Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of Chemotherapy
Uploaded by
Cecil Cacay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of Chemotherapy
Uploaded by
Cecil CacayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CORDILLERA CAREER DEVELOPMENT COLLEGE
Buyagan, Poblacion, La Trinidad, Benguet
COLLEGE OF HEALTH EDUCATION
NCM – 106
NURSING CARE PLAN
ON
THE EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY
Fatigue related to altered body chemistry: side effects of Chemotherapy secondary to breast cancer.
Disturbed Body Image: Alopecia related to the effects of Chemical Distraction.
Risk for deficient fluid volume related to effects of chemotherapy.
SUBMITTED BY: CECIL C. PABLO
SUBMITTED TO: MA’AM JIWANI MAE LAROZA
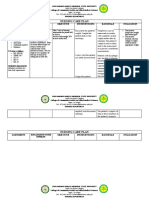
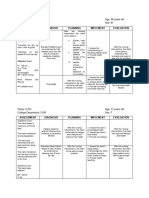
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM INTERVENTIONS
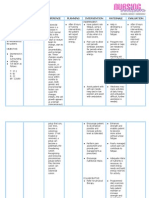
S – “kanaun ak mababanog Fatigue often gets worse STO – After 2 hours of Monitor vital signs To evaluate fluid Goal met, after 2
uray lang ag kuti ak ti bassit during chemotherapy rendering nursing care and status and hours of therapeutic
kt mabannog ak, isunga especially on the first session therapeutic communication, cardiopulmonary interventions, patient
kailangan dak iassist jai and it may get better until the patient will be able to response to activity. was able to
watcher ko”, as verbalized by next treatment. In addition, understand and demonstrate understand and
the patient. experiencing fatigue is proper techniques of rest To extend activity demonstrate proper
common on those having periods: Encourage to use of time/conserve energy techniques of rest
O – Body weakness noted, chemotherapy because it 1. Take frequent periods assistive devices. for other tasks. periods.
Ineffective role performance, destroys healthy cells in of rest, especially To avoid fall or He was able to
addition to the targeted cancer when going to the injury. understand the
BP – 90/70 mmHg cells. restroom, standing Instructed in methods importance of
RR – 22 cpm Fatigue may occur as the body and walking. to conserve energy. In order to save consuming balanced
PR – 75 bpm tries to repair the damage to Also, the patient will be able energy for the other diet.
(+) chemo healthy cells and tissues. to understand the importance tasks he/she needs to
Also, cancers can increase the of consuming a well balanced do.
body’s need for energy, diet. Encouraged To promote energy.
Nursing Diagnosis: weakens the muscles, cause nutritionally dense,
Fatigue related to altered body damage to certain organs or easy to prepare and
chemistry: side effects of alter the body’s hormones LTO – After 3 days of nursing consume foods, and
Chemotherapy secondary to may contribute to fatigue. intervention with medical avoidance of caffeine After 3 days of
breast cancer. management, the patient will and high sugar foods nursing intervention,
be able to do activities of and beverages. patient the patient
daily living independently. reports improved
The patient will be able to Assisted with self- sense of energy
report improved sense of care needs; assisted in To prevent further Patient managed to
energy. ambulation as needed. injury. perform activities of
daily living without
any assistance.
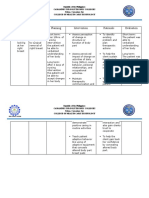
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM INTERVENTIONS
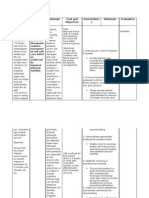
S – “Paggising ko kanina Chemotherapy may cause hair STO – After 2 days of nursing Discussed with the Aids in defining After 2 days of
napansin ko na nalalagas na loss all over the body — not intervention the patient will patient and family concerns to begin nursing intervention
yung buhok ko, nakakalbo na just on the scalp. Sometimes it be able to recognize alopecia how the therapy is problem solving the patient recognized
ako”, as verbalized by the includes eyelash, eyebrow, as the side effects of affecting the hair. process. Provides alopecia as the side
patient. armpit, pubic and other body chemotherapy and start information so patient effects of
hair also falls out. Some certain steps for medications and family can begin chemotherapy.
