Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control System L8
Uploaded by
Vedansh Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views19 pagesThe document summarizes lecture material on control systems from a Mechanical Engineering course. It covers topics like transient and steady state response analysis of second order systems, partial fraction expansion of higher order systems transfer functions, using MATLAB to analyze unit step responses, and Routh's stability criterion to determine system stability by analyzing the signs of coefficients in an array. It provides examples of applying these concepts and analyzing systems for stability.
Original Description:
Original Title
Control system L8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes lecture material on control systems from a Mechanical Engineering course. It covers topics like transient and steady state response analysis of second order systems, partial fraction expansion of higher order systems transfer functions, using MATLAB to analyze unit step responses, and Routh's stability criterion to determine system stability by analyzing the signs of coefficients in an array. It provides examples of applying these concepts and analyzing systems for stability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views19 pagesControl System L8
Uploaded by
Vedansh SinghThe document summarizes lecture material on control systems from a Mechanical Engineering course. It covers topics like transient and steady state response analysis of second order systems, partial fraction expansion of higher order systems transfer functions, using MATLAB to analyze unit step responses, and Routh's stability criterion to determine system stability by analyzing the signs of coefficients in an array. It provides examples of applying these concepts and analyzing systems for stability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Vibration and Control ( ME F319)
Control system
(Lecture 8)
Mechanical Engineering Dept.
Topic covered : Last Class
• Transient and Steady state response analysis
– Second Order system
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 2
Higher order systems
Close loop Transfer Function (CLTF)
for unit step input
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 3
Partial fraction expansion
Where coefficient ak is called the residue at
the pole at s=–pk
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 4
Partial fraction expansion: with MATLAB
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 5
Higher order systems: MATLAB codes
MATLAB code for unit step input
step(num,den) or, step(num,den,t)
step(A,B,C,D), or, step(A,B,C,D,t)
Example:
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 6
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 7
Under unit step response
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 8
Under unit impulse response
The unit-impulse response of a control system may be
obtained by using any of the impulse commands
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 9
Responses with initial condition
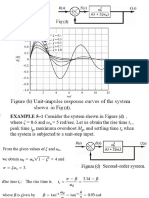
Example: Consider the mechanical system shown in Figure where m=1 kg,
b=3 N-sec/m, and k=2 N/m. Assume that at t=0 the mass m is pulled
downward such that x(0)=0.1 m and 𝒙 (0)=0.05 m/sec. The displacement
x(t) is measured from the equilibrium position before the mass is pulled
down. Obtain the motion of the mass subjected to the initial condition.
(Assume no external forcing function.)
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 10
ROUTH’S STABILITY CRITERION
• Routh’s stability criterion tells us whether or not there are
unstable roots in a polynomial equation without actually
solving for them.
• This stability criterion applies to polynomials with only a
finite number of terms.
• When the criterion is applied to a control system,
information about absolute stability can be obtained
directly from the coefficients of the characteristic equation
STEP1: Write the polynomial in s in the following form:
Ch. Equation: 1+OLTF= 0
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 11
ROUTH’S STABILITY CRITERION
STEP 2: Check necessary and sufficient condition:
• If any of the coefficients are zero or negative in the presence of at least
one positive coefficient, a root or roots exist that are imaginary or that
have positive real parts. Therefore, in such a case, the system is not
stable.
• For the absolute stability, there is no need to follow the procedure
further. Note that all the coefficients must be positive. This is a
necessary condition
• It is important to note that the condition that all the coefficients be
positive is not sufficient to assure stability. The necessary but not
sufficient condition for stability is that the coefficients of Equation all be
present and all have a positive sign. (If all a’s are negative, they can be
made positive by multiplying both sides of the equation by –1.:
Hurwitz test
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 12
ROUTH’S STABILITY CRITERION
STEP 3: If all coefficients
are positive, arrange the
coefficients of the
polynomial in rows and
columns according to the
following pattern:
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 13
ROUTH’S STABILITY CRITERION
Routh’s stability criterion: The necessary and
sufficient condition that all roots of ch. Equation
lie in the left-half s plane is that all the
coefficients of Equation be positive and all
terms in the first column of the array have
positive signs.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 14
Example: 1
Apply Routh’s stability criterion to the following fourth order
polynomial and construct the array of coefficients.
