Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management Control Systems
Uploaded by
ISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Control Systems
Uploaded by
ISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTENT
Unit 1: Introduction to Management Control System 1
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University
Unit 2: Strategic Management Framework 14
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University
Unit 3: Behavioural Considerations 25
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University
Unit 4: Responsibility Centers 48
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University
Unit 5: Transfer Pricing 102
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University
Unit 6: Strategic Planning for Management Control 128
Pooja, Lovely Professional University
Unit 7: Budgeting: Tool for Management Control 141
Pooja, Lovely Professional University
Unit 8: Management Control through Variance Analysis 165
Pooja, Lovely Professional University
Unit 9: Performance Measurement Systems 184
Pooja, Lovely Professional University
Unit 10: Interactive Control 200
Pooja, Lovely Professional University
Unit 11: Management Compensation 213
Sukhpreet Kaur, Lovely Professional University
Unit 12: Management Control for Differentiated Strategies 227
Sukhpreet Kaur, Lovely Professional University
Unit 13: Management Control of Service Organisation 238
Sukhpreet Kaur, Lovely Professional University
Unit 14: Management Control of MNC's 255
Sukhpreet Kaur, Lovely Professional University
Neha Tikoo, Lovely Professional University Unit 1: Introduction to Management Control System
Unit 1: Introduction to Management Control System Notes
CONTENTS
Objectives
Introduction
1.1 Meaning of Management Control System
1.2 Nature
1.2.1 Management
1.2.2 Control
1.2.3 System
1.3 Basic Concepts
1.3.1 Important Features of Management Control Systems
1.4 Impact of the Internet on Management Control
1.5 The Domain of Management Control System
1.6 Summary
1.7 Keywords
1.8 Review Questions
1.9 Further Readings
Objectives
After studying this unit, you will be able to:
Explain the meaning of management control system
Discuss the basic concepts involved in management control system
Recognize the nature of management control system
Identify the process of management control
Explain the scope of management control system
Discuss boundaries of management control
Introduction
The importance of the subject matter covered in the courseware has been felt on the collapse of
companies such as Tyco, Global crossing, WorldCom, and Enron because of the lapse in controls.
CEO and top management compensation in these companies were so heavily tied up with stock
options that executives were motivated to manipulate financials to buoy the short-term stock
price. Similarly long-term success of world class companies such as Emerson electric, Lincoln
Electric, New York Times, Worthington Industries, 3 M Corporation, Nucor Corporation, Dell
Computer, Wal-Mart, South West Airlines, Cisco Systems and Analog Devices were not just
because they have developed good strategies, but more importantly, they have designed systems
and processes that energize their employees to execute these strategies effectively.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 1
Management Control Systems
Notes 1.1 Meaning of Management Control System
A Management Control System (MCS) is a system. A system can be described as a series of steps
or phases consisting of an input phase, a processing phase, and an output phase. A control
system adds measurement, analysis and reporting phases to the system. Accounting methods
are often implemented and evaluated as part of a management control system. To control
financial activities within a company, the area may be broken down into financial and managerial
accounting. Financial accounting generally focuses on internal issues, such as reporting sales
costs, while managerial accounting may focus on methods for determining product costs.
While both areas cover business accounting issues, their methods of application generally differ,
and separate systems implemented by a management control system may aid in ensuring
reports remain accurate and impartial. Managerial accounting is typically responsible for
providing management with information on controlling costs and improving the production
process. Managerial accountants may also provide cost information on new products, make
pricing decisions and monitor actual and budgetary costs.
General financial accounting within management control systems aims to focus on a company’s
internal accounting issues. Financial accounting typically handles payroll and human resource
issues affecting employees within the company. Accounts in this area may also manage employee
costs and reimbursements under a control system.
Notes An MCS is a set of interrelated communication structures that facilitates the
processing of information for the purpose of assisting managers in co-coordinating the
parts and attaining the purpose of an organization on a continuous basis. All organizations
use control system both formal and informal. A system is an aggregate of machines and
people that work toward a common objective.
!
Caution Output is measured, compared against a plan, analyzed if judged significant, and
then reported back to the appropriate earlier phases of the system in the form of positive
or negative reinforcement.
In a management control system, data/information is typically fed back to managers of the
various system phases. Responsible managers will then take appropriate action based on the
data/information provided.
1.2 Nature
The role of the management is to organize, plan, integrate and interrelate organizational activities
to achieve organizational objectives. The achievement of these activities is facilitated by
management control systems. Management control, of course, is a core business function and
exists as a separate, well-established discipline within the management field. Management
Control Systems (MCS) theory is a useful integrative tool for organizing, explaining, and
understanding the jargon and concepts of performance measurement. Management control
systems consist of all organization structures, processes and subsystems designed to elicit behavior
that achieves the strategic objectives of an organization at the highest level of performance with
the least amount of unintended consequences and risk to the organization.
2 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
You might also like
- Management Control System Chapter 1Document14 pagesManagement Control System Chapter 1raplyhollow_68780740No ratings yet
- Management Control SystemsDocument287 pagesManagement Control SystemsMurtaza A Zaveri100% (2)
- Dode - Ebook MANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEMSDocument286 pagesDode - Ebook MANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEMSannisah nsa20100% (1)
- Nature of Management Control System: Mcs Is Must For Organisations Practicing DecentralisationDocument15 pagesNature of Management Control System: Mcs Is Must For Organisations Practicing DecentralisationdevilNo ratings yet
- Management Control System Module 1 NotesDocument14 pagesManagement Control System Module 1 NotesBhavnikNo ratings yet
- A222 - Topic 1 MacsDocument24 pagesA222 - Topic 1 MacsfiqNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemDocument324 pagesManagement Control Systemnesma sooppi100% (1)
- 01 - The Nature of Management Control SystemsDocument28 pages01 - The Nature of Management Control Systemsjasonkurniawan21No ratings yet
- Mcs Ch1 s1 Dan MaksiDocument25 pagesMcs Ch1 s1 Dan MaksiFauzia RahmahNo ratings yet
- Using Diagnostic and Interactive Control SystemDocument20 pagesUsing Diagnostic and Interactive Control SystemNovi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Contents: Chapter 1 Introduction To Management Control SystemDocument10 pagesChapter Contents: Chapter 1 Introduction To Management Control SystemNesru SirajNo ratings yet
- MCS1st SessionDocument29 pagesMCS1st SessionLea WigiartiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 The Nature of Management Control SystemsDocument21 pagesCH 1 The Nature of Management Control SystemsAurellia AngelineNo ratings yet
- Framework For Analysis: Ikke Devlina Yulidar 0510233076Document4 pagesFramework For Analysis: Ikke Devlina Yulidar 0510233076Ikke DephlinaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Management Control SystemDocument28 pagesNature of Management Control Systemurvidave1231211No ratings yet
- CH 1 Nature of MCSDocument28 pagesCH 1 Nature of MCSp4priyaaNo ratings yet
- SPM 1Document18 pagesSPM 1Alia AzharaNo ratings yet
- The Internal Auditing Handbook Supplement Five Management ControlsDocument14 pagesThe Internal Auditing Handbook Supplement Five Management ControlstgaNo ratings yet
- MCS All ChaptersDocument52 pagesMCS All Chaptersrohitkamble09No ratings yet
- Nature of Management Control System: Dr. Aayat FatimaDocument18 pagesNature of Management Control System: Dr. Aayat FatimaKashif TradingNo ratings yet
