Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QB Yr2 Sem2
QB Yr2 Sem2
Uploaded by
Ogwang hallan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views243 pagesOriginal Title
QB YR2 SEM2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views243 pagesQB Yr2 Sem2
QB Yr2 Sem2
Uploaded by
Ogwang hallanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 243
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester II 2020/2021 Examinations
MEC2204: Materials Science and Engineering I
Monday January 3, 2022
Duration: 3.0 Hours (1400 - 1700 Hours)
eee
Instructions:
+ The Examination paper contains Seven Questions.
+ Attempt any Five questions of your choice.
+ Each Question Carries 20 Marks
* Marks for each section are indicated in parentheses.
Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet
rovided.
Page| 1
ues 2 he
i tons in describing |
“ (a marks)
g. What are
(2marks)
1) Briefly describe the Bohr atomic model and some of its limitat
atomic structure -
as 21
1.2 Magnesium (Mg) has an atomic number (Z) of 12, and Oxygen (O) hi
the electronic configurations of these two elements? of bonding
type
1.3 Given the electronic configuration in 1.2 above, what is the most likely tYP eee)
in Mg-O compound, and why?
the
sn establishing
1.4 Why’is the yield point more important than the fracture point when es
(4 marks)
mechanical properties of a material?
1.5 Whatis the difference between? (amarks)
@) Resilience and toughness of a material ena)
b) Fatigue strength and creep strength Bester
1.6 A tensile test uses a test specimen that has a gage length of 60 mm and an cre
210 mm®. During the test, the specimen yields under a load of 98,000 N with ©
corresponding gage length of 60.23 mm and this is the 0.2% yield point. The mo
load of 180,000 N is reached at a gage length of 74.2 mm. Determine:
ximUM
Q) Tensile strength (2 marks)
b) Modulus of elasticity (3 marks)
{/ Question 2 (20 marks)
| 2.1 How do imperfections or defects arise within a crystalline material? (2 marks)
2
2 With illustrations describe the following defects in crystalline structures
@) Edge dislocation (3 marks)
b) Twin boundaries (3 marks)
¢} Interstitial defect (2 marks)
23 Calculate the energy for vacancy formation in silver, given that the equilibrium
24
number of vacancies at 800 °C (1073 K) is 3.6 x 102 m3, The atomic
ic weight and
density (at 800 °C) for silver are, respectively, 107.9 g/mol and 9.5. 5
g/cm’. (Avogadro's
number, Na= 6.02x102 atoms/mol, Boltzmann's Constant, k = 8.62 x 105 eV/atom-k)
; , . (6 marks:
Describe how grain boundaries are generated in crystalline structures, and hi :
these boundaries coniribute to the Phenomenon of strai pease
strain hardenin
9? (4 marks)
oy
ber pes Bo
ue
Im = 0
worn
jet <1
Se ie Nhe
Question 2.0 | 20 Marks]
2.1, Differentiate between vacancy diffusion and interstitial diffusion [4 marks]
22.With examples, briefly explain the difference between self-diffusion and inter-diffusion |
(3 marks}
2.3, Describe how the following factors influence diffusion in solids
a) Diffusing species [3 marks]
b) Temperature [3 marks]
2.4. Briefly explain the concept of a driving force, and what this force is for steady-state diffusion
[3 marks]
2.5. Compute the number of kilograms of hydrogen that pass per hour through a 6- mm-thick
of palladium having an area of 0.25 m? at 600°C. Assume a diffusion coefficient of 1.7 x 10m
that the concentrations at the high- and low-pressure sides of the plate are 2.0 and 0.4 kg
hydrogen per cubic meter of palladium, and that steady-state conditions have been attained
[4 marks]
‘she
Question 3 [20 marks]
3.1 Briefly describe the following strengthening mechanisms as applied to crystalline materials
a) Grain refinement \ {3 marks}
b) Strain hardening I [3 marks]
©) Precipitation hardening [3 marks]
3.2. Thermosets do not usually tolerate repeated cycles of heat treatment and.thus are. difficult
reform. However, thermosets are preferred to thermoplastics in many engineering des)
applications. Explain why [4 marks]
3.3.The molecular weight data for a polytetrafluoroethylene (—CF; — CF; —)q, material are tabulal
below. Compute (a) the number-average molecular weight, (b) the “ecehtaveage mole|
weight, and (c)the degree of polymerization. (the atomic weights of C, and F are and
g/mol, respectively) [7 marks]
Molecular weight range (gimol) Xi Wi
10,000-20,000 0.03 0.01
20,000-30,000 0.09 0.04
30,000-40,000 0.15 O11
40,000-50,000 0.25 0.23
50,000-60,000 0.22 0.24
60,000-70,000 014 0.18
70,000-80,000 0.08 0.12
80,000-90,000 0.04 0.07
End
hydrautig
(2 marks)
| estion 4 (20 marks}
to as
only referred
4.1, Explain why ordinary Portland cement Is comm
cement.
tion of glass ceramics.
4.2. Devitrification is a common process in the productio!
(2 mark:
Describe this process.
Ih. (4mar
4.3. Explain why window glass is brittle, yet other glasses are toug! ( rk:
4.4 Pouring hot water in ordinary glass causes glasses to crack. mee some
Classes of glass are successfully used as cooker tops. Explain this variation i
the behavior of glasses as engineering materials. (4 marks)
45 Explain the perfectly elastic stress-strain behavior of ceramics. (2 marks)
4.6 Mention any six functions of the ingredients that are added to silica during
glass production. ; ‘ emma
ion 5 marks:
5.1 Differentiate between creep strength and rupture strength of a material
(2 marks)
Vhy do ceramics have high hardness and low ductility as posed
fo en
ce » ‘
CE SS OO |
Question 7 (20 marks) |
7.1 Mention five co
applications,
i dical
i jals for biome:
mmon key factors that suit mater! ( marks) |
er (Cu) has 7=29,
72° Aluminum (Ai) has an atomic number of 7=13, and COpP
ments? (2 marks’
What are the electronic configurations of these two ele!
va" is most likely typ:
73 Given the above electronic configurations in 7.2, what is the aes
_ of Bonding in an Al-Cu alloy and why?
st
74 Me wont to make on alloy of composition 90a1% Al with the res Cy,
he atomic weights of Al and Cu are 26.98 amu and 63.55 am)
i
(4 marks)
(4 marks|
significance of interstitial di
lefects on mechanical Properties of
-
stion 1(20 marks
Wl
t happens to the microstructure when a ductile
hat, hay
1.3. Explain what,
i i |
terials are anisotropic. Identify what class of
1.4 Some ma
Describe the mechanism by which grain boundaries strengthen m
15 De
1.6 Ceramics are stronger than metals, however,
21 With reference to
te Rerat |
ure
Poge | 2 © does the first liquig forme
here defects in a materials StUcture m,
typical situations w!
ibe two typi
Describe
‘ay
ial’ ties a "re
| 10 a material's prope! ae
beneficial d materials may be less ductile than coarse ca
y fine graine’ ;
2. Explain why fine g . -
materials.
je in nally appli in agiven direction,
1d to an externally applied force in a giv
subjected to
predominantly exhibit this and why.
Aterigls
(2 Marks)
their use as Engineering
materials is limited.
