Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UPDATED Brochure For HDPE PIPE
Uploaded by
NoelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UPDATED Brochure For HDPE PIPE
Uploaded by
NoelCopyright:
Available Formats
HYDROPHIL HDPE PLAIN PIPES
SPECIFICATIONS
STANDARD Conforming to ISO 4427;2009. SDR PR
based on controlled outside diameter
SIZES 20mmØ to 500mmØ
Cutting lengths:
300m (for 20mmØ)
150m (for 25mmØ)
60m (for 40mmØ – 75mmØ)
50m (for 90mmØ and 110mmØ)
6m (for 160mmØ and above)
COLORS Blue, Black, Black w/ Blue, Black w/ Orange
MATERIAL HDPE Plastic Extrusion Compound PE 80
and PE 100
JOINT Butt fusion, electro-fusion, compression
METHODS fittings, mechanical jointing
Pipe Series
Nominal S 12.5 S 10 S8 S 6.3 S5 S4
Outside
Standard Dimension Ratio
Diame-
HDPE PIPES - A Case History ter (mm) SDR SDR SDR SDR SDR SDR
26 21 17 13.6 11 9
Japan Water Works Association - Damage to Water Work Pipes Nominal Pressure PN for δ S = 8MPa
During the Great Hanshin Awaji Earthquake and Their Evaluation, PE 80 - PN PN 8 PN 10 PN PN
1996 Feb. 6 12.5 16
PE 100 PN PN PN 10 PN PN 16 PN
HDPE Pipes - Strong against earthquakes and being recognized as 6.3 8 12.5 20
excellent materials by the Japan Water Works Association. Kobe Nominal Wall Thickness (mm)
City, the central area severely hit by the disaster, had leaks from 20 - - 1.20 1.47 1.82 2.30
water distribution pipes at approximately 1,600 locations caused 25 - - 1.50 2.00 2.30 3.00
by joints coming out (63%), broken pipes (20%), and other 32 - - 2.00 2.40 3.00 3.60
damages to the fixture (17%). Leaks from water supply pipes 40 - - 2.40 3.00 3.70 4.50
reached approximately 90,000 and most of them were broken 50 2.00 2.40 3.00 3.70 4.60 5.60
pipes. According to the report, there was no water leak problem 63 2.50 3.00 3.80 4.70 5.80 7.10
with the HDPE pipe. The rate of damage caused to each type of
75 2.90 3.60 4.50 5.60 6.80 8.40
pipe in three victim cities (Kobe, Nishinomiya, Ashiya) is shown
90 3.50 4.30 5.40 6.70 8.20 10.10
in Table 1. The situation of gas pipes which has longer
110 4.20 5.30 6.60 8.10 10.00 12.30
distribution length is shown in Table 2. Comparative analysis
shows there was also no damage to HDPE pipes. 160 6.20 7.70 9.50 11.80 14.60 17.90
225 8.60 10.80 13.40 16.60 20.50 25.20
Table 1 280 10.70 13.40 16.60 20.60 25.40 31.30
Comparative Rate of Damage of Each Type of Pipe 315 12.10 15.00 18.70 23.20 28.60 35.20
(for cities of Kobe, Nishinomiya and Ashiya) 355 13.60 16.90 21.10 26.10 32.20 39.70
Type of Pipe Rate of Damage 400 15.30 19.10 23.70 29.40 36.30 44.70
DCIP 0.488 450 17.20 21.50 26.70 33.10 40.90 50.30
CIP 1.508 500 19.10 23.90 29.70 36.80 45.40 55.80
PVC Pipes 1.430
Steel Pipes 0.437 APPLICATIONS
AC Pipes 1.782
PE Pipes 0.000 Water system Sludge lines
Transmission mainlines Industrial fluid piping
Table 2 Distribution mainlines Chemical process piping
Damage Conditions of Gas Distribution Pipes
Service connections Mining process piping
(Number of damaged portions of each type of low pressure gas Sanitation
distribution pipes) In-house plumbing
Irrigation for plantations Drainage pipes
Sprinkler systems Sewer pipes
Pipe Steel Pipe DCIP PE Industrial processes Waste water treatments
Total length (km) 21.338 12.204 1.458 Industrial waste and Downspouts
drain lines Gas piping
No. of damages 25.8 0.630 0
Rate of Damage (Place/ 1.210 0.052 0.000 ADVANTAGES
km)
High flexibility Corrosion resistant
High impact resistance Chemical resistant
Source: Resources and Energy Office, Gas Countermeasure Committee - Gas
Earthquake Countermeasure Study Group Report, 1996.
