Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wa0077.
Uploaded by
Shan MohdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wa0077.
Uploaded by
Shan MohdCopyright:
Available Formats
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
HERBAL SHAMPOO: BENEFITS, PREPARATION AND
EVALUATION.
Vineetha K1*, Vindhya V S1, Vishranth M B1, Yashasvi1, Shyam Surender Sain1,
A R Shabaraya1
1
Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India
Abstract:
Shampoos are the cosmetics preparations meant for cleansing the hair by removal of the dirt
grease from the hair shaft and scalp. There are wide range of synthetic shampoos available in
the market with different functions. But these synthetic shampoo shows harmful effect on the
hair and scalp like dryness of hair and keratin loss. Due to these reasons herbal shampoos has
evolved as an alternative to synthetic shampoo because of the safe and traditionally used
ingredients. Herbal shampoo is a cosmetic preparation which uses herbs and meant for
cleansing the hair and scalp just like regular shampoo. Many of the herbs are reported to have
beneficial affect on hair and are used in herbal shampoos.
Keywords: Synthetic shampoo, Herbal shampoo, cosmetics, Traditional ingredients.
Introduction:
Hair is an integral part of human beauty. In humans’ hair serves lot of purposes like protection
against external factors, sebum, apocrine sweat and pheromonas production and
thermoregulations [1]. Hair care products are primarily meant for cleansing the hair. It also
modifies the hair texture, provides nourishment to the hair and gives healthy look to the hair
[2].
Shampoo is the most common hair care cosmetic. It is available either in viscous liquid or
powder form, applied for cleaning hair and scalp from dirt, residues of previously applied hair
styling products and environmental pollutants [3]. In the early days shampoos were meant only
for cleansing hair and scalp, but the shampoos available today do much more than that. Along
with cleansing it leaves the hair easy to comb, lustrous and controllable while being convenient
to use [4]. Nowadays a wide range of shampoos are available in the market like synthetic,
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
herbal, medicated and non-medicated shampoos with different functions. Among these herbal
shampoos are most popular ones as they bear the impression of having better purity, safety and
efficacy.
Herbal shampoos are prepared from natural ingredients and are meant for cleansing hair and
scalp just like regular shampoo. These shampoos are free from side effects since no surfactants
are involved, has good stability and are less harmful compared to synthetic shampoo [5].
Synthetic shampoo contains surfactants. Long term use of these surfactants can lead to serious
effects like scalp irritation, loss of hair, drying of hair, greying of hair, split ends and eye
irritation. Due to these reasons the public is getting attracted towards herbal cosmetics due to
its insignificant side effects and inexpensive nature [6].
REQUIREMENTS OF SHAMPOO [4]:
• It should remove sebum and atmospheric pollutants from scalp and hair.
• It should remove the residues of previously applied hair styling lotions and sprays.
• It should deliver an optimal level of foam to satisfy the expectations of the user
• It should be nontoxic and non-irritating to the hair and scalp.
TYPES OF SHAMPOOS [1,4] :
Shampoos are of following types
• Powder shampoo
• Clear liquid shampoo
• Lotion shampoo
• Solid gel shampoo
• Medicated shampoo
• Liquid herbal shampoo
Specialized shampoo
• Baby shampoo
• Anti-dandruff shampoo
• Conditioning shampoo
• Two-layer shampoo
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
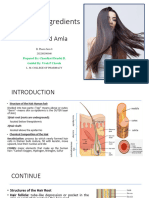
ANTAMONY OF HAIR [7]:
The hair is made up of 95% keratin a fibrous, helicoidal protein (shaped like a helix) that forms
part of the skin and all its attachments (body hair, nails etc.).
The hair structure consists of 3 different parts:
• Medulla: It is the innermost layer of the hair shaft, made up of an amorphous, soft, oily
substances.
• Cuticle: Thin protective outer layer that contains nutrients beneficial for hair growth. It
is highly keratinized with cells shaped like scales that are layered one over the other,
measuring about 60 micrometers long and about 6 micrometers wide.
• Cortex: It is the main constituent of the hair, containing long keratin chains which gives
elasticity, suppleness and resistance to the hair. The cells of the cortex are joined
together by an intercellular cement rich in lipids and proteins.
GROWTH CYCLE OF HAIR [8]:
Hair growth cycle consists of four phases:
• Anagen (growth phase): It is the growing phase. This phase lasts for several years.
• Catagen (transitional phase): during this phase the hair follicle shrinks and hair
growth slows.
• Telogen (resting phase): It is the resting phase where hair growth stops and new hair
begins the growth phase, pushing the old hair out.
• Exogen phase: last phase of hair growth cycle where hair strand completely detaches
from the scalp and sheds off.
Fig 1: Hair structure Fig 2: Growth Cycle of hair
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
HAIR PROBLEMS [9]:
• HAIR LOSS: The main reason behind the hair loss is Stress, medication, changes in
hormone and many hair styling products can contribute to hair loss.
• OILY HAIR/GREASY HAIR: Oily hair is caused by excessive production of natural oil
(sebum) by the scalp. Sebum is produced by sebaceous glands which sometimes “work
overtime’’ leading to excessive amount of oil.
• DANDRUFF: Dandruff is a non-inflammatory harmless skin condition that affects scalp
and might result in hair loss. It is scaly and adheres to the root of the hair.
• DRY HAIR: Dry hair occurs due to deficiency of proteins in the diet. Menopause, anemia,
hormonal imbalance, birth control pill can also lead to dry hair.
• SPILT ENDS: Splits ends occur when the hair ends dry and other reasons are exposure to
extreme weather conditions. Hair care techniques such as straightening and curling and
chemical hair products may cause spilt ends.
HERBS COMMONLY USED IN HERBAL SHAMPOO [1, 10]:
Botanical Common fi figure
Functions/uses Figure
name name.
Lawsonia Henna Promotes growth
Inermis of hair,
conditioner.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
Azadirachta Neem Antimicrobial
indica agent, Prevents the
dryness of hairs
and flaking of
hairs.
Ocimum Tulsi Antimicrobial and
sanctum anti-lice property
Embelica Indian Promotes hair
officinalis gooseberry/ growth, prevents
amla premature greying
and controls
dandruff.
Acacia Soap pod/ Retains natural oil
concinna Shikakai of hair, keeps hair
lustrous & healthy.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
Aloe Aloe vera Conditioning &
barbadensis moisturizing
effect.
Citrus lemon Lemon Maintains the pH
& imparts
fragrance to
preparation
Hibiscus China rose Prevents hair loss
rosa sinensis and hair growth
promoter
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
Sapindus Soap nut/ Detergent and
mukorossi Reetha antidandruff.
Trigonella Fenugreek Cleansing and
foenum softening.
graceum
chrysopogon Vetiver Antifungal,
ziznaniodes grass Antimicrobial
Zingiber Ginger Promotes hair
officinalis growth.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
Eclipta Bhringraj Hair tonic
prostrata
Withania Ashwagand Controls hair fall,
somnifera ha promotes hair
growth, improves
circulation of the
scalp.
Camellia Green tea Hair growth and
sinensis leaves enrichment
Bacopa Brahmi Supports the hair
monneri growth
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
PREPARATION METHODS [11,12]:
METHOD 1:
The following steps are employed for the formulation of polyherbal shampoo powder:
• Drying: All the ingredients required for the shampoo preparation are dried and
grinded.
• Weighing: All herbal powders required for the preparation are weighed separately.
• Size reduction: The weighed materials are subjected to size reduction using hand
driven mixer individually.
• Mixing: The fine powders are mixed methodically using mixer to form a
homogenous mixture.
• Sieving: The mixture is passed through sieve no 80, to get uniform size particles and
reduce the lumps.
• Packing and Labelling: Finally, the powder was packed and labelled suitably.
METHOD 2:
The following steps are involved in the preparation polyherbal liquid shampoo:
• Collection of materials: Ingredients required for the preparation are collected and
washed thoroughly and dried.
• Weighing: Ingredients are weighed individually and soaked overnight.
• Decoction preparation: Ingredients are boiled in the same water used for soaking on
medium flame, allow to cool and filter
• Incorporate preservative (eg: Methyl paraben) to prevent microbial growth
EVALUATION OF POLYHERBAL SHAMPOO POWDER [11,13]:
Organoleptic evaluation:
• Organoleptic evaluation includes the assessment of parameters such as color, odor,
texture taste etc.
General powder Characteristics:
• General powder characteristics includes the evaluation of parameters such bulk density,
particle size and angle of repose.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
i. Particle size: Particle size affects grittiness and spreading properties of powder.
