Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Digital Gap Essay
Uploaded by
kazzy Jumanji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesOriginal Title
The Digital Gap essay
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe Digital Gap Essay
Uploaded by
kazzy JumanjiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The Digital Gap: Bridging the Divide for Inclusive Development
Introduction: In today's interconnected world, digital technologies have become an
integral part of our daily lives, transforming how we communicate, access information,
and conduct business. However, not everyone has equal access to these technologies,
resulting in a digital gap or divide. The digital gap refers to the disparities in access to
and use of digital technologies among different individuals, communities, and regions.
This essay explores the impact of the digital gap, the factors contributing to its
existence, and the importance of bridging this divide for inclusive development.
I. The Impact of the Digital Gap:
1. Socioeconomic Inequality: The digital gap exacerbates existing socioeconomic
inequalities. Lack of access to digital technologies limits opportunities for education,
employment, and entrepreneurship, perpetuating a cycle of poverty and
marginalization. Those without digital access often face difficulties in accessing critical
services, job opportunities, and information necessary for personal and professional
growth.
2. Educational Disparities: Limited access to digital technologies hampers educational
opportunities. Students without access to digital tools may struggle to keep up with
online learning platforms, access educational resources, and develop digital literacy
skills. This further widens the educational gap and hinders the development of vital
21st-century skills.
3. Social Exclusion: The digital gap can contribute to social exclusion, as it limits
individuals' ability to connect with others, access social networks, and participate in the
digital economy. This exclusion can lead to reduced opportunities for social
engagement, civic participation, and cultural enrichment, further deepening social
inequalities.
II. Factors Contributing to the Digital Gap:
1. Infrastructure and Connectivity: Limited infrastructure, such as the lack of reliable
internet connectivity, particularly in rural and remote areas, poses a significant barrier to
digital access. Unequal distribution of internet infrastructure and the cost of internet
services contribute to the digital divide.
2. Affordability and Accessibility: High costs of digital devices, internet services, and data
plans make them inaccessible for many individuals, especially those with limited
financial resources. Affordability issues further hinder digital inclusion, particularly in
low-income communities.
3. Digital Skills and Literacy: Digital literacy skills are essential for individuals to effectively
use digital technologies. Insufficient access to education and training programs that
teach digital skills further widens the digital gap. Lack of digital literacy also affects
individuals' ability to critically evaluate information and navigate online platforms safely.
III. Bridging the Digital Gap for Inclusive Development:
1. Infrastructure Development: Governments and private entities should invest in
expanding internet infrastructure to underserved areas. Initiatives like building more
broadband networks, improving connectivity, and promoting public-private partnerships
can help bridge the infrastructure gap.
2. Affordability and Accessibility Initiatives: Efforts should be made to reduce the cost of
digital devices, internet services, and data plans. This can include subsidies, community-
based internet access centers, and collaborations between stakeholders to provide
affordable connectivity options.
3. Digital Skills Training and Education: Promoting digital literacy and providing training
programs to enhance digital skills are crucial for bridging the gap. Educational
institutions and governments should develop comprehensive digital literacy programs
that equip individuals with the necessary skills for the digital age.
4. Inclusive Policies and Regulation: Governments should enact policies that promote
digital inclusion and equitable access to digital technologies. This includes fostering
competition in the telecommunications sector, protecting user privacy, and ensuring
equal opportunities for all.
Conclusion: Bridging the digital gap is vital for creating an inclusive society and enabling
equitable development. Addressing infrastructure limitations, affordability issues, and
promoting digital literacy are essential steps toward closing this divide. By ensuring
universal access to digital technologies, we can unlock the full potential of individuals,
communities, and economies, fostering innovation, economic growth, and social
progress.
