Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pomodoro
Pomodoro
Uploaded by
A HOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pomodoro
Pomodoro
Uploaded by
A HCopyright:
Available Formats
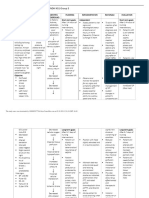
Treatment of hyperthyroidism, primary drug for Grave's
Indications
hyperthyroidism,
Pregnancy and nursing mothers, immune cross
Contraindications
reactivity with propylthiouracil
Anion Inhibitors (Methimazole,
Propylthiouracil) Pharmacokinetics
blocks synthesis of new thyroid hormo
ne;
Maculopapular rash, agranulocytosis, hepatitis,
Side Effects cholestatic jaundice, nausea, GI distress, altered t
aste or smell
Preparation for thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine
Indications
therapy, treatment of thyroid storm
Contraindications Pregnancy and nursing mothers, iodine allergy
Iodides
Inhibits release of thyroid hormone from gland,
Pharmacokinetics
decreases size and vascularity of gland
Metallic taste, salivary gland swelling, rash, iodism
Side Effects
(headache, coryza, conjunctivitis, angioedema)
Antithyroid agent Treatment of hyperthyroidism, primary treatment for
Indications Grave's hyperthyroidism, used when other t
reatments have failed or are contraindicated.
Pregnancy and nursing mothers, severe
Contraindications
ophthalmopathy
Radioactive Iodine
Concentrates in thyroid tissue and destroys thyroid
Pharmacokinetics
cells
Hypothyroidism, radiation sickness, transient
Side Effects
worsening of hyperthyroidism
Propranolol widely studied and used in the therapy of
Indications thyrotoxicosis, beta blockers cause clinical i
mprovement of hyperthyroid symptoms
Contraindications impotence
Adrenoceptor-Blocking Agents
(Metoprolol, Propranolol, Atenolol) Propranolol inhibits 5'-monodeiodinase that converts
L-thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyroni
Pharmacokinetics
ne (T3), competitively blocks both β1 and β2
adrenergic receptors.
Side Effects hypotension ,
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MMC 1Document6 pagesMMC 1A HNo ratings yet
- Writesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576Document1 pageWritesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576A HNo ratings yet
- Method fo-WPS OfficenDocument3 pagesMethod fo-WPS OfficenA HNo ratings yet
- Presentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02Document12 pagesPresentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02A HNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803Document2 pagesQuiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803A HNo ratings yet
- Model Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317Document3 pagesModel Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317A HNo ratings yet
- Shen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407Document13 pagesShen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407A HNo ratings yet
- Status and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingDocument8 pagesStatus and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingA HNo ratings yet
- I. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeDocument4 pagesI. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeA HNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesElectrochemistryA HNo ratings yet
- 4 5915746627611529826Document4 pages4 5915746627611529826A HNo ratings yet
- 19976251Document2 pages19976251A HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan StrokeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan StrokeA HNo ratings yet
- Mod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012Document3 pagesMod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012A HNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument16 pagesRelationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyA HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFA HNo ratings yet
- Turner's SyndromeDocument3 pagesTurner's SyndromeA HNo ratings yet
- NPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021Document14 pagesNPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021A HNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke Care Plan PaperDocument12 pagesIschemic Stroke Care Plan PaperA HNo ratings yet
- 2581 Fuel CellDocument6 pages2581 Fuel CellA HNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewDocument5 pagesFuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewA HNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument2 pagesPosterA HNo ratings yet
- WA0054mmmDocument4 pagesWA0054mmmA HNo ratings yet
- Practical For StudentsDocument50 pagesPractical For StudentsA HNo ratings yet
- Title-WPS OfficemjDocument1 pageTitle-WPS OfficemjA HNo ratings yet
- Writing Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphDocument12 pagesWriting Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphA HNo ratings yet
- Objective 1 - De-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesObjective 1 - De-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document4 pagesWa0001A HNo ratings yet
- Wa0018Document2 pagesWa0018A HNo ratings yet