9) Outline four factors that influence the properties of ceramics (4 marks) I
6) Identify four Properties of ceramics which favor their Choice in I
engineering Applications as ©PPosed to metals (4 marks)
D2 (20 marks: i
a equilibrium, Phase diagrams, describe the following terms,
Siving examples foreach
©) Congruent transtormations (2 marks) |
b) Eutectoig Teaction (2 marks) [
Sl Petitectic Teaction (2 marks) I
|
22 Refer to
‘ Ie leg, tin i
MO oiees heaten 8° lagram In Figure 1 for an alloy containing 30% |
ate,
ONSWer the follow, 9 slowly fro,
o tem, = ing the figu
ing Westions. Perature of 150°c. Using
(2, marks) |
i
|
i
s
Question 1.0 -
4.1. Briefly explain the concept of steady state as it applies to diffusion {2 marks]
4.2. What are the important variables that affect mass diffusion? {4 marks]
1
2
3, Explain why interstitial diffusion is normally more rapid than vacancy diffusion
(2 marks]
4
‘An FCC iron-carbon alloy initially containing 0.10wt% C is carburized at an
élevated temperature and in an atmosphere wherein the surface carbon
Concentration is maintained at 1.10wt’%. If after 48h the concentration of carbon is
0. 30wt% at a position 3.5mm below'the surface, determine the temperature at
which the treatment was carried out. Use the diffusion data in Table 1 for Carbon
Giffusion in Fe. Error function values are given in Table 2, if necessary. [12 marks] *
1
Table 1: Diffusion data
I-piffusing | Host Metal | Oo(m%7s) [Activation Energy, Qy Calculated Values
{_species_| ’ Kimol__[eViatom | TC) _ | Dlm"ts)
o-Fe(BCC) | 28x10" | 251 2.60 30x10
z er - i 18x10 _|
yFe(FCc) | Soxio™ | 264 aoa 41x10
UL | a fecal 78x10" _|
[ore 2x0” | 80 083 24x10" |
|" “5 \47x10?_|
Fe 2axto™ | 148 153 Sax107 |
pees. | is 53xi0"'_|
Cu Cu 78x10" 211 2.19 42x10 |
Zn. Cu) 2.4108 | 189 1.96 [40x10 |
AL Al 2.3x107 | 144 1.49 42x10 |
Cu Al __[6.5x10" [136 1.41 41x10 |
‘Mg_____ Al pa eextaees [2131 1.35 79x10 |
cu LN ~_[2i0™ [256 2.65 500 4.3x1077_|
a
|
Table 2: Error Function Values
{z erf(Z)_ |Z erf(Z)_|Z erf(Z)
o 0 0.55 0.5633_| 1.3 0.9340
0.025 | 0.0282 [0.60 [0.6030 [1.4 | 0.9523
005 10.0564 [0.65 10.6420 [4.5 | 0.9661
0.10 10.1125 [0.70 | 0.6778 [16 | 0.9763
015 10.1680.|075.. | 0.7112 [1.7 10.0838
0.20 (0.2227 [0.80 [0.7421 [1.8 | 0.9891
025 10.2763 (085 |0.7707 119 | 0.9928
0.30 | 0.3286 | 0.90 0.7970. | 2.0 0.9953
0.35 10.3794 | 0.95 0.8209 -| 2.2 0.9981
o40 10.4284 [1.0 | 0.8427 [2.4 | 0.9993
0.45 0.4755 _| 1.1 0.8802 | 2.6 0.9998
050 10.5205 [1.2 | 0.9103 | 28 | 0.9999
J
ort
4.2 What are the reasons for the technological imp
t! s
4.3 What are the major functions of the matrix pha
44
rials?
mat
gineering 2 Marks]
pane
ian nt
nd concrete 25°¢'
ce of composites? [5 Marks] y
an
2
e in a composite mere ne {
and reinforcing fibers
A fiberglass composite is composed of a matrix Se ataiiel S vinyl ice
of E-glass. The volume fraction of E-glass is 35 4 its modulus of elasticity is |
The density of the vinyl ester is 0.882g/cm’, ie its modulus of elasticity is
3.6GPa..The densily of E-glass is 2.6g/em* ant 2000mm is fabricated with E-
76.0GPa. A section of composite 10mm x 500mm x Fee a acctnreyiists are
glass fibres running longitudinally along the 2000mm dire
no voids in the composite. Determine:
[2 Marks]
a) Mass of vinyl ester in the section
; [2 Marks]
b) Mass of E-glass fibres in the section
c) Density of the composite [2 Marks]
@) The modulus of elasticity in the longitudinal (2000mm length) direction of the
fibre. (2 Marks]
|
e
Question 5.0-
5.1. Explain the perfectly elastic stress-strain behavior of ceramics, [4 Marks]
52 In relation to polymers, describe the glass transition temperature and cite one
5.3
5.4
5.5
Page |5
typical application of polymers for wh
ich glass transition temperature will have |
Practical ramifications,
[4 marks] x
State the major distinction between traditional ceramics and glass, [2 marks]
Why do ceramics have high hardness and low ductility as opposed to metals?
~ [2 marks}
What are glass ceramics? Cite three typical Applications
Of glass cerami
favorable properties that suit them for these applications. amebneeer’ the
[8 marks] x
duestion 6 /
A gear train is depicted in Fig. 06,
velocity
Of gear 1 is 50m rad/s cow, Wh;
ars if the
the direction and speed of rotation of all the ge
iat is the gear ratio of the train?
Ifthe modulus is 4 mm, calculate the distances between the axles,
angular
|
|
12 i
8
Number of Teeth
19
45
17
47,
MAKERERE vat UNIVERSITY
lie,
««“8)
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGig
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
End of Semester jl 2017/2018 Examinations
MEC2204: Peters Science and Engineering I
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING a
Monday May 7, 2018
|
Duration: 3.0 Hours (1400 - 1700 Hours)
|
‘ See
Instructions: |
The Examination paper contains Seven Questions,
Attempt any Five questions of your choice.
|
|
Each Question Carries 20 Ma rks |
Marks for each section are indicated in parentheses,
Indicate the attempted qu
estions on the top page of the answer bookl
rovided,
eee
Page | 1
Question 1 (20 marks)
oe, ‘ ive an
M1 Briefly describe what is meant by eutectoid solcitication, a jarks}
m
&xample of a practical application of this.
12 A binary alloy, solidifies completely from the melt at 779°C.
Giving rise to two sold Phases a (Ag-9 wt.% Cu) and B (Cu-8 wt.% Ag) at this
temperature. At room temperature these solid phases are pure Ag and pure
cu Tespectively, Given that the melting points of pure Ag and pure Cu are
960°C and 1085°C respectively, sketch and label fully the phase diagram of
the Ag-Cu system. [6 marks]
ht on:
3. Using the phase diagram in 1.2, estimate the proportions of a and B phases
Present at equilibrium in the above mentioned alloy (i) at just below 779°C,
‘nd [ii) atroom temperature.
[4 marks]
of composition Ag-20 wt.% Cu is Cooled slowly from the melt to room
€ such that equilibrium is maintained, Using the phase. diagram
iin 1.2 above; describe the key features of this Cooling process.
mics. [2 marks]
/Question 3 (20 marks)
3.1. Explain the perfectly elastic stress-strain behavior of cer"
|
tics between o pure metal
+ 3.2 What is the difference in melting characteris
itany exist? [3 marks]
element and an alloy metal, state any exceptions,
s
A
olyerystalline materials are isotropic despite | ‘
|
3.3. Explain why the properties of P
the fact that each crystal is anisotropic. [2 marks]
on-crystalline structures in
[2 marks]
3.4 What is the difference between crystalline and n
: materials?
:
F
:
3.5. Discuss the properties of ceramics in comparison to metals. [6 marks]
ention any five functions of the ingredients added to Silica during glass
: , [5 marks]
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
i DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING,
| SEMESTER Il TEST I! 2015/2016
2 MEC2204: MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 1
April 2%, 2016 TIME: 10:00AM -12:00PM
Attempt All Questions oie
* so} poh
wee a
Question One re oe oo
2) What are the important variables that affect mass diffusion? (marks) 7° * sce
b) Explain why interstitial diffusion is normally more.rapid than vacancy diffusion. (2 marks)
©) Nitriding is one of the processes used in surface Hardening of steel; sa, for steel plates used
on ploughs. A sheet of steel 1.5mm thick has nitrogen atmospheres on both’sides at 1200°C
and is permitted to achieve a steady state diffusion condition. The diffusion coefficient for
nitrogen in steel at this temperature is 6x10"''m’/s, and the diffusion flux is found to be
1.2x107kg/ms. Also, it is known that the concentration of nitrogen in the steel at the high
pressure surface is 4kg/m*. How far into the sheet from this high-pressure side will the
concentration be 2.0kg/m°, Assume a linear concentration profile. (5 marks)
4) Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.45 wt% ata
position 1.5mm into an iron —carbon alloy that initially contains 0.20 wt% C. The surface
concentration ts to be maintained at 1.20 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1000
. (Take Dp=2.3x10%m¥s, Qu=148kJ/mol, R=8.31J/mol-K). (Use the table of error function
values given at the back ) (9 marks) ee
‘e
see
RIN
Question Two oe wer
#) Describe the three general factors that determine the properties of a’composie material
(3 marks)
b) A polymer-matrix composite is unidirectionally reinforced with 60vol.% of E-glass hres.
The elastic moduli of the matrix and the fiber are 6.9 and 72.4GPa, respectively. Determine
the elastic modulus of the composite parallel to the fiber direction (5 marks)
e
eens
In an aligned and continuous glass fiber-reinforced nylon 6,6 composite, the
”4% of a load applied in the longitudinal direction. Using the data provided
a Shyree fy cola ye
2 hain [eng fh:
> Chain 4 Wy
> Indgqe hein . |
2. Ser © cal.
DN Alast ie! ses J
rerun Three : (2 marks)
a, Explain the perfectly elastic stress-strain behavior of ceramics et
| element ani
b, What is the difference in melting characteristics between # PLC ynctelcs @marks)
metal, state any exceptions, if any exist? é
: i fact that cacl
©. Explain why the properties of polycrystalline materials are isotropic despite the fact eerie
cerystal is anisotropic.
; i s in materials?
