Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8th - 24 04 2022
8th - 24 04 2022
Uploaded by
9473088058Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8th - 24 04 2022
8th - 24 04 2022
Uploaded by
9473088058Copyright:
Available Formats
Batch:- 8th Max.
Marks: 360
Time: 3Hrs Date:- 24/04/2022
Physics
1. Displacement is a ___________
(A) Vector quantity (B) Scalar quantity
(C) Either vector quantity or scalar quantity
(D) Neither vector quantity nor scalar quantity
2. A ball is thrown up with a certain velocity. It
attains a height of 40m and comes back to the (A) 8 km (B) 6 km
thrower. Then the (C) 10 km (D) 12 km
(A) total distance covered is 40m 10. Which of the following are correct
(B) magnitude of displacement is 80 m (A) distance = displacement
(C) displacement is zero
(D) total distance covered is zero Displacement
(B) 1
3. The distance travelled by a freely falling body is dis tan ce
proportional to
(A) the mass of the body displacement dis tan ce
(C) 1 (D) 0
(B) the square of the acceleration due to gravity. dis tan ce displacement
(C) the square of the time of fall 11. A horse runs a distance of 1200m in 3 min
(D) the time of fall and 20s.The speed of the horse is_________
4. A man goes 10 m towards North, then 20 m
(A) 60ms 1 (B) 65ms 1
towards east then displacement is
(A) 22.5 m (B) 25 m (C) 25.5 m (D) 30 m (C) 40ms 1 (D) 6ms 1
5. An athlete completes one round of a circular 12. A car moving on a straight road covers one
track of radius R in 40 sec. What will be his third of the distance with 20 km/hr and the rest
displacement at the end of 2 min. 20 sec. with 60 km/hr. The average speed is
(A) zero (B) 2R (C) 2R (D) 7R (A) 40km / hr (B) 80km / hr
6. A cyclist moves from a certain point X and
completes one revolution around a circular path 2
(C) 46 km / hr (D) 36 km/hr
of radius ‘r’. The distance travelled and 3
magnitude of displacement of the cyclist are 13. A 150 m long train is moving with a uniform
respectively. velocity of 45 km/h. The time taken by the train
r to cross a bridge of length 850 meters is
(A) 2r, r (B) , 2 (A) 56 sec (B) 68 sec
2 (C) 80 sec (D) 92 sec
(C)2r, zero (D) r, 2r 14. A bus is moving at 20ms–1. How much distance
7. Distance is a in kilometers will the bus cover in 25 minutes?
(A) vector quantities (A) 30 km (B) 19 km
(B) scalar quantities (C) 40 km (D) 50 km
(C) either scalar or, vector 15. A numerical ratio of velocity to speed of a
(D) neither scalar nor vector particle is always
8. An object moves along a straight path of 20m (A) zero (B) equal to one
and returns same point through same path (C) equal to or less than one
after a certain time. The displacement of object (D) less than one
is
(A) 20m (B) 40m (C) zero (D) 30m
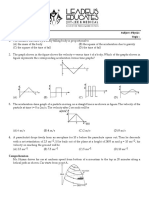
9. The displacement of object in given diagram
is
March ahead towards your y{; 1
Email Id:- lakshyamarch@gmail.com
Chemistry
16. Every matter has its own ...... and ......
23. Eraser, book, slate is solid matter which does not
a. Mass, volume b. Weight, mass
has.
c. Brittleness, tough d. Shape, shadow
a. Definite shape b. Distinct boundaries
17. ‘Panch Tatva’ of life.
c. Fixed velocity d. Fixed volume
a. Air, god, water, mother, father
24. Solid have.........
b. Air, fire, earth, sky, water
a. Negligible compatible
c. Air, god, water, soil, crop
b. Negligible compressible
d. Air, god, water, yield, money
c. Negligible volume
18. Matter is classified on the basis of ......
d. Negligible shape
a. Physical and chemical properties
25. Negligible compressiblility ........
b. Physical and biological properties
a. Soil b. Gas c. Water d. Solid
c. Chemical properties
26. Solids have tendency to maintain their ..... and ...
d. Biological and characteristcal properties
a. Shape, inside pressure
19. Any color which we detected by our eyes....
b. Shape, outside temperature
a. Due to light b. Due to air
c. Shape, outside force
c. Due to visible light d. Due to darkness
d. Shape, outside pressure
20. It is not the state of matter
27. Sugar and salt kept in different jars . they are .....
a. Solid b. Liquid
a. Soil b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solids
c. Soil d. Gas
28. Rubber can change their shape. It is .......
21. It is state of matter
a. Soil b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solids
a. Soil b. Air
29. Liquids have no fixes shape but have .........
c. Water d. Gas
a. Fixed velocity b. Fixed value
22. It is not solid.
c. Fixed temperature d. Fixed voulume
a. Book
30. Liquids can flow and change its ......
b. Completely Vegetables
a. Texture b. Size
c. Completely molten ice
c. Volume d. Shape
d. Ice bag
March ahead towards your y{; 2
Email Id:- lakshyamarch@gmail.com
Biology
March ahead towards your y{; 3
Email Id:- lakshyamarch@gmail.com
Maths
46. Every integer is a ………………… number. 57. Sum of two irrational number is
(A) whole (B) natural (A) rational (B) irrational
(C) rational (D) positive (C) natural number
47. Every ……………….. Number is smaller (D) rational or irrational
than 0. 58. Division of two irrational number is
(A) positive (B) rational (A) rational (B) irrational
(C) natural (D) negative (C) natural number (D) rational or irrational
1 1
48. The sum of
8
and
8
is ……………….. Write only the answer on the back side of
OMR Sheet.
1 1
(A) (B) (C) 0 (D) 1 59. Evaluate each of the following products:
4 4
(a) (-3) (-9) (-6) (12)
1 (b) (-1) (-5) (-7) (-3) (4)
49. …………
5
60. Find the value of the following
1 1 (a) (-2) 15625 + (-98) 15625
(A) (B) (C) 0 (D) 1
5 5 (b) 1487 327 + (-487) 327
3 0
50. 61. State, which is greater
5 15
(a) {(-2) – 5} (-6) and (-2) – 5 (-6)
(A) 9 (B) - 9 (C) - 3 (D) 3
(b) (8 – 9) 10 and 8 – 9 10
1 1
51. …………………….
2 2 3
62. The sum of two rational numbers is . If
1 5
(A) 1 (B) 0 (C) -1 (D)
4 9
one of the number is , find the other..
20
1
52. 8 ………………………
8
5
(A) - 1 (B) 1 (C) 8 (D) - 8 63. What number should be added to so
8
53. If a, a + 2 and a + 4 are prime numbers,
then the number of possible solutions for a 5
as to get ?
is : 9
(A) one (B) two
(C) three (D) None of these 2 4 5
54. If x and y are negative, then which of the 64. Subtract from the sum of , and
following statements is/are always true? 3 6 12
I. x + y is positive 4
II. xy is positive .
3
III. x – y is positive
(A) I only (B) II only 3
65. What should be subtracted from so as
(C) III only (D) I and III only 4
55. A positive integer, which when added to 5
1000, gives a sum which is greater than to get .
6
when it is multiplied by 100. This positive
2 3 2
integer is : 66. What should be added to to get ?
(A) 1 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 3 3 5 15
56. Sum of two rational number is
(A) rational (B) irrational
(C) natural number (D) integer
March ahead towards your y{; 4
Email Id:- lakshyamarch@gmail.com
3 2 65 12
67. What should be subtract from to get 72. Divide the sum of
12
and
7
by their
4 3
difference.
1
? 33
6 73. By what number should be divided to
16
68. Evaluate 11
get ?
12 7 3 1 1 4
(a)
5 20 14 7 10 74. The product of two rational numbers is 15.
If one of the numbers is –10, find the other.
