0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views3 pagesABCDE Approach to Emergency Assessment
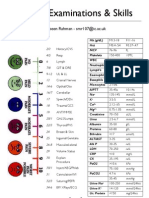
This document outlines the ABCDE approach for assessing and managing patients. It summarizes:
1) How to assess the airway for patency, obstruction, and appropriate maneuvers and adjuncts to open the airway.
2) How to evaluate breathing by assessing rate, pattern, inspection of chest, palpation, percussion and auscultation to diagnose problems like pneumonia, pulmonary edema, asthma, and pleural issues.
3) How to examine circulation by checking pulse, capillary refill time, temperature, and performing tests to diagnose causes of shock like hemorrhage, cardiac, septic or anaphylactic shock.
Uploaded by
Hala BahaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views3 pagesABCDE Approach to Emergency Assessment
This document outlines the ABCDE approach for assessing and managing patients. It summarizes:
1) How to assess the airway for patency, obstruction, and appropriate maneuvers and adjuncts to open the airway.
2) How to evaluate breathing by assessing rate, pattern, inspection of chest, palpation, percussion and auscultation to diagnose problems like pneumonia, pulmonary edema, asthma, and pleural issues.
3) How to examine circulation by checking pulse, capillary refill time, temperature, and performing tests to diagnose causes of shock like hemorrhage, cardiac, septic or anaphylactic shock.
Uploaded by
Hala BahaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd