Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female Reproductive System Glossary
Uploaded by
HASSAM KHAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesThe document defines key anatomical parts, conditions, procedures, tests, devices, and medications related to the female reproductive system. It provides definitions and equivalent terms for structures like the uterus, cervix, and vulva. It also defines common conditions such as HPV, mastitis, and preeclampsia. Reproductive procedures like mammograms, dilation and curettage, and cesarean sections are outlined. Finally, the summary lists various contraceptive methods and medications used in reproductive healthcare.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key anatomical parts, conditions, procedures, tests, devices, and medications related to the female reproductive system. It provides definitions and equivalent terms for structures like the uterus, cervix, and vulva. It also defines common conditions such as HPV, mastitis, and preeclampsia. Reproductive procedures like mammograms, dilation and curettage, and cesarean sections are outlined. Finally, the summary lists various contraceptive methods and medications used in reproductive healthcare.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesFemale Reproductive System Glossary
Uploaded by
HASSAM KHANThe document defines key anatomical parts, conditions, procedures, tests, devices, and medications related to the female reproductive system. It provides definitions and equivalent terms for structures like the uterus, cervix, and vulva. It also defines common conditions such as HPV, mastitis, and preeclampsia. Reproductive procedures like mammograms, dilation and curettage, and cesarean sections are outlined. Finally, the summary lists various contraceptive methods and medications used in reproductive healthcare.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
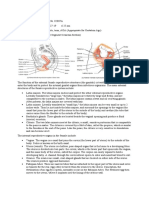
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM GLOSSARY
Anatomical Parts
Term Definition Equivalent Term
Mammary glands: Milk-producing gland of women.
Areola Dark-colored skin on the breast that
surrounds the nipple.
Nipple Protuberance of a mammary gland
upon which in the female the
lactiferous ducts open.
Vulva The female external genitals.
External opening of the vagina.
Labia The fleshy folds that surround the
opening of the vagina. The outer
folds (labia majora). The inner folds
are called the (labia minora).
Vagina Muscular tube leading from the
external genitals to the cervix.
Cervix Narrow end of the uterus that forms
a canal between the uterus and
vagina.
Uterus: Hollow, pear-shaped organ in a
woman's pelvis.
Endometrium: Inner layer of the uterus.
Myometrium Middle layer of the uterus, made up
of smooth muscle.
Perimetrium The outer serous layer of the uterus.
The serous layer secretes a
lubricating fluid that helps to reduce
friction.
Conditions
Term Definition Equivalent Term
HPV Human papilloma virus; responsible
for genital warts and cervical cancer.
Mastitis Inflammation of the breast.
Engorgement When the breast tissue overfills with
milk, blood and other fluids and is a
common problem in the early days
and weeks of breastfeeding.
Fibroids Benign tumors of muscular and
fibrous tissues, typically developing
in the wall of the uterus.
Sexually-Transmitted Diseases Diseases that can be transmitted by
sexual intercourse.
Menopause A period of life where menstruation
stops.
Genital Warts Small, rough hard bumps in the
genital area.
Ectopic Pregnancy A pregnancy in which the fetus
develops outside the uterus.
Endometriosis: Appearance of endometrial tissue
outside the uterus. It causes pain.
Adenomyosis Condition in which the inner lining of
the uterus breaks through the
muscle wall of the uterus.
Trichomoniasis An infection caused by parasitic
trichomonads.
Cervical Cancer A cancer that occurs in the cells of
the cervix.
Preeclampsia A high-blood pressure condition that
develops during pregnancy (20th
week).
Eclampsia: Onset of seizures or coma in a
pregnant woman with preeclampsia.
The seizures are not related to a
previously existing brain condition.
Gestational Diabetes Diabetes, when first diagnosed in
gestation.
Abortion The deliberate termination of a
human pregnancy, most often
performed during the first 28 weeks
of pregnancy
Miscarriage The expulsion of a fetus from the
uterus before it is able to survive
independently, (spontaneously or
because of an accident)
Procedures, Testing, & Devices
Term Definition Equivalent Term
Mammogram: An x-ray picture of the breast.
Dilation & Curettage A surgical procedure in which the
cervix is dilated (expanded) so that
the uterine lining can be scrapped.
Colposcopy A procedure in which a lighted,
magnifying instrument called
a colposcope is used to examine the
cervix.
Contraception Intentional prevention of
conception.
Mastectomy Removal of the breast.
Oophorectomy Removal of one or both ovaries.
Salpingectomy Removal of fallopian tubes.
Hysterectomy Removal of the uterus.
Cesarean Section (C-section) Type of surgery done to deliver a
baby.
Pelvic exam A procedure in which the doctor
checks your vulva, vagina, cervix,
ovaries, uterus, rectum and pelvis
for any abnormalities
Speculum Duck-bill-shaped device that doctors
use to see inside a hollow part of
your body and diagnose or treat
disease.
Pap smear A test carried out on a sample of
cells from the cervix to check for
abnormalities.