- Modified Chapter 1Document7 pagesModified Chapter 1Rahul GargNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEM by LlahmDocument18 pagesMANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEM by Llahmmelow_issNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Meaning Nature and Basic Concepts: ObjectivesDocument16 pagesIntroduction: Meaning Nature and Basic Concepts: ObjectivesKetema AsfawNo ratings yet
- Management Control System CH5Document36 pagesManagement Control System CH5Dinaol Teshome100% (1)
- TOPIC 8-ControllingDocument19 pagesTOPIC 8-Controllingrani aliasNo ratings yet
- Management Control Systems QDocument12 pagesManagement Control Systems QramyasrivinaNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemsDocument14 pagesManagement Control SystemsTejashree SavantNo ratings yet
- CH 09 ImaimDocument27 pagesCH 09 Imaimkevin echiverriNo ratings yet
- Controlling ProcessDocument3 pagesControlling ProcessRavi Kumar RabhaNo ratings yet
- Mcs NotesDocument196 pagesMcs NotesYonasNo ratings yet
- PPM Article Review-ControllingDocument7 pagesPPM Article Review-Controllinganisha kanbargiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of MCSDocument24 pagesBasic Concepts of MCSamit raningaNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemsDocument41 pagesManagement Control SystemsAmardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemDocument11 pagesManagement Control Systemi_sonetNo ratings yet
- For ManagementDocument13 pagesFor Managementsyed adilNo ratings yet
- Mcs Unit1 p1Document15 pagesMcs Unit1 p1imranNo ratings yet
- Controlling, Delegation and Interdepartment CoordinationDocument18 pagesControlling, Delegation and Interdepartment Coordinationmann chalaNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemDocument5 pagesManagement Control SystemArjun Sukumaran100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Goal Congruence and Management Control in Different OrganisationsDocument16 pagesChapter 2: Goal Congruence and Management Control in Different OrganisationsNhung KiềuNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemsDocument9 pagesManagement Control SystemsKetan BhandariNo ratings yet
- Management Control SystemDocument3 pagesManagement Control SystemArun NagarNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Management Control SystemDocument4 pagesAssignment On Management Control SystemFelix Yesudas0% (1)
- CH-7 MGTDocument5 pagesCH-7 MGTwaster dessieNo ratings yet
- Inflation AccountingDocument24 pagesInflation AccountingAbhinanda BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Written Report On Control ManagementDocument6 pagesWritten Report On Control ManagementSheda TawasilNo ratings yet
- MGMT-Control (WORD FORMAT)Document14 pagesMGMT-Control (WORD FORMAT)Yae'kult VIpincepe QuilabNo ratings yet
- Management Control System Unit-1Document11 pagesManagement Control System Unit-1sheleftmeNo ratings yet
- The Controlling Function in ManagementDocument50 pagesThe Controlling Function in Managementahetasam75% (4)
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2DK BalochNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Management Control System in Organisation..Document4 pagesEffectiveness of Management Control System in Organisation..Arjun SukumaranNo ratings yet
- Control System in ManagementDocument12 pagesControl System in ManagementSyed JunaidNo ratings yet
- A Key Component of Management Is ControllingDocument3 pagesA Key Component of Management Is Controllingmyrzakhmet.altynNo ratings yet
- Chapt Er 26: Nature and Process of ControllingDocument15 pagesChapt Er 26: Nature and Process of ControllingYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Management - ControlDocument20 pagesManagement - Controlrsikira7905No ratings yet
- Nature of MCSDocument29 pagesNature of MCSshabnurNo ratings yet
- Nature of MCSDocument30 pagesNature of MCSshahmonali694100% (1)
- MGT 1 Principles of MGT OrgDocument23 pagesMGT 1 Principles of MGT OrgJomari RealesNo ratings yet
- DF PDFDocument9 pagesDF PDFAnanda DuttaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Management Control SystemsDocument2 pagesThe Importance of Management Control SystemsISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
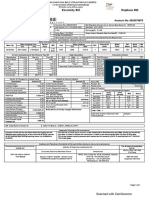