Lightweight Excellent flow characteristics
Cost effective
You might also like
- Duromax PPR Draft BroucherDocument4 pagesDuromax PPR Draft BroucherRishi MittalNo ratings yet
- HDPE Pipe and Fittings CatalogDocument84 pagesHDPE Pipe and Fittings Catalogz4zarrarNo ratings yet
- GF Indonesia Brochure PR UTS 0417 Garda SuryaDocument12 pagesGF Indonesia Brochure PR UTS 0417 Garda SuryaRival Juney Christian PatrasNo ratings yet
- Katalog HDPE GFDocument12 pagesKatalog HDPE GFArief Prabowo100% (1)
- Hdpe Pipe InformationDocument21 pagesHdpe Pipe Informationprasadnn2001No ratings yet
- Duromax PPR BroucherDocument4 pagesDuromax PPR BroucherRishi MittalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturer List - PE Pipe As Per IS 4984:2016: State Variety BrandDocument412 pagesManufacturer List - PE Pipe As Per IS 4984:2016: State Variety BrandÀVÎNÂSH RAAZNo ratings yet
- FRP Pipe Failures & Lessons To Be Learned: Paulin Webinar April 2008Document40 pagesFRP Pipe Failures & Lessons To Be Learned: Paulin Webinar April 2008bruno devinckNo ratings yet
- TE Cast Iron Hubless Double Spigot Pipes Fittings Product CatalogueDocument26 pagesTE Cast Iron Hubless Double Spigot Pipes Fittings Product CatalogueTimNo ratings yet
- PeDocument55 pagesPeمنير أحمدNo ratings yet
- HDPE PIPES Brochure PDFDocument12 pagesHDPE PIPES Brochure PDFonspsnonsNo ratings yet
- QuotationDocument14 pagesQuotationMiko AbiNo ratings yet
- Double ball automatic air valvesDocument2 pagesDouble ball automatic air valvesMohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- 9 Polyethylene Piping SystemDocument4 pages9 Polyethylene Piping SystemSwasti DixitNo ratings yet
- Effast PP PropertiesDocument16 pagesEffast PP PropertiesTiroshima MigaNo ratings yet
- PCS TripticofDocument6 pagesPCS Tripticofmartin TruffaNo ratings yet
- Enchaquetamiento TuberiasDocument41 pagesEnchaquetamiento TuberiasSara Otero ManriqueNo ratings yet
- TS 2002 - R1 PE100 - Ing PDFDocument16 pagesTS 2002 - R1 PE100 - Ing PDFDavid Luna MolinaNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Pe 100 High Density Polyethylene Pipes Technical SheetDocument16 pagesSilo - Tips Pe 100 High Density Polyethylene Pipes Technical SheetfazyroshanNo ratings yet
- 05 - Roof PlanDocument5 pages05 - Roof PlanfebousNo ratings yet
- 8.HSC SelamDocument2 pages8.HSC SelammanojNo ratings yet
- PERMASWAGE System Presentation (NXPowerLite)Document16 pagesPERMASWAGE System Presentation (NXPowerLite)Edwar ZulmiNo ratings yet
- Subject:: 1.0 Ground Floor Waterline QTY Unit Labor Cost Total CostDocument1 pageSubject:: 1.0 Ground Floor Waterline QTY Unit Labor Cost Total Costdhun mejiaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Muchami Hotel Plumbing DrainageDocument4 pagesProposed Muchami Hotel Plumbing DrainagefebousNo ratings yet
- 2.halambiyo Distribution Pipe Quantity: 3 Supply and Installation of Distribution Fittings and AccessoriesDocument5 pages2.halambiyo Distribution Pipe Quantity: 3 Supply and Installation of Distribution Fittings and AccessoriesAbi DemeNo ratings yet
- Apex Piping Catalogue 2020Document36 pagesApex Piping Catalogue 2020Insta PumpsNo ratings yet
- Bronze Relief Valve DN10 DN15 DN20Document2 pagesBronze Relief Valve DN10 DN15 DN20billNo ratings yet
- HDPE Corrugated Pipes & Fittings GuideDocument16 pagesHDPE Corrugated Pipes & Fittings GuidereemNo ratings yet
- MUNICIPAL CORPORATION WATER SUPPLY PROJECTDocument4 pagesMUNICIPAL CORPORATION WATER SUPPLY PROJECTeluru corporationNo ratings yet
- Across The Civilizations: Transporting WaterDocument20 pagesAcross The Civilizations: Transporting WaterKoduru SiddharthNo ratings yet
- NEISCO Technical Catalog 2020 Features UPVC Pressure FittingsDocument66 pagesNEISCO Technical Catalog 2020 Features UPVC Pressure FittingsKadiri El MoustaphaNo ratings yet
- Eluru Mig HSC DataDocument1 pageEluru Mig HSC DataSeph RjyNo ratings yet
- Bondstrand PDFDocument8 pagesBondstrand PDFkrisNo ratings yet
- 2Basement-Section-2 Sanitary & Plumbing WorkDocument25 pages2Basement-Section-2 Sanitary & Plumbing WorkSourov SamadderNo ratings yet
- ULPI uPVC Price List June 2017Document12 pagesULPI uPVC Price List June 2017ulpigm100% (1)
- HSS80 Heat Shrink Sleeve: Features & BenefitsDocument2 pagesHSS80 Heat Shrink Sleeve: Features & BenefitsAnonymous eEJDOR2100% (1)
- Apex Piping Revised 2Document36 pagesApex Piping Revised 2Eng Aggrey OsumaNo ratings yet
- 1607 HOBAS Pressure Pipe Systems WebDocument37 pages1607 HOBAS Pressure Pipe Systems Weballouche_abdNo ratings yet
- Weekly Progress & S-Curve Cathodic PLTU Belawan - Cod 16-Jun-19Document81 pagesWeekly Progress & S-Curve Cathodic PLTU Belawan - Cod 16-Jun-19Basten M H Silitonga100% (1)
- HDPE Al AdasaniDocument11 pagesHDPE Al AdasanisaravananNo ratings yet
- Easter NewDocument2 pagesEaster NewpdzawarNo ratings yet
- 1 MMP METI Fit CatalogueDocument16 pages1 MMP METI Fit CataloguemohdnazirNo ratings yet
- Western Irrigation System Pvt. LTD.: Quality in Every WayDocument8 pagesWestern Irrigation System Pvt. LTD.: Quality in Every WayRameshPrithivirajNo ratings yet
- DPI Plastics Durothene HDPE Pipe Brochure 2017Document7 pagesDPI Plastics Durothene HDPE Pipe Brochure 2017tinashemambarizaNo ratings yet
- 6.guraja Distribution Pipe Quantity: 3 Supply and Installation of Distribution Fittings and AccessoriesDocument5 pages6.guraja Distribution Pipe Quantity: 3 Supply and Installation of Distribution Fittings and AccessoriesAbi DemeNo ratings yet
- Ball Valve 375 Datasheet EnglishDocument4 pagesBall Valve 375 Datasheet EnglishElleuch HaithemNo ratings yet
- Pipe function resumeDocument14 pagesPipe function resumevyrgoNo ratings yet
- All Pipes BoqDocument27 pagesAll Pipes BoqAbi Deme100% (1)
- Brochure Pe Pipe WikaDocument44 pagesBrochure Pe Pipe WikaSyach FirmNo ratings yet
- 01 Al Munaif UPVC High Pressure FittingsDocument36 pages01 Al Munaif UPVC High Pressure FittingsmohammedNo ratings yet
- Clarification For HDPE Pipes Usage, and Water Flow MeterDocument1 pageClarification For HDPE Pipes Usage, and Water Flow MeterSamir AjiNo ratings yet
- Municipal Corporation Water Supply ProjectDocument4 pagesMunicipal Corporation Water Supply Projecteluru corporationNo ratings yet
- Trusted Plumbing SolutionsDocument12 pagesTrusted Plumbing Solutionsnatarajan palanisamy25% (4)
- Halock semi-flexible PE pipe systemDocument4 pagesHalock semi-flexible PE pipe systemwarung1bensinNo ratings yet
- 1409 HOBAS CC Pressure Pipe Systems WebDocument40 pages1409 HOBAS CC Pressure Pipe Systems WebShaun WongNo ratings yet
- Proposed Niper Campus at Guwahati, Assam. Girls Hostel (2 Blocks)Document3 pagesProposed Niper Campus at Guwahati, Assam. Girls Hostel (2 Blocks)kiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- Bill of Materials: BQMFC015150 BQMFC016200 BQMFC017250 BQMFC018300 BQMFC019350Document1 pageBill of Materials: BQMFC015150 BQMFC016200 BQMFC017250 BQMFC018300 BQMFC019350Muhammad IrsyadNo ratings yet
- CHIN LEAN - uPVC Pressure PipesDocument4 pagesCHIN LEAN - uPVC Pressure PipesTony JamesNo ratings yet
- Geotextiles and Geomembranes HandbookFrom EverandGeotextiles and Geomembranes HandbookT.S. IngoldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MBS 33Document5 pagesMBS 33NoelNo ratings yet
- Sensus WPD BrochureDocument4 pagesSensus WPD BrochureNoelNo ratings yet
- Linkwell Stock ItemsDocument6 pagesLinkwell Stock ItemsNoelNo ratings yet
- 04.aziz 2020 BP 8088DDocument24 pages04.aziz 2020 BP 8088DNoelNo ratings yet
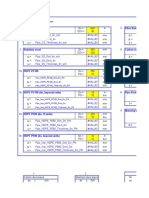
- W1 PDFDocument6 pagesW1 PDFNoelNo ratings yet
