Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JavaJDBC 1
Uploaded by
ujjawalr90270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesOriginal Title
JavaJDBC-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesJavaJDBC 1
Uploaded by
ujjawalr9027Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
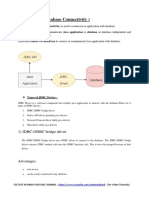
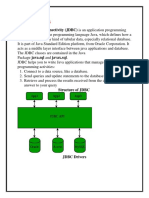
Java JDBC
• JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a
Java API to connect and execute the query with the
database. It is a part of JavaSE (Java Standard Edition).
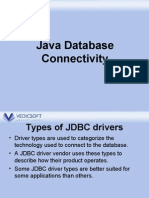
JDBC API uses JDBC drivers to connect with the
database. There are four types of JDBC drivers:
– JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver,
– Native Driver,
– Network Protocol Driver, and
– Thin Driver
• We can use JDBC API to access tabular data stored in
any relational database. By the help of JDBC API, we
can save, update, delete and fetch data from the
database. It is like Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
provided by Microsoft.
• The java.sql package contains classes and
interfaces for JDBC API. A list of
popular interfaces of JDBC API are given below:
– Driver interface
– Connection interface
– Statement interface
– PreparedStatement interface
– CallableStatement interface
– ResultSet interface
– ResultSetMetaData interface
– DatabaseMetaData interface
– RowSet interface
Why Should We Use JDBC
• Before JDBC, ODBC API was the database API to
connect and execute the query with the
database. But, ODBC API uses ODBC driver which
is written in C language (i.e. platform dependent
and unsecured). That is why Java has defined its
own API (JDBC API) that uses JDBC drivers
(written in Java language).
– We can use JDBC API to handle database using Java
program and can perform the following activities:
– Connect to the database
– Execute queries and update statements to the
database
– Retrieve the result received from the database.
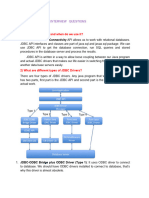
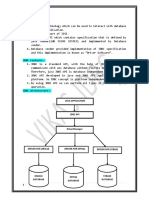
JDBC Driver
• JDBC Driver is a software component that
enables java application to interact with the
database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
– JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
– Native-API driver (partially java driver)
– Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
– Thin driver (fully java driver)
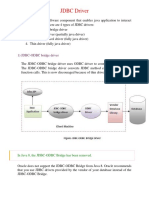
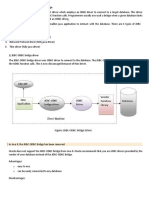
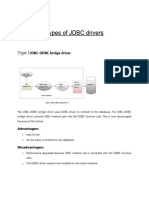
1) JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
• The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses ODBC driver to connect
to the database. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts
JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now
discouraged because of thin driver.
• Oracle does not support the JDBC-ODBC Bridge from Java 8.
Oracle recommends that you use JDBC drivers provided by
the vendor of your database instead of the JDBC-ODBC
Bridge.
• Advantages:
– easy to use.
– can be easily connected to any database.
• Disadvantages:
– Performance degraded because JDBC method call is converted
into the ODBC function calls.
– The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the client machine.
2) Native-API driver
• The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries
of the database. The driver converts JDBC
method calls into native calls of the database API.
It is not written entirely in java.
• Advantage:
– performance upgraded than JDBC-ODBC bridge driver.
• Disadvantage:
– The Native driver needs to be installed on the each
client machine.
– The Vendor client library needs to be installed on
client machine.
3) Network Protocol driver
• The Network Protocol driver uses middleware (application
server) that converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into
the vendor-specific database protocol. It is fully written in
java.
• Advantage:
– No client side library is required because of application server
that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing,
logging etc.
• Disadvantages:
– Network support is required on client machine.
– Requires database-specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
– Maintenance of Network Protocol driver becomes costly
because it requires database-specific coding to be done in the
middle tier.