You might also like
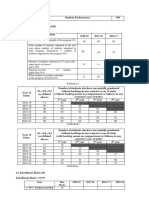
- Workfront Training Handbook - Worker GuideDocument25 pagesWorkfront Training Handbook - Worker Guidesaraes88100% (1)
- The Digital DivideDocument2 pagesThe Digital DividedeepkrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Digital Technology in LifeDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Digital Technology in LifeJunel AlapaNo ratings yet
- Configure Cisco SD-WAN for Multi-Tenant EnvironmentsDocument12 pagesConfigure Cisco SD-WAN for Multi-Tenant Environmentssoumen1977No ratings yet
- Digital Divide @monikaDocument6 pagesDigital Divide @monikaMonika JangidNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways The Digital Divide Effects EducationDocument10 pages5 Ways The Digital Divide Effects EducationPrincess Hermoso Cortez100% (1)
- GenEd10 - Digital DivideDocument4 pagesGenEd10 - Digital DivideGerry Lynne MabanoNo ratings yet
- Digital DivideDocument14 pagesDigital DivideTata Lagria100% (2)
- Digital EmpowermentDocument16 pagesDigital Empowermentannikamehra17No ratings yet
- Debate Against The MotionDocument2 pagesDebate Against The MotionSarthak SinghNo ratings yet
- Week 1a - Digital AccessDocument11 pagesWeek 1a - Digital AccessKaren Narvadez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Week 5-6 IteraDocument28 pagesWeek 5-6 IteraNicole ConsultaNo ratings yet
- The Digital Divide and Its Impact on Economic DevelopmentDocument2 pagesThe Digital Divide and Its Impact on Economic DevelopmentntanirudaNo ratings yet
- Digital Divide Slide 3Document11 pagesDigital Divide Slide 3arnielneminNo ratings yet
- Impact of ICT On Social DevelopmentDocument10 pagesImpact of ICT On Social DevelopmentMartinson AppiahNo ratings yet
- ICT in Education - PrintDocument71 pagesICT in Education - PrintSunitha Susan JoseNo ratings yet
- Tharntype-2 Decision CriteriaDocument2 pagesTharntype-2 Decision CriteriaLess BalesoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-The Digital DivideDocument6 pagesChapter 6-The Digital Divideshauryamehta07No ratings yet
- Module 1 Livin in The It EraDocument7 pagesModule 1 Livin in The It EraJeahn AliNo ratings yet
- Digital Divides and DisparitiesDocument2 pagesDigital Divides and Disparitiesharis8025No ratings yet
- ch4 DDDocument20 pagesch4 DDMagarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 - Social Context of ComputingDocument6 pagesLec 7 - Social Context of ComputingjohnNo ratings yet
- Addressing Digital DivideDocument6 pagesAddressing Digital DividekeerthiNo ratings yet
- Digital DivideDocument4 pagesDigital Dividealiciamalik2002No ratings yet
- Bridging the Digital Divide through Computer LiteracyDocument5 pagesBridging the Digital Divide through Computer LiteracyVidisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Living in It MidtermsDocument21 pagesLiving in It MidtermsAbelard Henry PelaezNo ratings yet
- Digital Divide, Concept of Digital Immigrants and Digital NativesDocument23 pagesDigital Divide, Concept of Digital Immigrants and Digital NativesAnju Alphonsa PaulNo ratings yet
- Issues Surrounding Access: Digital DivideDocument16 pagesIssues Surrounding Access: Digital Dividerehanah mohammedNo ratings yet
- Digital Divide and Measures Taken by Government of Pakistan: Executive SummaryDocument20 pagesDigital Divide and Measures Taken by Government of Pakistan: Executive SummarywaqarparachaNo ratings yet
- Digital Technology and Social ChangeDocument5 pagesDigital Technology and Social ChangeMedarlyn RealinNo ratings yet
- Ethical Case StudyDocument3 pagesEthical Case StudyVinay MishraNo ratings yet
- The Digital Divide, ICT: InternetDocument4 pagesThe Digital Divide, ICT: InternetSTEPHENNo ratings yet
- AP-PETA_2nd-QuarterDocument4 pagesAP-PETA_2nd-QuarterwalaNo ratings yet
- Poratewatch/paywatch/p Ay/index - CFM: Executive Excess 2005Document5 pagesPoratewatch/paywatch/p Ay/index - CFM: Executive Excess 2005Debra Hirsch DimasNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The Digital Divide: Moving Toward A More Equitable FutureDocument6 pagesSolutions To The Digital Divide: Moving Toward A More Equitable Futurejosephinenambeya34No ratings yet
- Digital Divide: DefinitionDocument4 pagesDigital Divide: DefinitionBhanNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument27 pagesPresentationVani AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Digital DivideDocument1 pageDigital DivideIntervalNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Digital Teachnology and Social ChangeDocument8 pagesModule 5-Digital Teachnology and Social Changejohnnyboy.galvanNo ratings yet
- ANJUDocument16 pagesANJUAnju Alphonsa PaulNo ratings yet
- Digitaldivide 170325153727Document38 pagesDigitaldivide 170325153727Rajeev Kumar GangwarNo ratings yet
- Ugc Net: General Paper On Teaching & Research AptitudeDocument24 pagesUgc Net: General Paper On Teaching & Research AptitudeAkarshika pandeyNo ratings yet
- Digital Divide: By: Nielmar C. DescalsoDocument217 pagesDigital Divide: By: Nielmar C. DescalsoZildjian Xavier LlagasNo ratings yet
- Digital WorldDocument7 pagesDigital Worldwarnakulasuriya.niranjalaNo ratings yet