HCG (Human Chorionic Hormone that helps maintain
Gonadotropin) pregnancy.
24-hour urine protein test A test that measures the amount of
albumin in your urine over 24 hours.
Non-Stress Test (NST) Monitoring the baby's heart rate
goes faster while resting or moving.
Oxytocin Challenge test Test done to see if the baby will
tolerate contractions during labor.
Intra-uterine device (IUD) Shaped like a "T", It
prevents pregnancy by
stopping sperm from reaching and
fertilizing eggs.
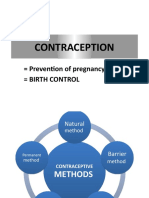
Medications
Hormonal birth control methods (The part highlighted is just a brand name, so you just
interpret it the same way in your target language)
Term Definition Equivalent Term
Birth Control Methods Different methods, used to prevent
pregnancy (hormones, barrier).
Oral Birth control pills Oral contraceptive, that prevent
(Levenorgestrel) ovulation. Has to be taken every day.
Injection (Depo-Provera) Contraceptive method that also
prevents ovulation (every 3 months).
Implant (Nexplanon) Small implant that goes in the arm,
design to release a specific dose of
hormones each day, to prevent
ovulation (3 years).
Misoprostol (Cytotec) A prescription medication that can
be used as a prophylaxis to
prevent NSAID-Induced Ulcers, as
pregnancy termination or induction
of labor.
You might also like
- JocelynPrieto OBGyneDocument7 pagesJocelynPrieto OBGyneAndrew Joever PrietoNo ratings yet
- Mother Baby TermsDocument3 pagesMother Baby TermschadnelsonNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument1 pageOvarian CystLoriene LopezNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument79 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemNaveen ChNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesReproductive SystemcjhundaleNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Medical Abortion Surgical Abortion EndometriosisDocument9 pagesAbdomen Medical Abortion Surgical Abortion EndometriosisKristine CustodioNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemMiguel Ashi GarciaNo ratings yet
- kan-di-DI-a-sis: CandidiasisDocument3 pageskan-di-DI-a-sis: CandidiasisLyza Cabuyao MayaniNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Document26 pagesSexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Vanessa Joyce Isleta100% (3)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument76 pagesEctopic PregnancyVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- Premature Rupture of The Membrane: Retnayu Pradanie, S.Kep., Ns 18/03/09Document9 pagesPremature Rupture of The Membrane: Retnayu Pradanie, S.Kep., Ns 18/03/09Mia PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Early Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahDocument33 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahShre RanjithamNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic-Nursing Part 2Document40 pagesGynecologic-Nursing Part 2jomariNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CystDocument3 pagesOvarian Cystralph_molina_3No ratings yet
- Medical Terms and Definitons Commonly Used in MCNDocument15 pagesMedical Terms and Definitons Commonly Used in MCNjoemel gregoriNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJonash MoralesNo ratings yet
- Definition of The DiseaseDocument17 pagesDefinition of The DiseaseLucille Jane Onlos CalibadanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemjpena.k11939116No ratings yet
- KKPMT IV Pertemuan 4 - Sistem Reproduksi WanitaDocument19 pagesKKPMT IV Pertemuan 4 - Sistem Reproduksi WanitaAyu Romadhona WinataNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System DiseasesDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive System DiseasesRichard Bueta0% (1)
- Cervix InformationDocument4 pagesCervix InformationEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- ENDOMETRIOMADocument8 pagesENDOMETRIOMAJennine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of UterusDocument12 pagesClinical Anatomy of UterusAsha dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Ob Terms A ZDocument81 pagesOb Terms A ZLorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rle FinalsDocument31 pagesRle FinalsMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- 2M Assisting in Gynecologic Exams and Self Breast Exam Testicular ExamDocument41 pages2M Assisting in Gynecologic Exams and Self Breast Exam Testicular Examvjson13No ratings yet
- Istilah Medis Dan Tindakan Medis Sistem Reproduksi WanitaDocument19 pagesIstilah Medis Dan Tindakan Medis Sistem Reproduksi WanitaJude Had a FarmNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDocument11 pagesCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- Cervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixDocument21 pagesCervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixnyseaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument23 pagesCase StudyLucero HyacinthNo ratings yet
- PregnancyDocument51 pagesPregnancyKhlouda HamadaNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingDocument37 pagesInfertility - Definition, Causes, Diagnostic Procedures AND CouncellingvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in MidwiferyDocument5 pagesTerminologies in MidwiferyrekhamolNo ratings yet
- Aetiology and Pathophysiology: Teachmeseries LTDDocument4 pagesAetiology and Pathophysiology: Teachmeseries LTDFaithful FrankNo ratings yet
- Preg Terms and DefDocument6 pagesPreg Terms and Defvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Final EditDocument11 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Final EditBRAIMA JOHNNo ratings yet