4) Thin driver
• The thin driver converts JDBC calls directly
into the vendor-specific database protocol.
That is why it is known as thin driver. It is fully
written in Java language.
• Advantage:
– Better performance than all other drivers.
– No software is required at client side or server
side.
• Disadvantage:
– Drivers depend on the Database.
You might also like
- How To Convert Oracle Reports To XML Publisher ReportDocument3 pagesHow To Convert Oracle Reports To XML Publisher ReportSridhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Store Management SystemDocument121 pagesMobile Store Management SystemDebarun Sen77% (44)
- Counter Manual PDFDocument101 pagesCounter Manual PDFkopperundeviNo ratings yet
- Internet Payment GatewayDocument25 pagesInternet Payment Gatewaymerahdelima100% (1)
- Prepared By:-Shraddha PonkiyaDocument18 pagesPrepared By:-Shraddha PonkiyashraddhaNo ratings yet
- A JDBC Driver Is A Software Component Enabling A Java Application To Interact With A DatabaseDocument8 pagesA JDBC Driver Is A Software Component Enabling A Java Application To Interact With A Databasezahiruddin_ahamed100% (1)
- CPC 1-04 PDFDocument88 pagesCPC 1-04 PDFFabian Etchenique80% (10)
- Unit8 JDBCDocument39 pagesUnit8 JDBCrambabudugyani100% (1)
- JDBC ArchitectureDocument5 pagesJDBC Architecturemelbin mathewNo ratings yet
- Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)Document60 pagesJava Database Connectivity (JDBC)Thanmayee ThanuNo ratings yet
- U1 L1 JDBCDocument20 pagesU1 L1 JDBCGarima TyagiNo ratings yet
- JDBC DriverDocument4 pagesJDBC DriverrambabudugyaniNo ratings yet
- Aim:-To Study About JDBC ODBC BridgeDocument4 pagesAim:-To Study About JDBC ODBC BridgeshailendraNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 JDBCDocument53 pagesUnit-4 JDBCKeerthika AngelNo ratings yet
- Java Data Base Connectivity Unit IiDocument41 pagesJava Data Base Connectivity Unit Iisanthi lathaNo ratings yet
- Interacting With DatabaseDocument83 pagesInteracting With DatabaseOnkar GuttiNo ratings yet
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) : 1) JDBC-ODBC Bridge DriverDocument3 pagesJDBC (Java Database Connectivity) : 1) JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driverpradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Java JDBC Driver - JavatpointDocument6 pagesJava JDBC Driver - JavatpointKeshav AvhadNo ratings yet
- JdbcquestionsDocument73 pagesJdbcquestionssubhabirajdarNo ratings yet
- Ecj Unit-1Document6 pagesEcj Unit-1azam AmeenNo ratings yet
- JSP PPTDocument37 pagesJSP PPTapi-3844034No ratings yet
- DAy 9 PPT JDBC - 1Document17 pagesDAy 9 PPT JDBC - 1isha sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.Jdbc Architecture:: Java Database ConnectivityDocument14 pages1.Jdbc Architecture:: Java Database ConnectivityDurga Sravani TumuluriNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3.2.1Document18 pagesLecture-3.2.1gdgdNo ratings yet
- What Is JDBCDocument16 pagesWhat Is JDBCbooressaa kachisooNo ratings yet
- Main Advjava Best NotesDocument165 pagesMain Advjava Best Notesharshadborse04No ratings yet
- JDBC Driver and Its TypesDocument8 pagesJDBC Driver and Its Typespraty888No ratings yet
- Types of Drivers: ArchitectureDocument9 pagesTypes of Drivers: ArchitecturejavatrainingNo ratings yet
- 7MCE1C3-Advanced Java ProgrammingDocument84 pages7MCE1C3-Advanced Java ProgrammingSarvasaisrinathNo ratings yet
- Java DataBase ConnectivityDocument24 pagesJava DataBase Connectivityapi-3866644No ratings yet
- Oopr212 Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesOopr212 Finals Reviewershawn mallariNo ratings yet