Particle size is determined by using microscopy techniques.
ii. Angle of repose:
Funnel method:
Required quantity of powder is allowed to flow through a funnel which is placed at a
height of 6 cm from horizontal base. The powder is allowed to flow to form a heap over
the paper on the horizontal plane. The radius and the height of the powder heap is noted
down.
iii. Bulk density:
Bulk Density is the ratio between the given mass of a powder and its bulk volume.
Dried powder is filled into a 50 ml measuring cylinder upto 50 ml mark. Then the
cylinder is tapped onto soft surface from a height of 1 inch at 2 second intervals. The
volume of the powder is measured. The Bulk Density is calculated by using the below
given formula.
Mass of the herbal shampoo
Bulk density =
Volume of the herbal shampoo
iv. Tapped density:
The tapped density is obtained after mechanically tapping container containing the
powder. Dried powder is filled into 50 ml measuring cylinder upto 50 ml mark. Then
the cylinder is tapped 100 times onto soft surface. The volume of powder is measured.
Weight of powder
Tapped density =
Tapped volume of powder
Physicochemical evaluation:
i. pH: The pH of the shampoo is measured by using pH meter.
ii. Washability: The ease and extent of washing can be checked manually by applying
on skin.
iii. Solubility: Solubility is ability of the substance to dissolve in solvent. Solubility test
is done by dissolving the sample in solvent followed by slight warming, cooling and
filtering. Then the residue obtained is weighed and noted down.
iv. Loss on drying: Loss on drying is the loss of mass expressed in percent m/m.
About 2 g of powder is taken in a Petridish and placed in a desiccator for 2 days over
calcium chloride crystals. Then the powder was taken and the weight is checked to
determine the loss during drying.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
• Dirt dispersion: Dirt dispersion ability of the shampoo can be determined by using Indian
ink. About 1% of shampoo solution taken in a test tube and 1 drop of India ink is added.
The test tube is stoppered and shaken for about 10 mins. The amount of ink present in the
foam is indicated as None, Light, Moderate, or Heavy.
• Wetting time: Canvas paper is used to determine the wetting time of shampoo. The canvas
was cut into disc shape with 1 inch diameter with an average weight of 0.44 g. the disc was
allowed to float on the surface of 1% shampoo solution and the time taken by the disc to
start sinking in the shampoo solution is noted as wetting time.
• Foaming index: 1% w/v solution of the shampoo powder is prepared. Solution is warmed
slightly for 30 mins, cooled, filtered and volume is made upto 100 ml. 1, 2,…10ml of
extract is taken separately in 10 test tubes and volume is made upto 10ml using water.
Shake the test tubes at a speed of 2 frequency per second for about 15 sec. then the test
tubes are kept aside for 15 mins without shaking. Foam height(a) is measured.
1000
Foaming index =
a
• Swelling index: About 1g of shampoo powder is taken into a glass stopper cylinder
containing 25ml of water. Then the measuring cylinder is shaken for 1 hour with an interval
of 10 mins. The solution is kept aside for 3 hrs without shaking. Volume is measured in ml.
• Nature of hair: By gathering the responses from volunteers’ nature of hair after washing
can be evaluated.
EVALUATION OF POLYHERBAL LIQUID SHAMPOO [14, 15]:
• Organoleptic evaluation/visual assessment:
The prepared formulations are evaluated in terms of color, clarity, odor etc.
• pH determination:
The pH of the shampoo is measured by using pH meter.
• Percentage of solid content determination:
4g of shampoo is taken in a previously weighed evaporating dish and evaporated by
placing the evaporating dish on the hot plate. The final weight is noted down.
Percentage of solid contents of shampoo left after complete evaporation is calculated.
• Rheological Evaluation:
The viscosity of the shampoo is determined by using Brookfield viscometer.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
• Surface tension measurement:
Stalagmometer is used for determining surface tension of shampoo using chromic acid
and purified water. The data was calculated by equation given below:
R3 = (W3 -W1) n1×R1/(W2-W1) n2×R2
Where,
W1 is the weight of empty beaker.
W2 is the weight of beaker with distilled water.
W3 is the weight of beaker with shampoo solution.
N1 is the no. of drops of distilled water.
N2 is the no. of drops of shampoo solution.
R1 is the surface tension of distilled water at room temperature.
R2 is the surface tension of shampoo solution.
• Foaming ability and Foaming stability:
The cylinder shake method is employed in the foaming ability and stability test. In this
method 50ml of the 1% shampoo solution is taken in a 250ml graduated cylinder and
covered the cylinder with hand. The cylinder is then shaken for 10 times. The volume
of the foam appeared due to shaking is measured after every one minute consecutively
for 5 minutes.
