Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mia Seed - #020 - Economic Change in The UK - The Changing UK Economy
Uploaded by
Mia SeedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mia Seed - #020 - Economic Change in The UK - The Changing UK Economy
Uploaded by
Mia SeedCopyright:
Available Formats
020 - Economic change in the UK
LO: how and why the industrial structure of the UK has changed.
Employment structure: primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary.
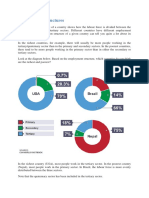
Employment structure is often shown as a pie chart.
2015 employment structure in th UK^
The employment structure in the UK from 1800 - 2015 (how it has changed)
- Jobs in the primary sector declined.
- Jobs in the manufacturing sector increased.
- A decrease in the number of people working in the secondary sector to the service /
tertiary sector. This increased.
- Since 2006, the quaternary sector has been introduced.
Why has the employment structure changed?
● Jobs in the primary sector were declining due to the increase in the use of machinery
Jobs in the manufacturing industry increased as factories were built and urbanisation
occurred
● A decrease in the number of people working in manufacturing as mechanisation
(introduction of robots etc.) replaced jobs along with increased competition from
abroad
● The service sector increased dramatically due to the introduction of public services,
the growth of financial services and an increase in leisure time and disposable
income
● Since the 1980s, the research and development sector has become increasingly
important.
Deindustrialisation
● A decline in manufacturing industry and the subsequent growth of the tertiary and
quaternary sector.
● In the UK this happened because:
○ Machines and technology replaced many people in modern industries.
○ Other countries can produce cheaper goods because labour is less expensive
there.
○ Lack of investment - high labour costs and outdated machinery made UK
products too expensive.
Traditional UK industries – coal mining, engineering and manufacturing have now declined.
Instead the UK is now a world centre for financial services, media, research and the creative
industries.
Globalisation: The growth and spread of ideas around the World. This can involve the
movement or spread of cultures, people, money, goods and information.
• The internet and mobile technology has allowed greater communication between
people in different countries.
• Larger ships mean that the cost of transporting goods between countries has
decreased.
• Economies of scale mean the cost per item can reduce when operating on a larger
scale.
You might also like
- WEEK 5-6 Landscapes of Secondary Activities Industrial RevolutionDocument10 pagesWEEK 5-6 Landscapes of Secondary Activities Industrial RevolutionJerlyn Mae Quiliope-Lumamba100% (1)
- A Socialist Policy For The GLC - Labour's London Manifesto 1981Document164 pagesA Socialist Policy For The GLC - Labour's London Manifesto 1981ind_labour_history100% (3)
- Igcse Economic Activity Revision PackDocument24 pagesIgcse Economic Activity Revision Packapi-232441790100% (2)
- Industrial SectorsDocument26 pagesIndustrial SectorsRaga Cipta PrakasihNo ratings yet
- Question-Answer Part: (Citation Ied19 /L 1033)Document9 pagesQuestion-Answer Part: (Citation Ied19 /L 1033)Alvee Musharrat Hridita 1825132No ratings yet
- The Lost Origins of Industrial GrowthDocument15 pagesThe Lost Origins of Industrial GrowthIPPRNo ratings yet
- Pazarlama Yöneti̇mi̇ SunumDocument8 pagesPazarlama Yöneti̇mi̇ SunumemreNo ratings yet
- GIT: Living in The IT Era: Lect Ure 01Document22 pagesGIT: Living in The IT Era: Lect Ure 01Darriane Joyce LealNo ratings yet
- Economics Case Studies and Examples 4.3.1 What Are The Causes and Effects of Globalisation?Document1 pageEconomics Case Studies and Examples 4.3.1 What Are The Causes and Effects of Globalisation?katiekapowNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Patterns of Industrialisation PDFDocument12 pagesUnit-6 Patterns of Industrialisation PDFNavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 - GlobalisationDocument5 pages3 - GlobalisationMROHANLONNo ratings yet
- ZIMSEC O LEVEL GEOGRAPHY FORM 4 - IndustryDocument30 pagesZIMSEC O LEVEL GEOGRAPHY FORM 4 - Industrycharles hofisiNo ratings yet
- The British Economy in The 19 and Early 20 Century 1. The Rise To Economic SupremacyDocument3 pagesThe British Economy in The 19 and Early 20 Century 1. The Rise To Economic SupremacyFlori StoianaNo ratings yet
- Industrialization 037Document14 pagesIndustrialization 037anzala noorNo ratings yet
- The Balance of Payments Provides Us With Important Information About Whether or Not A Country Is "Paying Its Way" in The International EconomyDocument6 pagesThe Balance of Payments Provides Us With Important Information About Whether or Not A Country Is "Paying Its Way" in The International EconomyankitaiimNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Revolution - A British LegacyDocument9 pagesThe Industrial Revolution - A British Legacyishana.meadows.23No ratings yet
- The Industrial RevolutionDocument2 pagesThe Industrial RevolutionJaume Martí TorrentNo ratings yet
- British Industrial RevDocument11 pagesBritish Industrial RevKhome WoodNo ratings yet
