Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FINALS Ophtha
Uploaded by
Gio GelilangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FINALS Ophtha
Uploaded by
Gio GelilangCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
All except one constitutes aqueous barrier: Ciliary Muscle
2. In what condition is disc edema not visualized in fundoscopy High Myopia (longer, bigger eyes)
3. Primary colors: Red , Green, Blue
4. In the perception of colors is it necessary to: a. Accept the presence of different cortical
visual sets
b. Accept the presence of different major
intralateral chamber body
c. It is affected by illumination
d. Postulate to different photoreceptors
e. None of the above
f. All of the above
5. The visibility spectrum is what 4 - 600 nm
6. In an infant, it is difficult to dilate the pupil because: Underdeveloped SYMpathetic nerve supply
7. Best differentiates papillitis from papilledema The visual acuity is almost always UNaffected in the
early stage
8. Clinical feature of amblyopia are the following except: Neutral density filters reduce visual acuity
9. Esotropia prism measurement is oriented as: a. Apex in / apex out
b. Base in / base out
10. Retinoschisis: It arises from peripheral cystoid degeneration of the
nerve fiber layer
11. Irisch nodule may be seen in the following conditions except: a. Neurofibromatosis
b. Metastatic Ca
c. Leimyoma
d. Juvenile xanthogranuloma
e. Tuberous Sclerosis
12. All of the following are true about malignant melanoma except: a. Usually managed by simple excision after
diagnosis is clearly established
b. Good prognosis
c. Epithelial in nature
d. Tend to develop in the inferior of the iris
e. It is not readily diagnosed with fluorescent
angiography ultrasound
13. Which of the following choices is a poor choice to treat pseudomonas a. Amikacin
keratitis b. Cefalotin
c. Perphenazine
d. Polymixin B
e. Tobramycin
f. None of the above
14. A man with retinitis pigmentosa marries his first cousin, their mothers are X - linked Recessive
sisters. Although there is no family history . . . . with 2 normal daughters, 2
normal sons . . . . not applicable for this pedigree?
15. The gene for retinitis pigmentosa is linked with Proximal portion of the short arm
16. If a recessive defect is observed in 1 / 10,000 persons, the chance of an 1 in 50
individual to become a carrier of a disease entity is:
17. Oculocutaneous albino marries a woman with normal color vision and 1/8
pigmentation. Their first birth is not albino . . . . . what is the risk of the second
child to have the same phenotype:
18. Which of the following histopathologic findings does not support the a. Full thickness corneal scar
diagnosis of sympathetic ophthalmia? b. Dalen Fuchs Nodules
c. Neovascularization of the retina
d. Lymphocytic infiltration of the uveal tract
19. If left untreated, which lesion is most likely to evolve into cancer? a. Actinic keratosis
b. Inverted follicular keratosis
c. Seborrheic keratosis
d. Intradermal Nevus
20. One year after a man had mild contusion, injury to the eye resulted to Angle recession
hyphemia. . . . most likely will exhibit one of the following:
21. When you enucleate an eye because of RB, the pathology report contains The tumor is present in the optic nerve, at the plane of
. . . . . . which has greatest prognostic importance? the surgical transection
22. In RB, all of the following are true except: The tumor often contains the Homer-Wright Rosettes
23. A female survivor of retinoblastoma with a positive family history has 2 50%
normal children. . . . . . . . the chances of having the third child developing RB
is approximately:
24. Contact lens wearer results in all of the following EXCEPT It decreases the availability of glucose for metabolic
use
25. If a child has cycloplegic refraction, OD +5, OS +1, (spherical) the Fully corrected
anisometropia should be:
26. Minus Lens: Biconcave
For nearsighted (myopic)
Eyes: LONGER and LARGER
27. Plus Lens: Biconvex
For farsighted (hyperopic)
Eyes: SMALLER, SHORTER
28. Presbyopia: Common among elderly women (60s)
MATCHING TYPE
29. Non-fenestrated endothelial cells Branch Retinal Arteriole