- cst 462s team 3 research paper - officialDocument22 pagescst 462s team 3 research paper - officialapi-686956026No ratings yet
- Unit 13 Digital Divide: StructureDocument14 pagesUnit 13 Digital Divide: StructureGyana SahooNo ratings yet
- AS IT Chapter 5Document2 pagesAS IT Chapter 5Vex Davies BanningNo ratings yet
- AS IT Chapter 5Document2 pagesAS IT Chapter 5Vex Davies BanningNo ratings yet
- Promoting Digital InclusivityDocument12 pagesPromoting Digital InclusivityFrench Mariee P. EdangNo ratings yet
- Developing Digital CitizensDocument4 pagesDeveloping Digital Citizensvigyorika477No ratings yet
- Understanding Digital Divide ConceptsDocument1 pageUnderstanding Digital Divide ConceptsAdrian CabalisaNo ratings yet
- DIgital Divide vs Digiral InequalityDocument2 pagesDIgital Divide vs Digiral Inequalitymatjustindelrosario04No ratings yet
- Digital DivideDocument7 pagesDigital Divideclientbururu1No ratings yet
- Ed Tech Issue Brandie Day-MedlinDocument6 pagesEd Tech Issue Brandie Day-Medlinapi-278370216No ratings yet
- Digital DivideDocument4 pagesDigital Dividesorol100% (3)
- Digital literac-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesDigital literac-WPS OfficehamsirujimarNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Cyber Literacy Digital Literacy PDFDocument12 pagesModule 7 Cyber Literacy Digital Literacy PDFmarvin pazNo ratings yet
- digital gender divideDocument4 pagesdigital gender divideSonia KhileriNo ratings yet
- It EraDocument24 pagesIt EraChristine mae HernandoNo ratings yet
- Tech 1 Module 5Document8 pagesTech 1 Module 5jenee kasumi aino nariesNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Arvi: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Arvi: Department of Civil Engineering39 - Deep MandokarNo ratings yet
- Recipe Recommendation by Ingredients DetectionDocument10 pagesRecipe Recommendation by Ingredients DetectionIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- T-MPLS: A Transport MPLS TechnologyDocument3 pagesT-MPLS: A Transport MPLS Technologydkmeta72102No ratings yet
- Customizing HCM HeadersDocument7 pagesCustomizing HCM Headersvemulapalli1100% (1)
- TS1. Computer History Overview-OSCADocument8 pagesTS1. Computer History Overview-OSCASadiqu ZzamanNo ratings yet
- TARGA DVD hc5100x PDFDocument37 pagesTARGA DVD hc5100x PDFLeandro EzquerraNo ratings yet
- PIM2 Fuel Injection Controller KitDocument4 pagesPIM2 Fuel Injection Controller KitmondorolaNo ratings yet
- Tesks List EksportDocument19 pagesTesks List EksportcvyunaallexamedikaNo ratings yet
- Vy Unit 3 Test - Storage Devices and MediaDocument4 pagesVy Unit 3 Test - Storage Devices and Mediaapi-327072135100% (1)
- HP LaserJet 4L - 4P Service ManualDocument306 pagesHP LaserJet 4L - 4P Service ManualimakingtxNo ratings yet
- N600X SystemServiceManual EN 10030881b001Document210 pagesN600X SystemServiceManual EN 10030881b001Electrónica BiomédicaNo ratings yet
- Engr002-Introduction To Engineering Dr. Ahmad El HajjDocument13 pagesEngr002-Introduction To Engineering Dr. Ahmad El HajjAli SabbahNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Electric ForkliftDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Electric ForkliftIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Aacable Wordpress Com Tag Block Adult Web Sites in MikrotikDocument7 pagesAacable Wordpress Com Tag Block Adult Web Sites in MikrotikganapareddyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Robotics Dr. Bob Williams, Mechanical Engineering, Ohio UniversityDocument25 pagesAn Introduction To Robotics Dr. Bob Williams, Mechanical Engineering, Ohio UniversitySertaç MalkoçNo ratings yet
- KPRIT-Civil-C4 - 2018-19Document16 pagesKPRIT-Civil-C4 - 2018-19civil deptNo ratings yet
- Scheduling, Preemption and Eviction - KubernetesDocument66 pagesScheduling, Preemption and Eviction - KubernetesFantahun FkadieNo ratings yet
- Framo Service Stations - Contact InfoDocument11 pagesFramo Service Stations - Contact InfoDeliu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Understanding Youth Unemployment and EducationDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Youth Unemployment and EducationIsha GargNo ratings yet
- Performance Sheet Drill Pipe: Pipe Body: Tubular AssemblyDocument3 pagesPerformance Sheet Drill Pipe: Pipe Body: Tubular AssemblyAboozar FathinejadNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Improvement of Plant Layout For Effective ProductionDocument7 pagesA Case Study On Improvement of Plant Layout For Effective ProductionHopestar Yen NhiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Screening ProcessDocument19 pagesPre-Screening Processode imanNo ratings yet
- Siemens Energy Company Presentation en 2022 PDF Original FileDocument29 pagesSiemens Energy Company Presentation en 2022 PDF Original FileSunil DashoraNo ratings yet
- Brkarc 2011Document261 pagesBrkarc 2011jramongvNo ratings yet
- ETO YES Training ManualDocument37 pagesETO YES Training ManualA NineNo ratings yet
- Smartliving 505 PDFDocument128 pagesSmartliving 505 PDFhmedi_ikbelNo ratings yet
- High Potential Cable TestingDocument1 pageHigh Potential Cable TestingAries dNo ratings yet
- Anx3110 PBDocument2 pagesAnx3110 PBzokiNo ratings yet