- Take Home Assignment Fisiologi Reproduksi Wanita: Dosen Mata Kuliah DR - Dr.Joserizal Serudji, Spog (K)Document31 pagesTake Home Assignment Fisiologi Reproduksi Wanita: Dosen Mata Kuliah DR - Dr.Joserizal Serudji, Spog (K)Al Hadad HarahapNo ratings yet
- Discussion of The Diseases ProcessDocument4 pagesDiscussion of The Diseases ProcessMica CoveyNo ratings yet
- Contraception: Prevention of Pregnancy Birth ControlDocument8 pagesContraception: Prevention of Pregnancy Birth ControlMay KiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument43 pagesMaternal and Child NursingSophia WongNo ratings yet
- Case 1 AbortionDocument18 pagesCase 1 AbortionEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Disorders in The Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesDisorders in The Reproductive SystemBeatriz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ovarian New Growth CASE REPORTDocument53 pagesOvarian New Growth CASE REPORTAbbey Jane Ayro69% (13)
- 3RD TrimesterDocument7 pages3RD TrimesterAmethystNo ratings yet
- PatientResources - Forms - Common Terms Pregnancy Birth EnglishDocument6 pagesPatientResources - Forms - Common Terms Pregnancy Birth EnglishMohammad Ya'Ser D. IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ApprDocument33 pagesDiagnostic ApprNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Patients Physiology and AnatomyDocument7 pagesPatients Physiology and AnatomysonggopNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyalynnavictoria67% (3)
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- Fibroids Miracle Cure: The Ultimate Fibroids Diet To Heal NaturallyFrom EverandFibroids Miracle Cure: The Ultimate Fibroids Diet To Heal NaturallyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Psych - Abnormal Sexuality and Sexual DysfunctionsDocument13 pagesPsych - Abnormal Sexuality and Sexual DysfunctionsMish Dizon-TanNo ratings yet
- Female Infertility PDFDocument2 pagesFemale Infertility PDFRod NeyNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Use and Unplanned Pregnancy Among Female Sex Workers in ZambiaDocument7 pagesContraceptive Use and Unplanned Pregnancy Among Female Sex Workers in ZambiaNiki Rizqi rachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument29 pagesFamily PlanningJocelleAcerdin100% (1)
- LaborDocument4 pagesLaborMENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.No ratings yet
- Lust PowerDocument13 pagesLust PowerChitto1970No ratings yet
- XaxaxDocument3 pagesXaxaxDarren BalbasNo ratings yet
- Kode Icd ObgynDocument4 pagesKode Icd ObgyndodiaryawanNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument16 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentDavid LeeNo ratings yet
- Carlin Smith Child Abuse FinalDocument12 pagesCarlin Smith Child Abuse FinalCarlin SmithNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Manual Final Report of The Obstetric Working Group of The National Health Insurance Board of The Netherlands (Abridged Version)Document35 pagesObstetric Manual Final Report of The Obstetric Working Group of The National Health Insurance Board of The Netherlands (Abridged Version)Islam AwniNo ratings yet
- Personal Development: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Family StructuresDocument25 pagesPersonal Development: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Family StructuresRodolfo galamayNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pediatric Research Ijpr 8 088Document6 pagesInternational Journal of Pediatric Research Ijpr 8 088desiNo ratings yet
- PBL Report 3 FixDocument24 pagesPBL Report 3 FixtiwiNo ratings yet
- Starchy's Complete Transcripts of - Neo & David Wygant - Sexual Mastery SeminarsDocument68 pagesStarchy's Complete Transcripts of - Neo & David Wygant - Sexual Mastery SeminarsRadu Moglan50% (2)
- Disease Control Priority-3Document23 pagesDisease Control Priority-3Abubakar Abdhoo100% (1)
- Job Predictions PDFDocument3 pagesJob Predictions PDFBhanu MurtyNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, ExploitationDocument13 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Abuse, ExploitationJo Marie Llamera Ebdani100% (1)
- Marriage in The African Traditional Religion Is A Communal Rather Than Individual AffairDocument3 pagesMarriage in The African Traditional Religion Is A Communal Rather Than Individual AffairMerito MhlangaNo ratings yet
- Science9 QuizDocument5 pagesScience9 QuizRotshen CasilacNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal WellbeingDocument24 pagesAssessment of Fetal WellbeingMukesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiDocument27 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiBasudev chNo ratings yet
- Birth Control and The Christian: Recent Discussion and Basic SuggestionsDocument28 pagesBirth Control and The Christian: Recent Discussion and Basic SuggestionsDavid Salazar100% (1)
- NP IiDocument11 pagesNP IiOlivia LowellNo ratings yet
- Ob ClinicsDocument13 pagesOb ClinicsLj chuaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Manfaat ASI EksklusifDocument2 pagesEbook Manfaat ASI EksklusifwishingbabyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument18 pagesCase StudyKrizza Jane AguroNo ratings yet
- Endometritis PDFDocument3 pagesEndometritis PDFNur azizah FitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Documento 7Document13 pagesDocumento 7Coca VerduzcoNo ratings yet