Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PT G10 Sci
PT G10 Sci
Uploaded by
Marife Guadalupe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesOriginal Title
PT_G10_SCI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesPT G10 Sci
PT G10 Sci
Uploaded by
Marife GuadalupeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
SCIENCE 10 (III)
NAME: ____________________________ GR.& SEC._________ SCORE:________
Directions: Read the sentences below and identify what they refer to from the given choices below
each. Write the letter of your answer directly in the blank.
_____1. What gland is being stimulated during exercise?
A. adrenal C. pituitary
B. parathyroid D. thyroid
_____2. Which of the following glands secrete a hormone that enables the body to produce T cells?
A. adrenal C. thymus
B. parathyroid D. thyroid
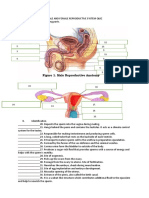
_____3. The organ that makes estrogen and progesterone is the __________.
A. hypothalamus C. pineal gland
B. ovary D. vagina
_____4. Which of the following glands produce hormones that controls the calcium levels the body?
A. adrenal C. pituitary
B. parathyroid D. thymus
_____5. Which of the following glands produce hormones that controls the heart rate and breathing in
times of emergency?
A. adrenal C. pituitary
B. pancreas D. thyroid
_____6. The hormones secreted by pancreas are insulin and ___________.
A. adrenaline C. glucagon
B. estrogen D. melatonin
_____7. When you are running to stay away from danger, what gland is being stimulated?
A. adrenal C. pituitary
B. pineal D. thyroid
_____8. It refers to the body's 'master gland' because it controls the activity of most other hormone-
secreting glands.
A. adrenal C. pituitary
B. parathyroid D. thyroid
_____9. Which of the following is NOT TRUE about the function of the endocrine system?
A. controls sexual reproduction
B. collect sensory input from the body
C. maintain homeostasis
D. regulate growth
_____10.What gland is involved if a person’s blood sugar level becomes unstable?
A. adrenal C. parathyroid
B. pancreas D. ovary
_____11.The nervous system uses electrical impulses to send messages through neurons while
___________ uses hormones to send messages to the target cells through the bloodstream.
A. circulatory system C. nervous system
B. endocrine system D. reproductive system
_____12.What is the purpose of the thyroid gland?
A. It releases insulin and glucagon to regulate sugar level.
B. It releases thyroxin and insulin to stimulate growth.
C. It releases thyroxin and calcitonin.
D. It releases adrenaline to prepare the body for action.
_____13.What is osteoporosis?
A. It is a condition characterized by imbalanced blood sugar.
B. A disorder characterized by apparent lack of aging.
C. A disorder characterized by impaired growth.
D. A disorder in which bones become fragile and breakable.
_____14.What do you call a rare condition that causes abnormal growth in children due to the
decrease in the production and secretion of growth hormones?
A. diabetes C. gigantism
B. dwarfism D. goiter
_____15.Which of the following shows a correct pairing of dysfunction and the involved endocrine
gland?
A. diabetes: ovaries C. goiter: thyroid
B. dwarfism: adrenal D. osteoporosis: pancreas
_____16. The ability to reproduce begins at _____.
A. adolescence C. childhood
B. adulthood D. infancy
_____17. Menstruation is a sign that a girl is _____.
A. already menopausal. C. capable of producing offspring.
B. already pregnant. D. not capable of reproduction.
_____18. Menstruation is the discharge of blood from the _____.
A. fallopian tube C. uterine wall
B. ovary D. vagina
_____19. An egg maybe released from the ovary through a process called ____.
A. Dilation C. Gestation
B. Fertilization D. Ovulation
_____20. What is considered as the ovulation day for regular menstrual cycle?
A. 1st day C. 20th day
B. 14th day D. 28th day
_____21. Which of the following produces ova and secretes estrogen and progesterone?
A. hypothalamus C. pituitary
B. ovary D. uterus
_____22. Hormones affect various processes in the body as they regulate the activities of organs,
tissues, and cells. Which of the following statements is true about female hormones? They _____.
A. act in very small amounts but estrogen must be dominant.
B. are sometimes released by organs.
C. cause pain and pelvic cramps.
D. trigger headaches.
_____23. Which hormone thickens uterine lining (endometrium) in preparation for implantation, and
inhibits FSH and LH?
A. estrogen C. LH
B. FSH D. progesterone
_____24. Which hormone helps control the menstrual cycle and stimulates the growth of eggs in the
ovaries?
A. follicle-stimulating hormone C. progesterone
B. luteinizing hormone D. testosterone
_____25. In the female human reproductive system, fertilization normally occurs in the _____.
A. cervix C. uterus
B. fallopian tube D. vagina
_____26. What are the main parts of the nervous system?
A. arteries, veins, and capillaries
B. brain, spinal cord, and nerves
C. hands, feet, and tongue
D. nose, toes, and tongues
_____27. Which part of the brain helps keep your balance so you don’t just fall or stumble while
walking?
