Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ADDICTIVE MANUFACTURING BIT Edited
Uploaded by
KJ SwiftOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ADDICTIVE MANUFACTURING BIT Edited
Uploaded by
KJ SwiftCopyright:
Available Formats
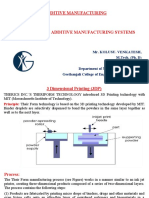
EBM Fused deposit modelling
This is an additive manufacturing machine The FDM machines from Stratasys melt
for sintering pure metal powder. The prefabricated wire-shaped thermoplastics
surface areas of a powder bed of the and lead the viscous melt through a
component contour are selectively melted heated nozzle specifically to the
with an electron beam in vacuum, which component. The stratification is done by
forms a layer after solidification (electron solidification due to heat conduction in
beam melting, EBM). The component is the partially finished component. The
created layer by layer according to the range of materials includes plastics such as
respective recoating. The Arcam EBM polycarbonate and ABS, but also high-
Control software needs slice files (SLC), performance thermoplastic plastics such
which are derived from STL data. To as polyphenylsulfones (PPSFS). In this
import the CAD data, to process the STL case, the thermoplastics and waxes are
data, to prepare individual construction supplied in the form of wire on rolls or
processes, and to slice the STL data sets, cartridges, are melted partially, and are
Arcam recommends the RP software extruded The nozzle head is guided by an
Magics (Materialise). Via the software, x-y plotter in the building plane. After
prepared building strategies can be coating a building plane, the base plate
selected or the operator can design his or with the model is lowered by a layer
her own. In the machine, practically all thickness, and the process begins anew
technically relevant materials can be with the next layer. ApplicationAreas:
melted. Arcam has a number of materials Conceptual models, function prototypes,
qualified for the process, but it also end products, series-identical
supports customized developments. components of investment castings,
There are three families of materials: tooling of moulding processes
steel, titanium materials, and CoCr alloys.
Application
Functional prototypes, end products.
Selective Laser Sintering
An additive manufacturing layer
technology, SLS involves the use of a high
power laser (for example, a carbon
dioxide laser) to fuse small particles of
plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powders
into a mass that has a desired three-
dimensional shape. The laser selectively
fuses powdered material by scanning
cross-sections generated from a 3-D
digital description of the part (for example
from a CAD file or scan data) on the
surface of a powder bed. After each cross-
section is scanned, the powder bed is
lowered by one layer thickness, a new
layer of material is applied on top, and the
process is repeated until the part is
completed.
SLM
Selective laser melting is able to process a
variety of alloys, allowing prototypes to
be functional hardware made out of the
same material as production components.
Since the components are built layer by
layer, it is possible to design complex
freeform geometries, internal features
and challenging internal passages that
could not be produced using conventional
manufacturing techniques such as casting
or otherwise machined. The process starts
by slicing the 3D CAD file data into layers,
usually from 20 to 100 micrometres thick,
creating a 2D cross-section of each layer;
this file format is the industry standard .stl
file used on most layer-based 3D printing
or stereolithography technologies.
Laminated object manufacturing:
These are prototypers based on layer
laminate manufacturing, which at Helisys,
is called laminated object manufacturing
(LOM, a protected name). Layer by layer
LASER an adhesive-coated film is adhered to a
A laser beam [1] created by a laser building platform or on the partially
generator is focused through a lens [2] completed model and contoured by the
onto the workpiece. Metal powder [3], or use of a CO2 laser plotter. All not-inherent
metal wire, is introduced at the focus of regions of the model are removed
the laser beam, where the metal powder manually after completion. Basically all
and workpiece melt and thus building on materials that are available as film can be
the surface. An inert gas [4] is supplied to used. Paper sheets are standard. In
protect both the laser and the melt from addition, plastics and ceramics are
contamination during the welding available, but they are not very common.
process. The cross section of the detail is The LOM machines currently do not play a
thus built-up step by step until the major role and are no longer sold. The
complete detail is created. The method description was left in this book because it
can also be used to repair damaged or reflects the common basic principle of all
worn surfaces and is then often described later developed machines from other
as laser welding with powder. manufacturers.
