Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Attachment 9 - CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE MATERIAL
Uploaded by
kamikita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageAttachment 9 - CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF PIPELINE MATERIAL
Uploaded by
kamikitaCHEMICAL ANALYSIS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Attachment 9.
Chemical Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel by Spark Atomic Emission
Spectrometry.
ASTM E415
Scope:
The ASTM E415 is a standard test technique for spark atomic emission spectrometry
examination of carbon and low-alloy steel. This test method applies to specimens with a
diameter large enough to overlap and seal the bore of the spark stand hole. This test technique
covers routine control analysis in iron and steelmaking activities as well as material analysis. It is
intended for specimens that have been chill-cast, rolled, or forged.
The spectrometric analysis of metals and alloys in this test method is primarily aimed to ensure
that such materials meet compositional standards. All users of this test technique are presumed
to be analysts capable of completing conventional laboratory operations skillfully and securely.
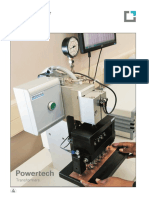
Test Procedure:
A capacitor discharge is created between the flat, ground surface of the disc specimen and a
conically shaped electrode in accordance with the ASTM E415 test protocol. The discharge is
stopped at a predetermined intensity time integral of one of the iron lines, or at a
predetermined time, and the relative radiant energies of the analytical lines are recorded. The
vacuum ultraviolet area contains the most sensitive lines of arsenic, boron, carbon, nitrogen,
phosphorus, sulphur, and tin. By vacating the spectrometer and flushing the spark chamber
with argon, the absorption of the radiation by air in this location is overcome.
Specimen Size:
The specimen thickness might vary considerably depending on the design of the spectrometer
stand, according to ASTM E415; however, a thickness between 10 mm and 38 mm has been
determined to be most practical.
Data:
When reference materials and specimens are of similar metallurgical condition and
composition, according to the ASTM E415 test procedure, better results are expected. It is not,
however, needed in all cases where this standard is used.
You might also like
- Progress in Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Analytical Atomic Spectroscopy: Volume 6C L ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Testing for Metal Finishing: Institute of Metal FinishingFrom EverandCorrosion Testing for Metal Finishing: Institute of Metal FinishingNo ratings yet
- Astm E415-2008Document9 pagesAstm E415-2008Syamsul AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel by Spark Atomic Emission SpectrometryDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel by Spark Atomic Emission SpectrometryMoisés OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Assessing IGC in 316(N) SS Using Electrochemical NoiseDocument7 pagesAssessing IGC in 316(N) SS Using Electrochemical Noiseandrew_yeap_2No ratings yet
- E2209 13Document6 pagesE2209 13diego rodriguez100% (1)
- Disbonding Characteristics of Pipeline Coatings by Direct Soil BurialDocument4 pagesDisbonding Characteristics of Pipeline Coatings by Direct Soil BurialduaddmsqvzesqmskcbNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Reactivation (EPR) For Detecting Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsDocument9 pagesElectrochemical Reactivation (EPR) For Detecting Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsAndres Carmona100% (1)
- Assessment of Galvanic Corrosion in Galvanic Couples of Sensitized and Nonsensitized AISI Type 304 Stainless Steel in Nitric AcidDocument12 pagesAssessment of Galvanic Corrosion in Galvanic Couples of Sensitized and Nonsensitized AISI Type 304 Stainless Steel in Nitric AcidRangga KomaraNo ratings yet
- Ipc2012 90213Document8 pagesIpc2012 90213Marcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- ASTM Standards - PDF 1Document8 pagesASTM Standards - PDF 1Atanu Das100% (1)
- Jte10988j DL.1207477 1Document6 pagesJte10988j DL.1207477 1Tatiane ChuvasNo ratings yet
- ALLOY 800 TUBE CRACK DETECTIONDocument9 pagesALLOY 800 TUBE CRACK DETECTIONETSNo ratings yet
- Applying Small Punch Creep Tests to Predict Rupture Times in Magnesium AlloysDocument6 pagesApplying Small Punch Creep Tests to Predict Rupture Times in Magnesium AlloysSanti Osorio DiezNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current TestingDocument1 pageEddy Current TestingNsidibe Michael EtimNo ratings yet
- Astm E-543-09 QaDocument11 pagesAstm E-543-09 QampusNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Contaminated Nuclear Plant Steel by LIBS: Presented By: Sajjad Ali Roll No: BSPHY-20-52 Department of PhysicsDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Contaminated Nuclear Plant Steel by LIBS: Presented By: Sajjad Ali Roll No: BSPHY-20-52 Department of PhysicsSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Astm F468-2012Document14 pagesAstm F468-2012Svetlana PerekopskayaNo ratings yet
- ASTM StandardsDocument8 pagesASTM Standardslokelooks75% (4)
- Application of EIS To The Study of Corrosion Behaviour of Sintered Ferritic Stainless Steels Before and After High-Temperature ExposureDocument8 pagesApplication of EIS To The Study of Corrosion Behaviour of Sintered Ferritic Stainless Steels Before and After High-Temperature ExposuremadacursaruNo ratings yet
