Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics Reviewer
Statistics Reviewer
Uploaded by
ellah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document discusses key concepts in statistics including types of variables, levels of measurement, random variables, properties of the normal distribution curve, and key terms like mean, variance, standard deviation, parameter, statistic, and sampling distribution. It defines nominal, ordinal, ratio and interval levels of measurement and gives examples. It also outlines properties that random variables and probabilities should satisfy.
Original Description:
Original Title
STATISTICS REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts in statistics including types of variables, levels of measurement, random variables, properties of the normal distribution curve, and key terms like mean, variance, standard deviation, parameter, statistic, and sampling distribution. It defines nominal, ordinal, ratio and interval levels of measurement and gives examples. It also outlines properties that random variables and probabilities should satisfy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesStatistics Reviewer
Statistics Reviewer
Uploaded by
ellahThe document discusses key concepts in statistics including types of variables, levels of measurement, random variables, properties of the normal distribution curve, and key terms like mean, variance, standard deviation, parameter, statistic, and sampling distribution. It defines nominal, ordinal, ratio and interval levels of measurement and gives examples. It also outlines properties that random variables and probabilities should satisfy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
STATISTICS REVIEWER
-is the planet earth bigger than venus-no
-what is the habit of your brother- no
-did u eat your bfast this morning- no
-what is the typical size of a filipino fam- yes
-planning or designing in a way that maximize content and minimizes bias
2 types of variables
•quali- categorical, what kind
•quanti- how much, how many
Four Levels of Measurement:
•Nominal- labeling, categorizing, naming example:age, sex, section, civil status
•Ordinal-arrange in sequence, ranks categories in order,
example: class ranking, educational bg, income, salary grade, scores, leader board, promotions/positions
•Ratio and Interval -same with one key difference
•Ratio-has true zero
example: weight, age, height
•Interval- no true zero
example: temperature, iq
-known and evenly space intervals between the values
Random variable
•random variable-numerical quantity that is measurable/assigned to an outcome of an experiment
•discrete-often a result of counting
•continuous-often a result of measuring
2 properties that should be satisfied
-sum of all probabilities is equal to 1
-each of the values of the probabilities is greater than or equal to zero but less than or equal to 1
getting the mean and variance
-mean- summation of x times the probability of x
-variance- summation of(x-mean)^2×p(x)
-sd- squareroot of variance
-mean-expected value
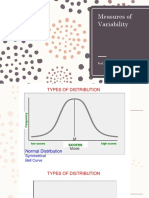
Properties of normal curve:
-bell-shaped
-symmetrical abt the mean
-total area is 1
-asymptotic
-2 inflection points
-highest point is the mean
-continuous
-mean and sd
When to the left: Area in the table as it is
When to the right: 1 minus area in the table
When in between: Subtract lower area from the higher area
-the higher the sd the wider the normal curve is
-the lower the sd the narrower the normal curve is
-identifying areas under the normal curve
•Percentile and Z-score
•Parameter - population
•Statistics - sample
•Sampling distribution
•Determining of possible samples
•Mean
You might also like
- Comm 215.MidtermReviewDocument71 pagesComm 215.MidtermReviewJose Carlos BulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDocument44 pagesLecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability: Prof. Michelle M. Mag-IsaDocument46 pagesMeasures of Variability: Prof. Michelle M. Mag-IsaMichelle MalabananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Intro To StatisticsDocument31 pagesChapter 1: Intro To StatisticsPohuyistNo ratings yet
- Review of Statistical Concepts AutosavedDocument58 pagesReview of Statistical Concepts Autosavedjose randyNo ratings yet
- 09 - Data Analysis - Descriptive StatisticsDocument23 pages09 - Data Analysis - Descriptive StatisticsNdaliNo ratings yet
- Scoring and Interpretation - Part 3Document25 pagesScoring and Interpretation - Part 3Rania AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Exploring DataDocument23 pagesChap 1 Exploring DataMbusoThabetheNo ratings yet
- Statistics For The Social Sciences: IntroductionsDocument111 pagesStatistics For The Social Sciences: IntroductionsRAMEEZ. ANo ratings yet
- Disseminate Information To Various Managerial LevelsDocument16 pagesDisseminate Information To Various Managerial LevelsDhruvina MerNo ratings yet
- Psychological Testing 2018 PDFDocument74 pagesPsychological Testing 2018 PDFJen CalaquiNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument19 pagesStatisticsAileen Grace DelimaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and MeasurementDocument35 pagesSampling and MeasurementAdel KaadanNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Unit-1)Document101 pagesStatistics (Unit-1)mannu02.manishNo ratings yet