? a ‘What is the difference between crystalline and non coaaling se semuctur - eas
&
Discuss the properties of ceramics in compurizanto mel eile» a Roe ay FSG marks)
Le oe Se oS re
£ Mention any four functionsiof the ingredients Des to ae avon glass production
ee = dowtrig cabion (4 marks)
: = quidiby * processing = Use thermel exparkor
ad dn ior pomdting wer
tee reaistone 200d akterck
= rRrachve popetien
Table 2: Tabuiation of error function values
Zz oe = | < erf(Z)
ee . 13 0.9340
ae 7.4 0.9523,
2.85 I [1.5 0.9661
ax pee LG 0.9763
nea : iz 0.9838
Sas ; 18 0.9894
0.9928
0.9953,
0.9987
0.9993,
0.9998,
0.9999
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
GINEERING, DESIGN, ART ANODFECHNOLOGY
MENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
COLLE
OF
DEPART!
SEMESTER [1 TEST [ 2015/2016
MEC2204: MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERINGL _*
april 14, 2016 TIME: 10:00AM -12:00PM
Question One (22)
A) Under what conditions might you expect. dend
ritic microstructure to form? Describe the
reasons for dendrite growth. (4 marks) * -
lete solid solubility above 812°C and a solvus al
lower temperatures. At300°C the maximum solubility of Ni in Au is 5.6%, and that of Au in
Nr is 19%, The melting points of the pure components are: gold, 1064°C and nickel, 1455°C.
Use these’data to sketch the phase diagram for this sysfem. (6 marks)
Ub) The Au-Ni binary alloy system shows compl
2) Use the attached lead-tin phase diagram to answer the following questions
ji) For the lead-tin phase diagram.in the attached figure, is it possible ‘0 design 2 solder
(lead-tin alloy) with a melting point of 260°C (500°F). [f so, what would be is nominal
composition? (4 marks)
Using the lead-tin phase diagram, determine the compositions of the liquie and solid
phases for a nominal composition of 40% Sn and 60% Pb at 204°C (40°F). (2 marks)
Por the preceding problem, use the inverse lever rule to determine the proportions of
liquid and solid phases present in the alloy.(4 marks)
iv) Using the lead:-tin, phase diagram, determine the liquid and solid phase compositions for a
nominal composition of 90% Sn and 10% Pb at 204°C (400°F). (2 marks)
juestion Two (15)
tS What is the difference between primary and secondary bonding in the structure of materials?
(4 marks)
{) Describe how ionic bonding works? (2 marks) ,
v- fc) Deseribe a Freikel Defect and a Schottky defect in a crystal lattice structure (4 marks) ©
(é) Do non-crystalline materials display the phenomenon of allotropy (or polymorphism)? Why
‘or why not? (3marks)
\ (© Whatis a solid solution in the context of alloys? (2 marks)
Question Three (20)
| 2) Differentiate between creep strength and rupture strength of a material (4 marks)
i entiate between tensile strength and yield strength of a material (4 marks)
a why the properties of polycrystalline materials are most often isotropic.
rence between elastic and x.
r MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
SEMESTER II TEST I 2014/2015
MEC2204: MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING |
April 9, 2015, TIME: 10:00AM -12:00PM
Attempt All Questions
'
Question One
a) Aluminum (Al) has an atomic number of Z=13, and copper (Cu) has Z=29. What are the
electronic configurations of these two elements? (4 marks)
~¥%) Given the above electronic configurations, what is the most likely type of bonding in an Al-
Cu alloy and why? (6 marks) ‘i
Question Two,
a) We want to make an alloy of composition 90at% Al with the rest Cu. Calculate the weight
percent of Al and Cu we need to melt together to form this alloy. The atomic weights of Al
t and Cu are 26.98.amu and 63.55 amu respectively (4 marks)
by Using the phase diagram in Figure |. what phases are present and what are their mass
i fractions at a temperature of 600°C fur an overatl alloy composition of 10 wt Cu? For the
alley composition, determine the composition of each of the phases presen at 600°C (6
marks)
Sampos ber |e
|
Question Three
a. Explain the perfectly elastic stress-strain behavior of ceramics
', What is the difference in melting characteristics between a pure metal element and an alloy
‘metal, state any exceptions, if any exist? “(3 marks)
Explain why the properties of polycrystalline materials are isotropic despite the fact that each
(2 marks)
crystal is anisotropic, (3 marks)
, eee
¢. What is the difference between crystalline and non-crystalline structures in materials?
E (2 marks)
¢. Discuss the properties of ceramics in comparison to metals @ aa
£ Mention any four functions of the ingredients added to silica during glass production
(4 marks)
oa 2: Tabulation of error function values
erfiz) Zz
0 0 0.55 pean 2 eri2)
0.025 0.0282 0.60 areas 3 0.9340
[0.05 0.0564 0.65 fee 1.4 0.9523
0.10 0.1125 0.70 0.6778 it 0.9661
pas 0.1680 0.75 0.7112 16 0.9763
20) 0.2297 0.80 0.7424 +2 0.9838
(ares 0.85 0.7707 7 3 0.9891
13280 0.90 0.7870 2a 0.9928
ee 0.95 0.8209 39 0.9953
. 1.0 0.8427 ial 0.9981
14 0.8802 26 0.9993
0.9103 on 0.9998,
28 0.9999)
33
| Guestion 2.0 [20 marks}
2.1 Describe how the following mechanisms influence strength
polycrystalline materials
i [4 marks
a) Precipitation hardening - tks]
mar
b) Strain hardening 4 a rks]
¢) Solid solution hardening rks]
2.2 Describe the Hall-Petch equation and specify its limitations in Predicting the
4
strength of materials. : [4 marks)
2.3 Explain why fine-grained materials are stronger than coarse grain u
materials [2 marks u
24 Describe the role of grain boundaries in strengthening of metals [2 marks} u |
™ e 4
‘¥ Question 3.0 [20 marks] whee t
1 Describe three factors that affect thé gfain size of a polycrystalline material,
[3 marks}
Properties as a function of
temperature between a highly crystalline thermo}
thermoplastic,
3.2 Desctibe the difference. in mechanical
plastic and an ‘amorphous
[4 marks}
How ore a polymers properties affected when it takes on a crystal
structure?
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND |
TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
END OF SEMESTER II 2019/2020 EXAMINATIONS
MEC2201: Electrical Engineering for Mechanical
Engineers IIT
Tuesday December 15, 2020
Duration: 3 Hours (0900 — 1200 hours)
ES
1. The examination paper contains six (6) questions.
2. Attempt any five questions of your choice.
3. Each question carries 20 marks
4, Marks for individual sections are indicated in parentheses.
5. Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet
provided.
6. Do not write any text on the question paper. Use the provided answer book for
F ing?
5. Which of the following greenhouse gas is contributed by cattle farming
a) Nitrous oxide
b) Methane
c) Carbon monoxide :
4) All of the mentioned ask
&. Which of the following is an example of a nuclear accident
a) Construction of dams
b) Burning of fossil fuels
c) Nuclear fusion
vd) Nuclear reactor core melt " :
7. Which of the following is the cleanest fossil fuel?
va) Natural gas
d) Petrol
©) Petroleum
) Coal
8. What is the objective of the main international treaty on climate charige?
a) To provide Scientific information on climate change .
b) To destabilise the greenhouse gas concentrations so that anthropogenic actions
interfere with the climate system .
C) To stabilise the greenhouse gas concentrations so that anthropogenic actions do not
interfere with the climate system -
¢) To bring peace between all countries
8. What is the aim of Paris Agreement in 2015? Note that C indicates Celsius.
F) 79 KeeP the decrease in global average temperature to below 2 degree C
®) To keep the decrease in glo al average temperature to above 2 degree C
C) To keep the increase in global average temperature to above 2 degree C ae
\t) To keep the increase in global average temperature to below 2 degree C
10. Where is the ozone hole located?
a) Asia
“) Antarctica
¢) Europe
d) America
11. What is main potential wa
a) Carbon
») Silicon
“<) Sulphur
) Nitrogen
12, Land requirement of a geothermal fa
2) greenhouse gas emissions”. 4ePends on
») hydrogen sulphide emission,
c) the wildite .
MA) amount of power capac
13. What's the main Problem itn
$2) Stain on environment absense gat countesn
atin poverty © damage and sel-heal
ter pollutant from a geothermal reservoir? -
) Higher energy consumption per capita |
d) Lower energy consumption per capita \
14, Which of the following best describes green economy?
a) A high carbon, resource inefficient and socially inclusive economy
1+) A low carbon, resource efficient and socially inclusive economy
c) A low carbon, resource inefficient and socially exclusive economy
4d) A high carbon, resource efficient and socially inclusive economy
48, Whats the goal of sustainability in any process?
a) To maintain the process finitely *
b) To eventually eliminate the process \
wc) To maintain the process indefinitely
) To support damaging the environment
16. Why is there a demand for tenewable sources of eneray?
a) Because they emit greenhouse gases
Yb) Because of low or zero carbon footprint
©) Because of the decreasing global temperatures « ‘ i
d) Because they are more efficient . * i|
17. What is total primary energy supply?
a) Total energy produced and used by humanity
b) Total energy consumed by humanity
\<) Sum of energy production minus storage changes
4) Sum of energy production including storage changes
48. What is the unit of total primary energy supply? {
a) Watts
) Kitchen waste
c) Residential garbage
@) Plastic covers
43. Which of the following is a product of pyrolysis of biomass?
2) Producer gas
b) Stee!
