Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anemia NCP
Uploaded by
Shaira Mae Fangon De GuzmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemia NCP
Uploaded by
Shaira Mae Fangon De GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
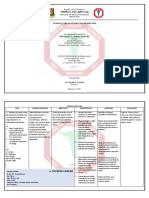
DON MARIANO MARCOS MEMORIAL STATE UNIVERSITY
South La Union Campus
College of Community Health and Allied Medical Sciences
Agoo, La Union
Tel. 072.682.06.63/cchams@dmmmsu.edu.ph
NURSING DEPARTMENT
NURSING CARE PLAN
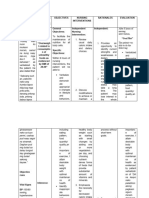
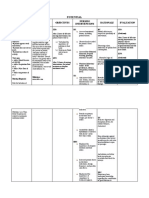
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVE INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
Subjective: Anemia occurs when there After 7 days of nursing Document the patient’s Weight loss can be Demonstrate
“nahihilo ako ma’am, tapos aren’t enough healthy red intervention the patient will progressive weight
weight. Weight the measured accurately
nang hihina po ako” blood cells to carry oxygen be able to: gain toward goal
to your body’s organs. As a Increase body weight 20% patient daily in the with a patient’s actual Demonstrate
Objective: result, it’s common to feel or more under ideal. mornings. weight rather than by behavior, lifestyle
Weakness cold and symptoms of estimate. The patient’s changes to regain
Chest pain tiredness or weakness. There and/or maintain
weight is also an ideal
Cold hands and feet are many different types of appropriate weight
anemia, but the most tool in the assessment
Dizziness
common type is iron- of a person’s nutritional
V/S taken as follows: deficiency anemia. You can requirements.
BP: 180/120 begin to ease symptoms of
TEMP: 36.7 this type of anemia by Assess what the patient Patients with dysphagia
adding iron to your diet. can safely eat and drink.
O2: 97 may be able to tolerate
PR: 97
thickened liquids and
RR: 19
pureed food. Assessing
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: what the patient can
Imbalance nutrition less tolerate will help
than body requirements support nutrition and
arrange food choices to
Weigh the patient become available.
DON MARIANO MARCOS MEMORIAL STATE UNIVERSITY
South La Union Campus
College of Community Health and Allied Medical Sciences
Agoo, La Union
Tel. 072.682.06.63/cchams@dmmmsu.edu.ph
NURSING DEPARTMENT
regularly and document The patient’s weight will
readings. help in the evaluation of
the patient’s progress.
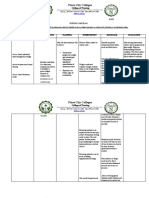
NURSING CARE PLAN
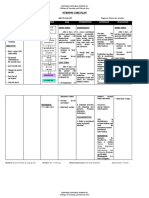
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVE INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM
DON MARIANO MARCOS MEMORIAL STATE UNIVERSITY
South La Union Campus
College of Community Health and Allied Medical Sciences
Agoo, La Union
Tel. 072.682.06.63/cchams@dmmmsu.edu.ph
NURSING DEPARTMENT
SUBJECTIVE: Obstructive uropathy is a After 8 hours of nursing Record accurate Goal met patient has
Namamanas ako at hindrance to normal urinary intervention the patient will intake and output Accurate I&O is displayed appropriate
nanghihina katawan ko” flow that can be caused by a display appropriate urinary Weight daily at same necessary for urinary output with specific
variety of structural and output with specific time of the day, on determining renal gravity/laboratory studies
OBJECTIVE: functional etiologies. This is gravity/laboratory studies same scale, with function and fluid near normal; stable weight;
a common and potentially near normal; v/s within same equipment and replacement needs V/S within the patient’s
Generalize edema serious condition that affects patient’s normal range; and clothing and reducing risk of normal range; absence of
Patient reports of people across all ages and absence of edema Assess skin dace, fluid overload edema
fatigue, weakness, walks of life. To avoid the dependent areas for Daily body weight is
and malaise morbidity and mortality edema best monitor of fluid
V/S taken as follows associated with this Plan oral fluid status
BP: 130/90 condition, it must be replacement within Edema occurs
TEMP: 36.7 promptly diagnosed and multiple restrictions primarily in
O2: 99% treated. This activity reviews dependent tissues of
PR: 107
RR: 22
the evaluation and the body
management of patients with Helps avoid periods
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: obstructive uropathy. It without fluid
FLUID VOLUME EXCESS represents a common minimizes boredom
R/T COMPROMISED presentation affecting of limited choices
REGULATORY multiple medical specialties
MECHANISM (RENAL and highlights the role of the
FAILURE) interprofessional team in
early identification and
improved care for patients
with this condition.