2MARKS
Binder jetting is an additive
manufacturing process in which an THERMAL BONDING
industrial printhead selectively deposits a Thermal bonding, also known as 'heat
liquid binding agent onto a thin layer of bonding' or melt bonding, is a process
powder particles — foundry sand, that actually melts the web together at
ceramics, metal or composites — to build fibre crossover points. In this process, the
high-value and one-of-a-kind parts and web is passed through a source of heat,
tooling. Binder jetting can be used to such as pressurized steam or hot air,
print a variety of materials including which causes fusion at fibre crossover
metals, sands and ceramics. Markets for points.
this process include industrial
applications, dental and medical devices, ADHESIVE BONDING
aerospace components, part casting, Adhesive Bonding is the process of
luxury applications. joining two surfaces together, usually
How electron beam function with the creation of a smooth bond. This
In EBM, electrons are released from a may involve the use of glue, epoxy, or one
heated tungsten filament; a wehnelt of a wide range of plastic agents which
electrode is used to control the bond either through the evaporation of a
convergence and intensity of the beam. solvent or through curing via heat, time,
The main advantages of this process are or pressure.
high degree of automation, high
productivity, high precision.
Powder based rpt application
1.3D Systems’ Selective Laser Sintering
(SLS)
2.Optomec's Laser Engineered Net
Shaping (LENS)
3.Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
4.Generis RP System
5.Precision Optical Manufacturing's
Direct Metal Deposition (DMDM).
Which process is suitable for extrusion
Material extrusion is the most used 3D
printing process. Fused Deposition
Modelling (FDM) is the most popular
Material Extrusion Process apart from
its open-source equivalent Fused
Filament Fabrication (FFF) which only
differs in way being legally
unconstrained.
What is the principle of LOM?
LOM technology uses adhesive-coated
paper, plastic, or metal laminates as a 3D
printing medium. These sheets of
material are glued together layer-by-
layer and cut into shape using a knife or
with laser cutting. Objects created using
LOM can then be further modified post
process by machining or drilling.
Limitation of ebm
Only works with a limited number of
metals (titanium and chromium-cobalt)
Reduced accuracy compared to laser
printers due to the slightly wider electron
beam. The materials and machines are
much more expensive than traditional
manufacturing methods.
EBM Fused deposit modelling
This is an additive manufacturing machine The FDM machines from Stratasys melt
for sintering pure metal powder. The prefabricated wire-shaped thermoplastics
surface areas of a powder bed of the and lead the viscous melt through a
component contour are selectively melted heated nozzle specifically to the
with an electron beam in vacuum, which component. The stratification is done by
forms a layer after solidification (electron solidification due to heat conduction in
beam melting, EBM). The component is the partially finished component. The
created layer by layer according to the range of materials includes plastics such as
respective recoating. The Arcam EBM polycarbonate and ABS, but also high-
Control software needs slice files (SLC), performance thermoplastic plastics such
which are derived from STL data. To as polyphenylsulfones (PPSFS). In this
import the CAD data, to process the STL case, the thermoplastics and waxes are
data, to prepare individual construction supplied in the form of wire on rolls or
processes, and to slice the STL data sets, cartridges, are melted partially, and are
Arcam recommends the RP software extruded The nozzle head is guided by an
Magics (Materialise). Via the software, x-y plotter in the building plane. After
prepared building strategies can be coating a building plane, the base plate
selected or the operator can design his or with the model is lowered by a layer
her own. In the machine, practically all thickness, and the process begins anew
technically relevant materials can be with the next layer. ApplicationAreas:
melted. Arcam has a number of materials Conceptual models, function prototypes,
qualified for the process, but it also end products, series-identical
supports customized developments. components of investment castings,
There are three families of materials: tooling of moulding processes
steel, titanium materials, and CoCr alloys.
Application
Functional prototypes, end products.
Selective Laser Sintering
An additive manufacturing layer
technology, SLS involves the use of a high
power laser (for example, a carbon
dioxide laser) to fuse small particles of
plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powders
into a mass that has a desired three-
dimensional shape. The laser selectively
fuses powdered material by scanning
cross-sections generated from a 3-D
digital description of the part (for example
from a CAD file or scan data) on the
surface of a powder bed. After each cross-
section is scanned, the powder bed is
lowered by one layer thickness, a new
layer of material is applied on top, and the
process is repeated until the part is
completed.
SLM
Selective laser melting is able to process a
variety of alloys, allowing prototypes to
be functional hardware made out of the
same material as production components.