• Wetting time test:
Canvas paper is used to determine the wetting time of shampoo. The canvas was cut
into disc shape with 1 inch diameter with an average weight of 0.44 g. the disc was
allowed to float on the surface of 1% shampoo solution and the time taken by the disc
to start sinking in the shampoo solution is noted as wetting time.
• Dirt dispersion test
About 1% of shampoo solution taken in a test tube and 1 drop of India ink is added.
The test tube is stoppered and shaken for about 10 mins. The amount of ink present in
the foam is indicated as None, Light, Moderate, or Heavy.
• Cleaning action:
About 1 g of grease is spread on non-adsorbent cotton and kept in conical flask
containing 1% shampoo solution. The conical flask is shaken for 1 hr in mechanical
shaker. Cotton is collected, dried and weighed. The amount of grease removed is
determined by using the equation given below:
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
T
DP = 100 (1 − C )
Where,
C - Weight of grease in control sample
T - Weight of grease in test sample
DP-Percentage of detergency power
• Skin sensitization test:
Guinea pigs are used for skin sensitization test. They are divided into 7 groups (n=3).
Hairs on the back of the guinea pigs are shaved previously. Shampoos are applied on
the onto nude skin of animals. Formalin solution (0.8 %v/v) is applied as a standard
irritant on animal. The application site is graded according to the erythema produced
as: 0-none, 1-slight, 2-well defined, 3-moderate, 4-scar formation(severe).
• Conditioning performance evaluation:
Artificial hair strands are collected from salon and are divided into two batch (control
and test) length 10 cm approximately. The test hair sample is washed with formulated
shampoo and control is the one without washing. The test sample has to be washed with
shampoo atleast for 10 times and sir dried. Blind touch test method is used for
determining the conditioning effect of shampoo. About 20 student volunteers are
selected and are made to touch the hair samples. The conditioning performance of the
shampoo is rated in terms of score1-4 (4-excellent, 3-good, 2-satisfactory and 1-poor)
Eye irritation test:
Albino rabbits can be used for performing eye irritation test. The prepared shampoo
solution is allowed to fall into eyes of six albino rabbits. The damage that is caused to
rabbit’s eye at different time intervals is recorded. Eye Irritation can be caused due to
ulceration, swelling of eyelid, blindness and hemorrhage.
CONCLUSION:
The present review focuses on the uses and importance of herbal shampoo. It includes the
awareness and need for the cosmetics with herbal ingredients, as it is strongly believed that the
herbal products are safe and free from side effects. It emphasizes on types, methods of
preparation and evaluation of polyherbal shampoos.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES:
[1]. Kothari S, Patidar K, Solanki R. Polyherbal Anti-Dandruff Shampoo: Basic Concept,
Benefits, and Challenges. Asian J. Pharm. 2018; 12(3): S849- 58.
[2]. Ankule A, Wani S D, Murkute P M, Pundkar A S. Multipurpose herbal powder shampoo.
World j. pharm. life sci. 2020; 6(5): 166- 182.
[3]. Gubitosa J, Rizzi V, Fini P, Cosma P. Hair Care Cosmetics: From Traditional Shampoo to
Solid Clay and Herbal Shampoo, A Review. Cosmetics. 2019; 6(13): 1-16.
[4]. Mottram F.J. Hair Shampoos. In: ButlerH. (eds)Poucher’s Perfumes, Cosmetics and Soaps.
10thed.Great Britain: academic publishers;1993.
[5]. Joshi N, Patidar K, Solanki R, Mahawar V. Preparation and evaluation of herbal hair
growth promoting shampoo formulation containing Piper betle and Psidium guajava leaves
extract. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2018; 12(4): S835- 39.
[6]. Pundkar A S, Ingale S P. Formulation and evaluation of herbal liquid shampoo. World J.
Pharm. Res. 2020;9(5):901-11.
[7]. https://activilong.com/en/content/95-structure-composition-of-the-hair/retrieved on
19/08/2021
[8]. https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/picture-of-the-hair/retrieved on
20/08/2021
[9]. Haritha PN, Supraja P, Samreen S, Hrudayanjali, Qureshi M, Sandya P, Swetha T., A
Review on Polyherbal Shampoo Powder. Int. J Pharm Res. 2021; 21(2): 346-63.
[10]. Jacob Rhea, Sakthivel KM, Kannan N, Guruvayoorappan C. Formulation of cost-
effective herbal shampoo powder: a comparative study with market shampoos. Int. J. Curr.
Res. 2015;7(2):12645-49.
[11]. Patil SS, Mane YJ, Mohite SK. Formulation and evaluation of herbal shampoo powder.
Int. J. Adv.Res.2015;3(3):939-46.
[12]. Pundkar A S, Ingale S P. Formulation and evaluation of herbal liquid shampoo. World J.
Pharm. Res. 2020;9(5):901-11.
[13]. Snehal1 W, Nitin K, Vaibhav B. Preparation & evaluation of antidandruff polyherbal
powder shampoo. Pharmacophore. 2014; 5(1): 77-84.
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
Journal of Xi’an Shiyou University, Natural Science Edition ISSN : 1673-064X
[14]. Vijayalakshmi A, Sangeetha S, Ranjith N. Formulation and evaluation of herbal shampoo.
Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2018;11(4);121-24.
[15]. Jaya Preethi P, Padmini K, Srikanth J, Lohitha M, Swetha K, Vengal Rao P.A Review on
herbal shampoo and its evaluation. Asian journal of pharmaceutical analysis. 2013; 3(4): 153-
56.
First Author: Vineetha K, Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College of Pharmacy,
Valachil, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India.
Second Author: Vindhya V S, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Mangaluru,
Karnataka, India
Third Author: Vishranth M B, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Mangaluru,
Karnataka, India
Fourth Author: Yashasvi, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Mangaluru, Karnataka,
India
Fifth Author: Shyam Surender Sain, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Mangaluru,
Karnataka, India
Sixth Author: A R Shabaraya, Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College of Pharmacy,
Valachil, Mangaluru, Karnataka, India.
Corresponding Author:
Vineetha K
Department of Pharmaceutics
Srinivas College of Pharmacy
Valachil, Mangaluru- 574143
Karnataka, India
http://xisdxjxsu.asia VOLUME 17 ISSUE 09 646-660
You might also like
- 5 of The Best Essential Oils For HairDocument13 pages5 of The Best Essential Oils For HairJyoti ShindeNo ratings yet
- The Rewards of Patience, Scheffel 2006Document9 pagesThe Rewards of Patience, Scheffel 2006NatitoPazGonzalezArmijoNo ratings yet
- Herbal Hair Care - VPCDocument27 pagesHerbal Hair Care - VPCSatyam DarjiNo ratings yet
- Tricology WordDocument26 pagesTricology WordDrushti KadamNo ratings yet
- Document 20231029073311Document7 pagesDocument 20231029073311Nhi YếnNo ratings yet
- 1 Iajps17062017Document7 pages1 Iajps17062017Baru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- g9 4th Beauty CareDocument132 pagesg9 4th Beauty CarePrimrose MazoNo ratings yet
- 16 Iajps16062017 PDFDocument13 pages16 Iajps16062017 PDFBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- 8 Herbs and Oils That Promote Hair GrowthDocument46 pages8 Herbs and Oils That Promote Hair Growthlara-usui100% (5)
- 17.preparation and Evaluation of Herbal Hair OilDocument7 pages17.preparation and Evaluation of Herbal Hair OiltmlNo ratings yet
- Design, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooDocument8 pagesDesign, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (3)
- Shampoo in English Is Derived From Hindi Chāmpo Champo Was Used For Head MassageDocument23 pagesShampoo in English Is Derived From Hindi Chāmpo Champo Was Used For Head Massageabdoamer.2553100% (1)
- Shampoo 3 PDFDocument14 pagesShampoo 3 PDFHimanshu JangirNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evalution of Herbal Hair OilDocument5 pagesFormulation and Evalution of Herbal Hair OilInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of Human HairDocument14 pagesThe Secrets of Human HairAlexander LukasNo ratings yet
- Shampoo by SHMDocument61 pagesShampoo by SHMmajumdarshiv100% (2)
- Hair CareDocument23 pagesHair Careapi-3736205100% (2)
- Evaluation and Preparation of Herbal Hair Oil With Some Fresh HerbsDocument11 pagesEvaluation and Preparation of Herbal Hair Oil With Some Fresh HerbsHaseeb ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 84 Rajdip Utane 1011Document6 pages84 Rajdip Utane 1011anuragNo ratings yet