¢) Agricultural residue
¢) Sodium -
44, What is anaerobic digestion?
a) Produces biogas by heating the biomass
2) Produces biogas using micro-organisms operating in anaerobic conditions ‘a
¢) Produces biogas by subjecting the biomass to high pressures
d) Produces biogas using micro-organisms operating in aerobic conditions
45. What is the increase in temperature per kilometer starting from the crust?
a) 15 degree Celsius
~~) 17 - 30 degree Celsius
¢) 100 degree Celsius
4) 50-87 degree Celsius e
46. What is continental drift?
'~4) Tectonic plates pushing against each other
>) Continents being pulled due to gravitational force
¢) Continents being pulled due to nuclear force
4) Tectonic plates expanding
47. pega electricity generation from geothermal energy?
4) Italians
¢) Americans
) Africans
s ae Re puieg is used to locate a geothermal site?
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
Department of Mechanical Engineering
College of Engineering, n Art and Technology
AEN2211: ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING I! / MEC2201: ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FOR
ME“HANICAL ENGEERS II
L
{
17 December 2021
Tutorial
DC Machines
a: lain the constructional details, working principle and applications-ofte'machines and
raat the gimature winding connections (lap windinas vs wave windings, full pitch vs
Short pitch coils, concentrated vs distributed windings).
What is the significance of commutator and brushes in a de machine?
. Compare lap and wave winding. Where each type is used and why?
. When do you use concentric winding?
State the types of de motors. What is the basis of the classification?
. What is the significance of back emf ina de motor?
- Using only well labelled schematic equivalent circuit diagrams illustrate the difference
between a long shunt compound DC generator and a'short shunt compound DC métor.
A four-péle DC machine has an armature of radius 12,5cm and an effective length of
26am. The poles cover 75% of the armature periphery. The armature winding consists of /
$B:colls, egch coil having se’"2n turns. The coils are accommodated in slots. The
aoa flux density under each pole is 7ST. If the armature is lap-wound
Determine the armature constant K,.
Determine the induced Armature Voltage (,) when the armature rotates at
1000 rpm
Determine the current inthe coil and the electromagnetic torque developed
fa |e=22N _ whenthe armature currentis 400 A.
} d) Determine the power developed by the armature
(a) to (d) in Qn. 6 above. Thi
le current rating
w
etic torque in newton-meters.
€) Determine the electromadii vil tne generated votiage and the. rpm of the
ero"! 2
™ ming Eo 2 4 3
gh
i) Noarmature reaction ~ veaction at 40A armature
2LUou
is tat
17. A2SKW, 250V de machine is separately excited, a stiats i 3 i Fe aaa ata
‘speed of 3000 spm. The open circuit voltage ig.250.) . -
| electromagnetic power ina torque at terminal voltage of (2) feat (b) 248.V. The
‘armature resistance is 0,05 ohms, Speed is held constant a J
48. A de shunt motor rated 10 KW connected to 250 V supply 's pa Dh ca 35A
Ra=
| ‘armature current running at a speed of 1260 rpm. Given
500 W.
fa) Determine the load torque if the rotational loss is
© Determine the motor efficiency if the shunt field resistance is 250 Ohms.
(c) Determine the armature current for the motor efficiency to be maximum and
its value. What is the :omesponding load torque and speed?
ji) 10% reduction of flux due to armature
current at no (ood Nez Ean
Synchronous Machines
4. Athree phaselip ane \+-pole, 50 Hz starconaested synchronous machine has
synchronous reaeiance of 16 ohms and negligible resistance. The machine is operating
SS as generator on 400 V bus-bars (assumed infinite)
= E Ge HIBS OS®
a) Determine the excitatigh emt (phase) and torque angle when the machine is
delivering rated KVA at 0.8 Pilaasing.
b) While supplying the samé real power as in part (a), the machine excitation is
raised by 20%. Find the stator current, power factor and torque angle.
With the field current held constant as in part (a), the power (real) load is.
increased till the steady-state power limit is reached. Calculate the maximum
power and KVAR delivered and also the stator current and power factor. Draw
the phasor diagram under these conditions.
oo
2 A ee ee apenrected synchronous motor has armature effective resistance of
ohms ynchronous reactance, of 8 ohms. It has stray loss of 2 KW. The motor is
‘operating at 600 V bus-b. ile supply
rete - is-bar while supplying a shaft load of 30 KW, it is drawing rated
a pecize the motor e ciency
ee . beeen eat and power angle?
lon calculate the maxim
. wy jum power output
responding net Output and the power angle en
Shik
jon motor Ge
d the Full load
ti
Question 3 [25 Marks} a three-phase induce
(4 Marks)
acteristics of aan
.1. Draw the torque-slip chai anne
a show the various regions of operation, the Maxinn
operating point. —_- -
ing (wou!
between squirel-cage and slip: a
3.2 Discuss briefly the differences na
rotor) induction motors.
Hz
60 V, Bpole, 60
3.3 The following results were obtained from a 3-phase, 100 hp, e al
stor-connected squirel-cage induction motor that runs at 8
No-Load test: 460 V (line), 60 Hz, 40,A, 4.2 kW
Blocked-Rotor test: 100 V, 60 Hz, 140 A, 8.0 kW
DC test on stator Resistance/phase = 0.076 ohms
The standstill reactances of the stator and rotor as seen on the stator side are
estimated to be in the ratio of 1:1,
(i) Determine the Parameters of the IEEE-recommended equivalent
circuit,
the rotor circuit,
ill) Calculate the maximum torque develo; li
= Ped and the slip at Which it
‘ (™)Colculate the stator current and its power factor,
EB UNIVERSITY
MAKERERE
TECHNOLOGY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
ING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEER
End of Semester II 2020/2021 Examinations
MEC2202/AEN2209: Theory of Machines
Tuesday 11'* January 2022
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 - 1200 Hours)
The Examination paper contains Six Questions.
Attempt any Four Questions of your choice
Each question carries 25 Marks,
Marks for each question or part of the
questions are indicated in parentheses.
Indicate the attempted questions o1
nthe te f thi
rovided. OP page of the answer booklet
1
through
from links,
;chanism
sion in building a me [8 marks]
Explain clearly the progres:
rechanism. : mples.
Pairs to a chain and eventually a me mechanism? Give exo!
What is meant by degrees of freedom ofa [5 marks]
; Figure 2.
‘Obtain the mobility of the mechanisms in Figure! and Fig
Figure 2: Mechanism 2
[6 marks]
Figure 3: Crate pushing Mechanism,
8C = 600mm, CD = 500mm,
line the position of D in the Configuration, shown. aoe
Hes at 10 rad/s eta ts at thei
it ‘as
= 200mm, AB = 1.5m, BO. = 400mm
UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester II 2019/2020 Examinations
MEC2202/AEN2209: Theory of Machines
Friday 11!" December 2020
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 - 1200 Hours)
Instructions:
| The Examination paper contains Six Questions.
® Attempt any Four Questions of your choice
* Each Question Carries 25 Marks
+ Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses.
* Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the onset booklet
jovided.
pair, a kinematic
aw using examples. explain the hierarchy from a kinematic
chain to. a mechanism.
12 st the various ways that slider crank mechanism is used in ee
{6 marks}
1g Mechanisms
[S marks}
Obtain the mobility of the following
41
4.2
43
Question 4 [25 marks] es possible with cam
{6 marks]
ion tyP'
Distinguish between the different follower motio
mechanisms da prime circle ofacam
, i ircle an'
Explain the difference between a base cit [marks]
and what their roles are.
fi ement of 40 mm
A radial follower for a press is to move through a displac
with cycloidal motion over 120° of cam rotation. The follower ese
the next 90° and then refums 40 mm with cycioidal motion in 120°. th
i) Depict the follower motion program on a $-0 plane ia
sequences yD a
ii) Calculate the S, V aiid A values for the follower for each 10°
ion only.
rotation of the cam. Do this for the first 120° of cam rotation only.
[9 marks]
Question 5 [25 marks}
A cutting blade is designed and represented by three masses arranged radially on a
shott as follows
5.1
5.2
5.3
‘Mass No. Mass (a) Centre Radius | Centre
(mm) Orientation
Angle
7 SCO 135 45°
2 750) 75 300°
3 450 12 Dios
Draw the radical force polygon for the shat ititrotates at 120
the blade is not balanced and determine the resultant force
Bm to show that
on the shaft.
Use the analytical method to determine the required ™OsS ond angular posi
of the bootancing mass which is fo be mounted at g Podon
fais of 250 mm, [2 marks}
Compare the results of 5.1 and 5.2 above
UNIVERSITyge
MAKERERE
w
= # ENGINEERING, Desi
conn EOF ART AND TECHNOLOGY :
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING w
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
== 33283 =
End of Semester I] 2018/2019 Examinations
MEC2202/AEN2209: Theory of Machines
Thursday 16 May 2019
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0700 - 1200 Hours)
==
Tistucion,
* The Examination paper contains Seven Questions.