30. Myoepithelial cells Anterior pigmented layer of iris
31. Basement Membrane Descemet’s Membrane
32. Central Connecting Cilium Rod Outer Segment
33. Elastic Fibers Bruch’s Membrane
34. Abducens nerve (CN VI) a. Undergoes partial decussations
b. Contains motor and sensory fibers
c. Traverses through the roof of the cavernous sinus
d. Decussates completely
e. Nucleus is located in the floor of the 4th ventricle
35. All of the following are true about cotton wool spots except:
a. They are often seen in hypertensive retinopathy
b. They are creamy or cloud-like and obscure
underlying vessels
c. They are the result of focal retinal ischemia
d. They are the clinical counterpart of swollen axons in
the nerve fiber layer
e. They are located in the outer retinal layers
36. Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
a. Undergoes partial decussations
b. Contains motor and sensory fibers
c. Traverses through the roof of the cavernous sinus
d. Decussates completely
e. Nucleus is located in the floor of the 4th ventricle
37. Elastic fibers Bruch’s Membrane
38. Choroidal nevi may have all of the following except: a. Subretinal neovascularization
b. Subretinal fluid
c. Overlying drusens
d. Overlying orange (Lipofuscin) spots
e. Variable growth patterns
39. All of the following are potential uses for monoclonal antibodies except: a. Identifying specific subsets of t-lymphocytes
b. Treatment of metastatic retinoblastoma
c. Improving radionuclide imaging techniques
d. Treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis
e. Identifying infections agents in biopsy specimens
40. Non-fenestrated endothelial cells a. Rod outer segment
b. Branch retinal arteriole
c. Descemet’s membrane
d. Bruch’s membrane
e. Anterior pigmented layer of the iris
41. Peripheral anterior synechiae may be seen in all of the following disease a. Blunt trauma with postcontusion angle recession
entities except: b. Chronic iridis
c. Angle closure glaucoma
d. Diabetes with rubeosis iridis
e. Primary open angle glaucoma
42. All of the following relate to a ring scrotoma except a. It is responsible for the jack-in-the-box
phenomenon
b. It is most noticeable in middle distances (between 3
and 12 feet)
c. It is produced by high plus lenses
d. It is eliminated by correct curve lenses
43. In which of the following conditions might it be helpful to enhance the a. Allergic conjunctivitis
immune response with an immuno-potentiating drug? b. Uveitis
c. Malignant melanoma of the choroid
d. Sympathetic ophthalmia
e. Urticaria
44. Presbyopia becomes sympathetic a. Earlier in patients with small pupils than in patients
with large pupils
b. Earlier in women than in men
c. In uncorrected hyperopes earlier than in
uncorrected myopes
d. In uncorrected myopes than in uncorrected
hyperopes
e. Earlier in men than women
45. The following histopathologic features are characteristic of chronic a. Staphyloma
glaucoma except
b. Loss of rods and cones
c. Decreased number of ganglion cells in the retina
d. Gliosis and thickening of the pial septa in the optic
nerve
e. None of the above
46. Trigeminal nerve (CN V) a. Traverses through the roof of the cavernous sinus
b. Nucleus is located in the floor of the 4th ventricle
c. Undergoes partial decussations
d. Decussates completely
e. Contains motor and sensory fibers
47. Cromolyn sodium has been a useful drug in the treatment of allergic a. Is an excellent antihistamine
conjunctivitis
b. Decreases the need for steroid and has low toxicity
and side effects
c. Degranulates mast cells better than steroid
d. Reduces eosinophil counts in the tears
e. Eliminates the need for using topical steroids
48. True statement about disturbances of ocular pigmentations a. Commonly found in the fundus of an infant with
congenital rubella syndrome
b. Those seen as oval hyperpigmentation in a section
of the fundus are congenital
c. Usually from an error in tyrosine metabolism
d. Usually results in heterochromia iridis
49. Which one of the following histopathologic findings does not support a a. Aggregations of epithelioid cells in a wear tract
diagnosis of ocular diabetes?
