0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views4 pagesTypes of JDBC Drivers Explained
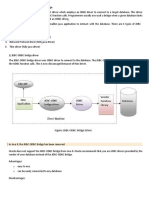
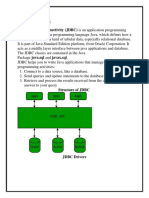
The document discusses the 4 types of JDBC drivers: 1) JDBC-ODBC bridge driver which uses ODBC but has been removed in Java 8, 2) Native-API driver which uses client-side libraries but requires installation, 3) Network Protocol driver which uses middleware and is fully Java but requires database-specific coding, 4) Thin driver which directly converts JDBC to database protocols and has best performance but depends on the database.
Uploaded by
rambabudugyaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
140 views4 pagesTypes of JDBC Drivers Explained
The document discusses the 4 types of JDBC drivers: 1) JDBC-ODBC bridge driver which uses ODBC but has been removed in Java 8, 2) Native-API driver which uses client-side libraries but requires installation, 3) Network Protocol driver which uses middleware and is fully Java but requires database-specific coding, 4) Thin driver which directly converts JDBC to database protocols and has best performance but depends on the database.
Uploaded by
rambabudugyaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd