Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8.2 Standard Electrode Potential
Uploaded by
RuoQi LeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8.2 Standard Electrode Potential
Uploaded by
RuoQi LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
8.
2 Standard Electrode Potential (2)
Application 3 : To compare the relative strength of oxidising & reducing agents. 10. By reference to electrode potentials in the Data Series, predict whether the reactions
Application 4 : To predict the stability of aqueous ions below would take place under standard conditions. Show how you determine your ans.
Application 5 : To predict the feasibility of a redox reaction to occur. a. 2Cl-(aq) + I2(s) → 2I-(aq) + Cl2(g) b. Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) → 2Fe3+(aq) + Sn2+(aq)
+ -
c. H2O2(aq) + 2H (aq) + 2I (aq) → 2H2O(l) + I2(s)
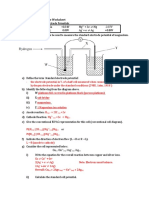
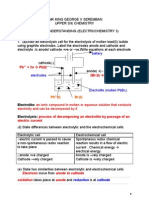
Application 6 : To calculate the minimum voltage required for electrolysis
Application 7 : To predict the reactivity. 11. Using Eo value from the Data Series, determine if
a. aluminium metal can displace iron(II) ions from its aqueous solution.
1. Determine the strength of the oxidising & reducing agent below b. hydrogen peroxide can oxidise Mn2+ to Mn3+.
Mg2+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ Mg(s) ; Eo = - 2.30 V c. manganese(IV) oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid at standard conditions.
Zn2+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ Zn(s) ; Eo = - 0.76 V
Fe2+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ Fe(s) ; Eo = - 0.44 V 12. a. Predict what happens when iron reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid
i. in the absence of air ii. in the presence of air.
2.Determine the strength of the oxidising agent & reducing agent below b. Hydrazine, N2H4 exists as N2H5+ in acidic solution.
N2 + 5H+ + 4eˉ ⇌ N2H5+ ; Eo = -0.17 V
I2(aq)+ 2 eˉ ⇌ 2Iˉ(aq); Eo = +0.54 V
Predict the reaction between acidified hydrazine and chlorine.
Br2(aq)+ 2eˉ⇌ 2Brˉ(aq); Eo = +1.07 V
Cl2(g) 2eˉ⇌ 2Clˉ(aq); Eo = +1.36 V 13. The standard electrode potential for several metals is shown below.
Metal ion/Metal P2+/P Q+/Q R3+/R S2+/S T3+/T
3. A voltaic cell is built from the following two half-equations. o
E /V +0.34 -2.71 -1.66 -0.13 +1.50
O3(g) + 2H+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ O2(g) + H2O(l) ; Eo = +2.08 V a. Arrange the above metal ions in the order of decreasing strength as oxidising agents.
Cl2(g) + 2eˉ ⇌ 2Clˉ(aq) ; Eo = +1.36 V b. Write the overall cell reaction equation of a galvanic cell that consists of Q +/Q and
a. Deduce the oxidising agent in the cell. R3+/R half-cells. Calculate the standard cell potential of this cell.
b. Write the cell diagram.
c. Calculate the standard cell potential. 14. Calculate the minimum voltage required to electrolyse an aqueous CuCl 2 to produce
Cu(s) & Cl2 (g) under standard conditions.
4. Given : Fe3+(aq) + eˉ ⇌ Fe2+(aq) ; Eo = + 0.77 V Cu2+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ Cu(s) ; Eo = + 0.34V Cl2 (g) + 2eˉ ⇌ 2Clˉ(aq) ; Eocell = + 1.36V
Comment on the stability of the ions.
15. Electrolysis of an aqueous potassium iodide solution produces hydrogen gas & iodine.
5.Compare the stability of the ions of the following system. Using information from the data series:
Co3+(aq) + eˉ ⇌ Co2+(aq); Eo = + 1.82 V a) calculate the minimum voltage required for electrolysis to occur.
b) determine which of the following electrochemical cell is suitable to electrolyse an
aqueous solution of potassium iodide at standard conditions
6.What happen when titanium is added to aqueous dilute acid ? Explain using
(i) Al(s) | Al3+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
values of standard electrode potential. (ii) Cu(s) | Cu2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
7. Determine if the following reaction is feasible. Given 16. Compare the electropositivity of the species below.
oxidation : 2Iˉ(aq)⇌ I2(s)+ 2eˉ; Eo1=- 0.54 V Zn2+(aq)+ 2eˉ ⇌ Zn(s) ; Eo = -0.76 V
reduction : Br2(aq)+ 2eˉ ⇌ 2Brˉ(aq); Eo2=+1.07 V Fe2+(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ Fe(s) ; Eo = -0.44 V
8. Predict whether the following reactions can take place under standard conditions. 17. Compare the reactivity of the species below.
(a)Reduction of Sn2+ to Sn by Mg Br2(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ 2Brˉ(aq) ; Eo = +1.07 V
(b)Oxidation of Clˉ to Cl2 by acidified Cr2O72-. Cl2(aq) + 2eˉ ⇌ 2Clˉ(aq) ; Eo = +1.36 V
9. Using Eo value from the Data Series, predict if a spontaneous reaction takes place
between
a. H2O2 and Cl2 b. H2O2 and I2 c. H2O2 and KI
You might also like
- Redox Test 2Document8 pagesRedox Test 2Arhum AliNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesElectrochemical Cells Worksheet AnswersNurul Hana Omar100% (2)
- Chapter 11Document20 pagesChapter 11helloblarg100% (1)
- INSULWOOD - A Scalable High-Porosity Wood For SoundDocument13 pagesINSULWOOD - A Scalable High-Porosity Wood For Soundnahomy.castillo.aNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesTopic 3 - ElectrochemistryMutasimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsDocument11 pagesTutorial 9 - Level 2 Worked SolutionsBloodCypherNo ratings yet
- C 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017Document16 pagesC 2 Amal 1 Galvanic 2017kjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Reduction-Oxidation Reactions and ElectrochemistryDocument14 pagesReduction-Oxidation Reactions and Electrochemistrykaushi123No ratings yet
- University of Zambia School of Natural Sciences Chemistry Department Tutorial Sheet 6 2021/2022Document2 pagesUniversity of Zambia School of Natural Sciences Chemistry Department Tutorial Sheet 6 2021/2022SAVIOUR BANDANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pagesTutorial 3 ElectrochemistrymunirahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Electrochem2Document1 pageTutorial Electrochem2irnihafizan6812No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment-2Document2 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment-2Akshara SreeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistrypriya yadavNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesElectrochemistryHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Past Year Question: ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesPast Year Question: ElectrochemistryLuk HKNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Document9 pagesWorksheet Chemo G 12 Unit Tu 22 2016Dagim YenenehNo ratings yet
- Redox Equilibrium Practice Worksheet 2023 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesRedox Equilibrium Practice Worksheet 2023 Answer KeyRadhika RaniNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 01 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 01 PDFYamini ChandelNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerDocument7 pagesTopic 9 (Galvanic Cell) - Tutorial - Level 2 AnswerCheng Xun LeeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Board Questions 2010Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Board Questions 2010amone nNo ratings yet
- MCQ - Test 3 With - KeyDocument6 pagesMCQ - Test 3 With - KeyShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- 2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDocument127 pages2122 Course Revision Questions Chemistry Level M T2 MSDana JrabNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry PYQ SDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry PYQ Spatiminati2020No ratings yet
- Electrolysis RevisionDocument7 pagesElectrolysis RevisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Day-5 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Document4 pagesDay-5 - In-Class Assignment - : Phase-1Arnab DasNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit10 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry FDocument8 pagesElectrochemistry FAshwin Balaji100% (1)
- Tutorial (Electrochemistry)Document4 pagesTutorial (Electrochemistry)Amir Aiman AniqNo ratings yet
- Redox Review - IB-Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesRedox Review - IB-Short QuestionsStephanie LeeNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions Jee ModuleDocument49 pagesLiquid Solutions Jee ModuleAfsheen TahiraNo ratings yet
- Subject: Chemistry Electrochemistry: Decreases PH of Solution (D) Electrolysis of CusoDocument28 pagesSubject: Chemistry Electrochemistry: Decreases PH of Solution (D) Electrolysis of CusoQwertyNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesElectrochemistryzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocument11 pagesElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Actual Repeat Paper 2013Document10 pagesActual Repeat Paper 2013Jasmeet Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- Soal ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaNo ratings yet
- Echem WKST KeyDocument7 pagesEchem WKST KeyNurul Hana OmarNo ratings yet
- Chem 114 - Quiz 2Document4 pagesChem 114 - Quiz 2anon_915449609No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Electrochemistry Structure and Essay 13-19Document5 pagesCHAPTER 9 Electrochemistry Structure and Essay 13-19peter edwardNo ratings yet
- Question 801367Document4 pagesQuestion 801367niveditasingh2472No ratings yet
- Voltaic Cell WorksheetDocument4 pagesVoltaic Cell WorksheetMary GinetaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryAnis IssabellaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Applications of RedoxDocument29 pagesElectrochemistry: Applications of RedoxrachelelkinNo ratings yet