b. Cystoid spaces in the outer layer of the retina that
are filled with lipoproteinaceous material
c. Vacuolization of the pigment epithelium of the iris
d. Neovascular membrane extending from the inner
surface to the retina through the internal limiting
membrane
50. A true (non-artifactitious) chronic retinal detachment would be described a. Retinal breaks with rounded margins
histopathologically by all of the following except:
b. Retinal microcysts
c. Drusen formation
d. Retroretinal membrane
e. Intact photoreceptors
51. Select the true statements about aplasia of the optic nerve a. The retinal vessels are absent
b. Aplasia may occur in an eye which appears normal
externally
c. An anterior coloboma occurs relatively frequently
with aplasia of the optic
d. The condition is usually bilateral
e. All of the above
52. Oculomotor nerve a. Nucleus is located in the floor of the 4th ventricle
b. Undergoes partial decussations
c. Traverses through the roof of the cavernous sinus
d. Contains motor and sensory fibers
e. Decussates completely
53. The insertion of the superior rectus muscle a. Overlies the thickest portion of the sclera
b. Located posterior to the ora serrata
c. Nearer the limbus then the insertion of the lateral
rectus muscle
d. Overlies the thinnest portion of the sclera
54. Which lesion has the best prognosis for life? a. Spindle cell melanoma confined to the iris
b. Spindle cell melanoma of the ciliary body
c. Spindle cell melanoma confined to the choroid
d. Melanocytoma of the optic nerve
e. Totally necrotic melanoma confined to the choroid
55. Which answer best characterize band keratopathy? a. Amyloid
b. Calcium
c. Copper
d. Fibrosis
e. Iron
56. Which statement comparing retinoblastoma to choroidal melanoma is a. Both tend to invade the optic nerve
false
b. Both undergo spontaneous necrosis
c. Both can be diagnosed by ocular ultrasonography
d. Both can give rise to neovascularization
e. Prognosis of both worsens with extraocular
extensions
57. The most likely source of a tumor metastatic to the choroid in a women is a. Colon
b. Cervix
c. Breast
d. Kidney
e. Lung
58. Optic nerve (CN II) a. Nucleus is located in the floor of the 4th ventricle
b. Undergoes partial decussations
c. Traverses through the roof of the cavernous sinus
d. Contains motor and sensory fibers
e. Decussates completely
59. A corrected curve lens is designed to a. Minimize glass thickness
b. Minimize marginal astigmatism
c. Reduce light reflection
d. Reduce spherical aberration
e. Improve light transmission
60. True about aniridia a. Cardiac anomalies often occur in the same
individual
b. In association with nystagmus, cataract, glaucoma
and corneal pannus
c. May be associated with lymphoma in children
d. Usually inherited as an autosomal recessive trait
e. None of the above
61. The hyaloid artery a. Regresses before birth
b. Forms a vascular plexus with the tunica vasculosa
lentis
c. Gives rise to the choroidal vessels
d. Branch of the carotid artery
e. Regresses before birth and forms a vascular plexus
with the tunica vasculosa lentils
f. All of the above
62. A tapetal-like reflex is seen in the fundus of some carriers of: a. Protanopia
b. Choroideremia
c. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa
d. Ocular albinism
e. X-linked juvenile retinoschisis
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Clinical Dermatology MorphologyDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Clinical Dermatology MorphologyJonnie Rose Louise WeeNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology (Review Center)Document12 pagesOral Pathology (Review Center)yellow rangerNo ratings yet
- Gen-Path-Oral-Path-Microbio-Complete (AutoRecovered)Document10 pagesGen-Path-Oral-Path-Microbio-Complete (AutoRecovered)DENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet
- Ophtha - Internship RecallsDocument6 pagesOphtha - Internship RecallsKate Alyssa CatonNo ratings yet
- AIIMS & NEET Ophthalmology Memory QuestionsDocument13 pagesAIIMS & NEET Ophthalmology Memory QuestionsRahul UNo ratings yet
- Ophtha Quiz - Ocular Manifestations of SystemicDocument3 pagesOphtha Quiz - Ocular Manifestations of SystemicAsif MohammedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Oral Cancer Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Oral Cancer Review QuestionsDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- 11 Neurology PDFDocument17 pages11 Neurology PDFalialison7666100% (1)
- Ophtha Quiz - NeurophthalmogyDocument2 pagesOphtha Quiz - NeurophthalmogyadiNo ratings yet
- Jogi. Mcqs-1Document47 pagesJogi. Mcqs-1Fazan Gem100% (3)
