Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxygen Enters The Blood in The Lungs The Separation of The Right Side and The Left Side of The Heart Is Useful To Keep Oxygenated and de
Uploaded by
D0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesoxygen x
Original Title
Oxygen enters the blood in the lungs The separation of the right side and the left side of the heart is useful to keep oxygenated and de
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentoxygen x
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesOxygen Enters The Blood in The Lungs The Separation of The Right Side and The Left Side of The Heart Is Useful To Keep Oxygenated and de
Uploaded by
Doxygen x
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
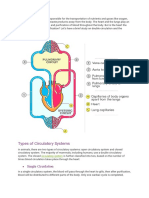
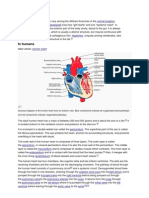
Oxygen enters the blood in the
lungs The separation of the
right side and the left side of
the heart is useful to keep
oxygenated and deoxygenated
blood from mixing. Such
separation allows a highly
efficient supply of oxygen to
the body. This is useful in
animals that have high energy
needs, such as birds and
mammals, which constantly
use energy to maintain their
body temperature. In animals
that do not use energy for this
purpose, the body temperature
depends on the temperature in
the environment. Such
animals, like amphibians or
many reptiles have three-
chambered hearts, and tolerate
some mixing of the
oxygenated and de-oxygenated
blood streams. Fishes, on the
other hand, have only two
chambers to their hearts, and
the blood is pumped to the
gills, is oxygenated there, and
passes directly to the rest of
the body. Thus, blood goes
only once through the heart in
the fish during one cycle of
passage through the body. On
the other hand, it goes through
the heart twice during each
cycle in other vertebrates. This
is known as double circulation
You might also like
- The Circulatory SystemsDocument35 pagesThe Circulatory SystemseffadilahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Animal's Circulartory System.Document2 pagesAnimal's Circulartory System.CHANON KIATKAWINWONGNo ratings yet
- The Heart Is A Muscular Organ Which Is As Big As Our FistDocument3 pagesThe Heart Is A Muscular Organ Which Is As Big As Our FistDNo ratings yet
- Extraordinary Blood Circulation in CrocodilesDocument5 pagesExtraordinary Blood Circulation in CrocodilesRudy Hermosillo100% (1)
- Animal Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesAnimal Circulatory SystemdsndcwnnfnhNo ratings yet
- First Semester 2020/2021Document34 pagesFirst Semester 2020/2021low luffecussNo ratings yet
- What Is An Open Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Open Circulatory SystemBarus LaubawisNo ratings yet
- Double CirculationDocument2 pagesDouble CirculationNamami DubeNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcDocument36 pagesComparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcNarasimha Murthy100% (4)
- Class CephalopodsDocument8 pagesClass Cephalopodsregine cernaNo ratings yet
- Zo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaDocument20 pagesZo 503 Comparative Physiology by DR - PoornimaAbhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- M.SC 1 Sem Paper 2Document18 pagesM.SC 1 Sem Paper 2Anju yadavNo ratings yet
- Biology - Animal TransportDocument5 pagesBiology - Animal Transportchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDocument60 pagesCirculation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDead Eye100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Evolution of The Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesEvolution of The Circulatory SystemSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Circulation + Composition of Blood + Vertebrate Heart + Invertebrate Heart + Blood VesselsDocument121 pagesCirculation + Composition of Blood + Vertebrate Heart + Invertebrate Heart + Blood VesselsReina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemKhawar HussainNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- g3. TransportationDocument30 pagesg3. TransportationKaycee Louchel OccenaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ReportDocument7 pagesCirculatory System ReportsathishkumarNo ratings yet
- Double CirculationDocument2 pagesDouble CirculationMonika KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System FrogDocument9 pagesCirculatory System FrogLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System PDFDocument1 pageCirculatory System PDFPorcia ScriptsNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesCompare and Contrast Process in Plants and AnimalsKimberly EamilaoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in FinfishDocument18 pagesCirculatory System in FinfishSalma SabirNo ratings yet
- Elesson 10 Bio 14mayDocument4 pagesElesson 10 Bio 14mayArchanaGuptaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesCirculatory SystemMerned Lopez100% (1)
- Biology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)Document7 pagesBiology Chapter - 1 (Part - 2)aaronNo ratings yet
- Comparing Various Closed Circulatory Systems: Mammals Frogs FishDocument12 pagesComparing Various Closed Circulatory Systems: Mammals Frogs Fishrishadabubecker100% (1)
- Lesson 6 Life Processes Part IIDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Life Processes Part IIjokerbladed19No ratings yet
- Closed Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesClosed Circulatory Systemfardhu91No ratings yet
- In Humans: Human HeartDocument9 pagesIn Humans: Human HeartDanagalla Venkat100% (2)
- Bio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10Document133 pagesBio T4 DLP KSSM Chapter 10fadilahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System of Frog For Class IxDocument7 pagesCirculatory System of Frog For Class IxSaindino SandNo ratings yet
- Subject Enrichment Activity For Term 2Document5 pagesSubject Enrichment Activity For Term 2AADITRYA JAINNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Circulatory System #1Document36 pagesVertebrate Circulatory System #1Josephine Ivy JumalaNo ratings yet
- As Biology NotesDocument48 pagesAs Biology Notesella100% (1)
- Life Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsDocument5 pagesLife Processes - Transport of Food and Minerals in Animals and PlantsmasaminathanNo ratings yet
- Respiration Through GillsDocument5 pagesRespiration Through GillsTehseen KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio 3RD Q LQ 1Document5 pagesBio 3RD Q LQ 1ytheresetiuNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2a CirculationDocument8 pagesWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Pt. 1Document10 pagesCirculatory Pt. 1Melvin Razon Espinola Jr.No ratings yet
- 6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalDocument13 pages6454f627e4b0ad3aaf22e06b OriginalSuprit JainNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 2 2Document32 pagesLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory SystembysshelarbyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Vascular TissueDocument8 pagesCirculatory System Vascular TissueDrSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Biologi A+Document5 pagesBiologi A+Alia NaimNo ratings yet
- Internal RespirationDocument9 pagesInternal RespirationRhose ReyesNo ratings yet
- Animal Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesAnimal Circulatory System'Immey Ssi MoyNo ratings yet
- Gist Class 10 Transport 1 & 2Document2 pagesGist Class 10 Transport 1 & 2Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpDocument3 pagesTRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- TB F3 Chapter 3Document77 pagesTB F3 Chapter 3Norzamani NordinNo ratings yet
- Amphibian Circulation - The FrogDocument15 pagesAmphibian Circulation - The FrogaraneyaNo ratings yet
- Amphibian Circulation - The FrogDocument15 pagesAmphibian Circulation - The FroghaasNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 9 ReviewerDocument5 pages1st Quarter Science 9 ReviewerM- Gonzales, Betchemar B.No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemjehanNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Eco and GeoDocument7 pagesEco and GeoDNo ratings yet
- History and CivicsDocument7 pagesHistory and CivicsDNo ratings yet
- Eco and GeoDocument7 pagesEco and GeoDNo ratings yet
- Nutrition 1Document8 pagesNutrition 1DNo ratings yet