- HL9Q&ADocument28 pagesHL9Q&ABrianNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyDocument3 pagesModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- Class Test - Redox - 2019Document1 pageClass Test - Redox - 2019Shraddhanjali sahaNo ratings yet
- 6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Document44 pages6433 Topper 21 129 510 2 43 Electrochemistry Up201612091847 1481289429 3Rishab PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Feasibility of Redox Reaction (S)Document22 pages2.4 Feasibility of Redox Reaction (S)Guru temp id-03 for KPM-Guru-TempNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument106 pagesElectrochemistrySeng IvanNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 8Document7 pages11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 8Gyani ChachaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GDocument15 pagesElectrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GandrewNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DmsDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 DmsCik ApaiNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios QuímicaDocument3 pagesEjercicios QuímicaAndreaForteRuizNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 2Document16 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 2Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesChapter 3 ElectrochemistryParam SoniNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ExerciseDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry ExerciseNuraina NabihahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Electrochemistrymeshal retteryNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - ApplicationsDocument18 pagesElectrochemistry - ApplicationsMNo ratings yet
- DP1HL Redox UT VCDocument5 pagesDP1HL Redox UT VCmarilee huntNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Financial Proposal - 2unitsDocument33 pagesFinancial Proposal - 2unitsEyob AdNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 0 " Ice: Ludwigshafen (Rhine), GermanyDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent 0 " Ice: Ludwigshafen (Rhine), Germanyهیمن مNo ratings yet
- Dyes NotesDocument3 pagesDyes NotesArianne BatallonesNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical CellsAlph BrickNo ratings yet
- Acido Citrico Jiangsu Guoxin UnionDocument1 pageAcido Citrico Jiangsu Guoxin UnionCalidad JuacopanNo ratings yet
- WTP PST Estimation R310.06.21Document16 pagesWTP PST Estimation R310.06.21juliyet strucNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Condition MonitoringDocument71 pagesPresentation On Condition MonitoringShahin Manjurul AlamNo ratings yet
- The Oolitization Rate Determination of Bentonite Moulding MixturesDocument4 pagesThe Oolitization Rate Determination of Bentonite Moulding Mixturesvivek1312No ratings yet
- Deep 4 ProcessDocument1 pageDeep 4 ProcessGeorge ChedraouiNo ratings yet
- Greenboro Polychem PVT LTDDocument57 pagesGreenboro Polychem PVT LTDMehdi MadaniNo ratings yet
- H B Anilox GuideDocument18 pagesH B Anilox GuideYasser BadrNo ratings yet
- Nanofilled Resin Composite Properties and Clinical Performance - A ReviewDocument18 pagesNanofilled Resin Composite Properties and Clinical Performance - A ReviewInside Dentistry educationNo ratings yet
- Guardex ENG 2023Document3 pagesGuardex ENG 2023MohamedNo ratings yet
- Indu Incompleted PDFDocument15 pagesIndu Incompleted PDFUday BagadeNo ratings yet
- Ensayos No DestructivosDocument2 pagesEnsayos No DestructivosOneill Vasquez AmayaNo ratings yet
- Strut System Catalog 2018Document308 pagesStrut System Catalog 2018angelo jay malubayNo ratings yet
- Kingspan - Trapezoidal Roof KS1000 RW - CAD Roof Codemark Set CM20104 - Q4 2020 - NZ - ENDocument62 pagesKingspan - Trapezoidal Roof KS1000 RW - CAD Roof Codemark Set CM20104 - Q4 2020 - NZ - ENTaurai ChiwanzaNo ratings yet
- Study On Mineral Water Consumption in RomaniaDocument9 pagesStudy On Mineral Water Consumption in RomaniaVasile LeniucNo ratings yet
- Summary Cube Test As of 07052019 (Nehemiah Wall)Document6 pagesSummary Cube Test As of 07052019 (Nehemiah Wall)Mohd Musa HashimNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Sample PapersDocument10 pages11 Chemistry Sample PapersPc xoixaNo ratings yet
- Astm B786Document6 pagesAstm B786cantigiNo ratings yet
- Tile Adhesive Standards and Their Relevance For Tile InstallationDocument6 pagesTile Adhesive Standards and Their Relevance For Tile InstallationAhmadAlsekaweNo ratings yet
- Smith 1992Document23 pagesSmith 1992Luisa CenchaNo ratings yet
- 2024 RedoxDocument4 pages2024 Redoxjoshualiew06No ratings yet
- Chemistry of PetroleumDocument23 pagesChemistry of PetroleumShehzad khanNo ratings yet
- NALCOOL 2000 - Automobile Coolant Corrosion InhibitorDocument2 pagesNALCOOL 2000 - Automobile Coolant Corrosion InhibitorChemEqualNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Questions That Came Out in The ExamDocument7 pagesDay 2 Questions That Came Out in The ExamAdrian Joshua BernagaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Yang H. Huang 1983 Stability Analysis of Earth Slopes PDFDocument307 pages10 - Yang H. Huang 1983 Stability Analysis of Earth Slopes PDFLuis VélezNo ratings yet
- Proraso Shaving Cream Common Ingredients of 3 TypesDocument2 pagesProraso Shaving Cream Common Ingredients of 3 Typeschimene madiNo ratings yet