Also comments on stability.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 15
ROUTH’S STABILITY CRITERION
• Routh’s stability criterion states that the number of roots of
Characteristics Equation with positive real parts is equal to
the number of changes in sign of the coefficients of the first
column of the array.
• It should be noted that the exact values of the terms in the
first column need not be known; instead, only the signs are
needed.
• The necessary and sufficient condition that all roots of ch.
Equation lie in the left-half s plane is that all the
coefficients of Equation be positive and all terms in the first
column of the array have positive signs.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 16
Special case: If a first-column term in any row is zero, but the remaining
terms are not zero or there is no remaining term, then the zero term is
replaced by a very small “ε” positive number and the rest of the array is
evaluated
The result is unchanged when the coefficients of any row are multiplied or
divided by a positive number in order to simplify the computation.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 17
Special case: If all the coefficients in any derived row are zero.
In such a case, the evaluation of the rest of the array can be continued by
forming an auxiliary polynomial with the coefficients of the last row and by
using the coefficients of the derivative of this polynomial in the next row.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 18
Example 2
Determine the range of K for stability.The closed-loop
transfer function is
ANS.
17 April 2023 Arun Kumar Jalan 19
You might also like
- Profound Meditation User ManualDocument21 pagesProfound Meditation User ManualJon Rossiter100% (2)
- Crystal Healing PresentationDocument24 pagesCrystal Healing Presentationperiasamy_nano100% (3)
- PV CALC 1Document25 pagesPV CALC 1Mohammad HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Theory of StructuresDocument35 pagesTheory of StructurespjNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusFrom EverandAn Introduction to Differential Geometry - With the Use of Tensor CalculusRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Trusses, Frames & MachinesDocument55 pagesTrusses, Frames & MachinesCivil RguktNo ratings yet
- Stability in Control SystemsDocument20 pagesStability in Control Systemssamir100% (1)
- Equilibrium of ForceDocument11 pagesEquilibrium of Forcehazheer164% (14)
- StabilityDocument20 pagesStabilityravalNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Series F12: Effective: April, 2011 Supersedes: March, 2011Document32 pagesService Manual Series F12: Effective: April, 2011 Supersedes: March, 2011Eduardo Alvarez HuizaNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional ElementDocument75 pagesOne Dimensional ElementBerkath Ali Khan50% (2)
- Routh-Hurwitz Stability CriterionDocument33 pagesRouth-Hurwitz Stability CriterionFarhan d'Avenger0% (1)
- Gas Pipeline HydraulicsDocument58 pagesGas Pipeline HydraulicsBakheit Layli100% (1)
- Bocker Giant Construction HoistDocument8 pagesBocker Giant Construction HoistRajanbabuNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument10 pagesStabilityBUSHRA BATOOLNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.0 Stability Analysis of FB Controlsystems TCE 5102Document30 pagesTopic 3.0 Stability Analysis of FB Controlsystems TCE 5102princekamutikanjoreNo ratings yet
- Week 7B - Online Classes - S2020Document21 pagesWeek 7B - Online Classes - S2020Muhammad Tayyab YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- 18-Stability Analysis - Routh Array and Root Locus Method-07!03!2024Document16 pages18-Stability Analysis - Routh Array and Root Locus Method-07!03!2024yadavpravin5151No ratings yet
- SME Official Layout Module+10Document20 pagesSME Official Layout Module+10JmbernabeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Analysis For External Reactions and Internal Resultants of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument14 pagesModule 2 - Analysis For External Reactions and Internal Resultants of Statically Determinate Structureskanser manNo ratings yet