Since the components are built layer by
layer, it is possible to design complex
freeform geometries, internal features
and challenging internal passages that
could not be produced using conventional
manufacturing techniques such as casting
or otherwise machined. The process starts
by slicing the 3D CAD file data into layers,
usually from 20 to 100 micrometres thick,
creating a 2D cross-section of each layer;
this file format is the industry standard .stl
file used on most layer-based 3D printing
or stereolithography technologies.
Laminated object manufacturing:
These are prototypers based on layer
laminate manufacturing, which at Helisys,
is called laminated object manufacturing
(LOM, a protected name). Layer by layer
LASER an adhesive-coated film is adhered to a
A laser beam [1] created by a laser building platform or on the partially
generator is focused through a lens [2] completed model and contoured by the
onto the workpiece. Metal powder [3], or use of a CO2 laser plotter. All not-inherent
metal wire, is introduced at the focus of regions of the model are removed
the laser beam, where the metal powder manually after completion. Basically all
and workpiece melt and thus building on materials that are available as film can be
the surface. An inert gas [4] is supplied to used. Paper sheets are standard. In
protect both the laser and the melt from addition, plastics and ceramics are
contamination during the welding available, but they are not very common.
process. The cross section of the detail is The LOM machines currently do not play a
thus built-up step by step until the major role and are no longer sold. The
complete detail is created. The method description was left in this book because it
can also be used to repair damaged or reflects the common basic principle of all
worn surfaces and is then often described later developed machines from other
as laser welding with powder. manufacturers.
2MARKS
Binder jetting is an additive
manufacturing process in which an THERMAL BONDING
industrial printhead selectively deposits a Thermal bonding, also known as 'heat
liquid binding agent onto a thin layer of bonding' or melt bonding, is a process
powder particles — foundry sand, that actually melts the web together at
ceramics, metal or composites — to build fibre crossover points. In this process, the
high-value and one-of-a-kind parts and web is passed through a source of heat,
tooling. Binder jetting can be used to such as pressurized steam or hot air,
print a variety of materials including which causes fusion at fibre crossover
metals, sands and ceramics. Markets for points.
this process include industrial
applications, dental and medical devices, ADHESIVE BONDING
aerospace components, part casting, Adhesive Bonding is the process of
luxury applications. joining two surfaces together, usually
How electron beam function with the creation of a smooth bond. This
In EBM, electrons are released from a may involve the use of glue, epoxy, or one
heated tungsten filament; a wehnelt of a wide range of plastic agents which
electrode is used to control the bond either through the evaporation of a
convergence and intensity of the beam. solvent or through curing via heat, time,
The main advantages of this process are or pressure.
high degree of automation, high
productivity, high precision.
Powder based rpt application
1.3D Systems’ Selective Laser Sintering
(SLS)
2.Optomec's Laser Engineered Net
Shaping (LENS)
3.Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
4.Generis RP System
5.Precision Optical Manufacturing's
Direct Metal Deposition (DMDM).
Which process is suitable for extrusion
Material extrusion is the most used 3D
printing process. Fused Deposition
Modelling (FDM) is the most popular
Material Extrusion Process apart from
its open-source equivalent Fused
Filament Fabrication (FFF) which only
differs in way being legally
unconstrained.
What is the principle of LOM?
LOM technology uses adhesive-coated
paper, plastic, or metal laminates as a 3D
printing medium. These sheets of
material are glued together layer-by-
layer and cut into shape using a knife or
with laser cutting. Objects created using
LOM can then be further modified post
process by machining or drilling.
Limitation of ebm
Only works with a limited number of
metals (titanium and chromium-cobalt)
Reduced accuracy compared to laser
printers due to the slightly wider electron
beam. The materials and machines are
much more expensive than traditional
manufacturing methods.
EBM Fused deposit modelling
This is an additive manufacturing machine The FDM machines from Stratasys melt
for sintering pure metal powder. The prefabricated wire-shaped thermoplastics
surface areas of a powder bed of the and lead the viscous melt through a
component contour are selectively melted heated nozzle specifically to the
with an electron beam in vacuum, which component. The stratification is done by
forms a layer after solidification (electron solidification due to heat conduction in
beam melting, EBM). The component is the partially finished component. The
created layer by layer according to the range of materials includes plastics such as
respective recoating. The Arcam EBM polycarbonate and ABS, but also high-
Control software needs slice files (SLC), performance thermoplastic plastics such
which are derived from STL data. To as polyphenylsulfones (PPSFS). In this
import the CAD data, to process the STL case, the thermoplastics and waxes are
data, to prepare individual construction supplied in the form of wire on rolls or
processes, and to slice the STL data sets, cartridges, are melted partially, and are
Arcam recommends the RP software extruded The nozzle head is guided by an
Magics (Materialise). Via the software, x-y plotter in the building plane. After
prepared building strategies can be coating a building plane, the base plate
selected or the operator can design his or with the model is lowered by a layer
her own. In the machine, practically all thickness, and the process begins anew
technically relevant materials can be with the next layer. ApplicationAreas:
melted. Arcam has a number of materials Conceptual models, function prototypes,
qualified for the process, but it also end products, series-identical
supports customized developments. components of investment castings,
There are three families of materials: tooling of moulding processes
steel, titanium materials, and CoCr alloys.
Application
Functional prototypes, end products.
Selective Laser Sintering
An additive manufacturing layer
technology, SLS involves the use of a high
power laser (for example, a carbon
dioxide laser) to fuse small particles of
plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powders
into a mass that has a desired three-
dimensional shape. The laser selectively
fuses powdered material by scanning
cross-sections generated from a 3-D
digital description of the part (for example
from a CAD file or scan data) on the
surface of a powder bed. After each cross-
section is scanned, the powder bed is
lowered by one layer thickness, a new
layer of material is applied on top, and the
process is repeated until the part is
completed.
SLM
Selective laser melting is able to process a
variety of alloys, allowing prototypes to
be functional hardware made out of the
same material as production components.
Since the components are built layer by
layer, it is possible to design complex
freeform geometries, internal features
and challenging internal passages that
could not be produced using conventional
manufacturing techniques such as casting
or otherwise machined. The process starts
by slicing the 3D CAD file data into layers,
usually from 20 to 100 micrometres thick,
creating a 2D cross-section of each layer;
this file format is the industry standard .stl
file used on most layer-based 3D printing
or stereolithography technologies.
Laminated object manufacturing:
These are prototypers based on layer
laminate manufacturing, which at Helisys,
is called laminated object manufacturing
(LOM, a protected name). Layer by layer
LASER an adhesive-coated film is adhered to a
A laser beam [1] created by a laser building platform or on the partially
generator is focused through a lens [2] completed model and contoured by the
onto the workpiece. Metal powder [3], or use of a CO2 laser plotter. All not-inherent
metal wire, is introduced at the focus of regions of the model are removed
the laser beam, where the metal powder manually after completion. Basically all
and workpiece melt and thus building on materials that are available as film can be
the surface. An inert gas [4] is supplied to used. Paper sheets are standard. In
protect both the laser and the melt from addition, plastics and ceramics are
contamination during the welding available, but they are not very common.
process. The cross section of the detail is The LOM machines currently do not play a
thus built-up step by step until the major role and are no longer sold. The
complete detail is created. The method description was left in this book because it
can also be used to repair damaged or reflects the common basic principle of all
worn surfaces and is then often described later developed machines from other
as laser welding with powder. manufacturers.
2MARKS
Binder jetting is an additive
manufacturing process in which an THERMAL BONDING
industrial printhead selectively deposits a Thermal bonding, also known as 'heat
liquid binding agent onto a thin layer of bonding' or melt bonding, is a process
powder particles — foundry sand, that actually melts the web together at
ceramics, metal or composites — to build fibre crossover points. In this process, the
high-value and one-of-a-kind parts and web is passed through a source of heat,
tooling. Binder jetting can be used to such as pressurized steam or hot air,
print a variety of materials including which causes fusion at fibre crossover
metals, sands and ceramics. Markets for points.
this process include industrial
applications, dental and medical devices, ADHESIVE BONDING
aerospace components, part casting, Adhesive Bonding is the process of
luxury applications. joining two surfaces together, usually
How electron beam function with the creation of a smooth bond. This
In EBM, electrons are released from a may involve the use of glue, epoxy, or one
heated tungsten filament; a wehnelt of a wide range of plastic agents which
electrode is used to control the bond either through the evaporation of a
convergence and intensity of the beam. solvent or through curing via heat, time,
The main advantages of this process are or pressure.
high degree of automation, high
productivity, high precision.
