Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chlorine Dioxid-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Malik RohailCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chlorine Dioxid-WPS Office
Uploaded by
Malik RohailCopyright:
Available Formats
Chlorine dioxide remove phenolic compound
Chlorine dioxide (ClO2) is a powerful oxidizing agent commonly used for water treatment, disinfection,
and odor control. It is known to effectively remove a wide range of contaminants, including phenolic
compounds.
Phenolic compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached
to an aromatic ring. They are commonly found in industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff, and certain
manufacturing processes. Phenolic compounds can be toxic and pose environmental hazards.
Chlorine dioxide can react with phenolic compounds through oxidation reactions, breaking down their
chemical structure and rendering them less harmful or even completely removing them. The oxidative
properties of chlorine dioxide enable it to oxidize the phenolic compounds, leading to their degradation
into simpler and less toxic byproducts.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of chlorine dioxide in removing phenolic compounds can
vary depending on various factors, including the concentration of chlorine dioxide, contact time, pH
levels, and the specific characteristics of the phenolic compound. In some cases, additional treatment
steps or combinations with other chemicals may be required to achieve optimal removal efficiency.
When using chlorine dioxide for phenolic compound removal or any water treatment application, it is
crucial to follow proper dosing guidelines and adhere to regulatory requirements to ensure safe and
effective treatment while minimizing any potential risks to human health and the environment.
You might also like
- Chlorine DioxideDocument9 pagesChlorine Dioxidejavier mascherano100% (1)
- DisinfectionDocument82 pagesDisinfectionJoby AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Sanitizers for Food PlantsDocument9 pagesSanitizers for Food PlantsAldamir AcostaNo ratings yet
- Additional Info From The USA On Chlorine DioxideDocument2 pagesAdditional Info From The USA On Chlorine DioxideAlexandra AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oxidation Processes FinalDocument17 pagesAdvanced Oxidation Processes Finalapi-3703229100% (2)
- Constructed Wetlands for Tertiary TreatmentDocument24 pagesConstructed Wetlands for Tertiary TreatmentHrithik BaradiaNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Efficacy: Michel Van Schaik, Aquaox LLCDocument5 pagesChlorine Efficacy: Michel Van Schaik, Aquaox LLCIsmailNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chlorite as an Active Ingredient in Decontamination TechnologiesDocument21 pagesSodium Chlorite as an Active Ingredient in Decontamination TechnologiesFocal BuzzNo ratings yet
- FAQ Chlorine Dioxide - European Version April 2017Document16 pagesFAQ Chlorine Dioxide - European Version April 2017Long Thuận100% (1)
- Enviromail 65 - Adsorbable Organic Halides AOX - May 2013Document2 pagesEnviromail 65 - Adsorbable Organic Halides AOX - May 2013fisheriesNo ratings yet
- Oxynol Brochure OMSB 070809Document10 pagesOxynol Brochure OMSB 070809Saravanan RasayaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Chemicals05Document2 pagesWastewater Treatment Chemicals05Subodh KantNo ratings yet
- Organic Odor Control With Chlorine DioxideDocument3 pagesOrganic Odor Control With Chlorine DioxideCostas AggelidisNo ratings yet
- Industry BiocidesDocument6 pagesIndustry BiocidesCristiOtopeniNo ratings yet
- CE 121 ChlorinationDocument13 pagesCE 121 ChlorinationVincent Salarda BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Effluent Treatment: Lecture 5Document10 pagesTechniques For Effluent Treatment: Lecture 5Mohammed Rayyan NNo ratings yet
- A Simple and Efficient Method For Removal of Phenolic Contaminants in Wastewater Using Covalent Immobilized Horseradish PeroxidaseDocument12 pagesA Simple and Efficient Method For Removal of Phenolic Contaminants in Wastewater Using Covalent Immobilized Horseradish PeroxidaseniteshacharyaNo ratings yet