- Extention of Routh's Stability Criterion For The Analytic Conditions of Spontaneous Self Excitation in Induction GeneratorsDocument6 pagesExtention of Routh's Stability Criterion For The Analytic Conditions of Spontaneous Self Excitation in Induction GeneratorsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ruth Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument22 pagesRuth Herwitz Stability CriterionMD MUSFIQUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Examples For Stability AnalysisDocument36 pagesExamples For Stability AnalysisMhabad ZebariNo ratings yet
- Module-17 - Routh-Hurwitz Criterion: EE3101-Control Systems EngineeringDocument8 pagesModule-17 - Routh-Hurwitz Criterion: EE3101-Control Systems EngineeringhariNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument18 pagesControl Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Bounded Output Stability, Which Can Be Employed in The Design and Analysis of Process Control SystemsDocument8 pagesBounded Output Stability, Which Can Be Employed in The Design and Analysis of Process Control Systemsd_k_ÜNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Kinematic Analysis of Parallel Kinematic Manipulators - Inverse and Forward KinematicsDocument21 pagesCH 4 Kinematic Analysis of Parallel Kinematic Manipulators - Inverse and Forward KinematicsMbuso MadidaNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifDocument34 pagesBiomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifJpradha KamalNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsDocument30 pages2.3 Stability of Feedback Control SystemsJust RobotNo ratings yet
- Theory of StructuresDocument35 pagesTheory of StructuresPatricia Nicole ElediaNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics - 1 - Lecture5Document21 pagesStructural Mechanics - 1 - Lecture5SHARM .A.No ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument30 pagesControl Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Stabilty Routh HurwitzDocument33 pagesStabilty Routh HurwitzAhmad SherNo ratings yet
- Robust Pole Placement Using Linear Quadratic Regulator Weight Selection AlgorithmDocument5 pagesRobust Pole Placement Using Linear Quadratic Regulator Weight Selection AlgorithmijsretNo ratings yet
- 505 - Lec 11 PDFDocument28 pages505 - Lec 11 PDFUdara DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument28 pagesStabilityDaniel MengeshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Document33 pages1 Stability-Analysis (Important)Tahmid ShihabNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) : Lecture-7 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument30 pagesControl Systems (CS) : Lecture-7 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Analysis of Plane MechanismsDocument12 pagesKinematic Analysis of Plane MechanismsEdison PilcoNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture19-20 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument24 pagesFeedback Control Systems (FCS) : Lecture19-20 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionRajNo ratings yet
- 6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionDocument30 pages6 Module 6 Routh Hurwitz CriterionJyotirmayee Panda100% (1)
- Control System L7Document19 pagesControl System L7Vedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 StabilityDocument30 pagesChap 6 StabilitySumeyye AstalNo ratings yet
- Stability: Term Paper - IPC Made by - Krishna Patel (18BCH045)Document28 pagesStability: Term Paper - IPC Made by - Krishna Patel (18BCH045)PATEL KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Law of PolygonDocument7 pagesLaw of Polygonuser10150% (10)
- Biomedical Control SystemsDocument3 pagesBiomedical Control SystemsNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topological Analysis of 6-Joint Serial Manipulators and Their Inverse Kinematic SolutionsDocument37 pagesTopological Analysis of 6-Joint Serial Manipulators and Their Inverse Kinematic SolutionsBENLAHRECH Djamal EddNo ratings yet
- EM - PPT - FinalpptxDocument28 pagesEM - PPT - FinalpptxShawn HunterNo ratings yet
- Chatper 4 FEM Procedure and Spring Element PDFDocument9 pagesChatper 4 FEM Procedure and Spring Element PDFVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Control System L3Document17 pagesControl System L3Vedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document20 pagesChapter 6Duncan KingNo ratings yet
- Second Order Analysis of StructuresDocument10 pagesSecond Order Analysis of Structuresanimesh91No ratings yet