- HairRevolution! PDFDocument78 pagesHairRevolution! PDFLarisa S.100% (1)
- 84 Raj Dip Utane 1011Document6 pages84 Raj Dip Utane 1011DrBipin DevaniNo ratings yet
- Radico-Organic-product-manual With HerbsDocument37 pagesRadico-Organic-product-manual With HerbsBeaula LazarusNo ratings yet
- Hair Product Formation - Project ProposalDocument4 pagesHair Product Formation - Project ProposalLee ViramNo ratings yet
- G19 Shampooing Procedure GuideDocument6 pagesG19 Shampooing Procedure GuideJenn Contado Apura100% (1)
- Benefits of Using Aloe VeraDocument1 pageBenefits of Using Aloe Verasofienicole982No ratings yet
- The Wonder of Herbs To Treat-AlopeciaDocument7 pagesThe Wonder of Herbs To Treat-AlopeciaLuca JohnNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Hair DyeDocument7 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Herbal Hair DyeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Aileen PamulaklakinNo ratings yet
- Science Ip 2019Document12 pagesScience Ip 2019Yzsa TomaganNo ratings yet
- Formulation & Evaluation of Herbal ShampooDocument18 pagesFormulation & Evaluation of Herbal ShampooFarhad ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Surender Herbal FINALDocument29 pagesSurender Herbal FINALSaira KhatunNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument71 pagesHair Careking100% (16)
- Herbal Hair Remedies from Natures PharmacyFrom EverandHerbal Hair Remedies from Natures PharmacyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- From Earth To Hair Reviewing Herbal Shampoo BarDocument8 pagesFrom Earth To Hair Reviewing Herbal Shampoo BarDarshana BafnaNo ratings yet
- Your Dosha Profile Is Shown Below.: I. Bhavesh's Current Ayurvedic ProfileDocument15 pagesYour Dosha Profile Is Shown Below.: I. Bhavesh's Current Ayurvedic ProfilehelloNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Herbello - An Herbal Antidandruff ShampooDocument9 pagesPreparation of Herbello - An Herbal Antidandruff ShampooSANo ratings yet
- 860-Article Text-4533-1-10-20220428Document7 pages860-Article Text-4533-1-10-20220428Nur Putri OktavianaNo ratings yet
- Herbal CosmeticsDocument40 pagesHerbal CosmeticsBiren Shah100% (1)
- Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Shampoo: Suyog Sunil Bhagwat Dr. N. J. Paulbudhe College of PharmacyDocument10 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Herbal Shampoo: Suyog Sunil Bhagwat Dr. N. J. Paulbudhe College of Pharmacysof vitalNo ratings yet
- Hair CareDocument7 pagesHair CarelordregulusNo ratings yet
- Green Minimal Organic Product Launch BookletDocument10 pagesGreen Minimal Organic Product Launch BookletAngyy RRNo ratings yet
- EBP OIR Body UpdatedDocument12 pagesEBP OIR Body Updatedsumuduni costhaNo ratings yet
- Label M Work HolepDocument36 pagesLabel M Work HolepNilesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Tle9l2 20240319 205418 0000Document20 pagesTle9l2 20240319 205418 0000gladysavila101No ratings yet
- SOCUS Hair Treatment Shampoo Group 1 WISEDocument10 pagesSOCUS Hair Treatment Shampoo Group 1 WISERola Elaisa Irish, M.No ratings yet
- New Product Development-3Document17 pagesNew Product Development-3Abdul RasheedNo ratings yet
- Ask The ExpertsDocument7 pagesAsk The ExpertsJoeresaKyleZerdaIbarraNo ratings yet
- Hair TipsDocument22 pagesHair Tipstequilagemini100% (2)
- ABR PropolisDocument9 pagesABR PropolisUmeerNo ratings yet
- Capture D'écran . 2021-09-07 À 19.22.17Document1 pageCapture D'écran . 2021-09-07 À 19.22.17dsjdhNo ratings yet
- 006-Kesharaj - Hiar Vitalizing HerbsDocument14 pages006-Kesharaj - Hiar Vitalizing HerbsRaghottam KattiNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Hair ConditionerDocument4 pagesLiterature Review of Hair Conditioneraflsjizaf100% (1)
- Benefits of Hair and Scalp CareDocument28 pagesBenefits of Hair and Scalp Carecherry d.bandola100% (1)
- Draelos2013 PDFDocument6 pagesDraelos2013 PDFRini Nurul fauziyahNo ratings yet
- Herbalcosmetics Roleofherbals 200509170918Document23 pagesHerbalcosmetics Roleofherbals 200509170918pratikshaNo ratings yet
- Hair ShampoooDocument17 pagesHair ShampoooCherie Banzon100% (1)
