Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology m7 Post Task Caparas
Pharmacology m7 Post Task Caparas
Uploaded by
Gretta Caparas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesPharmacology m7 Post Task Caparas
Pharmacology m7 Post Task Caparas
Uploaded by
Gretta CaparasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
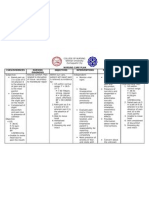
PHARMACOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Potassium-Sparing GENERIC NAME: Spironolactone
ROUTE: Oral route BRAND NAME: Aldactone
ACTION THERAPEUTIC USES REASON GIVEN (DISEASE STATES)
o Spironolactone blocks the sodium o The primary therapeutic outcome o Hypertension
retaining and potassium excreting associated with spironolactone - Spironolactone is used in
and magnesium excreting therapy is diuresis, with reduction combination with other medicines
properties of aldosterone, resulting of edema and improvement in to treat high blood pressure
in a loss of water with the increased symptoms related to excessive fluid (hypertension).
sodium excretion. accumulation and heart failure. o Heart Failure
- Spironolactone is also used to
lessen the need for hospitalization
for heart failure.
o Hyperaldosteronism
- Spironolactone competitively
binds receptors at the aldosterone-
dependent sodium-potassium
exchange site in the distal
convoluted renal tubule. It provides
diuretic and antihypertensive
effects, causing increased excretion
of sodium and water, while
retaining potassium.
Caparas, Margretta Alyssa T. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN2A-2
2A2 Subgroup 5 = Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
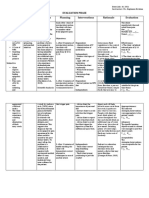
NURSING PROCESS
PRE-ADMINISTRATION POST ADMINISTRATION NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
ASSESSMENT EVALUATION
o Obtain a history of drugs taken o Evaluate the effectiveness of o Note the half-life of spironolactone.
daily. potassium-sparing diuretics. o With a long half-life, the drug is
o Note whether the patient is taking a o Fluid retention (edema) should be usually administered once a day,
potassium supplement or using a decreased or absent. sometimes twice a day
salt substitute. o Determine whether urine output o Monitor urinary output it should
o Assess vital signs, serum has increased and whether serum increase
electrolytes, weight, and urine potassium level is within the o Record vital signs and report any
output for baseline levels. normal range. abnormal changes
o Compare the patient’s drug dose o Observe for signs and symptoms of
with the recommended dose, and hyperkalemia (serum potassium
report any discrepancy. >5.0 mEq/L). nausea, diarrhea,
o Note whether the patient is abdominal cramps, etc.
hypersensitive to sulfonamides. o Administer spironolactone in the
morning and not in the evening to
avoid nocturia
● PATIENT TEACHING
General
o Teach patients to take
spironolactone with or after meals
to avoid nausea
o Encourage patients not to
discontinue the drug without
consulting a health care provider
Side Effects
o Caution patients to avoid exposure
to direct sunlight because
spironolactone can cause
photosensitivity
Caparas, Margretta Alyssa T. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN2A-2
2A2 Subgroup 5 = Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
o Advise patients to report possible
side effects such as rash, dizziness,
weakness, and GTI upset
● DIET
o Advise patients with high serum
potassium levels to avoid foods rich
in potassium when taking
potassium-sparing diuretics
● CULTURAL CONSIDERATIONS
o Use both hands to show respect
when offering a prescription,
instructions, or pamphlets to Asians
and Pacific Islanders
Caparas, Margretta Alyssa T. PHARMACOLOGY
BSN2A-2
2A2 Subgroup 5 = Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
You might also like
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CADocument8 pagesDrug Study CAAna Marie Besa Battung-ZalunNo ratings yet
- Chart View Admission Lab WorkDocument4 pagesChart View Admission Lab Workania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of VSDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of VSDMarlon Cruz0% (1)
- NCP. MOuth SoreDocument1 pageNCP. MOuth SoreChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Brokenshire CollegeJai GoNo ratings yet
- 6 PathophysiologyDocument2 pages6 PathophysiologyAJ SnowhiNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocument7 pagesAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkNo ratings yet
- LOVASTATINDocument2 pagesLOVASTATINAngel CatalanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- C. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesC. Nursing Care PlanJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Name of The DrugDocument2 pagesName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cefazolin and Vit KDocument2 pagesDrug Study Cefazolin and Vit KFrancis Lawrence AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidVaibhav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - EVALUATION PHASEChezka Orton Swift BolintiamNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- JM Drug Study CaseDocument4 pagesJM Drug Study CaseMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreDocument5 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreteuuuuNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocument5 pagesCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDocument1 pageDischarge Plan For AppendectomyMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument2 pagesVitamin KMuvs RazonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Meclizine Is An Antagonist atJayson Ray AbellarNo ratings yet
- Npi NCMHDocument6 pagesNpi NCMHJoshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AzathioprineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AzathioprineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Final Eb ReflectionDocument2 pagesFinal Eb Reflectionapi-238460511No ratings yet
- DrugStudy MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrugStudy MetoclopramideAshknee Khainna AlejoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HepatitisDocument7 pagesDrug Study HepatitisKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- CPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCPD Concept MapShandle Dynne Baena100% (1)
- Drug Study PonstanDocument1 pageDrug Study PonstanRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AmoebiasisDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY - AmoebiasisErika NicaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration IndicationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration IndicationBrian BaggayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocument2 pagesJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 203Document3 pagesDrug Study 203Daniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CholangioDocument10 pagesDrug Study - CholangioClaireMutiaNo ratings yet
- NCP Mandibular)Document5 pagesNCP Mandibular)yellarfNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNo ratings yet
- DS OfloxacinDocument2 pagesDS OfloxacinjessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareDocument1 pageThalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNo ratings yet
- CelecoxibDocument3 pagesCelecoxibapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 pagesTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- M7 - Post Task - CaparasDocument8 pagesM7 - Post Task - CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- Pre-Task-Module 3-CaparasDocument3 pagesPre-Task-Module 3-CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- Mcs-M1-Post Task - CaparasDocument1 pageMcs-M1-Post Task - CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- Bioethics m4. Post Task de Leon Bsn2bDocument4 pagesBioethics m4. Post Task de Leon Bsn2bGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- STS M6 L1 Cia1 - CaparasDocument1 pageSTS M6 L1 Cia1 - CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet
- STS M6 L4 Cia2 - CaparasDocument2 pagesSTS M6 L4 Cia2 - CaparasGretta CaparasNo ratings yet