- Routh-Hurwtz Criterion & Root-Locus Criteria: Stability of Feedback Control SystemsDocument19 pagesRouth-Hurwtz Criterion & Root-Locus Criteria: Stability of Feedback Control Systemsember_memoriesNo ratings yet
- System StabilityDocument16 pagesSystem Stabilityeugeni madaNo ratings yet
- Stability: Sistem Pengendalian Otomatik Departemen Teknik Fisika Ftirs - ItsDocument32 pagesStability: Sistem Pengendalian Otomatik Departemen Teknik Fisika Ftirs - ItsUliya Rifda HanifaNo ratings yet
- Control 05Document27 pagesControl 05أحمد تركي كحيوشNo ratings yet
- Stability of Linear Systems: DR K P Mohandas, Professor, NIT CalicutDocument7 pagesStability of Linear Systems: DR K P Mohandas, Professor, NIT Calicutsuresh1virdiNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Document22 pagesTransient and Steady State Response Analysis: Module - 3Rajath UpadhyaNo ratings yet
- SAT PresentationDocument30 pagesSAT Presentationukesh_kumarNo ratings yet
- Design of A Linear State Feedback ControllerDocument27 pagesDesign of A Linear State Feedback ControllerMohammad IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Parta Roth Herwitz Stability CriterionDocument28 pagesParta Roth Herwitz Stability CriterionVeena Divya KrishnappaNo ratings yet
- Trifocal Tensor: Exploring Depth, Motion, and Structure in Computer VisionFrom EverandTrifocal Tensor: Exploring Depth, Motion, and Structure in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Direct Linear Transformation: Practical Applications and Techniques in Computer VisionFrom EverandDirect Linear Transformation: Practical Applications and Techniques in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Mess Menu From 16th To 30th April-23Document5 pagesMess Menu From 16th To 30th April-23Vedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Control System L7Document19 pagesControl System L7Vedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Control System L3Document17 pagesControl System L3Vedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Method of FEMDocument27 pagesMethod of FEMVedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- FEM FramesDocument3 pagesFEM FramesVedansh SinghNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeRavi RajNo ratings yet
- Pressure GaugeDocument2 pagesPressure GaugeVishnu PatilNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Curcumin On Metal IonsDocument2 pagesThe Effect of Curcumin On Metal IonsLai ChungyiNo ratings yet
- ASMI CoCrDocument5 pagesASMI CoCrprimaNo ratings yet
- PI Datasheet P-882 - P-888 20150123 PDFDocument5 pagesPI Datasheet P-882 - P-888 20150123 PDFNuraidinAzisNo ratings yet
- Sample Investigatory Project - Class-11Document11 pagesSample Investigatory Project - Class-11Varun SinghNo ratings yet
- Kryotech Problem StatementDocument2 pagesKryotech Problem StatementMohammed MohsinNo ratings yet
- Physics II - Lab 1 - Coulomb's LawDocument4 pagesPhysics II - Lab 1 - Coulomb's LawKestin ComeauxNo ratings yet
- ELJODocument3 pagesELJOElvira CuestaNo ratings yet
- Engg AnalysisDocument117 pagesEngg AnalysisrajeshtaladiNo ratings yet
- VC.9.9.M.E. Soil MechanicsDocument13 pagesVC.9.9.M.E. Soil Mechanicsvinoth_mani_1No ratings yet
- Class 9 Physics Worksheet FinalDocument5 pagesClass 9 Physics Worksheet FinalTwisha JainNo ratings yet
- Homework 2-Problems PDFDocument3 pagesHomework 2-Problems PDFMaria AtaligNo ratings yet
- Nahom KelemuDocument121 pagesNahom KelemuKing RogoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Air Permeability MeasurementDocument4 pagesLaboratory Manual For Air Permeability Measurementadeelsn0% (2)
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/33Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/33Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- Technical CatalogueDocument320 pagesTechnical Cataloguevellas_jeg50% (2)
- The Importance of MathDocument14 pagesThe Importance of Mathtayyaba_shahid1100% (3)
- CH 105+ +solutions 3Document21 pagesCH 105+ +solutions 3UmarNo ratings yet
- Transducer PDFDocument27 pagesTransducer PDFGAJANAN M NAIKNo ratings yet
- Time, Speed AND DistanceDocument41 pagesTime, Speed AND DistanceBriti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Skills AssignmentDocument18 pagesExperimental Skills AssignmentGayathri cnNo ratings yet
- Bangalore University TIME TABLE (Tentative)Document1 pageBangalore University TIME TABLE (Tentative)Manjot SinghNo ratings yet