A. cerebellum C. pituitary gland
B. medulla oblongata D. spinal cord
_____28. Which of the following is TRUE about central nervous system?
A.It can be classified as somatic and autonomic nervous system.
B. It is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
C. It is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and hormones.
D. It is composed of cranial and spinal nerves.
_____29. You felt hungry because you haven’t eaten your food for lunch trying to finish home works.
Which of the following is the best response to the given stimulus?
A. Continue work. C. Ignore the situation.
B. Eat. D. Shout out loud.
_____30. Instructions from the brain to the target organs is carried by _________.
A. receptors C. sense organs
B. nerves D. hormones
_____31. What are the building blocks of proteins?
A. amino acid C. glucose
B. fatty acid D. nucleotides
_____32. What is the molecule that serves as the “blueprint” of life?
A. deoxyribonucleic acid C. ribonucleic acid
B. messenger RNA D. transfer RNA
_____33. What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
A. adenine, cytosine, uracil only
B. adenine, cytosine, thymine only
C. adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine
D. adenine, cytosine, guanine, uracil
_____34. Which is the correct complement pairing of bases in DNA?
A. adenine-guanine, cytosine-guanine
B. adenine-cytosine, guanine-thymine
C. adenine-thymine, cytosine-guanine
D. uracil adenine, cytosine-guanine
_____35. Which of the following sequences of DNA bases is complementary to the sequence: ATC-
GTG-CCC
A. TAG-CAC-GGG C. AUG-CAC-GGG
B. TAG-TAT-GGG D. AUG-TAT-GGG
_____36. What do you call the genetic mutation that causes a codon that should code for a specific
amino acid to be changed into a stop codon ?
A. a chromosomal mutation. C. a nonsense mutation
B. a frame shift mutation.. D. a silent mutation.
_____37. A genetic mutation that does not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of the
resulting protein is called
A. a chromosomal mutation. C.a nonsense mutation.
B. a frame shift mutation. D.a silent mutation.
_____38. This is a mutation that causes a section of the chromosome to be broken out and reinserted
backwards. This is known as
A. deletion. C. inversion.
B. insertion. D. translocation.
_____39. Persons with Down syndrome usually have ______ copies of chromosome 21.
A. no B. one C. two D. three
_____40. If a segment of a chromosome is present several times more than normal due to unequal
crossing-over, it is called ________.
A. a deletion C. an inversion
B. duplication D. a translocation
_____41. An adaptation promotes ________.
A. chance to survive C. chance to survive and reproduce
B. chance to reproduce D. None of the above
_____42. The criterion used to determine if an organism is a new species is based on ________.
A. time C. reproduction
B. geography D. physical traits
_____43. Where can most fossils be found?
A. Black soil C. Granite rock
B. Lava flows D. Sedimentary rock
_____44. Vertebrate forelimbs are most likely to be discussed in ________.
A. Ecology C. Biogeography
B. Embryology D. Comparative anatomy
_____45. Which of the following statements does NOT describe Darwin's theory of natural selection?
A. The members of a population of the organisms will strive.
B. Populations tend to replicate in minimal numbers.
C. Members of a population have genetic differences.
D. Some members of a inhabitants have adaptive behaviors.
_____46. Which of the following describes mutation?
A. A result of inbreeding.
B. Any change in the structure of chromosomes.
C. Change in gene pool due to migration.
D. Differential survival and reproduction of organisms.
_____47. What agent of evolutionary change can result to a population with limited variation due
entirely to chance?
A. Mutation C. Genetic drift
B. Gene flow D. Inbreeding
_____48. What do you call the process that results to the formation of new species because of
evolution?
A. Speciation C. Reproduction
B. Mutation D. Migration
_____49. Who is the first evolutionist to believe that organisms change?
A. Jean Baptiste de Lamarck C. Charles Darwin
B. Richard Dawkins D. Steve Jones
_____50. It is commonly observed in plants and in some kinds of animals and a very good example of
non-random mating.
A. Genetic drift C. Gene flow
B. Inbreeding D. Mutation
_____51. When a change occurs in the environment, what will organisms do?
A. adapt C. die
B. adapt, migrate or die D. migrate or die
_____52. Which of the following is an ecosystem?
A. rice field C. temperature
B. sunlight D. thunderstorm
_____53. A person breeds rabbits in a cage. After a few generations, the breeder observes that the
rabbits are more aggressive towards each other, the young are less healthy and more young rabbits
die. What do you think will happen to the population of rabbits?
A. The population will not be affected.
B. The population will decrease.
C. The population will increase.
D. The population will remain the same.
_____54. What is the significance of species diversity?
A. High species diversity tends to be more productive and sustainable.
B. High species diversity tends to create chaos in an ecosystem.
C. More diverse ecosystem has lesser ability to withstand environmental stressors.
D. Species minimize interaction with their environment, thus perform certain functions.
_____55. Why are invasive species a threat to biodiversity?
A. They can be of help to other organisms.
B. They can be beneficial to humans.
C. They can increase the number of resources.
D. They can outcompete native organisms for their resources.
_____56. Which is the adverse effect of high fertility and rapid population growth?
A. Over supply of job opportunities
B. Effects of large families on child development
C. Less urbanization and crowding
D. Increased equalities in education
_____57. The statement “250 individuals per square kilometer” most likely refers to _________.
A. population C. population distribution
B. population density D. population growth
_____58. Which of the following causes a decreasing wildlife population in most of the places in our
country?
