Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PAST TENSES (1) Explicación
Uploaded by
Alicia Di C�sareOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PAST TENSES (1) Explicación
Uploaded by
Alicia Di C�sareCopyright:
Available Formats
PAST TENSES
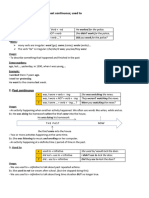
PAST SIMPLE:
Form:
- Affirmative: Regular verbs: verb -e + “d” lived / verb + “ed” walked, played / verb –consonant + “y”,
drop the “y” and add “ied” try – tried BUT verb –vowel + “y” + “ed” enjoy – enjoyed / (1 syllable)
verb –CVC, double the last consonant and add “ed” stop – stopped.
They watched a great film last night. She found all the information on the Internet yesterday.
Irregular verbs (Second column from the list) went, understood, knew, etc.
- Negative: “didn’t” + verb (base form) He didn’t see his girlfriend at the party last night.
- Interrogative: (Wh- word) + “Did” + subject + verb (base form)? Did they tell you the latest news?
Uses: to talk about finished actions, events that started and finished at a specific time in the past. The time when
the action happened can be stated or understood from context.
- To talk about a single event: The judge started his job in 1998.
- To refer to Past STATES (≠ activity verbs): I didn’t understand my teacher.
- To tell the main events of a story in order: I went to the park and I saw a crowd of people.
Time expressions: yesterday, last (week / Saturday), (a month) ago, the day before yesterday, in 2000 (year), in
February (month), in the 1990’s (decade), the 20th century, from … to …
PAST CONTINUOUS:
Form:
- Affirmative: was / were + verb “–ing”
- Negative: wasn’t / weren’t + verb “-ing”
- Interrogative: (Wh-word) + was / were + subject + verb “-ing”? Were you working last night?
Uses:
- To describe an action that was in progress at a specific time in the past: At ten o’clock yesterday, I was
walking to the station.
- To describe a temporary situation in the past: We were staying with our cousins.
- To set the scene in a story or gives background information: I was walking along the road one
evening…
- Longer actions interrupted by shorter actions. WHEN (used with the Past Simple for the interrupting
action). WHILE / AS (used with the Past Continuous for the interrupted action):
Tom was eating dinner when Mary arrived.
While/As Tom was eating dinner, Mary arrived.
- To describe two actions in progress at the same time in the past. Use WHILE or AS
She was doing some research while/as she was teaching.
BUT: They fell in love WHEN they met (one action after the other)
You might also like
- Simple Past Regular Verbs Informative SheetDocument2 pagesSimple Past Regular Verbs Informative SheetPedro FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesSimple Past Past Continuoushuong ngo theNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument5 pagesVerb PatternsMaria Florencia EspilocinNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses TheoryDocument4 pagesPast Tenses TheoryÁngela Naranjo GómezNo ratings yet
- Facultad de Derecho Y Ciencia Politica Escuela Profesional de DerechoDocument4 pagesFacultad de Derecho Y Ciencia Politica Escuela Profesional de DerechoLeticia Alfaro FerreyrosNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Versus Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast Simple Versus Past ContinuousZiba Rezai SepasiNo ratings yet
- Past Tense SimpleDocument3 pagesPast Tense SimpleMellNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses: 1. Show Continuous Action in The PastDocument2 pagesPast Tenses: 1. Show Continuous Action in The PastbeecozaNo ratings yet
- Past TensesDocument12 pagesPast Tensesn andNo ratings yet
- K 2Document20 pagesK 2Nadea OctaryanaNo ratings yet
- S+ Vb-Ed/ Forma A Ii-A A Verbului Neregulat S+ Did + Not + VB Did + S+ VB ?Document4 pagesS+ Vb-Ed/ Forma A Ii-A A Verbului Neregulat S+ Did + Not + VB Did + S+ VB ?OTILIA INA CRĂCEANo ratings yet
- Quá KH Đơn (Past Simple) : 1. Form: (+) S + Was/ Were + N/AdjDocument8 pagesQuá KH Đơn (Past Simple) : 1. Form: (+) S + Was/ Were + N/AdjKHÁNHNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary Present Tenses.: 1-. Yes / No Questions: Questions Which Ask You To Answer: Yes or NoDocument3 pagesGrammar Summary Present Tenses.: 1-. Yes / No Questions: Questions Which Ask You To Answer: Yes or NoEmmy RocaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense: I Often Watched Documenter MoviesDocument3 pagesSimple Past Tense: I Often Watched Documenter MoviesPanjul IdNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument4 pagesContentsEdinson Aguinaga ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- The Past Simple Tense With Lexical VerbsDocument19 pagesThe Past Simple Tense With Lexical VerbsShahad ShakirNo ratings yet
