0% found this document useful (0 votes)
644 views71 pagesSubgrade Preparation in Road Construction
This document discusses road construction, specifically subgrade preparation and improvement. It covers subgrade preparation which involves site clearance, earthwork like excavation and embankment construction, and compaction. Special techniques are needed for constructing embankments through marshy areas. The document also discusses sub-base course construction and checking the prepared subgrade.
Uploaded by
amareCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
644 views71 pagesSubgrade Preparation in Road Construction
This document discusses road construction, specifically subgrade preparation and improvement. It covers subgrade preparation which involves site clearance, earthwork like excavation and embankment construction, and compaction. Special techniques are needed for constructing embankments through marshy areas. The document also discusses sub-base course construction and checking the prepared subgrade.
Uploaded by
amareCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
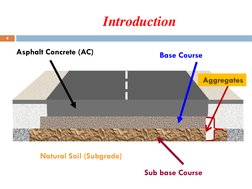
- Introduction: Describes the scope of road construction and highway pavement structures.
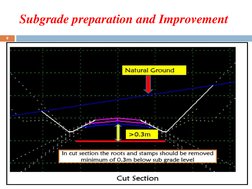
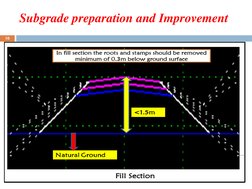
- Subgrade Preparation and Improvement: Details the processes and operations involved in preparing and improving the subgrade, including site clearance and earthwork.
- Sub-Base Course Construction: Explains the construction of sub-base layers, functions, material requirements, and preparation procedures.
- Base Course Construction: Covers the role of the base course in pavement structure, types, and construction steps.
- Construction of Asphalt Concrete: Discusses the layers and procedures involved in asphalt concrete pavement construction.