- CPSP Demo Mcqs - 2022Document24 pagesCPSP Demo Mcqs - 2022Farhan AfzalNo ratings yet
- RetinaDocument11 pagesRetinaSophia NuelleNo ratings yet
- Ophtha Quiz - INI CET High Yield TopicsDocument3 pagesOphtha Quiz - INI CET High Yield TopicsAsif MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2 OS To PrintDocument12 pages2 OS To PrintDENTAL REVIEWER ONLY0% (1)
- Neet TestDocument26 pagesNeet Testanurag sharmaNo ratings yet
- Final SET 2 Formated by PSB in HomeDocument28 pagesFinal SET 2 Formated by PSB in HomeBikram KarkiNo ratings yet
- Ortho Chennai Test 2020Document4 pagesOrtho Chennai Test 2020ArvindhanNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Pathology Exam 2nd 20016Document3 pagesUrinary System Pathology Exam 2nd 20016الهاشميNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology (Final) PDFDocument15 pagesOphthalmology (Final) PDFadi100% (2)
- Ophtha Quiz - NeurophthalmologyDocument2 pagesOphtha Quiz - NeurophthalmologyadiNo ratings yet
- 3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDocument25 pages3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet
- ENTDocument5 pagesENTjohn denver floresNo ratings yet
- 17th Session Grand Test-2 Qus. 26-Feb-2017Document10 pages17th Session Grand Test-2 Qus. 26-Feb-2017Satya AsatyaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument177 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFNishankumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Name: Year Level: Date: Score: /20 Exam NumberDocument2 pagesName: Year Level: Date: Score: /20 Exam NumberMoritz SolivenNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Introduction: Table 11-1. Glaucoma Classified According To EtiologyDocument28 pagesGlaucoma: Introduction: Table 11-1. Glaucoma Classified According To EtiologyPradnya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Fmge June 2021: QuestionsDocument13 pagesFmge June 2021: QuestionsSUBHADIPNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: Aiims MedeasyDocument19 pagesGeneral Surgery: Aiims Medeasyvk100% (2)
- Optho Diams QDocument5 pagesOptho Diams QShawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO Revised + Extra QsDocument68 pagesPHYSIO Revised + Extra Qsdoaa naieemNo ratings yet
- Answer: FDocument8 pagesAnswer: FChethranNo ratings yet
- Ophtha Quiz - Glaucoma & UveitisDocument3 pagesOphtha Quiz - Glaucoma & UveitisadiNo ratings yet
- IBQs & MCQsDocument58 pagesIBQs & MCQsskNo ratings yet
- EntDocument26 pagesEntNuriaNo ratings yet
- PCol - AnesthDocument6 pagesPCol - AnesthRichelle100% (1)
- Bhatia MCQ Oral Max SurgeryDocument49 pagesBhatia MCQ Oral Max SurgeryAhmed Marmash100% (1)
- Eye Mcqs . Usman Ali TatlaDocument12 pagesEye Mcqs . Usman Ali TatlaMedic GuruNo ratings yet
- Eye McqsDocument15 pagesEye Mcqsusama100% (2)
- Kims PapersDocument5 pagesKims Papersmhaider8503No ratings yet
- Dr. Marwah'S Test Series Whatsapp Number: 9873835363, 8447982490,9717143789Document15 pagesDr. Marwah'S Test Series Whatsapp Number: 9873835363, 8447982490,97171437891S@M1No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On ToxicologyDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On ToxicologyManthar Rathore100% (1)
- Answendo PerioDocument5 pagesAnswendo Periof9fhzxszqcNo ratings yet
- Pathology Board Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesPathology Board Exam QuestionschristinejoanNo ratings yet
- Mosbys - Oral Diagnosis Oral Surgery and Radiology 2015Document6 pagesMosbys - Oral Diagnosis Oral Surgery and Radiology 2015LangNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ophthalmology OSHMUDocument27 pagesMCQ Ophthalmology OSHMUPlutonic HeartNo ratings yet
- 7 AIIMS May 11 PDFDocument38 pages7 AIIMS May 11 PDFSayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Eval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010Document3 pagesEval Exam-Ans Key-Ref-Onco - 2010marlon armamento100% (1)
- Nle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDDocument12 pagesNle FC Manila 2023 May - EDITEDAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Quiz GlaucomaDocument2 pagesOphthalmology Quiz GlaucomaMohammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Fmge Dec 2019: QuestionsDocument16 pagesFmge Dec 2019: QuestionsSUBHADIPNo ratings yet
- NEET MDS Mock TestDocument158 pagesNEET MDS Mock TestAysha NazrinNo ratings yet
- Dental Hygiene Board Exam Sample QuestionsDocument3 pagesDental Hygiene Board Exam Sample Questionsgeislernet100% (5)