chemotherapy drugs are more in hair care and treatment. to prepare cognitively Started to maintain
O – Brittle hair, falls when likely than others to cause Seek information and actively and emotionally for hygiene and hair
lathered, breaks of at the hair loss, and different doses pursue growth. loss. grooming
surface of the scalp. can cause anything from a Validates reality of
Anxious behavior. mere thinning to complete patient’s feelings and
Avoids looking at or touching baldness. Acknowledged gives permission to
the body part. Presence of alopecia is difficulties patient take whatever After 5 days of
another form of tissue LTO – After 5 days of nursing may be experiencing. measures are nursing intervention,
disruption common in patients intervention the patient will Give information that necessary to cope the patient was able to
with cancer who receive be able to verbalize an counseling is often with what is verbalized relief of
chemotherapy. The extent of understanding of body necessary and happening. anxiety and
alopecia depends on the dose changes. important in the adaptation to
Nursing Diagnosis – and duration of therapy. This Verbalize relief of anxiety and adaptation process. To begin to actual/altered image.
Disturbed Body Image: cause damage in stem cells adaptation to actual or altered Encouraged the incorporate changes Identify positive and
Alopecia related to the effects and hair follicles. body image. patient to look into the body. negative feelings to
of Chemical Distraction. at/touch affected body Facilitates coping. self image. States that
part. hair loss is temporary.
Offer positive
reinforcement for
efforts made (e.g.,
wearing makeup or
using wigs)
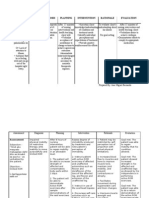
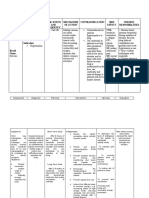
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
PROBLEM INTERVENTIONS
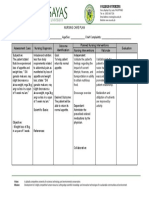
S – “namin lima en nga Vomiting occur when STO – After 4 hours of Monitor vital signs. To evaluate fluid After 4 hours of
nagsarsarwa manipud idi chemotherapy drugs stimulate an nursing interventions, the status and nursing intervention,
agsapa”, as verbalized by the area of the brain called the patient will be able to cardiopulmonary the patient and
patient’s watcher. chemoreceptor trigger zone. identify individual risk family acknowledged
response to activity.
Deficient Fluid Volume is factors and appropriate the individual risk
interventions. Provides information factors of vomiting
decreased intravascular, about overall fluid
O – Weak in appearance, interstitial, and/or intracellular Monitor intake and and appropriate
poor skin turgor, sunken output, estimate balance, as well as interventions.
fluid. This refers to dehydration, guidelines for fluid
eyeballs. Emesis basin at bed water loss alone without change in insensible fluid loss.
replacement.
side. Pale conjunctiva and sodium. To note signs of
mucus membrane. dehydration, such as
dry skin and mucous After 3 days of
Vital Signs as follows: membranes, poor nursing
LTO – After 3 days of Assessed skin and skin turgor, and interventions, the
T: 36.6 nursing interventions, the oral mucous delayed capillary client maintains fluid
PR: 86 bpm patient will maintain fluid membrane. refill. volume at functional
RR: 18 cpm volume at a functional level To stop or limit fluid level and has good
BP: 110/70 as evidenced by good skin losses. skin turgor and moist
turgor and balanced intake mucous membrane.
and output.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Demonstrates behaviors in This enhances
Risk for deficient fluid order to maintain fluid cooperation with the
volume related to effects of volume. Administer regimen and
chemotherapy. medications as achievement goals.
prescribed.