- Tubing Inspection Using Multiple NDT TechniquesDocument4 pagesTubing Inspection Using Multiple NDT TechniquesshifaNo ratings yet
- Nonferrous Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, and Studs For General UseDocument15 pagesNonferrous Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, and Studs For General Usejuniuni18No ratings yet
- A 751Document7 pagesA 751Senthilkumar DharmarajNo ratings yet
- Auto UT PIpe InspectionDocument16 pagesAuto UT PIpe InspectionMohd Azrul AzmanNo ratings yet
- Norma ASTM E415 15 PDFDocument11 pagesNorma ASTM E415 15 PDFCarlos VivesNo ratings yet
- Core Steel Tester 2013Document4 pagesCore Steel Tester 2013Batcas EloyNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Emission Techniques in Corrosion MonitoringDocument67 pagesAcoustic Emission Techniques in Corrosion MonitoringiJordanScribdNo ratings yet
- EPRI Atlas of Steamside Oxide ObservationsDocument12 pagesEPRI Atlas of Steamside Oxide Observationsekrem turan100% (2)
- Astm A343&343m 2003 PDFDocument16 pagesAstm A343&343m 2003 PDFSilverio AcuñaNo ratings yet
- A867-03 (2013) Standard Specification For Iron-Silicon Relay SteelsDocument4 pagesA867-03 (2013) Standard Specification For Iron-Silicon Relay SteelsdcardonasterNo ratings yet
- Coated Stainless Steel 441 As Interconnect Material For Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Evolution of Electrical PropertiesDocument7 pagesCoated Stainless Steel 441 As Interconnect Material For Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Evolution of Electrical PropertiesJags BuddyNo ratings yet
- E 1652 - 03 - Rte2ntiDocument8 pagesE 1652 - 03 - Rte2ntiLemir LopezNo ratings yet
- fe37ce57a5889b5d045543493c664376Document10 pagesfe37ce57a5889b5d045543493c664376pela210No ratings yet
- Corte Por Plasma 9Document4 pagesCorte Por Plasma 9Ronny De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Astm F468M 1997Document7 pagesAstm F468M 1997Jesse ChenNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current MeasurementsDocument4 pagesEddy Current MeasurementsBassam AbdelazeemNo ratings yet
- PDFsam_B 367 - 13Document6 pagesPDFsam_B 367 - 13mike.jensen0581No ratings yet
- Analysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry: Standard Test Method ForDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Cast Iron by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry: Standard Test Method ForcommandoNo ratings yet
- Corte Por Plasma 8Document13 pagesCorte Por Plasma 8Ronny De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Two API Steels For Iron Ore PipelinesDocument7 pagesMicrostructure and Mechanical Properties of Two API Steels For Iron Ore PipelinesNilesh MistryNo ratings yet
- Destructive and Non-Destructive Material Testing: Presented by Santosh PunaskarDocument18 pagesDestructive and Non-Destructive Material Testing: Presented by Santosh PunaskarSantosh Iim LucknowNo ratings yet
- IGC TestDocument2 pagesIGC TestHiren PanchalNo ratings yet
- Carburization Investigation PDFDocument12 pagesCarburization Investigation PDFArjed Ali ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Measuring Power Frequency Magnetic Properties of Flat-Rolled Electrical Steels Using Small Single Sheet TestersDocument5 pagesMeasuring Power Frequency Magnetic Properties of Flat-Rolled Electrical Steels Using Small Single Sheet TestersNgoc BangNo ratings yet
- Tubing and CasingDocument10 pagesTubing and CasingEnd LabNo ratings yet
- 4.MEET 315LA MatScie Engineering ME Lab Module 4Document44 pages4.MEET 315LA MatScie Engineering ME Lab Module 4Cj TilamNo ratings yet
- G61-86R03E1.1207958-1 (Polarização)Document5 pagesG61-86R03E1.1207958-1 (Polarização)Fabricio Benedito DestroNo ratings yet
- Astm G42 - 11 PDFDocument8 pagesAstm G42 - 11 PDFJavier Celada100% (1)
- Core Steel Tester 2013Document4 pagesCore Steel Tester 2013Fernando RapisardiNo ratings yet
- Velocity in MetalsDocument30 pagesVelocity in MetalsChegwe CorneliusNo ratings yet
- C876Document7 pagesC876grats_singcoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E415-14 (Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry)Document9 pagesASTM E415-14 (Analysis of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel by Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry)Said MohamedNo ratings yet
- KFK4221Document25 pagesKFK4221tl41No ratings yet
- Making Potentiostatic and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization MeasurementsDocument12 pagesMaking Potentiostatic and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization MeasurementsHelga Viviana AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Astm F90-14Document4 pagesAstm F90-14Rafael ScatolinNo ratings yet
- Astm A999 A999m 13Document11 pagesAstm A999 A999m 13islamakthamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Aging Effect on Oxide Films in Dissimilar Metal WeldsDocument9 pagesThermal Aging Effect on Oxide Films in Dissimilar Metal WeldsOscarCastilloNavaNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Measurement Techniques in Steel ReinforcedDocument15 pagesCorrosion Measurement Techniques in Steel ReinforcedVidhun RavindranNo ratings yet
- Cast Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument36 pagesCast Duplex Stainless Steelsxevi00No ratings yet
- The Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39From EverandThe Mechanical and Physical Properties of the British Standard EN Steels (B.S. 970 - 1955): EN 21 to EN 39Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)