Powder based rpt application
1.3D Systems’ Selective Laser Sintering
(SLS)
2.Optomec's Laser Engineered Net
Shaping (LENS)
3.Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
4.Generis RP System
5.Precision Optical Manufacturing's
Direct Metal Deposition (DMDM).
Which process is suitable for extrusion
Material extrusion is the most used 3D
printing process. Fused Deposition
Modelling (FDM) is the most popular
Material Extrusion Process apart from
its open-source equivalent Fused
Filament Fabrication (FFF) which only
differs in way being legally
unconstrained.
What is the principle of LOM?
LOM technology uses adhesive-coated
paper, plastic, or metal laminates as a 3D
printing medium. These sheets of
material are glued together layer-by-
layer and cut into shape using a knife or
with laser cutting. Objects created using
LOM can then be further modified post
process by machining or drilling.
Limitation of ebm
Only works with a limited number of
metals (titanium and chromium-cobalt)
Reduced accuracy compared to laser
printers due to the slightly wider electron
beam. The materials and machines are
much more expensive than traditional
manufacturing methods.
You might also like
- Thesis MastersDocument61 pagesThesis MastersCherub GundalaNo ratings yet
- Types of Additive Manufacturing TechnologyDocument7 pagesTypes of Additive Manufacturing Technologydeekamittal100% (1)
- BND Suggested Additive Manufacturing by Prof. B. DoloiDocument82 pagesBND Suggested Additive Manufacturing by Prof. B. DoloiTamojit MondalNo ratings yet
- Laser Sintering Guide: SLS, LENS & Ceramic PartsDocument5 pagesLaser Sintering Guide: SLS, LENS & Ceramic PartsVS AnoopNo ratings yet
- ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMSDocument19 pagesADDITIVE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMSnarasimhanaiduNo ratings yet
- Rapid Pro To TypingDocument21 pagesRapid Pro To TypingRaman KingNo ratings yet
- A Review of Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) Aspects and Various Processes Used in ItDocument9 pagesA Review of Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) Aspects and Various Processes Used in ItIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Key DifferencesDocument12 pages3D Printing vs CNC Machining: Key DifferencesAKASHNo ratings yet
- Selective Laser MeltingDocument12 pagesSelective Laser MeltingAngry BirdNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing Notes Unit II Solid Based RPSDocument10 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Notes Unit II Solid Based RPSVenkata Naveen MaddaliNo ratings yet
- Optimisation of SLM 3D Printing Process Through Simulation and Experimental AnalysisDocument10 pagesOptimisation of SLM 3D Printing Process Through Simulation and Experimental Analysispritish_09No ratings yet
- Sinhgad College of Engineering, Pune - 41Document11 pagesSinhgad College of Engineering, Pune - 41NikNo ratings yet
- 3D Printer InformationDocument16 pages3D Printer Informationmahesh mulikNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Rapid PrototypingDocument7 pagesCase Study On Rapid PrototypingSachin KumbharNo ratings yet
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Process ExplainedDocument5 pagesSelective Laser Sintering (SLS) Process ExplainedMunaf BadeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 3D PrinterDocument11 pagesIntroduction To 3D PrinterNilanka HarshaniNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sintering Parameters and Flow Agent on Tensile Properties of Elastomer PartsDocument12 pagesEffect of Sintering Parameters and Flow Agent on Tensile Properties of Elastomer PartsmakrsnakminesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document30 pagesUnit 3Sattya Devi ThapaNo ratings yet
- Powder Bed Fusion - DMLS, SLS, SLM, MJF, EBMDocument2 pagesPowder Bed Fusion - DMLS, SLS, SLM, MJF, EBMYeabsraNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument16 pages3D Printingsagar_sgrNo ratings yet
- Laser Polishing A Review of A Constantly Growing TDocument41 pagesLaser Polishing A Review of A Constantly Growing TNa Wee KwongNo ratings yet
- Fused Deposition Modelling of Synthetic FibersDocument15 pagesFused Deposition Modelling of Synthetic Fibersaariyaraj.pNo ratings yet