A. Loss of limiting factor C. Loss of habitat
B. Loss of natural disturbances D. Loss of carrying capacity
_____59. Based on the given statements, how will you describe the yearly percentage change of
Philippine population growth in the last four years?
I. The current population of Philippines in 2021 is 111,046,913, a 1.34% increase from 2020.
II. The population of Philippines in 2020 was 109,581,078, a 1.35% increase from 2019.
III. The population of Philippines in 2019 was 108,116,615, a 1.37% increase from 2018.
IV. The population of Philippines in 2018 was 106,651,394, a 1.41% increase from 2017.
A. The Philippine population growth is stable.
B. The Philippine population growth is decreasing.
C. The Philippine population growth increases rapidly.
D. The Philippine population growth increases slowly.
_____60. A limiting factor is an environmental condition that restricts the growth distribution of a
population within an ecosystem. Which of the following limiting factors would increase due to the
number of individuals in a population?
A. increase temperature C. natural disaster
B. disease D. unusual weather
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Male and Female Reproductive System QuizDocument2 pagesMale and Female Reproductive System QuizMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- PT G10 ScienceDocument7 pagesPT G10 ScienceMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Composing An Effective Paragraph - English 8 - Lecture 4Document38 pagesComposing An Effective Paragraph - English 8 - Lecture 4Marife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- English - Grade 8 - Second Periodic TestDocument3 pagesEnglish - Grade 8 - Second Periodic TestMarife Guadalupe100% (3)
- Module 2-English Worksheet-SourcesDocument2 pagesModule 2-English Worksheet-SourcesMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Persuasive EssayDocument1 pagePersuasive EssayMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Analyzing Literature As A Mirror To A Shared HeritageDocument1 pageQuiz On Analyzing Literature As A Mirror To A Shared HeritageMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 2nd QDocument5 pagesGenphysics 2nd QMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- At The BeginningDocument1 pageAt The BeginningMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Eng8-Summarizing ActivityDocument2 pagesEng8-Summarizing ActivityMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Activity English 8Document2 pagesModule 3 Activity English 8Marife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam 22-23Document7 pagesSecond Quarter Exam 22-23Marife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 19-Impulse, Momentum and CollisionDocument59 pagesLesson 19-Impulse, Momentum and CollisionMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Second Quarter ExamMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Charles' Law ActivityDocument1 pageCharles' Law ActivityMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log 8 English Week 3 THIRDDocument10 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log 8 English Week 3 THIRDMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Over The Past y-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageOver The Past y-WPS OfficeMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- RPMS With Movs and AnnotationsDocument152 pagesRPMS With Movs and AnnotationsMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Identified Issues and ConcernDocument1 pageIdentified Issues and ConcernMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Marigold Answer Key - MirrorDocument2 pagesMarigold Answer Key - MirrorMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Check Your Understanding-KinematicsDocument2 pagesCheck Your Understanding-KinematicsMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH-8-LESSON 1 - FACT AND OPINION PowerpointDocument7 pagesENGLISH-8-LESSON 1 - FACT AND OPINION PowerpointMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1 12 Q1 Week4 5 MOD5 Cabuntucan, George MARVIN ABARADocument55 pagesGenPhys1 12 Q1 Week4 5 MOD5 Cabuntucan, George MARVIN ABARAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1 12 Q1 Week3 MOD4 Taguicana, Nove Lheen MARVIN ABARADocument63 pagesGenPhys1 12 Q1 Week3 MOD4 Taguicana, Nove Lheen MARVIN ABARAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- 1ST QuarterDocument27 pages1ST QuarterMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1 12 Q1 Week2 MOD3 Mateo, Charlotte MARVIN ABARADocument41 pagesGenPhys1 12 Q1 Week2 MOD3 Mateo, Charlotte MARVIN ABARAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1-12-Q1-Week6-Mod6-MELC - Agullana, Roshela R. - Abara, Marvin Q. - ROSHELA AGULLANADocument32 pagesGenPhys1-12-Q1-Week6-Mod6-MELC - Agullana, Roshela R. - Abara, Marvin Q. - ROSHELA AGULLANAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Writing Bibliography WorksheetDocument1 pageWriting Bibliography WorksheetMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1 12 Q1 Week7 8 MOD7 Salvador, Flordeliza MARVIN ABARADocument67 pagesGenPhys1 12 Q1 Week7 8 MOD7 Salvador, Flordeliza MARVIN ABARAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- GenPhys1 12 Q1 Week1 MOD1 Mateo, Maezel Joice MARVIN ABARADocument23 pagesGenPhys1 12 Q1 Week1 MOD1 Mateo, Maezel Joice MARVIN ABARAMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet