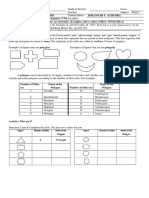
MATHEMATICS
GRADE 9
DATE: ……………………………………….
TOPIC: Geometry 2D Shapes
CONCEPTS & SKILLS TO BE ACHIEVED:
By the end of the lesson learners should know and be able to:
Revise 2 D shapes: Triangles and Quadrilaterals
Solve problems relating the above shapes
DBE Workbook, Sasol-Inzalo book, Textbooks,
RESOURCES:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mLeNaZcy-hE
ONLINE RESOURCES https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xEzm8wBSpAc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K3h-PpaSwQI
DAY 1: INTERIOR ANGLES OF A TRIANGLE
LESSON DEVELOPMENT
Recap our knowledge on Triangles. We
write it
A triangle is a closed shape with three sides and three interior angles.
as….
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle add up to 𝟏𝟖𝟎°. [ ∠' s of ∆=180°]
Therefor in any triangle:
𝑎 𝑏
𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 180° 𝑐
80°
40° + 60° + 80° = 180°
40°
60°
110° + 𝑥 + 30° = 180° 𝑥
30° 110°
Grade 9 Page 1 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�You need to determine the size of the of the missing angles in each of the
following diagrams.
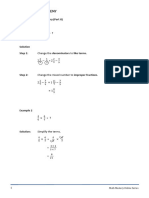
1. Solve for 𝑥 SOLUTION
𝑎 + 40° + 65° = 180° [ ∠′ 𝑠 𝑜𝑓∆= 180°]
𝑎 + 105° = 180°
𝑎 = 180° − 105°
𝑎 = 75°
2.
105° 𝑏 105° + 55° + b = ___ ° [∠′ 𝑠 𝑜𝑓∆= 180°]
____ ° + 𝑏 = 180°
𝑏 = 180° − _______ You need to fill
55° 𝑏 = ________ in the missing
information:
3. Detemine the value of 𝑎 in the
diagram below: 3𝑎 + ___ + 2𝑎 = 180° [________________________]
9𝑎 = 180°
𝑎 = 20° Add like
4𝑎
Remember you can check your answer! terms
Solve
If 𝑎 = 20° 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 3𝑎 = 3 × 20° = 60° equation
4𝑎 = 80° and
3𝑎 2𝑎
2𝑎 = 40°
60° + 80° + 40° = 180°
ACTIVITY 1
Grade 9 Page 2 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�Do the following exercises, applying what you have learnt today. FIRST ATTEMPT TO DO ALL THE
PROBLEMS BEFORE YOU CHECK YOUR ANSWERS IN THE MEMORANDUM BELOW
Calculate the size of the unknown angles. You need to provide reasons.
1. 2.
𝑥 + 15°
3𝑥 − 25°
3. In the figure AB ∥ ED, AĈD = 95° 4. In the figure KL ∥ MO, ML̂N=53° and LM
̂ N=60°.
and D ̂ = 30°. Determine the size of the following angles with
reasons.
(a) N̂1
(b) L̂2
(c) L̂3
Determine with reasons:
(a) Ĉ1
̂
(b) E
̂
(c) A
Memo: Activity 1
1. 2.
52° + 79° + 𝑥 = 180° [∠′ 𝑠 of ∆= 180°] (𝑥 + 15°) + 𝑥 + (3𝑥 − 25°) = 180° [∠′ 𝑠 of ∆= 180°]
𝑥 + 131° = 180° 5𝑥 − 10° = 180°
𝑥 = 180° − 131° 5𝑥 = 180° + 10°
𝑥 = 49° 5𝑥 = 190°
𝑥 = 38°
3. 4.
(a) 𝐶̂1 = 180° − 95° [ Str line] (a) 𝑁 ̂1 = 180° − (60° + 53°) [∠′ 𝑠 𝑜𝑓∆= 180°]
= 85° 𝑁̂ = 67°
(b) 𝐸̂ + 85° + 30° = 180° (b) 𝐿̂2 = 𝑀 ̂ [ 𝑎𝑙𝑡 ∠′ 𝑠; 𝐾𝐿 ∥ 𝑀𝑂]
[∠′ 𝑠 𝑜𝑓∆] 𝐿̂2 = 60°
𝐸̂ = 180° − 115° = 65° (c) 𝐿̂3 = 𝑁̂1 [ 𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑠 ∠′ 𝑠; 𝐾𝐿 ∥ 𝑀𝑂]
(c) 𝐴̂ + 𝐸̂ = 180° [ co − int ∠′ s; AB ∥ DE] 𝐿̂3 = 67°
𝐴̂ = 180° − 65° = 115°
Grade 9 Page 3 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
� DAY 2: Types of Triangles
Types of Triangles. Do you remember?
All angles are Isosceles Scalene
Different lengths
equal
90° angle
All sides are equal Two angles equal All sides may have
Each angle= 60° Two sides are the different lengths
same length • All angles may be
different
Right-Angled
Equilateral
Let’s apply this knowledge to some problems.