6 7 19
(b) 2 75. Observe the following number line and
7 9 21
answer the questions given below.
6 5 4 15
(c)
7 6 9 7 ● ●
7
● ●
5
● ● ● ●
1
● ● ● ● ● ●
1
●6 ● ●
7
1 0 3 1 2
2
69. Simplify
4
4 4 4 4 4 4
4 3 9 10 1 3 5 7
(a) (i) Which of the two numbers and is
5 2 5 3 2 4
4 4
1
3 7
15 1 smaller?
(b) 1
2 4 18 7 4 1 7
(ii) Arrange 2, , ,1, 0 in the ascending
13 15
7 8 3 1 4 4
(c) order.
9 2 3 5 5 2
3
3 5 9 4 5 6 (iii) Which of the two numbers and 0 is
(d) 4
11 6 12 3 13 15
greater?
(iv) W hich is the greatest number from
28
70. The product of two rational numbers is . 6 1
81 2, and ?
4 4
14
If one of the number is , find the other..
27
3
71. By what number should be multiply ,
14
5
so that the product may be .
12
March ahead towards your y{; 5
Email Id:- lakshyamarch@gmail.com
You might also like
- Bille Jean Jazz Piano Sheet MusicDocument14 pagesBille Jean Jazz Piano Sheet MusicDanial Farhadi100% (1)
- NLM and Projectile Test PaperDocument7 pagesNLM and Projectile Test Papershriyansh singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7: 802.1X: Wireless NetworksDocument13 pagesLab 7: 802.1X: Wireless NetworksJosel ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Stock Preparation DIP Paper Machine BCTMP WH: NotesDocument2 pagesStock Preparation DIP Paper Machine BCTMP WH: NotesFajar MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Exam Practice QuestionsDocument8 pagesExam Practice QuestionsolivijaNo ratings yet
- Determining The Truthfulness and Accuracy of The Material ViewedDocument9 pagesDetermining The Truthfulness and Accuracy of The Material ViewedEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Physics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Document7 pagesPhysics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Abhay Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be ExercisesDocument8 pagesVerb To Be ExercisesSofia MorenoNo ratings yet
- TrustDocument2 pagesTrustkelvin black50% (2)
- Countries and NationalitiesDocument1 pageCountries and NationalitiesenahudiNo ratings yet
- Class - 9th: Part - I PhysicsDocument8 pagesClass - 9th: Part - I PhysicsShivam ZakhmiNo ratings yet
- 8th - 16 04 2023Document5 pages8th - 16 04 20239473088058No ratings yet
- 3rd FNT All BatchesDocument230 pages3rd FNT All Batcheskuldeeplohana89No ratings yet
- Worksheet D22 Dec 2022Document4 pagesWorksheet D22 Dec 2022PrinceNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics MCQ DataDocument7 pages1st Year Physics MCQ Dataahmadsubhani72No ratings yet
- Lakshy17 09 23Document3 pagesLakshy17 09 23sarma e.mNo ratings yet
- PSG 2018Document7 pagesPSG 2018MR. EXPLORERNo ratings yet
- GRD English 2018Document7 pagesGRD English 2018K JeyarajNo ratings yet
- 2022 Physics Mid-Year EXAM G9Document10 pages2022 Physics Mid-Year EXAM G9Imon BrownNo ratings yet
- Isso - Class 07 - Practice PaperDocument9 pagesIsso - Class 07 - Practice PaperRaghavendra Rao TholetiNo ratings yet
- Railway Recruitment Board Examination, Ahmedabad: January 2005 Question Paper (Fully Solved)Document10 pagesRailway Recruitment Board Examination, Ahmedabad: January 2005 Question Paper (Fully Solved)avee1984No ratings yet
- MCQ Sci 2Document9 pagesMCQ Sci 2hardikvats30No ratings yet
- Physics Aiims PatternDocument7 pagesPhysics Aiims PatternMuhammad YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Duration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180 Class - IX (Going To X)Document10 pagesDuration: 2 Hrs. - Maximum Marks: 180 Class - IX (Going To X)Sandeep RevliyaNo ratings yet
- 1 VectorDocument4 pages1 VectorB AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Phy 101 PQ 2-1Document2 pagesPhy 101 PQ 2-1Daniel olayioyeNo ratings yet
