Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Redox Equilibrium Practice Worksheet 2023 Answer Key
Uploaded by
Radhika Rani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesRedox Equilibrium Practice Worksheet 2023 Answer Key
Uploaded by
Radhika RaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Redox Equilibrium Practice Worksheet
Standard Electrode Potentials
Cu2+ + 2e- ⇌ Cu +0.34V Mg2+ + 2e- ⇌ Mg -2.37V
+ -
2H + 2e ⇌ H2 0.00V Ag+ + e- ⇌ Ag +0.80V
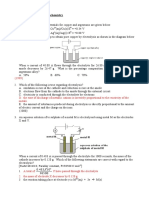
1. The cell shown below can be used to measure the standard electrode potential of magnesium.
a) Define the term ‘standard electrode potential’.
- the electrode potential, in V, of a half-cell measured when connected to a standard
hydrogen electrode under the standard conditions (298K, 1atm, 1M H +)
b) Identify the following from the diagram above.
i) W platinum foil covered in platinum black (porous platinum)
ii) X salt bridge
iii) Y magnesium
iv) Z 1 Magnesium ion solution
c) Anode reaction: H2(g) 2H+(aq) +2e-
d) Cathode Reaction: Mg2+(aq) +2e- Mg(s)
e) Give the conventional IUPAC representation for this cell (conventional cell diagram).
Pt|H2(g) |2H+(aq)||Mg2+(aq)|Mg(s) or
Pt[H2(g)] |2H+(aq)||Mg2+(aq)|Mg(s)
f) Indicate the direction of electron flow (L →R or R →L).
L →R (anode to cathode)
g) Consider the cell represented below.
Cu(s) ǀCu2+(aq) ǁAg+(aq) ǀAg(s)
i) Write the equation for the overall reaction between copper and silver ions.
Cu ⇌ Cu2+ + 2e-
2(Ag+ + e- ⇌ Ag) Note: Electrons must balance.
+ -
2Ag + 2e ⇌ 2Ag)
Overall: Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
ii) Calculate the standard cell potential.
°Ecell = °Ecathode - °Eanode = 0.80V –(+0.34) = +0.46V
h) Considering the standard electrode potentials given, identify:
i) the strongest oxidizing agent – Ag+
ii) the strongest reducing agent - Mg
You might also like
- Electrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesElectrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersNurul Hana Omar100% (2)
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Galvanic Cell, Its Representation & Salt BridgeDocument28 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Galvanic Cell, Its Representation & Salt BridgeGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Electrochemistrymeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Standard Electrode PotentialDocument1 page8.2 Standard Electrode PotentialRuoQi LeeNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesTopic 3 - ElectrochemistryMutasimNo ratings yet
- 6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Document44 pages6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Rishab PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Practice ProblemsDocument16 pagesCH 11 Practice ProblemsAnivia12100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument106 pagesElectrochemistrySeng IvanNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Test 3 With - KeyDocument6 pagesMCQ - Test 3 With - KeyShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- C 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017Document16 pagesC 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Tutorial Definitions and ReactionsDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry Tutorial Definitions and ReactionsmunirahNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Oxidation Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesReduction-Oxidation Reactions and Electrochemistrykaushi123No ratings yet
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyDocument3 pagesModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Chapter QuestionsDocument10 pagesElectrochemistry Chapter QuestionsTarek GhaddarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and its applicationsDocument39 pagesElectrochemistry and its applicationsHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Board Questions 2010-2020Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Board Questions 2010-2020amone nNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry worksheet covering EMF of cells, standard electrode potentials, electrolysis, Faraday's lawDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry worksheet covering EMF of cells, standard electrode potentials, electrolysis, Faraday's lawpankaj singhNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions Jee ModuleDocument49 pagesLiquid Solutions Jee ModuleAfsheen TahiraNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectrochemical Cell QuestionsLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Electrochem2Document1 pageTutorial Electrochem2irnihafizan6812No ratings yet
- AJ98172 Tutorial Topic 9Document2 pagesAJ98172 Tutorial Topic 9WilfredNo ratings yet
- SRI CHAITANYA IIT ACADEMY CHEMISTRY DOCUMENTDocument19 pagesSRI CHAITANYA IIT ACADEMY CHEMISTRY DOCUMENTggk20130% (2)