1. Calculate 𝑥 in the follwing Solution:
diagram: Complete where needed.
B 𝐴̂ = 𝐶̂ [∠′ 𝑠 opposite = sides]
A
64° ∴ 𝐴̂ = 𝐶̂ = 𝑥
𝑥 + 𝑥 + 64° = ______ [∠' s of ∆=180°]
2𝑥 + 64° = 180°
2𝑥 = 180° − 64°
𝑥
2𝑥 = ________
C 𝑥 = 58°
2. ABCD is a paralellogram.
Determine with reasons the size of:
̂ = 55°
(a) B [∠′ s opposite = sides]
̂ + 55° + ___ = 180°
(b) A [∠' s of ∆=180°]
̂ = 180° − 110°°
A
̂ = 70°
A
(a) ̂1
B
(b) ̂
A (c) 𝐵̂2 = ____ [ corres ∠′ 𝑠; AE ∥ BF]
(c) ̂2
B
ACTIVITY 2
1. Name each of these triangles.
Grade 9 Page 4 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
� 2. 3.
Determine the size of the unknown
angles. 46°
𝑥
𝑦
𝑥
65°
𝑦
MEMORANDUM: ACTIVITY 2:
1. (a) scalene
(b) isosceles
(c) right-angled triangle
2. 𝑥 = 60° [∠' s opposite=sides]
𝑦 = 180° − 60° [str line]
3. 2𝑥 = 180° − 46° [ ∠' s opposite=sides]
2𝑥 = 134°
𝑥 = 67°
𝑦 = 180° − 90° − 65° [∠′ 𝑠 𝑜𝑓∆= 180°]
𝑦 = 35°
Grade 9 Page 5 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
� DAY 3: The exterior angle of a triangle
Let’s study the diagrams below:
Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Diagram 3
70°
(a) 50° 42°
40°
𝑎 𝑎 𝑏
𝑏
𝑎 𝑏
Complete:
𝑎 = 180° − ( 70° + 40°) 𝑎 = 180° − (50° + ______) 𝑎 = 180° − (____ + 42°)
𝑎 = 180° − 110° 𝑎 = 180° − 100° 𝑎 = 180° − 132°
𝑎 = 70° 𝑎 = 80° 𝑎 = 48°
𝑏 = 180° − 70° [∠’s on str line] 𝑏 = 180 − 80° [__________] 𝑏 = _____________
[∠’s on str line]
𝑏= 𝑏= 𝑏=
This is the
b
exterior angle
a 𝐚+𝐛
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the SUM of the opposite interior angles.
[ ext ∠ of ∆]
In the above sketches
Use this for your reason
Diagram 1: 𝑏 = 70° + 40° = 110°
Diagram 2: 𝑏 = 50° + 50° = 100°
Diagram 3: 𝑏 = 90° + 42° = 132°
`1. Determine the values of 𝑥 and 𝑦. Solution:
𝑥 = _______________ [ext ∠ of ∆]
𝑦
= ______________
18°
̂ = ________ [ ∠’ s opp=sides ]
C
𝑦 = 180° − 2𝑥 [ ___________________ ]
𝑦 = ___________
𝑥 59°
Grade 9 Page 6 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�2. Determine the size of the letters in Solution:
the sketch below: Fill in the gaps
N
̂ N=a+10°+46° [ ______________ ]
JK
D 136° = 𝑎 + 56°
𝑎 + 10° 𝑎 = 136° − 56°
𝑎 = 80°
∴N ̂ =80°+10°=90°
136° 𝑏 46° M 𝑏 = 180° − (90° + ____) [ ____________ ]
K 𝑏 = 44°
J 𝑐
D F 𝑐 = 44° + 90° [ _______________ ]
𝑐 = 134°
ACTIVITY 3
1. Determine the values of 𝑥 and 𝑦. ̂ C.
2. Find the value of BA
3. In ∆PQR, QR is extended to S. Determine the size of 𝑄̂ .
4. Study the figure below:
(a) Caculate the size 𝑄̂2
(b) Hence calculate the size of 𝑀𝑂̂𝑁. 2
Grade 9 Page 7 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�MEMORANDUM: ACTIVITY 3:
1. 𝑦 = 56° + 32° [ext ∠ of ∆] 2. 3𝑦 + 𝐵𝐴̂𝐶 = 5𝑦 [ext ∠ of ∆]
𝑦 = 88° 𝐵𝐴̂𝐶 = 5𝑦 − 3𝑦
𝑥 = 56° + (32° + 12°) [ext ∠ of ∆] 𝐵𝐴̂𝐶 = 2𝑦
𝑥 = 56° + 44° But 4𝑦 + 5𝑦 = 180° [Str line]
𝑥 = 100° 9𝑦 = 180°
𝑦 = 20°
𝐵𝐴̂𝐶 = 2(20°)
= 40°
3. 2𝑥 + 7𝑥 = 180° [Str line] ̂
4. (a) 𝑄2 + 55° = 180° [𝑐𝑜 − 𝑖𝑛𝑡 ∠ ; 𝑃𝑄 ∥ 𝑀𝑁]
9𝑥 = 180° ̂
𝑄2 = 125°
𝑥 = 20°
(b) 2𝑥 − 5° + 3𝑥 + 40 = 125° [ext ∠ of ∆]
𝑄̂ + 4𝑥 = 7𝑥 [ext ∠ of ∆] 5𝑥 − 35° = 140°
̂
𝑄 = 3𝑥 5𝑥 = 175°
𝑄̂ = 2(20°) = 40° 𝑥 = 35°
𝑀𝑂̂𝑁 = 2(35°) − 5°
= 70° − 5°
= 65°
IT IS IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER:
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle add
up to 𝟏𝟖𝟎°.