- Ultimate Guide To Managing Frizzy Hair - SkinKraftDocument7 pagesUltimate Guide To Managing Frizzy Hair - SkinKraftPriya PatelNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument9 pagesReview of Related LiteratureEugel ann AgpayNo ratings yet
- Your Hair can Mean a Lot-All About Hair Care-An Illustrated BookFrom EverandYour Hair can Mean a Lot-All About Hair Care-An Illustrated BookNo ratings yet
- Anthocyanin Extraction 1Document5 pagesAnthocyanin Extraction 1gowthamanNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 1 Summative Test 1Document6 pagesScience 6 Quarter 1 Summative Test 1ydel pascuaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsLovelyrabbit26No ratings yet
- A Solubility Study of The Boric Acid-Water-Sorbitol System Various TemperaturesDocument5 pagesA Solubility Study of The Boric Acid-Water-Sorbitol System Various TemperaturesAnonymous m1eSE8gmkNo ratings yet
- MS02Document10 pagesMS02Arash AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of OMU - Final Complete 2022Document55 pagesSyllabus of OMU - Final Complete 2022Mohamed Babiker SulimanNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument28 pagesAlkanesLeticia0% (1)
- The Venturi Aeration Process:: Understanding Oxygen Transfer and Wastewater ConditioningDocument23 pagesThe Venturi Aeration Process:: Understanding Oxygen Transfer and Wastewater ConditioningKumarNo ratings yet
- AnaChem PPT 1Document23 pagesAnaChem PPT 1Jei HernandezNo ratings yet
- Objective QuestionsDocument4 pagesObjective QuestionsJacelynNo ratings yet
- Synthesis 0732: Isolating Caffeine From Tea: DescriptionsDocument5 pagesSynthesis 0732: Isolating Caffeine From Tea: Descriptionsjayven minguillanNo ratings yet
- HCNDocument12 pagesHCNAsriNovitaSariJuremiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument291 pagesIGCSE ChemistryDhruvil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Gas AbsorptionDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Gas Absorptionafdtbbhtz100% (1)
- 1introduction To Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument41 pages1introduction To Pharmaceutical ChemistryBad BoyNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Topics and Guide To Revision: Name: - ClassDocument16 pagesYear 7 Science Topics and Guide To Revision: Name: - ClassmrudulaNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Precipitation of CaCO3 1999 PDFDocument9 pagesMicrobiological Precipitation of CaCO3 1999 PDFmsohailashrafNo ratings yet
- Properties of Penetrants in Penetrant TestingDocument2 pagesProperties of Penetrants in Penetrant TestingHarry FrankNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesWater and Its Treatment Lecture NotesRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- A02 303Document15 pagesA02 303jaimeNo ratings yet
- Earth Electrodes, Ground Enhancing Products and Earth PitsDocument1 pageEarth Electrodes, Ground Enhancing Products and Earth PitsLuis Ivan Moreno ParraNo ratings yet
- Britishhomoeopat 00 BritialaDocument448 pagesBritishhomoeopat 00 BritialaAlbena Trifonova0% (2)
- The Medicinal Plants of TheDocument180 pagesThe Medicinal Plants of TheRein Alcira100% (2)
- Mikhania C.E., S.farm, M.si, Apt - PPT DownloadDocument46 pagesMikhania C.E., S.farm, M.si, Apt - PPT DownloadKetrin IlvaniaNo ratings yet
- Rachel Adams Jana Dengler Megan Macleod Kyla Sask Rachel Adams Jana Dengler Megan Macleod Kyla SaskDocument31 pagesRachel Adams Jana Dengler Megan Macleod Kyla Sask Rachel Adams Jana Dengler Megan Macleod Kyla Saskbetengaan2100% (1)
- Unit 1 Preformulation IPI 2021-22Document90 pagesUnit 1 Preformulation IPI 2021-22Neha SinghNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Document15 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41TimNo ratings yet
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Jessica Fernando, C. VedhiDocument7 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: Jessica Fernando, C. VedhiCarlos CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Inkompatibilitas 2015Document49 pagesInkompatibilitas 2015Anonymous u4wls7No ratings yet