- wp2009 010Document50 pageswp2009 010Kyle MerrittNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Industrial RevolutionDocument11 pagesIntroduction To The Industrial RevolutionMathusan LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Why Are Some Countries Rich andDocument77 pagesWhy Are Some Countries Rich andAndre UlianovNo ratings yet
- HW 16. Decline and DetroitDocument22 pagesHW 16. Decline and DetroitbennettmariaclaraNo ratings yet
- Globalization EconomyDocument33 pagesGlobalization EconomyhaldoisNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevelationDocument5 pagesIndustrial RevelationKazi. S. A. Raj. Zishan 1520478631No ratings yet
- File 52374Document11 pagesFile 52374SuyogPatilNo ratings yet
- Industry Pt3 - Employment StructuresDocument5 pagesIndustry Pt3 - Employment StructuresMakanaka SambureniNo ratings yet
- Compilation IRDocument21 pagesCompilation IRNurolHuda SerujiNo ratings yet
- Industrial AgeDocument18 pagesIndustrial Agegarry-kunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 (A) - Evolution of Production Sytems - Industrial RevolutionsDocument23 pagesLecture 6 (A) - Evolution of Production Sytems - Industrial Revolutionsdub911No ratings yet
- Role of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Document13 pagesRole of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Lianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and Business - Introduction: Enter Your Search Terms Submit Search FormDocument4 pagesGlobalisation and Business - Introduction: Enter Your Search Terms Submit Search FormPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Industry at Global LevelDocument23 pagesIndustry at Global LevelDiana ZaheuNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of CE in UKDocument40 pagesSWOT Analysis of CE in UKk1l2d3100% (1)
- 940/1 (U1) 2021 STPM 940/1 2022Document24 pages940/1 (U1) 2021 STPM 940/1 2022NorshahidaNo ratings yet
- Essay On Historical Background of Construction Industry in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesEssay On Historical Background of Construction Industry in EthiopiaPoii G100% (1)
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyDocument51 pagesHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and Technologyblueviolet21No ratings yet
- National Infrastructure Plan 251010Document52 pagesNational Infrastructure Plan 251010himanshu_nigamNo ratings yet
- Will Hutton 2020Document8 pagesWill Hutton 2020MishealNo ratings yet
- Social and Economic Changes in A Rural Area of Population DeclineDocument4 pagesSocial and Economic Changes in A Rural Area of Population DeclineAvy BatraNo ratings yet
- Industrialization in BangladeshDocument33 pagesIndustrialization in Bangladeshjaberalislam57% (7)
- Industrial Revolution: Unit 3 Chapter 9Document15 pagesIndustrial Revolution: Unit 3 Chapter 9api-501798779No ratings yet
- Roll - 19 (SOC-13) 3205Document18 pagesRoll - 19 (SOC-13) 3205Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Industrialisation in BritainDocument3 pagesIndustrialisation in BritainSenetor Brian BakariNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 What Are The Causes and Effects of GlobalisationDocument4 pages4.3.1 What Are The Causes and Effects of GlobalisationUnderTheWaterNo ratings yet
- Industrialization and UrbanizationDocument7 pagesIndustrialization and UrbanizationJaffy BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Lec#01Document51 pagesLec#01Muhammad MoizNo ratings yet
- Documento Sin TítuloDocument3 pagesDocumento Sin TítuloJuliana Piñeres CabrejoNo ratings yet
- Third Industrial Revolution and Planning Working Paper 1Document23 pagesThird Industrial Revolution and Planning Working Paper 1Adrian FuentesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Planning ConceptDocument9 pages2.1 Planning Conceptsujancrestha9876No ratings yet
- Economy of Uk: - Service SectorDocument18 pagesEconomy of Uk: - Service SectorKeith BrittoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-05 Industrial Patterns During The Five Year Plans in IndiaDocument8 pagesUNIT-05 Industrial Patterns During The Five Year Plans in IndiaSAJAHAN MOLLANo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Natural Resources and Industrial ProductionFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Natural Resources and Industrial ProductionNo ratings yet
- International Business: BUSE 608Document38 pagesInternational Business: BUSE 608Abdulrahman AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- Regenerating Places RevisionDocument19 pagesRegenerating Places Revisionapi-407286530No ratings yet
- U.2Economic HistoryDocument4 pagesU.2Economic HistoryJoseNo ratings yet
- Globalisation: People and The Planet - Globalisation - 3Document5 pagesGlobalisation: People and The Planet - Globalisation - 3MROHANLONNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution 2Document10 pagesIndustrial Revolution 2Saubhik MishraNo ratings yet
- Lec # 01 Introduction To Construction ManagementDocument37 pagesLec # 01 Introduction To Construction ManagementNoor Uddin ZangiNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesstquinn864443No ratings yet
- Technological Knowhow and Industrial GrowthDocument14 pagesTechnological Knowhow and Industrial Growthanon_764315No ratings yet