- Grade Xi-Sci Physics Worksheet For (Half Yearly)Document7 pagesGrade Xi-Sci Physics Worksheet For (Half Yearly)AlokNo ratings yet
- Class IXDocument9 pagesClass IXJ SoujanyaNo ratings yet
- XI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Document4 pagesXI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Muneeb AlamNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice Sheet 1-15Document24 pagesDaily Practice Sheet 1-15kraken monsterNo ratings yet
- Top 300 General Science PYQ Questions For CDS II 2021Document56 pagesTop 300 General Science PYQ Questions For CDS II 20213021 Akash joshNo ratings yet
- XI Physics (Objective)Document5 pagesXI Physics (Objective)xsai7879No ratings yet
- Physics Summer Vacation Homework by Abdullah SufianDocument15 pagesPhysics Summer Vacation Homework by Abdullah SufianMoon boyNo ratings yet
- 8th - 23 04 2023Document1 page8th - 23 04 20239473088058No ratings yet
- Half Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Document6 pagesHalf Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Darth VaderNo ratings yet
- Class - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsDocument26 pagesClass - 11 Vedantu Physics Chp-2 Objective Questions With SolutionsAloke kr. MondalNo ratings yet
- Ouat 2015 PCBDocument10 pagesOuat 2015 PCBAswini Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Mock Phase 1 Mains Test For PractiseDocument3 pagesMock Phase 1 Mains Test For PractiseRocky WaterNo ratings yet
- 8th - 08 05 2022Document2 pages8th - 08 05 20229473088058No ratings yet
- Science Sample 1 MCQDocument11 pagesScience Sample 1 MCQJEETNo ratings yet
- MCQ SciDocument11 pagesMCQ Scihardikvats30No ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)Document3 pagesPRACTICE TEST - (Vectors & KM) : Pattern-1 Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-6)chaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- 2022 Physics Mid-Year EXAM G9Document11 pages2022 Physics Mid-Year EXAM G9Imon BrownNo ratings yet
- Reason (R) : Spikes Increase Friction Between TheDocument2 pagesReason (R) : Spikes Increase Friction Between ThepullaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8th TestDocument10 pagesClass 8th Testnsw52274No ratings yet
- PW - AITS - NT-24: PhysicsDocument21 pagesPW - AITS - NT-24: PhysicsOfficers IasNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Wallah QuestionsDocument25 pagesPhyiscs Wallah QuestionsFreedom Fighters FanNo ratings yet
- NTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Document6 pagesNTSE Support Program: SESSION: 2019-20Anita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MCQ'sDocument1 pageCivil Engineering MCQ'sNISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- Physics Questionnaire-FinalDocument7 pagesPhysics Questionnaire-FinalMike Jerome MugaNo ratings yet
- 11TH CH 1 - 13 80M Paper 3Document3 pages11TH CH 1 - 13 80M Paper 3Tacco BladeNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Asked in SSC CGL 1667820460184 OBDocument9 pagesPhysics Questions Asked in SSC CGL 1667820460184 OBApki mautNo ratings yet
- Objective Type Questions Chapter # 4 Motion in Two DimensionDocument2 pagesObjective Type Questions Chapter # 4 Motion in Two DimensionRao Arslan Rajput100% (3)
- NEET Test Series 29Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 29RavvaNo ratings yet
- Complete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFDocument5 pagesComplete NSO - SOF Physics (Part 1) - Practice Sheet Notes - (Only PDFsrijanapple5No ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument6 pagesPhysics QPch22b039No ratings yet
- Physics MCQDocument11 pagesPhysics MCQIyzSpookyNo ratings yet
- XI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedDocument22 pagesXI MCQ UP To ROTATION-converted-compressedEkamjot SINGHNo ratings yet
- Posts Included in Ccs-I Examination (GROUP-I SERVICES) (2007)Document17 pagesPosts Included in Ccs-I Examination (GROUP-I SERVICES) (2007)rathaiNo ratings yet
- Kerala PMT 2005Document4 pagesKerala PMT 2005Praveen Kumarpillai100% (1)
- Uranium Talent Search Examination (Utse) - 2013: Physics SectionDocument5 pagesUranium Talent Search Examination (Utse) - 2013: Physics SectionDebasis KarNo ratings yet
- Roll No 13 Phy Term 1 PaperDocument6 pagesRoll No 13 Phy Term 1 Papershamini sasikumarNo ratings yet
- 9th Class PolynomialsDocument10 pages9th Class PolynomialsTu nahi Hai voNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper 1 PDFDocument5 pagesModel Test Paper 1 PDFShaunak ThakarNo ratings yet
- 8th - 01 05 2022Document5 pages8th - 01 05 20229473088058No ratings yet
- Cbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12Document8 pagesCbse 2024 by Neeraj Class 12sciencepedia9No ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument58 pagesSet TheoryLeslie Vine DelosoNo ratings yet
- Libero 08Document52 pagesLibero 08Luis OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Febiana Eka W-932217918-Outline ProposalDocument2 pagesFebiana Eka W-932217918-Outline ProposalFebiana WardaNo ratings yet
- HibernateDocument73 pagesHibernateapi-27399718100% (1)
- Lbr-Ex: Enhanced Part Libraries, Scripts and User Language Programs For EagleDocument11 pagesLbr-Ex: Enhanced Part Libraries, Scripts and User Language Programs For EagleMamas YonoNo ratings yet
- Sky Limit Coreldraw ExamDocument2 pagesSky Limit Coreldraw ExamJoseph DamuosNo ratings yet
- Epicor ICEDocument61 pagesEpicor ICEIvan FaneiteNo ratings yet
- TSL552 Task Development WritingDocument4 pagesTSL552 Task Development WritingFATIHAH NUR HANA FADHLULLAHNo ratings yet
- Theories J Rationale and Evidence Supporting MTB-MLE Developmental Learning TheoriesDocument2 pagesTheories J Rationale and Evidence Supporting MTB-MLE Developmental Learning TheoriesChanie Lynn MahinayNo ratings yet
- Hungarian Greek Catholic ChurchDocument4 pagesHungarian Greek Catholic Churchnovascotta343No ratings yet
- R01-教師用書pdf檔 (套紅) (When Shocked in Rome)Document8 pagesR01-教師用書pdf檔 (套紅) (When Shocked in Rome)YuehNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Did Rizal RetractDocument2 pagesActivity 4 Did Rizal RetractmjNo ratings yet
- Lanmark-10G Cable: DescriptionDocument3 pagesLanmark-10G Cable: Descriptionange ettienNo ratings yet
- 7 Colours of A RainbowDocument20 pages7 Colours of A RainbowElena RalucaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document63 pagesChapter 1PrathameshNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesLecture NotesKereshlin MichaelNo ratings yet
- Politécnico Rafaela Marrero Paulino Practice # 2 Teacher: Mirian NúñezDocument3 pagesPolitécnico Rafaela Marrero Paulino Practice # 2 Teacher: Mirian NúñezHeidy Veronica Victoria ValdezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Book of RomansDocument3 pagesIntroduction To The Book of RomansOkokon BasseyNo ratings yet
- Balkan Revisions To The Myth of Central EuropeDocument26 pagesBalkan Revisions To The Myth of Central EuropeLeonardo SoaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 JournalDocument6 pagesUnit 3 JournalRohan PadhyaNo ratings yet
- Devnet 2340Document41 pagesDevnet 2340Cesar David Felix CardenasNo ratings yet
- SQL and Xquery Tutorial For Ibm Db2, Part 1Document26 pagesSQL and Xquery Tutorial For Ibm Db2, Part 1Anup Dudani100% (1)