Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table Biochem Pathway
Table Biochem Pathway
Uploaded by
Aron Anthony Romey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesTable Biochem Pathway
Table Biochem Pathway
Uploaded by
Aron Anthony RomeyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
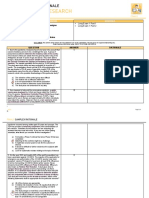
WHAT IS IT
FOR?
WHERE
DOES IT
OCCUR?
SUBSTRATE
END-
PRODUCTS
RATE
LIMITING
STEP
RATE
LIMITING
ENZYME
GLYCOLYSIS
Converts glucose into 3
carbon compounds to
provide energy
Mec type: emp
Cytosol
Glucose
2 molecules of
pyruvate / lactate
Fructose-6-phosphate
= fructose 1,6-
bisphosphate
Phosphofructokinase 1
GLUCONEOGENESIS
‘Synthesizing glucose from non-
carb sources to prevent
hypoglycemia during fasting
Liver (90%)
Kidney (10%)
Mitochondria and cytosol
Intermediates of glycolysis
and the TCA
Lactate through the Cori Cycle
Glycerol and propionyl CoA
from triacylglycerols
Carbon skeletons of
lucogenic amino acids
Glucose
Fructose 1 ,6-bisphosphate —
Fructose 6-phosphate
Fructose 1 ,6-bisphosphatase
GLYCOGENESIS
‘Synthesis of glycogen
Liver
Muscle
Cytosol
a-D-glucose
Glycogen
Elongation of glycogen
chains
(alpha 1,4)
Glycogen synthase
GLYCOGENOLYSIS
Mobilizing stored glycogen
Liver
Muscle
Cytosol
Glycogen
Glucose in liver
Glucose-6-phosphate in
muscle
Shortening of glycogen
chains
Glycogen phosphorylase
CITRIC ACID PENTOSE PHOSPHATE = LIPOGENESIS LIPOLYSIS / BETA-
CYCLE PATHWAY / HMP. OXIDATION
_ SHUNT | |
WHAT IST Major pathway formation of ~~ Produces NADPH ‘Synihesis of fay = Removal of acetyl CoA
FOR? ate + Produces ritose 5-phosphate acids, speciticaly, fragments from the ends of fatty
required for biosynthesis of palmitate acids
nudeotides + Also yielding NADH and FADH2.
+ Provides a mechanism for the in the process
metabolic use of 5-carbon sugars + Acetyl CoA can enter the citio
+ Take Note: Neither produces nor ‘acid cycle
consumes ATP NADH and
+ FADH2 can enter the ETC
WHERE Mitochondria: + RBCs and tissues that produce -—Lver, kidnay, brain, Tissues that can use fatty acids
DOES IT ‘Mitochondrial matrix lipids (liver, adipose tissue, lung, mammary gland, a8 energy source, primarily
‘occuR? adronals, thyroid testes, lactating and adipose tissue o In muscle and liver
mammaries) the cytosol * Falty acid activation occurs in
+ Inthe cytosol the cytosol
© Beoxidation occurs in the
‘mitochondria
SUBSTRATE AcetyCoA Glucose-6-phosphate + Acetyl - CoA Palmitate
END. 2002 NADPH Paimitoy! CoA B Acetyl CoA, 7 NADH, 7 FADH2
PRODUCTS 1GTP Ribose-5-phosphate
1/NADH
1 FADH2
RATE Isoctrate > @- Glucose-6-phosphate — 6- ‘Acetyl CoA + HCO3- + Translocation of fatty acyl CoA from
LIMITING ketoglutarate hosphogluconate ‘ATP + Malonyl CoA the cytosol to the mitochondria
STEP
RATE Isocirate dehydrogenase _Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Acetyl CoA Carnitine-palmitoy transferase
LIMITING carboxylase
ENZYME
KETOGENESIS
WHAT IS IT FOR? Synthesis of ketone bodies,
WHERE DOES IT
OCCUR?
SUBSTRATE
END-PRODUCTS
RATE LIMITING
STEP
RATE LIMITING
ENZYME
alternative fuel for peripheral
tissues
Liver, mitochondria
Acetyl Coa
Acetoacetate
b-hydroxybutyrate
acetone
Acetoacetyl-CoA > HMG CoA
HMG-CoA synthetase
CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS
ALL TISSUES
Cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum
Acetyl-CoA
Cholesterol
HMG CoA -> mevalonate
HMG CoA REDUCTASE
UREA CYCLE
Conversion of nitrogenous waste to
urea
LIVER ONLY
Mitochondria
Cytosol
NH3
Aspartate
co2
Urea
NH3 + CO2 > Carbamoyl
phosphate
‘Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MDR LE 1 SamplexDocument15 pagesMDR LE 1 SamplexAron Anthony RomeyNo ratings yet
- Lab9 Semen Anaylysis AguayoDocument3 pagesLab9 Semen Anaylysis AguayoAron Anthony RomeyNo ratings yet
- Titans AnatomyDocument355 pagesTitans AnatomyAron Anthony RomeyNo ratings yet
- Power and Flexibility 1Document95 pagesPower and Flexibility 1Aron Anthony RomeyNo ratings yet