- View BillDocument1 pageView BillISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
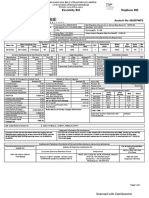
- View BillDocument1 pageView BillISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
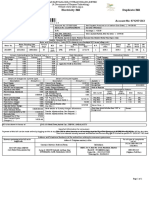
- View BillDocument1 pageView BillISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
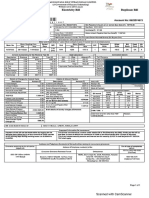
- View Bill LovelyDocument1 pageView Bill LovelyISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
- View BillDocument1 pageView BillISOFINE PRIVATE LIMITEDNo ratings yet
- Proof Load Test Cert - New 25t Bow Shackle For WOM Double Ram BOPDocument2 pagesProof Load Test Cert - New 25t Bow Shackle For WOM Double Ram BOPmujeebNo ratings yet
- Project Organization: Chapter FourDocument32 pagesProject Organization: Chapter Fourgeachew mihiretuNo ratings yet
- Updated List of Common Codes For CFS 3 2019 10-30-06!40!35Document1 pageUpdated List of Common Codes For CFS 3 2019 10-30-06!40!35Jpvasu DevanNo ratings yet
- Vizpcarshd v001Document10 pagesVizpcarshd v001Cliff OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Bi Draft 2.0Document15 pagesBi Draft 2.0Sofia KNo ratings yet
- Intro To Rice Retail.Document5 pagesIntro To Rice Retail.maha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Structure 1 - Merged - CompressedDocument3 pagesStructure 1 - Merged - CompressedsujatmikoNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Enga Gement ActivitiesDocument7 pagesPreliminary Enga Gement ActivitiesJuliana ChengNo ratings yet
- Norsok Standard R-003 Safe Use of Lifting EquipmentDocument58 pagesNorsok Standard R-003 Safe Use of Lifting EquipmentDing Liu100% (1)
- Assessment 2: Last Day of Submission: 23 March 2023Document44 pagesAssessment 2: Last Day of Submission: 23 March 2023Adolfo DiazNo ratings yet
- VLSPDFREPORTDocument7 pagesVLSPDFREPORTranvijayNo ratings yet
- Guidelines UGCF BCOMP 2.1 Corporate AccountingDocument7 pagesGuidelines UGCF BCOMP 2.1 Corporate AccountingShiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Test of Control Working PaperDocument4 pagesTest of Control Working PaperMich Angeles50% (2)
- Live Chat USDDocument5 pagesLive Chat USD13217061 DevanandaNo ratings yet
- ADS Chapter 302 USAID Direct ContractingDocument83 pagesADS Chapter 302 USAID Direct Contractinggern strongthornNo ratings yet
- Customer PerspectiveDocument3 pagesCustomer PerspectiveSakshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 1 Essentials of Entrepreneurship and Small Business ManagementDocument3 pagesSummary Chapter 1 Essentials of Entrepreneurship and Small Business ManagementRameen AlviNo ratings yet
- PPT 02Document33 pagesPPT 02Diaz Hesron Deo SimorangkirNo ratings yet
- 14 - Project Procurement Management (Online LectureDocument19 pages14 - Project Procurement Management (Online LectureAftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2Document10 pagesCbmec 2Ivy Joy ComediaNo ratings yet
- Ayush GuptaDocument2 pagesAyush GuptaThe Cultural CommitteeNo ratings yet
- Turnover LetterDocument3 pagesTurnover LetterGEARLINES TRUCKING 2022No ratings yet
- Statement of PurposeDocument2 pagesStatement of PurposeMustafa AliNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss DiscountDocument34 pagesProfit Loss DiscountMusicLover21 AdityansinghNo ratings yet
- JD Asst Manager-QA ForgingDocument2 pagesJD Asst Manager-QA ForgingParveen (Atam Valves)No ratings yet
- (KODE 05) - BI - CP (Kuantitatif) - Q1 - (Edited)Document9 pages(KODE 05) - BI - CP (Kuantitatif) - Q1 - (Edited)Arif Kathon SubhektiNo ratings yet
- Biodata Sheet - Vere Technical 2022-2023 FixedDocument7 pagesBiodata Sheet - Vere Technical 2022-2023 FixedjessyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Events After Reporting PeriodDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Events After Reporting Periodsonchaenyoung2No ratings yet
- 1 Logbook For Registered Chs Candidates - Rev 6 19/02/2016Document16 pages1 Logbook For Registered Chs Candidates - Rev 6 19/02/2016Amukelani100% (1)
- V 6 o JDks 4Document3 pagesV 6 o JDks 4Noel JenningsNo ratings yet