- JDBC ResultsetDocument24 pagesJDBC ResultsetNeha NaikNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 JDBC Programming 28012018 040330AMDocument22 pagesUnit 2 JDBC Programming 28012018 040330AMVani ShettyNo ratings yet
- DBC Driver ManagerDocument6 pagesDBC Driver ManagerpacharneajayNo ratings yet
- JDBC Driver ManagerDocument9 pagesJDBC Driver ManagersowmiyaasNo ratings yet
- Is A Collection of Andasetof .: Dbms Interrelated Data Methods To Manipulate That Data Advantages of DBMSDocument24 pagesIs A Collection of Andasetof .: Dbms Interrelated Data Methods To Manipulate That Data Advantages of DBMSrajagopaldNo ratings yet
- Types of JDBC DriversDocument12 pagesTypes of JDBC Driversshubhangi100% (1)
- By Abdo A. December 2018/19: (Java Database Connection)Document47 pagesBy Abdo A. December 2018/19: (Java Database Connection)Chala BojaNo ratings yet
- O JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, o Native Driver, o Network Protocol Driver, and o Thin DriverDocument16 pagesO JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, o Native Driver, o Network Protocol Driver, and o Thin Driverlepeci7607No ratings yet
- JDBC DRIVERDocument5 pagesJDBC DRIVERmananrawat537No ratings yet
- JDBC MaterialDocument34 pagesJDBC MaterialLakshmman JsltechNo ratings yet
- Java Database ConnectvityDocument32 pagesJava Database ConnectvitySHIVAM PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Kaveri College of Arts, Science and Commerce: Tybsc (CS) Java JDBCDocument82 pagesKaveri College of Arts, Science and Commerce: Tybsc (CS) Java JDBCPallavijoNo ratings yet
- Module4 JDBC PDFDocument24 pagesModule4 JDBC PDFVTU ML WorkshopNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Java Database Programming: 5.1.1 JDBC CharacteristicsDocument60 pages5.1 Java Database Programming: 5.1.1 JDBC Characteristicsarunlalds100% (1)
- Module 5Document62 pagesModule 5eng21am0096No ratings yet
- JDBC Driver TypesDocument5 pagesJDBC Driver TypesSuneet PadhiNo ratings yet
- Types of JDBC DriversDocument2 pagesTypes of JDBC DriversRahul MathankarNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii (Working With Database) What Is ODBC?Document25 pagesUnit - Iii (Working With Database) What Is ODBC?Duvva SairamNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Using Java (ECSE102L) : (Java Database Connectivity-Jdbc)Document42 pagesObject Oriented Programming Using Java (ECSE102L) : (Java Database Connectivity-Jdbc)Insight KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- JDBC Drivers: Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) Is An Application ProgrammingDocument6 pagesJDBC Drivers: Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) Is An Application Programmingsupriya028No ratings yet
- Java JDBCDocument17 pagesJava JDBCDhruv KushwahNo ratings yet
- ppt5Document32 pagesppt5khushbuagrawal15122005No ratings yet
- JDBC Programming in JavaDocument22 pagesJDBC Programming in JavaSneha KatakamNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument39 pagesJDBCapi-26757811No ratings yet
- JDBC PDFDocument56 pagesJDBC PDFMohit vazaNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument22 pagesJDBCvedicsoft100% (2)
- Best Practices To Improve Performance in JDBCDocument20 pagesBest Practices To Improve Performance in JDBCAnirban PoddarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document71 pagesUnit - 1rahul.makwana.6500No ratings yet
- Java Database Connectivity: History and ImplementationDocument20 pagesJava Database Connectivity: History and Implementationatul211988No ratings yet