+ Attempt any five questions of your choice
* Each Question Carries 20 Marks
+ Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses.
+ Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet,
provided.
= =
phy
N.B. A MEMO MUST BE INCLUDED WITH ASSIGNMENT RESULTS,
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
Department of Mechanical Engineering,
MEC2202 Theory of Machines
Assignment #2. «Due 19" Mareh’2015 (Submit indidually)
Position and Velocity Analysis of Mechanisms,
ioo.uring, ee
The figure below shows a mechanism for a two-cylinder eee isva Chee
articulated connecting rod. It is given that O2A= 50 mm, ‘rad
mm and DC= 125mm, ‘The crank OzA rotates clockwise at ’
Perform the following analyses.
a)
Graphically, determine the Positions ar
orientation and velocity of the articut
and 300°
Using the analytical method, obtain the equations for the Positions and velocities of B, C
and D and the angular orientations and velocities ofthe articulated connecting rod given
that
©) Compare the values obtained from a) and b) above
Plot graphs of positions and velocities of B, C and D
Yelocity ofthe articulated connecting rod against &
ind velocities of B, C and D and the angular
‘ated connecting rod for the angles 8; = 0°, 30°, 90°
b)
and the angular orientation and
UNIVERSITY
MAKERERE
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester |] 2015/2016 Examinations
MEC2202/AEN2209: Theary of Machines
Monday 23 May 2016
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 - 1200 Hours)
Instructions:
* The Examination paper contains Seven Questions.
« Attempt any Five questions of your choice.
* Each Question Carries 20 Marks
* Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses,
+ Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet
BREUER NE EH EH HE Eee es
Question 3 (20 marks)
i flengthr
Fig. Q3 shows an oscillating cylinder mechanism in which rank aa ae
Uniformly clockwise at © rad/sec, Derive all the expressions ect
iston rod.
lar velocity of piston re
Velocity of the piston relative to the cylinder walls and the angu! [20 marks]
mrotates
determine
interms of crank angle, r, w and the base dimensions ¢ and d.
x i | Fig, @3 .
Question 4 (20 Marks)
Itis desired to design a cam with the following specifications: Roller in-line follower;
RISE = 25 mm, base circle radius = 20 mm, roller radius = 5 Mmm; RISE for 120° of cam
rotation, DWELL for the
kg femaining period. Draw the cam Profile; clearly indicating the regions where the. RISE,
_ PWELL and FALL follower motion take place, [20 marks]
rotation, DWELL for 60° of cam Totation, FALL for 90° of cam.
ai
, MAKERERE UNIVERSITY.
| DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
‘wecaz02 THEORY OF MACHINES 2014/15
FINAL EXAMINATION
4 DATE: Monday 28" May 2018 TIME: 09,00 - 12,00 Hours
Eee ce
OP nsiwctions i) Attempt ons
4 2) Neat Diagrarns must be drawn where necessary
E 3) Figures to the right indicate ull marks
4) Use of an electronic pocket calculator is alowed
; 5)___ Assume suitable data, if necessary
Question
s a) Explain the differences between the following; giving relevant examples
1 Mechanism and machine
4 Oscillating and rotary motion
Wi, Tangential, radial and coriolis acceleration ¥
| bd) Determine the DOF of the following kinematic chain
aaa
Question 2:
For the mechanism shown in Fig, Q2, OA rates at 15 rad/s coUAtErdockwise. Determine the velocities
f at points 8, Cand D and the angular velocities of links, AB, O,BC and CB.when 2 = 120°,
- 20
220 c
. All dimensions in mm
[20 Marks}
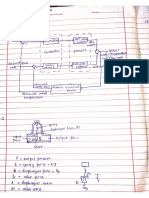
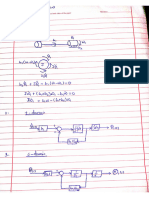
TiRpos the term instrumentation system and use a block diagram to illustrate it.
(4 Marks)
1.2. Define and classify with relevant examples the “unit of measurement”. _ (6 Marks)
1.3. Distinguish between accuracy and precision, and explain why Cerone
characteristics are relevant in instrumentation Engineering, (5 Marks) |
ir lic ir i ring.
j 1.4 Discuss the term intelligent instruments as used in Instrumentation Seanssray ane
| Question 2 ; Py peel
| 21 Distinguish between analogue and digital instruments, (4 Mart
2.2. Describe the operation of one example of each instrument in 2.1 above. (6 Marks)
23 A technician wants to buy a controller, persuade him or her to buy an electronic
‘one instead of a pneumatic one. (6 Marks)
24 A maintenance Engineer wants to keep track of maintenance schedules; describe
the device he or she must use to implement the application. List at least two other
devices in that family, (4 Marks)
Question 3 [20 Marks]
3.1 Distinguish between an error and offset in relation to measurement, (3 Marks)
3.2 John tests an instrument whose true val
Consistently on one side of that value. St
Causes and solutions to such an error.
lue is known. The results obtained were
late the type of error and suggest possible
33 Ina measurement experiment, a set
413 430) was obtained, determine ti
| Comment on reliability of the results
Of values (398 420 394 416 404 408 400 490 396
the mean, variance, and standard deviation.
3.4 Aspring balance is calibrated in a
load-defiection characteristics ar
in an environment at a
Characteristics are given in T
n environment at a temperature of 20°C andthe |
fe shown in Table 1. The same device is then used |
temperature of 30 °C, and the load-deflection
able 2. Determine the
Zero drift and sensitivity drift per
°C change in ambient temperature. a Marks)
‘Table 1: Load-Deflection Characteristic at 20 Degrees
Load (kg) ) 1 2.
Deflection {mm) oO 20 40
‘Table 2: Load-Deflection Characteristics at 30 Degrees.
Load (kg) oO 1 =
Deflection {mm) 5 ee 49
Hii.
coring for Mechanical Engineers 1 (MEC2201), Test Two
Electrical Engin
20" March 2019
‘Answer Both Questions in 50 Minutes
Question One {20 Marks}
a) Define and classify transducers. {5 Marks]
b) John intends to design a circuit that detects approaching objects; use your knowledge on
instruments and measurements to advise him on basic devices required. [4 Marks]
c) Define a thermocouple, and draw an equivalent circuit of an ideal thermocouple. [3 Marks]
4d) Distinguish between analogue and digital instrument. [4 Marks]
¢) With the help of block diagram(s), describe a control system. [4 Marks}
Question Two [20 Marks}
a) With the help of relevant examples, explain the term “energy sources”. [5 Marks}
) While there are several energy sources, which can be applied for various reasons, argue for the
promotion of renewable energy use. [4 Marks}
c) Describe what you understand by a power system starting from biomass and using direct
combustion. } [5 Marks]
d) State the first law of thermodynamics, and explain the various energy forms and conversions
involved in a traditional hydropower plant. {6 Marks]
END
MAKERERE UNIVERSITY
Y
| COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOG
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester II 2016/2017 Examinations
MEC2201: Electrical Engineering for Mechanical Engineers IL
Monday June 12, 2017 >
Duration: 3.0 Hours (1400 - 1700 Hours)
Instructions
* The Examination paper contains Six Questions,
+ Attempt any Five questions of your choice,
* Each Question Carries 20 Marks
+ Marks for each section are indicated in parentheses,
Indicate the cttempted questions on the top Page of the answer booklet provided.
a ctions?
that are the main elements ina measurenrent system and what are thelr fun
sh elements are not needed in som, measurement systems and why®
' {8 Marks) -
nv : ,
Passive instruments means. Give examples of |.
Of these two.classes of Instruments? ;
a | [6 Man
2.1. Distinguish between Passive ar
Passive filters?
mid active fiers What are some of the drawbacks of |
oth : [5 Marks] . ~
is advantage
22 Explain one application of an Instrumentation amplifier, What is it
comperedl with the standard operational ampiitier?
2.3 State the advantages of digital meters
_ of applications are analogue meters sti
(3 Marks]
over thelr analogue counterparts. What sort
ll Commonly used for? . 14 Marks]. -
Two coils, Aand B are placed such that
le B has 3000 tums. When the
current in A is
the flux linking it is changing at a ra
te of ImWb/s,
Changing at a rate of SO0A/s,
Determine;
Pi the omtincuced in each coil ; {2 Marks}
- ii) The Self-inductance of each coll {2 Marks] *
[2 Marks}
[2 Marks)
iil) The mutual inductance of each coil
tor as applied to qe
BS 1 distribution fact
‘ 5.1 Briefly describe the terms pitch factor an [2 Marks] |
. meecernno: sel ingle layer armature Winding !