- Ophthalmology and obstetrics/gynecology exam questionsDocument10 pagesOphthalmology and obstetrics/gynecology exam questionsOmesh PrathirajaNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Skin Conditions and TreatmentsDocument8 pagesDermatology Skin Conditions and TreatmentsMichael NyaataNo ratings yet
- Retina conditions, eye diseases and vision loss causesDocument4 pagesRetina conditions, eye diseases and vision loss causesSyam k rajNo ratings yet
- ZPretest Oralhis Micbio.Document6 pagesZPretest Oralhis Micbio.leemia1030No ratings yet
- Integumentary Post TestDocument7 pagesIntegumentary Post TestJay AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Anatomía Relacional de Los Músculos MiméticosDocument5 pagesAnatomía Relacional de Los Músculos MiméticosLizeth Conde OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Brick AssDocument12 pagesBrick AssInaf NafiNo ratings yet
- BASF Puristar R3-12 - BF-9220 - PuriStar - R3-12 - PDS - Rev.2020-12 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesBASF Puristar R3-12 - BF-9220 - PuriStar - R3-12 - PDS - Rev.2020-12 Spec SheetAlNo ratings yet
- Steps in Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument28 pagesSteps in Balancing Redox ReactionsRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- PAES 422-1-2012 - Agricultural Structures - Poultry Dressing Slaughtering Plan - Part 1 Small Sca PDFDocument32 pagesPAES 422-1-2012 - Agricultural Structures - Poultry Dressing Slaughtering Plan - Part 1 Small Sca PDFJohn VelacioNo ratings yet
- h04 High Sulphidation Epithermal Au Ag CuDocument6 pagesh04 High Sulphidation Epithermal Au Ag CuErenz Emerald AlexandriteNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation Guidelines for DentistsDocument18 pagesConscious Sedation Guidelines for DentistsAnna NgNo ratings yet
- The Giant First YearDocument1,234 pagesThe Giant First YearEthan DyerNo ratings yet
- Ia On Solubility EquilibriumDocument8 pagesIa On Solubility Equilibriumapi-235913605100% (1)
- Banking Question PapersDocument12 pagesBanking Question Papersmohak khinNo ratings yet
- Clearing Clutter With Eft PDFDocument23 pagesClearing Clutter With Eft PDFIftikhar Hassun100% (2)
- Method Statement - 23apr18Document5 pagesMethod Statement - 23apr18hinitahNo ratings yet
- Ureteral Trauma Profile in Soetomo Hospital January 2006 - December 2011Document9 pagesUreteral Trauma Profile in Soetomo Hospital January 2006 - December 2011Nurhafidin RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument218 pagesPDFRague MiueiNo ratings yet
- Example Hospital Development PlanDocument6 pagesExample Hospital Development PlanMary Jean Gelito0% (1)
- Spain-Final ProjectDocument29 pagesSpain-Final Projectapi-264431075No ratings yet
- Materials System Specification: 04-SAMSS-001 21 December 2008 Gate Valves Valves Standards Committee MembersDocument10 pagesMaterials System Specification: 04-SAMSS-001 21 December 2008 Gate Valves Valves Standards Committee MembersAkilesh Aravindakshan100% (1)
- 17 Subcon RequirementsDocument38 pages17 Subcon RequirementsMohammed MinhajNo ratings yet
- Pro XP Manual Electrostatic Guns For Waterborne ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPro XP Manual Electrostatic Guns For Waterborne ApplicationsDiogo MatosNo ratings yet
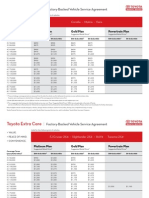
- Toyota Extra Care Factory Vehicle Service PlansDocument5 pagesToyota Extra Care Factory Vehicle Service PlansAnjihartsNo ratings yet
- CP107 Vol II-ERT 2B - 12-Dec 2019 (PA) - 3Document209 pagesCP107 Vol II-ERT 2B - 12-Dec 2019 (PA) - 3NghiaNo ratings yet
- Calcium chloride MSDSDocument5 pagesCalcium chloride MSDSDarshilNo ratings yet
- Moderate and Extreme HypofractionationDocument32 pagesModerate and Extreme HypofractionationsamuelfsjNo ratings yet
- 1 Design Engineering Drawings For The EasyDry M500 JD Version PDFDocument169 pages1 Design Engineering Drawings For The EasyDry M500 JD Version PDFSelim Lukman100% (1)
- ACCOMPLISHMENT REPORT School Managed Canteen and WINsDocument7 pagesACCOMPLISHMENT REPORT School Managed Canteen and WINsJohnson Daquiaog BenitezNo ratings yet
- Allis Chalmers 840 840b Articulated Wheel Loader Forklift Parts CatalogDocument20 pagesAllis Chalmers 840 840b Articulated Wheel Loader Forklift Parts CatalogCarl100% (42)
- IQCODE English Short FormDocument3 pagesIQCODE English Short FormMihai ZamfirNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I BCM211: Zatilfarihiah RasdiDocument24 pagesBiochemistry I BCM211: Zatilfarihiah Rasdiستي نوراسيقينNo ratings yet
- PDF Fcuk CTLG 2020 Split 01Document46 pagesPDF Fcuk CTLG 2020 Split 01Ted Andrew AbalosNo ratings yet
- Comp Carlyle Torque PDFDocument125 pagesComp Carlyle Torque PDFjsnavarro1o100% (2)