- Tutorial (Electrochemistry)Document4 pagesTutorial (Electrochemistry)Amir Aiman AniqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9/19 (71 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument28 pagesChapter 9/19 (71 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- Question 801367Document4 pagesQuestion 801367niveditasingh2472No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry MCQ SendDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry MCQ SendRajendra ChikkamathNo ratings yet
- Echem WKST KeyDocument7 pagesEchem WKST KeyNurul Hana OmarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry concepts and calculationsDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry concepts and calculationsSukanya PaulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryAndreaForteRuizNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: (See Page 3 For Formulas and An Answer Key) P R A C T I C E T E S TDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry: (See Page 3 For Formulas and An Answer Key) P R A C T I C E T E S TBiniyam haileNo ratings yet
- AP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Document7 pagesAP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Vineeth SendilrajNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Applications of RedoxDocument29 pagesElectrochemistry: Applications of RedoxrachelelkinNo ratings yet
- Practice Electrochemistry - 1Document5 pagesPractice Electrochemistry - 1ervaldiNo ratings yet
- Low-cost lithium-copper air fuel cell reactions and E° calculationsDocument11 pagesLow-cost lithium-copper air fuel cell reactions and E° calculationsBloodCypherNo ratings yet
- When A Non-Spontaneous Redox Reaction Is Made To Occur by Putting Electrical Energy Into The SystemDocument11 pagesWhen A Non-Spontaneous Redox Reaction Is Made To Occur by Putting Electrical Energy Into The SystemArdit QerimiNo ratings yet
- LT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Document3 pagesLT Iit Che DPT - 15 - 21.02.2024Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- 02 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages02 ElectrochemistryGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYChangha ParkNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Concepts and CalculationsDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Concepts and CalculationsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DmsDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 DmsCik ApaiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Galvanic CellsDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Galvanic CellsKester Yuree L. GimongalaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry AssignmentDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry AssignmentSulekha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Discovering Electrochemical Cells: PGCC CHM 102 SinexDocument36 pagesDiscovering Electrochemical Cells: PGCC CHM 102 Sinexavi0341No ratings yet
- Electrochem AP HW ProblemsDocument3 pagesElectrochem AP HW ProblemsBrandon DuanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-1410 A Pratyush Dubey0% (1)
- Topic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesTopic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerCheng Xun LeeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ProblemsDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry Problemsamrutmasaguppi1108No ratings yet
- ElectrozzDocument24 pagesElectrozzangelaskatsNo ratings yet
- Voltaic Cell WorksheetDocument4 pagesVoltaic Cell WorksheetMary GinetaNo ratings yet
- Day-5 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Document4 pagesDay-5 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Arnab DasNo ratings yet
- Predict the feasibility of redox reactionsDocument22 pagesPredict the feasibility of redox reactionsGuru temp id-03 for KPM-Guru-TempNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Venugopal JujhavarappuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - ApplicationsDocument18 pagesElectrochemistry - ApplicationsMNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocument11 pagesElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Cell Potentials ExplainedDocument3 pagesCell Potentials ExplainedervaldiNo ratings yet
- Soal ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaNo ratings yet
- A2 Extension1 Electrochemistry and RedoxDocument10 pagesA2 Extension1 Electrochemistry and RedoxDavid MathewsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Electrochemistry PPT Slides Part 2Document30 pagesModule 1 Electrochemistry PPT Slides Part 2May TampusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesChapter 17 ElectrochemistryBeastUnleashed28No ratings yet