- W1 PDFDocument6 pagesW1 PDFNoelNo ratings yet
- FiberTite Membrane Waterproofing SystemDocument10 pagesFiberTite Membrane Waterproofing SystemSylvester PadacaNo ratings yet
- Catalog Pompe City PumpsDocument52 pagesCatalog Pompe City PumpsoanaNo ratings yet
- NPC Storm DrainDocument12 pagesNPC Storm DrainJob BalayanNo ratings yet
- SAES-S-030 Storm Water Drainage SystemsDocument10 pagesSAES-S-030 Storm Water Drainage SystemsWaqar Ahmed100% (1)
- Subgrade Material Classification and Compaction MethodsDocument50 pagesSubgrade Material Classification and Compaction MethodsEmm Zeeshan DanishNo ratings yet
- BrinkSA Bro-1112 PDFDocument12 pagesBrinkSA Bro-1112 PDFSamir GanguliNo ratings yet
- Manas 3rd Semester Seminar Report PDFDocument33 pagesManas 3rd Semester Seminar Report PDFManas Pratim DadharaNo ratings yet
- Allectus 18-0-8Document1 pageAllectus 18-0-8Cory HansonNo ratings yet
- Vertical DrainsDocument85 pagesVertical DrainsDương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Poland Sokolowka River: Restoration of A Municipal River For Stormwater Management and Improvement of Quality of Life - University of LodzDocument16 pagesPoland Sokolowka River: Restoration of A Municipal River For Stormwater Management and Improvement of Quality of Life - University of LodzFree Rain Garden ManualsNo ratings yet
- 255.1-2478 FiltrationDocument40 pages255.1-2478 FiltrationDOUNIA BELLACHENo ratings yet
- John e John. FinalDocument59 pagesJohn e John. FinalChris JosephNo ratings yet
- Guide For Design of Jointed Concrete Pavements For Streets and Local RoadsDocument32 pagesGuide For Design of Jointed Concrete Pavements For Streets and Local RoadsFelipe Alfredo Martinez Interiano100% (1)
- CDW WoksDocument44 pagesCDW Woksjenj1No ratings yet
- Haccp Manual: New Foods LimitedDocument204 pagesHaccp Manual: New Foods LimitedHotna OktariaNo ratings yet
- Windrose Green Section 2 PlansDocument36 pagesWindrose Green Section 2 PlansJR ZunigaNo ratings yet
- SD1997 07 Final ReportDocument109 pagesSD1997 07 Final ReportEstebanChiangNo ratings yet
- Urban Drainage ThailandDocument13 pagesUrban Drainage ThailandAdiNo ratings yet
- DEQ Order On Fauquier Landfill 2017Document9 pagesDEQ Order On Fauquier Landfill 2017Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Design of Open Channels TR No. 25Document293 pagesDesign of Open Channels TR No. 25Kathleen NoonanNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Scheme for Dhummavad VillageDocument43 pagesWater Supply Scheme for Dhummavad Villageprachi_borkar100% (4)
- National Building Regulations 1996 Li 1630Document244 pagesNational Building Regulations 1996 Li 1630Andrews DonkorNo ratings yet
- GEPCO Annual Report AnalysisDocument131 pagesGEPCO Annual Report AnalysisSyedAshirBukhariNo ratings yet
- Vegetable F Production: Biru Gidi IrrigatedDocument35 pagesVegetable F Production: Biru Gidi Irrigatedsileshi Angerasa100% (1)
- Guidance Note On Leachate Management For Municipal Solid Waste LandfillsDocument30 pagesGuidance Note On Leachate Management For Municipal Solid Waste LandfillstrtrtretertertNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Playground PlanningDocument63 pagesA Guide To Playground PlanningVenus SorianoNo ratings yet
- Act 354Document15 pagesAct 354M.Afiq.FNo ratings yet
- RFP App A Solar Technical SpecificationDocument50 pagesRFP App A Solar Technical SpecificationarunghandwalNo ratings yet
- Public Market Drainage System Problem in The Municipality of ClaveriaDocument7 pagesPublic Market Drainage System Problem in The Municipality of ClaveriaAngelica Auguis CañeteNo ratings yet
- ACO Balcony and Terrace Stainless Steel Drainage Catalogue 2018 01Document9 pagesACO Balcony and Terrace Stainless Steel Drainage Catalogue 2018 01Jose VicenteNo ratings yet