- JdigsgDocument2 pagesJdigsgAjvnNo ratings yet
- REVIEWAV3Document9 pagesREVIEWAV3Cậu Ba Họ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Past Tense NotesDocument3 pagesPast Tense NotesTeyHa AreZam100% (1)
- 3 - Tenses of The VerbDocument31 pages3 - Tenses of The VerbJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous Vs Past Perfect in EnglishDocument4 pagesPast Simple Vs Past Continuous Vs Past Perfect in EnglishAzahara Márquez ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannDocument30 pagesPast Tenses: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannStudent Sokha ChanchesdaNo ratings yet
- Bài 4 Past SimpleDocument3 pagesBài 4 Past Simplehuyenpn2003No ratings yet
- The Past Simple-Past Continuous-1º EsoDocument24 pagesThe Past Simple-Past Continuous-1º EsoflikiNo ratings yet
- Narrative TensesDocument12 pagesNarrative TensesHeber Gonzalez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Enjoy, Explain, Keep, Etc) Determine, Offer, Expect, Wait, Manage, Refuse, Etc)Document12 pagesEnjoy, Explain, Keep, Etc) Determine, Offer, Expect, Wait, Manage, Refuse, Etc)NOT PotNo ratings yet
- Ing X Bab 2 SMT 1 (Recount Text)Document6 pagesIng X Bab 2 SMT 1 (Recount Text)Fajar Akbar GemilangNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument1 pagePast SimpleMihaela EneNo ratings yet
- Review of Verb TensesDocument7 pagesReview of Verb Tensesmavibla07No ratings yet
- PAST Tenses - PPTDocument24 pagesPAST Tenses - PPTbaba ioanaNo ratings yet
- Sinteza TIMPURIDocument4 pagesSinteza TIMPURILoredanaNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns and Past TensesDocument3 pagesRelative Pronouns and Past TensesRoberto RodriguesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledMahmoudalhassaniNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Presentt ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Vs Presentt ContinuousAndreea-Raluca ManeaNo ratings yet
- English 7 Past and Past Perfect PowerpointDocument16 pagesEnglish 7 Past and Past Perfect PowerpointRhea Mae TorresNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument35 pagesSimple Past TenseNurul Hudah100% (1)
- Van Pham Tieng Anh Co Ban Nang CaoDocument20 pagesVan Pham Tieng Anh Co Ban Nang CaoHa TranNo ratings yet
- 01 Past Simple Past Continuous GrammarDocument2 pages01 Past Simple Past Continuous GrammarMariana Filgueira ChiossoniNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPast Continuous TenseDr. Amr AboelmagdNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument17 pagesPast Simplemaria-28095No ratings yet
- Simple Past Tens1Document5 pagesSimple Past Tens1Sandra KundingNo ratings yet
- Guide About Past Continuous 3rd YearDocument22 pagesGuide About Past Continuous 3rd YearConoMaeOdaNo ratings yet
- Review of Present and Past TensesDocument2 pagesReview of Present and Past TensesPedro López de la Osa Clemente MorenoNo ratings yet
- Present Tense SimpleDocument16 pagesPresent Tense SimpleIrina SerseaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past TenseDocument9 pagesSimple Past TenseSandra KundingNo ratings yet
- BAB 10 KLS 8 SEMESTER 2 TerbaruDocument3 pagesBAB 10 KLS 8 SEMESTER 2 TerbaruJoshua SudarsonoNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect & Past Perfect ContinuousDocument5 pagesNarrative Tenses: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect & Past Perfect ContinuousLaura Irina Lara SánchezNo ratings yet
- Theory Simple ContinuousDocument2 pagesTheory Simple Continuousflower powerNo ratings yet
- English Tenses: The Simple PresentDocument14 pagesEnglish Tenses: The Simple PresentadasalbatecuNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect - Past Simple - Past ContinuousDocument17 pagesPast Perfect - Past Simple - Past ContinuousSamuelConstantineNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument4 pagesTENSES19Hoàng Thanh ThảoDHQT14A1NDNo ratings yet
- Grammar Verb Tenses Chart 2 - 3esoDocument2 pagesGrammar Verb Tenses Chart 2 - 3esoTRK68No ratings yet
- 9th Grade Review UnitDocument37 pages9th Grade Review UnitMarcia Zelaya ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Past Tenses: Simple Past Past Continuous Past PerfectDocument25 pagesPast Tenses: Simple Past Past Continuous Past PerfectNur Amanina AzhariNo ratings yet
- Past Simplevs Past Cont.Document13 pagesPast Simplevs Past Cont.dandreamerNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument26 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousBalonash Q SclipiciNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Past ContinuousDocument12 pagesSimple Past and Past ContinuousHenry SaputroNo ratings yet
- Grammar Past Simple and ContinuousDocument4 pagesGrammar Past Simple and ContinuousElla MachaalanyNo ratings yet