You might also like
- NCP - AnemiaDocument4 pagesNCP - AnemiaShaira Mae Fangon De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Improved NutritionDocument2 pagesImproved NutritionDaintyGarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP of Patient With GastritisDocument4 pagesNCP of Patient With GastritisBer AnneNo ratings yet
- NCP1Document3 pagesNCP1kkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageGestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanASIS, MARK ANTHONY M.No ratings yet
- Mindanao State University: Nursing Care Plan For Cancer DiseasesDocument11 pagesMindanao State University: Nursing Care Plan For Cancer DiseasesAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- 2 PlanDocument8 pages2 PlanAyobami AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with ConstipationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with ConstipationRawan KNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument2 pagesNCP Case PresLevin MenpinNo ratings yet
- NCM105AR Lab Group 2 Nutrition Care Plan PDFDocument6 pagesNCM105AR Lab Group 2 Nutrition Care Plan PDFKIMBERLY CABATONo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges: College of NursingDocument20 pagesPines City Colleges: College of NursingMara Jon Ocden CasibenNo ratings yet
- ADIMEe 1Document2 pagesADIMEe 1Jhen HannawayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Mikaella GacostaNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesWesleyan Nursing Care PlanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Breast Ca NCPDocument3 pagesBreast Ca NCPThirdy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Care Plan for Severe MalnutritionDocument3 pagesNutrition Care Plan for Severe Malnutritioncharles estradaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Rochelle Maglangit RagoDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Rochelle Maglangit RagoRochelle RagoNo ratings yet
- PCC College of Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesPCC College of Nursing Care PlanEspiridionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgery Patient with Risk of MalnutritionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgery Patient with Risk of MalnutritionSandra ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Potential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesPotential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for imbalanced nutrition and activity intoleranceDocument2 pagesNursing care for imbalanced nutrition and activity intoleranceKimberly Maine Arias BustrilloNo ratings yet
- NCP Ovarian CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Ovarian Cancerwendy gaetosNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines ManilaDocument6 pagesUniversity of The Philippines ManilaTessa Lisbury SteakNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSIS OverweightDocument7 pagesDIAGNOSIS OverweightWappy WepwepNo ratings yet
- Ed 2020 1Document25 pagesEd 2020 1Alejandra Loyo MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanFrances CalaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPJalishia Mae DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- NDT Hospital DietDocument16 pagesNDT Hospital DietJoan BabieraNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument7 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionNora VarshavskiNo ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementDocument6 pagesA Nursing Care Plan On: Loose Bowel MovementakoitsmeNo ratings yet
- Imbalance Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument4 pagesImbalance Nutrition Less Than Body Requirementshatred heartNo ratings yet
- Askep Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesAskep Bahasa InggrisVia Eliadora TogatoropNo ratings yet
- Mata Kuliah Keperawatan Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesMata Kuliah Keperawatan Bahasa InggrisVia Eliadora TogatoropNo ratings yet
- Visca, Baybay City, Leyte, PHILIPPINES Tel. No.: (053) 563-7226 Email Address: Nursing@vsu - Edu.ph Website: WWW - Vsu.edu - PHDocument1 pageVisca, Baybay City, Leyte, PHILIPPINES Tel. No.: (053) 563-7226 Email Address: Nursing@vsu - Edu.ph Website: WWW - Vsu.edu - PHLouella CastroNo ratings yet
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- End of Life Care Plan Done Beard Codi JDocument5 pagesEnd of Life Care Plan Done Beard Codi Japi-657096442No ratings yet
- Ncp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitDocument3 pagesNcp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan Nursing Care Plan for Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument3 pagesWesleyan Nursing Care Plan for Iron Deficiency AnemiaPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Template For Care Plan AssignmentDocument8 pagesTemplate For Care Plan AssignmentAnn OgoloNo ratings yet
- "Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care ProcessDocument2 pages"Nagsusuka Ang Anak Ko.": Nursing Care Processgeorgia50% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationLea CortesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Req NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Req NCPkarthi karthi50% (2)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPFran LanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Intervention Rationale EvaluationTracy TinNo ratings yet
- ncp-eatingDocument1 pagencp-eatingsnow.parconNo ratings yet
- 2b1 Casepress CompiledDocument48 pages2b1 Casepress Compiledandrei jinNo ratings yet
- Segal, A Et Al (2004) Post-Surgical Refusal To Eat (Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa or A New Eating Disorder? A Case SeriesDocument8 pagesSegal, A Et Al (2004) Post-Surgical Refusal To Eat (Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa or A New Eating Disorder? A Case Seriesasdrubal5martinezNo ratings yet
- CHA NCPDocument6 pagesCHA NCPMonty_Legaspi_5664No ratings yet
- University of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingDocument23 pagesUniversity of The East Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center, Inc. College of NursingReina RamonesNo ratings yet
- NCP & Discharge PlanningDocument12 pagesNCP & Discharge PlanningStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pancreatic Cancer 1711036796Document20 pagesNutrition in Pancreatic Cancer 1711036796Azakari1993No ratings yet
- The Pernicious Anaemia Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint For Complete Pernicious Anaemia ManagementFrom EverandThe Pernicious Anaemia Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint For Complete Pernicious Anaemia ManagementNo ratings yet