Engage patient and
client in fluid
management plan.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan Colorectal CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Colorectal Cancerderic88% (34)
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with LymphedemaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Patient with Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Liver CirrhosisDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan for Liver CirrhosisKayki Louise75% (4)
- NCP - FatigueDocument3 pagesNCP - Fatigueitsmeaya100% (1)
- NCP FatigueDocument3 pagesNCP FatigueKateLayaog100% (2)
- NCP Modified Radical MastectomyDocument5 pagesNCP Modified Radical MastectomyIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan ON The Effects of ChemotherapyCecil CacayNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Document2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Kathleen Martinez100% (1)
- Wesleyan Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesWesleyan Nursing Care PlanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Format - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesFormat - Comprehensive Nursing Care PlanVillanueva Gerald Jr LNo ratings yet
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- DIAGNOSIS OverweightDocument7 pagesDIAGNOSIS OverweightWappy WepwepNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHAally ChandraNo ratings yet
- SLU Nursing Care Plan for Gastric MassDocument3 pagesSLU Nursing Care Plan for Gastric MassSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-1: Medical Diagnoses: Colorectal CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan-1: Medical Diagnoses: Colorectal CancerBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateDocument5 pagesNCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateAngel KateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Rochelle Maglangit RagoDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Rochelle Maglangit RagoRochelle RagoNo ratings yet
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument5 pagesArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanperezNo ratings yet
- Visca, Baybay City, Leyte, PHILIPPINES Tel. No.: (053) 563-7226 Email Address: Nursing@vsu - Edu.ph Website: WWW - Vsu.edu - PHDocument1 pageVisca, Baybay City, Leyte, PHILIPPINES Tel. No.: (053) 563-7226 Email Address: Nursing@vsu - Edu.ph Website: WWW - Vsu.edu - PHLouella CastroNo ratings yet
- 2 PlanDocument8 pages2 PlanAyobami AdeleyeNo ratings yet
- Improving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesImproving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- CancerDocument3 pagesCancerShaira De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancer NCPDocument7 pagesOvarian Cancer NCPAsterlyn Coniendo100% (1)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitDocument3 pagesNcp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- NCP MakingDocument2 pagesNCP MakingMinakaNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument3 pagesAnemia NCPShaira Mae Fangon De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Physical MobilityDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Physical MobilityTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- NURSINGCAREPLANDocument5 pagesNURSINGCAREPLANJulius AtencioNo ratings yet
- NCP Breast CancerDocument2 pagesNCP Breast CancerErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- Case 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)Document2 pagesCase 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)je-ann catedralNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPmiguel_bernardo_5100% (1)
- Casilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Document3 pagesCasilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Ynalie Casilan100% (1)
- CamaristaCM - Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesCamaristaCM - Nursing Care PlanColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Potential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesPotential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONDocument5 pagesASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONRussel SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP Post OpDocument2 pagesNCP Post OpEyanah Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- ncp3-health-teachingDocument2 pagesncp3-health-teachingjardinanbalagsojoweeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implement Evaluation: Name: K.A. Age: 58 Years Old College Department: CAIS Sex: MDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implement Evaluation: Name: K.A. Age: 58 Years Old College Department: CAIS Sex: MJulius Mathew EnopiaNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument3 pagesNCP FormJasmine diokNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundicepamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Edited-Readiness For Enhanced Health ManagementDocument2 pagesEdited-Readiness For Enhanced Health ManagementWappy WepwepNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-Hepatitis A - B (Team Lion Queen)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan-Hepatitis A - B (Team Lion Queen)Calvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceKian Justin HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Idc NCPDocument14 pagesIdc NCPEnrique BabierraNo ratings yet
- Abad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAbad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIzhiel AbadNo ratings yet
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Nursing Students Learn Gynecologic Cancer CareDocument4 pagesDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Nursing Students Learn Gynecologic Cancer CareJoselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- NCP1Document3 pagesNCP1kkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Polarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouFrom EverandPolarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)