Prep Timetable 2023 PDFDocument1 pageForm 2 Prep Timetable 2023 PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
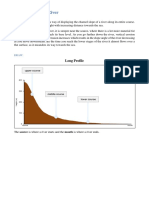
- Rivers Pt5 River Profiles PDFDocument5 pagesRivers Pt5 River Profiles PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Reformation in EnglandDocument1 pageReformation in EnglandBuhle M.No ratings yet
- The Giver Questions Chapters 14-16Document1 pageThe Giver Questions Chapters 14-16Buhle M.100% (1)
- Rivers PT 9 River Flood Management PDFDocument4 pagesRivers PT 9 River Flood Management PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Key Signature - Musical Notation - Britannica PDFDocument2 pagesKey Signature - Musical Notation - Britannica PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Timetable PDFDocument1 pageTimetable PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Rivers PT 7 Meanders and Oxbow Lakes PDFDocument4 pagesRivers PT 7 Meanders and Oxbow Lakes PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Grammar Test 5 PDFDocument3 pagesGrammar Test 5 PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Grammar Test 13 PDFDocument2 pagesGrammar Test 13 PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Rivers PT 8 Floodplains Levees and Deltas PDFDocument6 pagesRivers PT 8 Floodplains Levees and Deltas PDFBuhle M.No ratings yet
- Form 2 Test 2 10Document2 pagesForm 2 Test 2 10Buhle M.No ratings yet
- The History Side of AfricaDocument3 pagesThe History Side of AfricaBuhle M.No ratings yet