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the
sum of the opposite interior angles
Apply the properties of the different triangles at all times.
Grade 9 Page 8 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
� DAY 4 and 5: Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a closed shape with four sides.
Important Fact
The sum of the interior angles adds up to 𝟑𝟔𝟎°
Types of Quadrilaterals
Special quadrilaterals Properties
Parallelogram Opposite sides are equal
Opposite angles are parallel
Opposite angles are equal
Diagonals bisect each other
Rectangle Opposite sides are equal
Opposite sides are parallel
Angles = 90°
Diagonals are equal
Diagonals bisect each other
Square All sides are equal
Opposite sides are parallel
Angles = 90°
Diagonals are equal
Diagonals bisect each other
Diagonals bisect each other at right
angles
Diagonals bisect the interior angles
Rhombus
Grade 9 Page 9 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
� All sides are equal
Opposite sides are parallel
Opposite angles are equal
Diagonals bisect each other at
right angles.
Diagonals bisect the interior
angles
Diagonals are equal
Diagonals bisect each other
Trapesium
One pair of opposite sides are
parallel.
Kite
Two pairs of adjacents sides equal.
Opposite angles between unequal
sides are equal.
One diagonal of the kite bisects the
other diagonal at 90°.
One diagonal bisects the interior
angles.
Application
Determine the value of the unknown Steps
angles in the shape. 1. Identify the shape – paralellogram
2. Apply properties - opposite angles
are equal
𝒅 = 𝟒𝟓° [ 𝒐𝒑𝒑 ∠ 𝒐𝒇 𝒑𝒂𝒓𝒎]
3. Identify parts – parallel lines
𝒅 + 𝒆 = 𝟏𝟖𝟎° [𝒄𝒐 − 𝒊𝒏𝒕 ∠; ∥ 𝒍𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒔
𝒆 = 𝟏𝟖𝟎° − 𝟒𝟓°
𝒆 = 𝟏𝟑𝟓°
Grade 9 Page 10 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�ACTIVITY 4
Do the following exercises, applying what you have learnt today. FIRST ATTEMPT TO
DO ALL THE PROBLEMS BEFORE YOU CHECK YOUR ANSWERS IN THE MEMORANDUM
BELOW.
̂C = 𝑦
1. ABCD is a parallelogram with EA
and DÂ B = 𝑥.
Calculate:
(a) ̂1
D
(b) 𝑦
(c) ̂1
A
2. MNPQ is a trapesium with MQ=MN and
NQ⊥QP. Determine, with reasons, the
sizes of 𝑎, 𝑏, 𝑐 and 𝑑.
3. Calculate, with reasons the value of 𝑥.
Grade 9 Page 11 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�Previous examination paper.
Memorandum: Activity 4
2.
1. (a) ̂ 1 = 75°
D [alt ∠' s; AD ∥ BC] 𝑎 = 180° − (90° + 65°) [int ∠ of ∆]
(b) 𝑦 = 48° + 75° [ext ∠ of ∆] 𝑎 = 25°
𝑦 = 123° 𝑎=𝑏 [alt ∠' s; MQ ∥ NP]
𝑏 = 25°
(c) 𝐴̂1 = 180° − 123° [str line]
𝐴̂1 = 57° 𝑏=𝑐 [ equal ∠' s opposite equal sides]
𝑐 = 25°
𝑑 = 180° − 50° [int ∠'s of ∆]
𝑑 = 130°
3. 4.
𝐸̂1 = 2𝑥 + 15° [ equal ∠′ 𝑠 opposite = sides] 𝑥 = 85° [alt ∠' s; AC ∥ HF]
𝐻̂1 = 𝑥 [ diagonal bisects angle] 𝑦 = 180° − 85° [co-interior ∠' s; BF ∥ CD]
2(2𝑥 + 15°) + 2𝑥 = 180° [int ∠ of ∆] 𝑦 = 95°
4𝑥 + 30° + 2𝑥 = 180°
6𝑥 = 150°
𝑥 = 25°
Grade 9 Page 12 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes
�CONSOLIDATION
IT IS IMPORTANT TO REMEMBER:
You need to identify the shape
You need to know the properties of the shape
Show all markings on your sketch.
Grade 9 Page 13 of 13
Geometry of 2D shapes