- Disinfection of WaterDocument18 pagesDisinfection of WaterPaulpablo ZaireNo ratings yet
- M1-L10 Domestic Water TreatmentDocument17 pagesM1-L10 Domestic Water Treatmentgaurav toppoNo ratings yet
- Fungi in Landfill Leachate Treatment Process: Yanan Ren and Qiuyan YuanDocument16 pagesFungi in Landfill Leachate Treatment Process: Yanan Ren and Qiuyan Yuankj185No ratings yet
- Additives Used in Pulping ProcessesDocument22 pagesAdditives Used in Pulping ProcessesDesi Puryani100% (2)
- Chapter 6 DisinfectionDocument12 pagesChapter 6 DisinfectionMuluken MelesseNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric AcidDocument5 pagesHydrochloric AcidOFURUM FRANKLYNNo ratings yet
- Water recovery from rinse wastewater using AOPsDocument3 pagesWater recovery from rinse wastewater using AOPsWONG TSNo ratings yet
- DisinfectionDocument5 pagesDisinfectiondave tafadzwa kuyeriNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Chlorination: Basic Properties and Key Points For Effective DisinfectionDocument8 pagesPostharvest Chlorination: Basic Properties and Key Points For Effective DisinfectionGaganpreetNo ratings yet
- Active Vs Stabilized Chlorine DioxideDocument4 pagesActive Vs Stabilized Chlorine DioxideClaudiusNo ratings yet
- 216 Disinfectants Part 2Document83 pages216 Disinfectants Part 2Alaa SalemNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Production of VCM 2.1 Process Flow Diagram of Production of VCMDocument7 pages2.0 Production of VCM 2.1 Process Flow Diagram of Production of VCMabdul qaharNo ratings yet
- Application of Permanganate in The Oxidation of Micropollutants: A Mini ReviewDocument9 pagesApplication of Permanganate in The Oxidation of Micropollutants: A Mini Reviewisaacwong620No ratings yet
- Chapt - 4 CHLORINE DIOXIDE PDFDocument41 pagesChapt - 4 CHLORINE DIOXIDE PDFRaul Tixe100% (4)
- fumigantsDocument15 pagesfumigantsSri. SiriNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chlorine DioxideDocument2 pages07 - Chlorine Dioxidepaygate591No ratings yet
- Chlorine Dioxide Do You Really Need It This Will Help You Decide!Document8 pagesChlorine Dioxide Do You Really Need It This Will Help You Decide!Pristine WaterNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment Techniques Under 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesEffluent Treatment Techniques Under 40 CharactersAnkur SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Bleach & Enzyme Wet ProcessingDocument40 pagesBleach & Enzyme Wet ProcessingTasbir HasanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials and AstringentsDocument34 pagesAntimicrobials and AstringentsAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Calcium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide As Neutralizer in Coagulation For Reducing Fluoride in Hazardous WastewaterDocument6 pagesThe Effectiveness of Calcium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide As Neutralizer in Coagulation For Reducing Fluoride in Hazardous WastewaterMoses BravoNo ratings yet
- WATER DisinfectionDocument8 pagesWATER Disinfectionnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- Calciumsodiumhypochlorite PDFDocument20 pagesCalciumsodiumhypochlorite PDFCHE.ENG1734No ratings yet
- 405 ProfilesDocument2 pages405 Profilesทรงพลกายบริบูรณ์No ratings yet
- Disinfection 2023Document18 pagesDisinfection 2023Francis Mutema MahofaNo ratings yet
- Disinfection SlidesDocument29 pagesDisinfection SlidesptfNo ratings yet
- Key Operating Strategies For Chlorine Disinfection Operating Systems Gerald F. Connell Consultant Warminster, PADocument6 pagesKey Operating Strategies For Chlorine Disinfection Operating Systems Gerald F. Connell Consultant Warminster, PAsyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- ClO2 Kill E Coli Study CaseDocument7 pagesClO2 Kill E Coli Study CaseAri WijayaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Chlorination: Chlorine ChemistryDocument4 pagesCooling Water Chlorination: Chlorine Chemistrymnasiroleslami100% (1)