Fa es tar connected sing}
hase, 16 pole alternator has a si re aaa
i ne slots and 10 conductors per slot, If thealternator runs ca RM ahd the
flux per pole is 50 mWb, determine; ; aaa
i)’ The frequency of the generated voltage. ae
# ii) . The phase voltage . : . a a na a
Hage’. ee me ‘ ea
ii] Thedine voltag seed
A shunt generator delivers 195A'at @ terminal potential difference c
| gmotire resistonce and shunt figid feslstance, dre 0.620 and! 50% respectively,
iron und fiction lossés are equdl to 980, Fin “ eee eee
R Fi peer eerie Sh [2 Marks]
i) The emf generated
il) The copper losses [2 Marks}
[2 Marks}
iil) The output of the prime mover
| iv) The mechanical efficiency, electrical efficiency and overall efficiency,
[4 Marks)
Question 6 (20 Marks)
6.1 With the aid of a diagram, describe the principie of operation of a de motor, |
; {6 Marks]
6.2, A de motor takes Qn armature current of 1 10A at 480V. The armature circuit
Tesstance is 0.20. The machine hos é poles and the armature is lap connected with
864 conductors and the flux per pole is 0,05Wb. Calculate; 4+" ae
i) The speed of the machine, att [2 Marks}
ii)The torque developed by the armature: [2. Marks}
63 A 4pole, 240, wave Connected shunt m
') The total torque
li) Useful torque
i ful
;
MAKERERE Wer UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MB@M ANIC AL ENISHDEER WNC
End of Semester Il 2020/2021 Examinations
MEC2208; COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR MECHANICAL
ENGINEERS
Wednesday January 5" , 2022
| Duration: 3,0 Hours (0900 = 1200 Hours)
. wa Framination paper contains Seven Questions,
‘Question ane k Compubory, Attempt any other tour questions of your choice,
Feel Question Caries 20 Marks
Javks for eaeh Question are indicated in parentheses,
t@ the atlempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet provided —
ane
jiece of code.
pam ieiinteeialiy index <-10/ ndextt)
= 3tindex;
orrect it. (4 marks)
sample_array [index]
Briefly discuss what is wrong wi
Briefly discuss the bubble sort algorithm.
ith the above code and ¢
Consider an array
2.2, 3.8, use the bul
of student Grade Point
pble sort algorithm to
6.2
‘Averages (GPAS) 4.5, 34, 9.2, 2.5, 3.5, 4.2. , :
ate code that would sort these eight numbers ond dIspicy them in descending |
order. (6 marks)
4&3 Using o few ines of code, wite statements to differentiate betwee? static and
dynamic memory allocation. Explain the cases where each may apply (6 Marks)
64 — Using examples, explain the differences between pointers ari dite t et ee
in programming. Outline any two applications of pointers. ces
7.1 Explain the difference between sequential ond randem-ocee.s files. Discuss the
po Meattance of extemal fs n programming (5 marks)
2. Study the code snippet below and explain its purpose indicating the expected
‘output. (3 marks)
#include
Hinclude
#include
teing namespace std:
intmain()
{
igstrean inf ("File txt"):
de (line)
( |
cerr << "Oh oh, File.txt could not be opened for
Feading!" << endl go = eae |
exit(1); |
, |
white (inf)
a
string strinput;
Getline(inf, steInput) ;
4 cose SS strnput ends |
return0;
y
7.3. Define exception ha i i
indling in C++. Citin
Rallagiccnientoncing nce ing at least one example, discuss the levels
7.4 What do you und i Co
jerstand by Object Oriented P. it igh
‘advantages of the Object Oriented osrerna8 (Corl oa
7.5 Outline and explain the prit Se eas Canons) ad
plain the primary features of OOP
(4 Marks)
5)Page
- &
MAKERERE yer UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester II 2019/2020 Examinations
MEC2203: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR MECHANICAL
ENGINEERS
Monday December 7" , 2020
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 - 1200 Hours)
—
Instructions:
* The Examination paper contains Seven Questions.
* Question one is Compulsory. Attempt any other four questions of your choice.
» Each Question Carries 20 Marks
* Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses.
» Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet provided
» You are required to observe all the ANSI/ISO coding standards and conventions
a8 sel ecto,
ng stvations identity the type of cons :
t
(4 marks)
Beh cs V241/34 1/4 41/5 + ...4 1/10
@ in the list of temperatures from an experiment
F %!
x in the number of days of sick leave taken by employees in a
partment
“Testin it ifferent values of its arguments
i) tion to see how it performs for differen: C
Es Eoismonts including a while loop, that ore required to calculate y/t)
@ equation:
[-37 +5 30
al 6
Ne | sas r<0
8 of franging between -
() You do not need to it
12 and 12 in steps of 4. Display each value of t
write a complete Program but you should include
statements for all the variables that you use, (8 Marks).
ample, explain what the continue statement would do inside ofa
ol (2 Marks)
q
Question 6 (20 Marks)
61 Observe the following piece of code.
int sample_array[10) ;
for(int index = 1; index <=10; indext+)
sample_array[index] = 3*index; (mia nates)
Briefly discuss what is wrong with the above code and correct a oro ee
62 Draw the associated flow chart and perform a dry run on the faeces)
below showing the results at each iteration stage.
double GPA[S}=(4.3, 3.2, 4.5, 2.6); //Grade Point Averages
// sorting the array
i for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
for (int j=0; <5; j++)
af (GPA[i] < GPA[3})
t
double temp = GPA[i];
GPALi] = GPA(3};
GPAI3] = temp;
Y . ”
63 Using a few lines of code, briefly lustrate how to dynamically (i) allocate and (i)
de-ollocate a float array A{10] using the new and delete operators (4 Marks) F
‘| 64 Using examples, explain the differences between pointers and references as use
in programming. Outline any two applications of pointers. (4 marks)
| ‘Question 7 (20 Marks j
7.1 You have been conducting an experiment in the laboratory and logged |
temperature data. You need to store these temperatures to an external data file. |
j (a) Write statements that create an ofstream object named outfile and connects
it to the external file EXP.DAT. (3 marks)
(6) Write a loop that prompts the user to enter input data, reads a temperature
ftom the keyboard, and writes it to fle EXP.DAT. Assume there are SIZE elements,
where SIZE is an int, (4 marks)
72 Define exception handling in C++. Identify at least one exception that can occur
ot hardware, language, and program levels, respectively. (4 Marks) i
1! 73 What do you understand by Object Oriented Programming (OOP)? Highlight the |
i Scvantages of the Object Oriented Programming approach, (4 Marks)
7.4 Outline and explain the Primary features of OOP (5 Marks)
5|Page
ITY
MAKERERE UNIVERS ae
F ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND rece
Seno OF MECHANICAL Prue i
meses COMPUTER Bede ReNiNG oa Met
| Time: 14:15-15:
| Date: Friday 8 March 2020
ids and
Attempt all three problems observing all ANSI/ISO coding standa:
‘mpt al re
conventions,
Problem One:
* Program behaviour
* Key problem objects
* Operations heeded to solve the problem
* Algorithm
Using the ANsisis tite the complete C++
Problem. Expicin roach taken in
(c) Categorize the a
arriving at the final program, (8 Marks)
Toss that Could be inoduced in such
(d) How Would such a Program by
(b)
1 standards, w,
© Program (4 Marks)
© maintained and/or improved in future? Give
Meaningful Suggestions. = (5 Marks)
Problem Two: =
2.1) Assuming that x y, ‘andzore boolean Fe ssiOns with the values fq tue, and false,
respectively. Find the value of £71 ot the following boolean SAPFESSIONS. (5 Marks)
(a) x aa 4 D) x Bay | fiz ()x Bary 1]
(d) kag (e)xt VR&Z
22 Outing the three basic Confrol sttuctuses (3 Marks) )
23 list the sixrelational operators, (3 Marks)
24 AssuméThe declaw ions Wx
| intnumber = 123, =
| double rate = 23.45678;_. PECKSIO N.
Show preci:
1[Page
oo
MAKERERE yer UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, DESIGN, ART AND TECHNOLOGY |
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING |
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester Il 2018/2019 Examinations
MEC2203: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR MECHANICAL @
ENGINEERS
Tuesday May 14, 2018
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 - 1200 Hours)
a
Instructions:
The Examination paper contains Six Questions.
Question one is Compulsory. Attempt any other four questions of your choice.
Each Question Carries 20 Marks
Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses.
Indicate the attempted questions on the top page of the answer booklet provided
You are required to observe all the ANSI/ISO coding standards and conventions
; atural languages?
Jronment IDE) (4 Marks)
(16 Marks)
urces along @
aera, Hee timid
‘will settle Into a steady state. This
grid of cells and simulating 1
Pp ture in each interior cell (ij) will be the average of
Be rer boun sate + T(i#1,j) + TELJ-1) + 1, J41))/4
P a program to determine the steady state temperature distribution in the
by representing the plate as a two-dimensional array with NROWS rows and
columns. NROWS and NCOLS should be declared as global constants | |
# use 20 for both values). In the program, the final temperature data
¢ Be written to an external fle named temp.dat instead of (or in addition to)
inal screen,
‘Your program should do the following:
Declare 2 seporate two-dimensional ar
maintain the
pore! loentran eameerghe, aes for the top, bottom, left, right sides, Also
‘Prompt "ature Tlij) for the interior cel Hiali it
_ Palle and alsplay the intial contents of the femp array on the, onae ‘emp uingltia
sd temp to ola
2? Over al the interior c
Pmellll = 0.25+(o1any9-1) +
NG) -
0. a convergence.criterion,
el (but not the edge cells!)
| Question 1(20 Marks) . os
1 i do you understand by the term “Computer
ign process. f four test scores. The four tex
program desOr thn fo find the wei ae format: {5 Mark
2 Design an algorithm 10 fine Tr ieare given in the following pl la
(® ™ scores and their respective ocreréilas (Sex| htJ=
ramming"? Briefly discuss the |
or [6 Marks} |
ae
orel weight] dint a
tostsc 5
- ; (eo Center
For example, sample data is as follows: on fie Your tet Semen 40)
7 Cou << SN
sory Vat %) Gin BBS &
95 0.35 ynx A,
. 85 0.15 wm
65 0.30
\d wand t are double variables. Whg}
1.3Suppose that x, y, and zare int variables an Se ee
valve is assigned to each of these variables after the last stater aie
17; ;
15; |
x+y / 4;
xi3at4;
17/3 + 6.5;
x /4.0+15% 4 - 3.5; .
1.4 Using appropriate examples, distinguish between the following [4 Marks}
(a) Operator precedence and associativity
{b) Integer overflow and underflow |
me KH
6+ Question 2 (20 Marks)
2.1 What do you understand by “Standard iostreams". Briefly describe the I/O closs
B Pasicucicxclitosi
hierarchy " [4 Marks]
2.2 Which header file must Be included to use the following functions?
[4 Marks]
(a) setprecision #) {b) pow (Cc) labs (d) exit Q
23 Determine whether the value, irue or faise, for each of the following Boolean
expressions, assuming that the valve of the variable count is 0 and the value of the
voriable lintis 10, Give your answer as one of the vdlues true oF false.
[6 Marks]
(9) “(count == 2) ce (x 7) || ( limit < 20) '% 77
(c) ((limit/count > 7) g& ( Limit < 0)
24 Show the precise output from the following series of cout instructions, Assume these |
~ ate the intiol values of the variables. Assume the ios: : fixed has been set along
with ios: :showpoint.. The precision has not been set to any value initially.
int x = 123; [6 Marks]
double z = 42.35353;
(a) cout <<
setw (6) << x << x;
\ (b) cout << x << setw (5) << x;
{c) cout << se isi
tprecision (4) << setus) <= strlen(str2)) , |
strl = str2; vet .
(9) if (stromp(stri,'str2) < 0)
cout << "strl is less that str2." << endl; nleled .
:
63 What do you understand by Obj
5|Page
Rina Nb tara Memmi cay | Race
F. ifstream.open("oxp.dat") j
sian
a innuislesent
r
3 Rea :
XK. rannum = A + static_cast( rand (B-A) ) /RAND_MAX;
De tarda scgecd tee cath)
Mean de ord 9 cone tee DY
OutFile. open ("exp,dat", doa: !app) /
5.4Using a few lines of code, briefly illustrate how to dynamically (i) allocate and (i) de-
allocate a float array A[10) using the new and delete operators [4 Marks]
Question 6 (20 Marks)
Define exception handling in C++, Identify at least one exception that can occur at
hardware, language, and program levels, respectively. [4 Marks}
6.2 Consider the following C++ code:
int lowerbinit;
int divisor;
int result;
try
t
cout << “Entering the try block.” << endl;
Af (divisor = 0)
throw 0;
£ (lowerLinit < 100)
throw string (“Lower limit violation.”);
result = lowerLinit / divisor;
cout << “Exiting the try block.” << endl;
?
catch {int x)
{
cout << “Exception: “ <<'x << endl;
result = 120;
?
catch (string str)
«
cout << “Exception: << str << endl;
)
cout << “After the catch block” << endl;
Whot is the output if:
Q) The valve of lowerLimit is 50, and the value of divisor is 102
[2 Marks}
b) The value of lowerLimit is 50, and the value of divisor is 0? [2 Marks]
¢) The value of lowerLimit is 150, and the value of divisors 10 [2 Marks}
d) The value of lowerlimit is 150, and the value of ivisor is 02 [2 Marks}
ject Oriented Programming (OOP)? Outline and
explain the two important components of software objects,
[4 Marks}
6.5 What are the main differences between abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance,
and polymorphisrn? [4 Marks]
Fanman 2 Ra te SB) saeatic_castcdouble>( rand() ) /RAND OX;
annum = A + (B — A)#static_cast( rand() )/RAND_MAK;
muoe
. 4fstrean.open("exp.dat") /
AnFile.close();
inFile. open ("exp.dat", ios
ran_int = 1+ rand()$5;
AnFile.open("exp. dat") ;
Fennus =A + acacie,castcdouble>( rand(B-A)_) /RAND_M\¢;
inFile. append ("exp.dat") +
ran_int = 1+ rand()#(4 - 1);
outFile. open ("exp.dat", ios: :app) ; F
5.4Using a few lines of code, briefly illustrate how to dynamically (i) allocate and
allocate a float array A[10] using the new and delete operators [4 Marks}
Question 6 (20 Marks) 1
6.1 Define exception handling in C++. Identify at least one exception that can occur at
hardware, language, and program levels, respectively. [4 Marks}
6.2 Consider the following C++ code:
int lowerLinit;
int divisor;
int result;
“kt Runde
ral i
‘
cout << “Entering the try block.” << endl;
if (divisor = 0)
throw 0;
if (lowerLinit < 100)
throw string (“Lower limit violation.”) ;
result = lowerbinit / divisor;
cout << “Exiting the try block.” << endl;
3
catch {int x)
{
cout << “Exception: " <<'x << endl;
result = 120;
}
catch (string str)
{
cout << “Exception: << str << endl;
,
cout << “After the catch block” << endl;
Whot is the output if:
Q) The value of lowerLimit is 50, and the value of divisor is 10? [2 Marks]
5) The value of lowerlimit is 50, and the value of divisoris 02 [2 Marks] |
¢) The value of lowerlimitis 150, and the value of divisor is 102 [2 Marks]
) The valve of lowerLimitis 150, and the value of divisor is 02 [2 Marks]
6.3 What do you understand by Object Oriented Programming (OOP)? Outline and
explain the two important components of software objects [4 Marks}
6.5 What are the main differences between abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance,
and polymorphism? [4 Marks]
5|Page
| MAKERERE wer UNIVERSITY |
SIGN, ART AND
E OF ENGINEERING, DE
T° TECHNOLOGY
ae
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
End of Semester If 2015/2016 Examinations
| |
MEC2203: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR MECHANICAL
ENGINEERS
Wednesday May 18, 2016
Duration: 3.0 Hours (0900 — 1200 Hours)
Instruct
¢ The Examination paper contains Six Questions,
* Attempt any five questions of your choice,
* Each Question Carries 20 Marks
* Marks for each question are indicated in parentheses,
attempted questions on the lop page of the answer booklet provided
ed to observe all ANSI/ISO codi lards and pore
BE (3<'207)7
{cout << “a is less than 20\n"7
| ra
23 Using nested if, write C++ statements that define the value of the following Peay
* x -~-5 x<0 and y>0
fey= |], 2x Sy +6 xeOand y<=3
y-10"x?-3 x=4 or y=5 |
° otherwise
ing an example, explain how a loop
is an “infinite loop” i ful? Us
2.4 What is an “infinite loop” and how can it be use! To middle of its ‘block? [4 Marks}
can be structured so that it terminates with a statement in
Marks : ;
3.1 For each of the following situations, explain which type of loop (while, do-while, or for)
would work best: [4 Marks]
(a) Summing a series such as 1/2 + 1/3 +1/4+ 1/5 +...+ 1/10
(®) Reading in the list of exam scores for one student.
(©) Testing a function to see how it performs for different values of its arguments.
(@) Reading in the number of days of sick leave taken by employees in a department. |
3.2 Using an appropriate example, briefly explain the term zero-based indexing [4 Marks]
3.3 Study the following code fragment and answer the questions below:
const int LENGTH = 21;
char message[LENGTH] ;
inter a sentence on the line below." << endl;
|
| cin >> message[i];
| +H;
)
while (i < LENGTH - 1 && message[i] != '\n');
message(i] = '\O'; // Terminate stri NUL char
cout << message << endl; ogee .
(@) Suppose that in response to the interacti
respi Prompt, the interactive user types the following line and
Please go away.
_ What will the output of the code fragment look like?