- Fig 1.1 Principle of Layer Manufacturing ProcessDocument39 pagesFig 1.1 Principle of Layer Manufacturing ProcessgauravNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Rapid Prototyping: Presented byDocument29 pagesSeminar On Rapid Prototyping: Presented byksNo ratings yet
- Trade 2 PDFDocument7 pagesTrade 2 PDFRajveer Singh SachdevNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing: Additive Manufacturing GuideDocument10 pages3D Printing: Additive Manufacturing GuideKelvin Dale YubidiNo ratings yet
- latticestructuredesignforAM ResearchgateDocument22 pageslatticestructuredesignforAM ResearchgateUttam AnimireddyNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing - Technology Applications and Research NeedsDocument29 pagesAdditive Manufacturing - Technology Applications and Research NeedsCRISA3000000No ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing WorksheetDocument8 pagesAdditive Manufacturing WorksheetMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topology Optimization NotesDocument8 pagesTopology Optimization NotesJon SnowNo ratings yet
- 3D PrintingDocument11 pages3D PrintingDat BoiNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing and NanotechnologyDocument18 pages3D Printing and NanotechnologyJoyitaNo ratings yet
- RAPID PROTOTYPING TECHNOLOGIESDocument11 pagesRAPID PROTOTYPING TECHNOLOGIESAbhishek TuliNo ratings yet
- AMT Notes Unit-3Document30 pagesAMT Notes Unit-3Suddapally VIVEK ReddyNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing ReportDocument15 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Reportbalakumarankeb100% (1)
- 3D Printing Lab Manual: WorkingDocument7 pages3D Printing Lab Manual: WorkingJithin67% (3)
- Additive ManufacturingDocument64 pagesAdditive ManufacturingYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing: A New Era in Manufacturing TechnologiesDocument7 pages3D Printing: A New Era in Manufacturing TechnologiesashishNo ratings yet
- 3dprintingpracticelab 230710091102 b46f4fddDocument36 pages3dprintingpracticelab 230710091102 b46f4fddchantiNo ratings yet
- Atm 2022 1 004Document5 pagesAtm 2022 1 004joskov71No ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EnginneringDocument11 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EnginneringViraj SukaleNo ratings yet
- Different Types of 3D Printers Selective Laser Sintering: Sls Process Physical Phenomena in Sls A Ray Tracing ModelDocument11 pagesDifferent Types of 3D Printers Selective Laser Sintering: Sls Process Physical Phenomena in Sls A Ray Tracing ModelGuruprasad B SNo ratings yet
- Workshop_3D_Printing_report_Document11 pagesWorkshop_3D_Printing_report_Sathvik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping: Create Something QuicklyDocument8 pagesRapid Prototyping: Create Something QuicklyAnonymous ecgeyhVNo ratings yet
- Instituto Tecnológico de Gustavo A. Madero IiDocument10 pagesInstituto Tecnológico de Gustavo A. Madero IiMarcos ZarateNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument4 pagesAdditive ManufacturingUttam AnimireddyNo ratings yet
- Computers and Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesDocument33 pagesComputers and Additive Manufacturing TechnologiesKîshØr PåshÅNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument9 pagesAdditive ManufacturingEsteban EroNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing: N. Sinha Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT KanpurDocument64 pagesAdditive Manufacturing: N. Sinha Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpurganesh dongreNo ratings yet
- Laser Polishing of 3D Printed Metallic ComponentsDocument10 pagesLaser Polishing of 3D Printed Metallic ComponentsMahaboob BashaNo ratings yet
- Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) guideDocument3 pagesDirect metal laser sintering (DMLS) guideDharshan KofiNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Copper Filament for Layered FabricationDocument6 pages3D Printing Copper Filament for Layered FabricationReinaldi Luthfi AmirNo ratings yet
- ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING On 18.5.20Document10 pagesADDITIVE MANUFACTURING On 18.5.20aravindNo ratings yet