- Chlorine Dioxide, Ozone, Cold Plazma, Dense Phase Carbon Dioxide: Mechanism, Applications, TheoryDocument60 pagesChlorine Dioxide, Ozone, Cold Plazma, Dense Phase Carbon Dioxide: Mechanism, Applications, TheoryBüşra GültekinNo ratings yet
- AkzoNobel - Hydrogen Peroxide Product Information Manual - December 2015 - tcm56-94028 - 2Document32 pagesAkzoNobel - Hydrogen Peroxide Product Information Manual - December 2015 - tcm56-94028 - 2PungkyRamadhaniPamungkasAminotoNo ratings yet
- Disinfection Techniques and Factors LectureDocument32 pagesDisinfection Techniques and Factors LectureJames Korbla Dodzi HillsNo ratings yet
- Chlorination of Cooling Water Systems PDFDocument4 pagesChlorination of Cooling Water Systems PDFhappale2002No ratings yet
- Chemical Oxidation Organics FentonDocument10 pagesChemical Oxidation Organics FentonBa Khoa TranNo ratings yet
- KayserDocument1 pageKayserللطالب مطالبNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide TherapyDocument31 pagesHydrogen Peroxide TherapySavoryHubbard100% (1)
- DechlorinationDocument2 pagesDechlorinationMohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- Sulfure Dioxide, Recognizing The Characteristics and Toxicological EffectsDocument5 pagesSulfure Dioxide, Recognizing The Characteristics and Toxicological EffectsMarco TebaldiNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument30 pagesInvestigatory ProjectvedanggamezNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hydrogen peroxide uses for the body: 31 5 Minute Remedies! Discover Uses for Hydrogen Peroxide including Mouthwash & Bad Breath, Teeth Whitening, Acne, Ear Wax, Hair, Allergy & Nasal Spray and MOREFrom EverandHydrogen peroxide uses for the body: 31 5 Minute Remedies! Discover Uses for Hydrogen Peroxide including Mouthwash & Bad Breath, Teeth Whitening, Acne, Ear Wax, Hair, Allergy & Nasal Spray and MORERating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Aliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesFrom EverandAliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNo ratings yet
- Failures of PtiDocument2 pagesFailures of PtiMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- NotificationDocument1 pageNotificationMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Psycology 2Document7 pagesPsycology 2Malik RohailNo ratings yet
- Yasir Ameen CVDocument1 pageYasir Ameen CVMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Definition of ProofreadingDocument1 pageDefinition of ProofreadingMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Abdur Rehman Report 17 05 202Document40 pagesAbdur Rehman Report 17 05 202Malik RohailNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument1 pageDownloadMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Younas Thesis 16 05 2023Document60 pagesYounas Thesis 16 05 2023Malik RohailNo ratings yet
- Oil Price Impact on PakistanDocument8 pagesOil Price Impact on PakistanMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Spring Semester 2021 Re TranscriptDocument1 pageSpring Semester 2021 Re TranscriptMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- New Doc 05-09-2023 08.20Document2 pagesNew Doc 05-09-2023 08.20Malik RohailNo ratings yet
- Zeeshan ResumeDocument2 pagesZeeshan ResumeMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument1 pageDownloadMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Written Test Roll No SlipDocument2 pagesWritten Test Roll No SlipMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Motivational TheoryDocument4 pagesMotivational TheoryMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Fee ChallanDocument1 pageFee ChallanMalik RohailNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 13 00164Document18 pagesIjerph 13 00164Malik RohailNo ratings yet
- Front PageeeDocument1 pageFront PageeeMalik RohailNo ratings yet
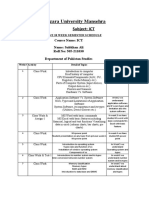
- Hazara University MansehraDocument2 pagesHazara University MansehraMalik RohailNo ratings yet
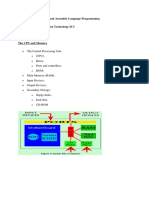
- CPU and Memory Organization in Computer SystemsDocument10 pagesCPU and Memory Organization in Computer SystemsMalik RohailNo ratings yet