-(b) Suppose that the statement "oi . | [2 Marks
(messageli}}; ™*P*89°L41 "is replaced by the statement |
What will the output of the code fragment Mest oc
ype olwing ie resin SUSE te pomp
a
15 4,51, 3.42, 3.21, 2.53, 3.56, 4.80, 2.22,
isplay them in
[8 marks]
int Average:
34. y of student Grade Poi ; i
Se Fee hat would sort these eight numbers and di
descending order.
ue rk
yn 4 (20
4.1 Using illustratio
function overloading. How is it important? [4 Marks]
execution of the program.
4.2 Given the following set of statements. Write the final results after aes
explain the term
Ant func (int a, int b) {
a t= 2;
i cout << Mann
#include
const float EarthRad = 6371;
| const float Pi = 3.1416;
float getLatitude() ;
float getLongtitude() ;
float calcDistance (float lati, float 1at2, float longi, float 1eng2)
t int main() {
i float lat2, lati. long2, longi;
latl = gethatitude() ;
longi = gethongtitude() ;
lat2 = getLatitude();
long2 = getLongtitude() ;
float distance = calcDistance(lat1. lat2, long, 1ong2);
cout << "The surface distance between the two points is ";
cout << distance << " kilometres" << endl; .
)
float getLatitude()
{
‘int degrees, minutes;
float seconds, fdegrets;
cout << 'Enter the latitude in degrees, ninute: a Ch
cin >> degrees > minutes >> seconds; 1 eel
fdegrees = degrees + (minutes/60.0) + (sec. ;
fdeqrees = fdegrees * Pi / 180; Sa
return fdegrees;
void gettongti tude ()
{ int degrees, minut; i
float seconds, fdegrees; minutes, and seconds\
cout << "Enter the longtitude in degrees,
gin >> degrees >> minutes >> second 4, 2600)
degrees = degrees + (ninutes/60.
fdegrees = fdegrees * Pi / 100;
return fdegrees fi
é oat longi, float long2);
float calcDistance(float lati, float 1at2, £/
t
float longbitf = fabs (longi - long2);
Af (longDiff >= Pi) longDiff -= Pis
float temp = sin(lati)*sin(lat2) +
08 (ati) *c08 (1at2) *coa (LongDif£) ;
float surfaceDist = EarthRad * acos (tmp); } Aiertcat ache. Bt
[4 Marks]
44 Define exception handling in C++. Identify at least two exceptions
‘hardware, language, and program levels, respectively.
ks
5.1 You are required to write temperature readings from an experiment to a data file.
(@ Write statements that create an ofstream object named outFile and connect it to the
extemal file EXPT.DAT, eel
(@) Write a loop that prompts the user to enter input data, reads a temperature from the
Keyboard, and writes it to the file EXPT.DAT. Assume there are SIZE elements, where SIZE
is an int. [3 Marks]
5.2 Complete the following program (by filling in the missing lines 3, 8, 20, and 21) so that it
Will read data from the file “sample.dat” and print out the data. [4 Marks]
@ Sinclude <¢atrean>
(2) #include
@)
(4) using namespace std;
(5) int main()
(6) ‘
o} ifstream inf ("Sample.dat"
(8) =
(9) t
(20) // Print an error and exit
a1) corr << "Uh oh, 5:
1 Sample.dat could not be open
ep Sel ¢ not be opened for
(13) exit (1) ;
»
// While thore's sti stuse lore
while (int) sate
t
| ea ,
March 9, 2020
| MEC 2205 CAT
| Maximum time allowed: 1.5 hours
1. List three (3) factors that infilence drag on a body (3 marks) i
2. Giving one specific example, briefly explain the commercial implication of
drag on automobiles (4marks)
3. Briefly explain why it is necessary to control boundary layer development.
(2 marks)
4. Inan experiment where velocity profiles were measured at the trailing edge|
. of the flat plate, the boundary layer above the plate was found to be fully’
developed and 4.4 cm thick. The air density is 1.27kg/m3 and the
undisturbed velocity was 33 m/s. For such an experiment, develop \
expressions that can be useci to determine
§ a) The boundary layer thickness (4 marks) a
x 5) The skin-friction coefficient per unit width (6 marks) > 4S
Hence calculate the following
¢) The length of the turbulent boundary layer (5 marks)
a) The drag force on the plate per meter span (5 marks) |
4
Assume the boundary layer extends to the leading edge of the plate, and that
02s
0.861% = oad } rec j
. applies; where ‘C' is a Constant
the equation
that depends on the distance *
the undisturbed flow and Sis th
of air as 1.310" Ns/ma
of
sity
om the source at radi @ OX-axis. If the
Us F = 250 mm is 0.28 m/s, and t
' ss, determine the position coordinates of t
ra MAKERERE UNIVERSITY .
Faculty of Technology
Department of Mechanical Engineering i
Bachelor of Science in Mechanical/Agricultural Engineering
| Year Il Semester Il 2008/2009 CAT I
i MEC2203 Computer Programming.
Date: Friday 13" March 2009 Time: 14 00-1520 Hours
Attempt at moxt Two Questions
Question One
2) What is computer programming?
Computer Programming (programming or coding) is the process of writing, testing,
debugging/roubleshooting, and maintaining the source code of computer programs. This source
(G marks)
code is written in a programming language. The code may be a modification of an existing source
‘or something completely new. The purpose of programming is to create a program that exhibits a
certain desired behaviour (customization),
») Briefly discuss the five major software quality attributes addressed by modern
programming. (5 marks)
Whatever the approach to software development may be, the final program must satisfy some
fandamental properties. The following five properties are among the most relevant: \
Effciency/Performance: the amount of system resources a program consumes (processor time,
te ran eee, slow devices, network bandwidth and to some extent even user interaction), the less
the better.
Robustness: bow well a program anticipates situations of data type conflict and other
inmatbilities that result in un time errors and program halts, The focus i
interaction and the handling of exceptions
is mainly on user
Architecture ,
me hitecture of a software system or software architecture refers to an abstract representation of
The arc
that system. Architecture is concerned with making sure the software system will meet the
king,
a
requirements of the product, as well as ensuring that future requirements can be addressed, The
tecture step also addresses interfaces betwoen the software system and other software
Saas as well as the underlying hardware or the host operating system.
iv) Design, Implementation and Testing
Implementation is the part of the process where software engineers actually program the code for
the project.
Software Testing is an integral and important part of the software development process. This part of
the process ensures that bugs are recognized as early as possible,
Documenting the internal design of software for the purpose of future maintenance and
ceahancement is done throughout development. This may also include the authoring of an API, be it
external or internal,
% Deployment and Maintenance
Deployment starts after the code is appropriately
otherwise distributed into a production environment.
Software Training and Support is important because a large percentage of software Projects fail
Because the developers fail to realize that it doesn't matter how much time and planning a
evelopment team puts into creating software if nobody in an organization ends up using it. People
Sr @fien resistant to change and avoid venturing into an unfamiliar area, so. se a Part of the
Geployment phase, its very important to have training classes for new elients of your software,
tested, is approved for release and sold or
Question Two
3) What isan integrated Development Environment (pe) (3 marks)
In computing, an integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides
SOmprebensive facilities to software developers for software development. An IDE normally
consists of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build automation tools, and (usually)
a debugger. Sometimes a version control system and Various tools are integrated to simplify the
sonsiruction of a GUI Many modem IDEs also have a class browser, an object inspector, and a
Glass hierarchy diagram, for use with object oriented software development,
th but the term is used widel: :
i ut th 'Y t9 refer to
t Is. simple software development toolchain consists rae
compiler and linker to transform the source code into an executabl
vide interfaces to the operatin; ‘em. A complex product such an
You might also like
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument14 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Https - WWW - Nira.go - Ug - Media - 2024 - 02 - RECRUITMENT-OF-TEMPORARY-STAFF-ADVERT-2024-finalDocument32 pagesHttps - WWW - Nira.go - Ug - Media - 2024 - 02 - RECRUITMENT-OF-TEMPORARY-STAFF-ADVERT-2024-finalOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Kayo Cuk Lango Processes and StagesDocument12 pagesKayo Cuk Lango Processes and StagesOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 (B) SolutionDocument3 pagesProblem Set 3 (B) SolutionOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 (A) SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem Set 3 (A) SolutionOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines, TestDocument2 pagesTheory of Machines, TestOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab ReportDocument14 pagesHeat Transfer Lab ReportOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument1 pageBudgetOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Busitema PROVISIONAL GOVT Admission ListDocument3 pages2023 Busitema PROVISIONAL GOVT Admission ListOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- 44 Timeless Secrets To Looking 10 Years Younger 4.3Document42 pages44 Timeless Secrets To Looking 10 Years Younger 4.3Ogwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Solution To Theory of Machines AssignmentDocument4 pagesSolution To Theory of Machines AssignmentOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Dangote Campaign Team Press StatementDocument1 pageDangote Campaign Team Press StatementOgwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Design and Optimization of Piezoelectric Transducer (PZT-5H Stack)Document16 pagesDesign and Optimization of Piezoelectric Transducer (PZT-5H Stack)Ogwang hallanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)