- Additive ManufacturingDocument18 pagesAdditive ManufacturingKaran KavanalNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing and Naval Architecture A Literature ReviewDocument10 pages3D Printing and Naval Architecture A Literature Reviewhamed sadaghianNo ratings yet
- Selective Laser SinteringDocument5 pagesSelective Laser Sinteringmanoharanpark_433315No ratings yet
- Activity 1 NewDocument11 pagesActivity 1 NewsuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Ijser: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) MechanismDocument3 pagesIjser: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) MechanismSamir BoseNo ratings yet
- FDM 3D Printing GuideDocument39 pagesFDM 3D Printing GuideSujith S NairNo ratings yet
- QSP-01 FR-01 Masterlist of QMSDocument5 pagesQSP-01 FR-01 Masterlist of QMSWan Mohd FarzrinNo ratings yet
- SOLIDWORKS Simulation ProfessionalDocument1 pageSOLIDWORKS Simulation ProfessionalpinguituxNo ratings yet
- Ebook - Panton ChairDocument68 pagesEbook - Panton Chairchemino76No ratings yet
- MAPs Limited Contention ProtocolsDocument60 pagesMAPs Limited Contention ProtocolsSahilPrabhakar100% (1)
- Thesis DocumentationDocument69 pagesThesis DocumentationKamiru ChanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Reaction RateDocument4 pagesEffect of Enzyme Concentration on Reaction RateormattNo ratings yet
- M.tech Petroleum EngineeringDocument2 pagesM.tech Petroleum EngineeringAqinwandeNo ratings yet
- HistorianRetrieval PDFDocument233 pagesHistorianRetrieval PDFynnaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLelCrisNo ratings yet
- EBR-EPG Eng 02 2155065Document2 pagesEBR-EPG Eng 02 2155065Драгиша Небитни ТрифуновићNo ratings yet
- 18a.security GSM & CDMADocument18 pages18a.security GSM & CDMAwcdma123No ratings yet
- MOSFET Amplifier Large Signal AnalysisDocument21 pagesMOSFET Amplifier Large Signal AnalysisRaghav100% (1)
- Cooling Water System : Daily Log Sheet Date: .. Shift TimeDocument4 pagesCooling Water System : Daily Log Sheet Date: .. Shift TimeNata ChaNo ratings yet
- 1.blowers Air Supply Silencer PDFDocument8 pages1.blowers Air Supply Silencer PDFYendry Huezo RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ziegler-Mfm-3480 Manual-E1R0Document78 pagesZiegler-Mfm-3480 Manual-E1R0Naveed Syed MohammadNo ratings yet
- Honeywell L91B Manual (En)Document10 pagesHoneywell L91B Manual (En)Alejandro GilNo ratings yet
- Guia Técnico - Tomadas Industriais PDFDocument26 pagesGuia Técnico - Tomadas Industriais PDFNuno HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Inversor Min Growatt 8000 TL XDocument2 pagesInversor Min Growatt 8000 TL XIngenieria 2No ratings yet
- 03814Document22 pages03814Cloud BeezerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Material For CBSE Class-12Document246 pagesChemistry Study Material For CBSE Class-12Apex Institute75% (4)
- Capacity Method For PV PlantDocument38 pagesCapacity Method For PV PlantAzree Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Practical 1: AIM:-Write All The Queries For Data DefinitionDocument15 pagesPractical 1: AIM:-Write All The Queries For Data DefinitionPoojaNo ratings yet
- Series S6500 User ManualDocument24 pagesSeries S6500 User ManualRoberto CarlosNo ratings yet
- PRICE E1203257Mrev4-20-EST-JON EPPM MARAFIQ STG 5&6 FPS OPTION 2Document13 pagesPRICE E1203257Mrev4-20-EST-JON EPPM MARAFIQ STG 5&6 FPS OPTION 2AliZenatiNo ratings yet
- Autosar Sws Spi HandlerdriverDocument76 pagesAutosar Sws Spi Handlerdriverkrnl386No ratings yet
- Bituseal Liquid: Heavy Duty Bituminous CoatingDocument2 pagesBituseal Liquid: Heavy Duty Bituminous Coatingengramir07No ratings yet
- VIN plate decoding and Mopar part illustrationsDocument429 pagesVIN plate decoding and Mopar part illustrationsJay Andrews100% (2)
- Device and Method For Adaptive Control of Blanks MachiningDocument4 pagesDevice and Method For Adaptive Control of Blanks MachiningspriditisNo ratings yet
- Gramhal Massachusetts Institute of Technology Echoing Green Mittal InstituteDocument1 pageGramhal Massachusetts Institute of Technology Echoing Green Mittal InstituteStephen HasslerNo ratings yet