- 7.data Analysis 1Document22 pages7.data Analysis 1Pamela GabrielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document38 pagesLecture 1Vishnu VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document39 pagesLecture 3Amine HadjiNo ratings yet
- Quants Theory MBA SEM-1Document11 pagesQuants Theory MBA SEM-1Pranil VermaNo ratings yet
- 5 Random Var PDFDocument74 pages5 Random Var PDFkrishnakishoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics: February 21, 2006Document34 pagesIntroduction To Statistics: February 21, 2006Fatima RiveraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument6 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldHilom Baho Kag BabaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics DISPERSION & NORMAL CURVEDocument29 pagesAdvanced Statistics DISPERSION & NORMAL CURVEGregorio Gamboa Maniti IINo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Statistics in Psychological AssessmentDocument25 pagesWeek 5 - Statistics in Psychological AssessmentTAZHA MADIZON ANNE MORENONo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDocument4 pagesDescriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDipak Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Stati Stics: There Are Three Kinds of Lies: Lies, Damned Lies, A ND Statistics." (B.Disraeli)Document39 pagesIntroduction To Stati Stics: There Are Three Kinds of Lies: Lies, Damned Lies, A ND Statistics." (B.Disraeli)Mohammad Ameen UjjanNo ratings yet
- Graphical Descriptive Statistics Lec 1Document18 pagesGraphical Descriptive Statistics Lec 1Adeel NasirNo ratings yet
- Attitude Measurement - MKTG 526Document13 pagesAttitude Measurement - MKTG 526mahiaryaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency & VariabilityDocument25 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency & Variabilityelune121No ratings yet
- Week 4 Statistics Recap MAKING MEANING OF MEASUREMENTS & RAW TEST SCORESDocument39 pagesWeek 4 Statistics Recap MAKING MEANING OF MEASUREMENTS & RAW TEST SCORESAceNo ratings yet
- Ge 4 - Midterm Learning MaterialDocument93 pagesGe 4 - Midterm Learning MaterialBobbie BobierNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Lecture 4 - Descriptive Statistics - SlidesDocument20 pages2021 - Lecture 4 - Descriptive Statistics - SlidesFanelo FelicityNo ratings yet
- Definitions in Statistics - 01Document43 pagesDefinitions in Statistics - 01Prudence MasimbeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Descriptive Stat.Document39 pagesChapter 4 Descriptive Stat.Jason CamaNo ratings yet
- Beed 7 ReviewerDocument8 pagesBeed 7 ReviewerPauline TindocNo ratings yet
- Advance Data Analysis - StudentsDocument82 pagesAdvance Data Analysis - StudentsAdhy popzNo ratings yet
- Sampling Human Pop1Document49 pagesSampling Human Pop1juliepink14No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument30 pagesSamplingShrutiNo ratings yet
- Statistics: I. II. Iii. IVDocument6 pagesStatistics: I. II. Iii. IVjhatanakaNo ratings yet
- ST2007S - Lecture-02-Sampling and Descriptive StaticsDocument43 pagesST2007S - Lecture-02-Sampling and Descriptive Staticsponku75No ratings yet
- Research Methods: Introduction To Inferential StatisticsDocument35 pagesResearch Methods: Introduction To Inferential StatisticsColinNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Data ManagementDocument8 pagesStatistics and Data Managementveldortempest1No ratings yet
- Presentation Mbs712Document15 pagesPresentation Mbs712Lizel MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Statistics LectureDocument41 pagesIntro To Statistics LectureACCESS PHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document25 pagesLecture 1Rabia ChNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument93 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceCesar LobatoNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument27 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceDr. Sanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Sample MeansDocument32 pagesDistribution of Sample MeansEva Elžbieta SventickaitėNo ratings yet
- Slides Chp03 Stats 20221Document41 pagesSlides Chp03 Stats 20221nadiaNo ratings yet
- Statistics For BegineersDocument28 pagesStatistics For BegineersAditya GoleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Normative Distribution and Descriptive StatisticsDocument51 pagesLecture 2 - Normative Distribution and Descriptive StatisticsefkjhNo ratings yet
- 2 Knowing Data & VisualizationDocument51 pages2 Knowing Data & VisualizationMarcoNo ratings yet
- Mean Median ModeDocument36 pagesMean Median Modenikhil_bajaj2001No ratings yet
- Business Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyDocument44 pagesBusiness Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyJee HiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document39 pagesTopic 4sid suchakNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument25 pagesBusiness Statisticsshreyash436No ratings yet
- Cpe106 Notes For PrelimDocument3 pagesCpe106 Notes For PrelimNur-Hanifah PACOTENo ratings yet
- Stats BasicsDocument58 pagesStats BasicsRavi goelNo ratings yet