- Unit-1 Advanced JavaDocument16 pagesUnit-1 Advanced JavaMohit PalveNo ratings yet
- Java for Beginners: Learn the Essentials of Object-Oriented ProgrammingFrom EverandJava for Beginners: Learn the Essentials of Object-Oriented ProgrammingNo ratings yet
- Java/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandJava/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Applets 1Document6 pagesApplets 1Darkseid UxasNo ratings yet
- Java NetworkingDocument13 pagesJava Networkingujjawalr9027No ratings yet
- Why Use Inheritance in JavaDocument6 pagesWhy Use Inheritance in JavaKUNAL SALUNKHENo ratings yet
- Java LayoutManagersDocument16 pagesJava LayoutManagersujjawalr9027No ratings yet
- Access Modifiers in JavaDocument5 pagesAccess Modifiers in JavaPrajakta Dhamanskar CRCENo ratings yet
- Unit 4 INNOVATION & ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument8 pagesUnit 4 INNOVATION & ENTREPRENEURSHIPujjawalr9027No ratings yet
- Software Requirement SpecificationDocument8 pagesSoftware Requirement SpecificationZYSHANNo ratings yet
- There Are 2 Types of Bapi'sDocument3 pagesThere Are 2 Types of Bapi'sTrainning ABAPNo ratings yet
- Java Lab ManualDocument58 pagesJava Lab ManualSRIHITHA YELISETTINo ratings yet
- ERPSystem Week1Document3 pagesERPSystem Week1Donny NayoanNo ratings yet
- MO 101 QuestionsDocument5 pagesMO 101 Questionsjames scottNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysisin Mobile Application DevelopmentDocument7 pagesRisk Analysisin Mobile Application DevelopmentChazNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument17 pagesReadmearamis01No ratings yet
- ReservationsManual en PDFDocument26 pagesReservationsManual en PDFAlen KuharićNo ratings yet
- Powersploit Cheat Sheet: Getting StartedDocument2 pagesPowersploit Cheat Sheet: Getting Startedcayu8138No ratings yet
- Imp, BLTDocument3 pagesImp, BLTNARENDRANo ratings yet
- Ltepa Wireshark AluDocument54 pagesLtepa Wireshark AluShakir SNo ratings yet
- JAVA Programming MCA 205 Pre-Requisite Based Study MaterialDocument25 pagesJAVA Programming MCA 205 Pre-Requisite Based Study MaterialAshi SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 F2F PDF PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 F2F PDF PDFGarethNgNo ratings yet
- 1-2 AVR Studio TutorialDocument8 pages1-2 AVR Studio TutorialZaini AascNo ratings yet
- 2381 - TQ Analyst - UGDocument430 pages2381 - TQ Analyst - UGDenis Audrey50% (2)
- PVFRNDocument21 pagesPVFRNbilo044No ratings yet
- SAP Server For Practice Through ESXi VirtualizationDocument30 pagesSAP Server For Practice Through ESXi VirtualizationRamesh HarshanNo ratings yet
- Bus Station ProjectDocument98 pagesBus Station Projectshemsedin shukre86% (7)
- WHITE PAPER Samsung A Guide To Going Mobile Only With Samsung DeX 08052018 PDFDocument17 pagesWHITE PAPER Samsung A Guide To Going Mobile Only With Samsung DeX 08052018 PDFgavin brazierNo ratings yet
- Opps Real Time CodeDocument30 pagesOpps Real Time CodeSoumabha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- DFSTutorialDocument219 pagesDFSTutorialpradeepu538No ratings yet
- Best Brain ICT Mock For September 2021Document16 pagesBest Brain ICT Mock For September 2021King QwesiNo ratings yet
- Install and Configure Postal Mail Server On UbuntuDocument2 pagesInstall and Configure Postal Mail Server On UbuntuTeam LeaderNo ratings yet
- Se Lab Case Study FinalDocument12 pagesSe Lab Case Study FinalRajkumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 5Document17 pagesChapter 4 5Deyeck VergaNo ratings yet