Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5 1
Uploaded by
BELMONTE, Christian Justin R.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views6 pagesComputer Information System Audit Chapter 5 part 1
Original Title
Chapter-5-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComputer Information System Audit Chapter 5 part 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views6 pagesChapter 5 1
Uploaded by
BELMONTE, Christian Justin R.Computer Information System Audit Chapter 5 part 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
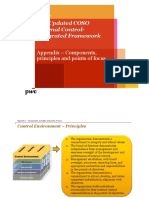
Chapter 5 The COSO Framework is typically represented in
the form of a cube showing the components of
Control Frameworks
internal control, three categories of objectives, and
Controls are processes that restraints; processes the entity’s structure, which is represented by the
and procedures that regulate, guide, and protect an third dimension.
organization.
The COSO IC-IF helps companies across industries
Internal controls are practices put in place to create and sizes to measure effectiveness of their controls.
value for stakeholders and minimize risks, so
frameworks make it easier to manage these
diverging dynamics and evaluate the results more
systematically.
COSO’s Internal Control Integrated Framework (IC-
IF) is arguably the most widely known internal
controls framework in the world.
The National Commission on Fraudulent Financial
Reporting, was chaired by James C. Treadway,
recommended to create a framework of internal
control.
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations
(COSO) of the Treadway Commission is a private
sector initiative founded in 1985 to sponsor the The COSO cube have 17 principles:
National Commission on Fraudulent Financial
Control Environment
Reporting. The sponsors are:
1. Commitment to integrity and ethical values
- Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA)
2. BOD exercises oversight responsibility
- American Institute of Certified Public
3. Establish structure, authority, and
Accountants (AICPA)
responsibility
- American Accounting Association (AAA)
4. Commitment to competence
- Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)
5. Enforce accountability
- Financial Executives Institute (FEI)
- Representatives from industry public Risk Assessment
accounting and investment firms
- New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) 6. Set suitable objectives
7. Identify and analyzes risks
COSO’s goal was to improve the quality of financial 8. Assess risk of fraud
reporting through a focus on corporate governance, 9. Identify and analyze significant change
ethical practices, and internal control. Emphasis is
also given to ERM and fraud deterrence. Control Activities
COSO issued the IC-IF in 1992, which was revised 10. Select and develop control activities
and reissued in May 2013 and was effective from 11. Select and develop IT GCCs
December 15, 2014. 12. Mobilize through policies and procedures
The 2013 COSO IC-IF contains 17 principles Information and Communication
representing the fundamental concepts associated 13. Use relevant information
with each component. 14. Communicate internally
COSO states that an entity can achieve effective 15. Communicate externally
internal control by applying all principles, which Monitoring Activities
apply to all operations, reporting, and compliance
objectives. 16. Conduct ongoing/separate evaluations
17. Evaluate and communicate deficiencies
This refers to the workplace environment,
characterized by the way the organization is
The 1992 COSO Framework
structured, the manner of leadership, the degree of
The 1992 COSO framework was the first to openness, management’s operating style, having
implement the use of “The COSO Pyramid” which and practicing the tenets of its code of ethics, and
laid out the five tenets of COSO control components, statement of values.
Control Environment, Risk Assessment, Control
This also includes the tone at the top and the degree
Activities, Information & Communication and
to which there is congruence between
Monitoring Activities.
management’s talk and its walk.
Starting from the bottom up, where the completion of
The tone at the top is set and promoted by the
one level naturally leads to the completion of the
board of directors and senior management, and it
next, these components work together to support the
refers to the general attitude, integrity, and ethical
risk management mission, strategy and all related
practices of these individuals. It drives ethical
business objectives for the company.
conduct within the organization.
Organizational culture is the collection of learned
beliefs, traditions, and guides for behavior shared
among members of the organization. It defines and
expresses shared assumptions, values, and beliefs
and it is manifested in many ways, including formal
rules and policies, norms of daily behavior, physical
settings, and modes of dress, special language,
myth, rituals, heroes, and stories.
A healthy culture and ethical environment advances
employee morale, and it also helps to improve
productivity and efficiency.
The control environment also includes the activities
related to the competence and development of
personnel, the assignment of authority and
Monitoring activities - Once the COSO framework is responsibility, and the organizational structure.
implemented, it needs to be regularly monitored to
verify the controls are functioning as they should. According to Trompenaars, organizational culture
includes three key elements:
Control activities - Control activities come in
response to the risk items identified. These are steps 1. The general relationship between employees
taken to mitigate risk across an organization. and their organizations
2. The vertical or hierarchical system of
Risk Assessment - Risk assessments ensure authority defining superiors and
businesses are acknowledging relevant risk items. subordinates (clear reporting line; POV of top
Assessments also provide reasonable assurance management – a clear reporting line
that a business is managing risk to an acceptable promotes accountability)
level. 3. The general views of employees about the
organization’s destiny, purpose, and goals,
Control environment - The entire organization must
and their place in it.
be adhering to standard practices. This means
controls are implemented in every business unit. While acting with integrity and fairness generally
characterizes ethical behavior, the following are
Information and communication – must be
some examples of unethical behavior that auditor
happening at every level.
should be on the lookout for:
Control Environment
1. Undue emphasis on bottom-line
This is the company itself; the working environment. performance – placing an unreasonable
emphasis on this in ways that it becomes the staff. This can be done through company’s
main consideration, it is likely that ethical newsletter, e-mail, and intranet posts.
behaviors will be produced. 3. Running lunch and learn or brown bag lunch
2. High-pressure sales tactics – when sales
Form over Substance
practices are more focused on extracting
funds from customers, the This consists of management practices whereby on
mischaracterization of the company’s the surface it appears as though an essential activity
products and services increases. has been performed, when in fact that is not so. -
3. Kickbacks or bribes – illicit payments made Example: Signatures are in papers but did not
to someone who has facilitated a transaction undergo thorough review.
or appointment.
Principles underlying the Control Environment
Communication, Consistency, and Belief in the are:
Message
1. Commitment to integrity and ethical
It is important for management to communicate values
clearly, consistently, and often what is allowed and - the organization should demonstrate a
what is not. By setting clear expectations there is a commitment to integrity and ethical values.
better chance that they will be followed. But being - The organization should show through their
followed depends to a large extent on management actions, and by rewarding ethical behavior
“walking the talk” and demonstrating through their and castigating unethical behavior, that they
actions that they believe in the messages. are committed to integrity and ethical values.
- Management must care not only about what
When there are inconsistencies between what
is achieved but by also how those results are
management says is the expected behavior, and
achieved.
their own behavior, employees will see management
- Organization must care about how
as hypocritical.
employees, communities, customers,
Having a code of ethics, codes of conduct, and vendors, and other stakeholders are treated
conflict of interest statement is very important to and it imposes prompt and appropriate
formally establish the expectations for proper sanctions on those that deviate from these
conducts. expectations.
2. BOD exercises oversight responsibility
Code of ethics should act as a guideline or
- BOD demonstrates independence from
reference point for acceptable behavior and ethical
management and exercises oversight of the
decision-making. They should be values based,
development and performance of internal
motivate employees to conduct themselves in
control
ethical ways, support the questioning of authority
- Passive BOD are terrible for internal control
when ethics are challenged, and hold employees
as they display limited oversight over
accountable when rules are broken.
management actions
Companies may or may not have ethical values but - Key responsibilities of BOD: provide a
as professionals, we should adhere to our own mission and vision for the organization, set
professional code of ethics. expectations for management, authorize
investments that show its priorities, look out
There are two ways to ensure code of ethics are for the interests of the company’s owners
observed and followed: - BOD is not unduly influenced by the
1. New employees should receive these management. If not, the audit committee of
documents upon hire and sign-off indicating the board must at least be independent
they agree to abide by them. Training should 3. Establish structure, authority, and
also be required. These should be followed responsibility
by annual refresher training. - Management establishes, with board
2. Short articles, vignettes, scenarios, and oversight, structures, reporting lines, and
surveys that are distributed periodically to all appropriate authorities and responsibilities in
the pursuit of objectives
- The organizational structure must facilitate They refer to the entity’s management style, as
the assignment of responsibilities that will reflected in the corporate culture, values,
ensure smooth flow of information down in philosophy, and operating style, the organizational
the chain of command and back in the form structure, and policies and procedures in place.
of feedback (performance results, concerns,
Typical areas of interest include (familiarize lang
requests for needed resources)
daw, not memorize):
4. Commitment to competence
- Organization demonstrates a commitment to - Controls over management override
attract, develop, and retain competent - The company’s risk assessment
individuals in alignment with objectives. methodology and techniques that identify
- As the primary means of production for many both risks and owners of risk
organizations, employee recruitment, - Extent and quality of controls over
selection, training, and development, centralized processing, including shared
compensation, and promotion should be service environments and outsource service
based on competence, proven potential, providers
commitment, and performance. - Controls to monitor results of operations
- People that do not meet the technical and - Controls over the preparation, review, and
ethical expectations of the organization communication of period-end financial and
should undergo appropriate training and operational reporting, both internally and
receive appropriate sanctions. externally
- Failing to deal with performance and ethical - Policies that address significant business
breakdowns jeopardizes the organization’s control and risk management practices
chances of achieving its objectives. - The extent, accuracy, and suitability of
5. Enforce accountability policies and procedures related to
- The organization holds individuals governance, operations, risk management,
accountable for their internal control control, and compliance expectations
responsibilities in the pursuit of objectives - Hiring and retention practices
- When control activities are assigned, it is - Fraud prevention and detection controls,
imperative that management sets clear including analytical procedures
expectations that these activities must be - The competence, scope, and depth of the
performed. work of the internal audit function
- By setting accountabilities clearly, and - Effectiveness of the whistle-blower hotline
enforcing compliance with them, the control - Adherence to the word and spirit of the code
environment will benefit from the discipline, of conduct
follow through, and stability that internal - IT environment and organizations
controls provide. - Results of organizational self-assessment
- Objectives define the direction of the reviews
organization and measure of its success - The depth of oversight of the company’s
while controls provide protection that disclosure committee
necessary activities will be carried out to - The extent, competence, consistency, and
mitigate risks and increase the likelihood that extent of tone setting and oversight
those objectives will be achieved. displayed by the BOD, senior and middle
management in their role as governance
Entity Level Controls
providers
These are controls on surface levels and are - Assignment of authority and responsibility
applicable to the whole company. across all layers of the organizational
structure
These are used to determine if an organization’s
- Account reconciliations, variance analysis
value, systems, policies, and processes would
reporting, and related corrective measures
enable or dissuade fraud and encourage proper
- Effectiveness of the mechanism to remediate
conduct.
control weaknesses
- Management triggers embedded within IT events are opportunities while negative events
systems are risks.
- The establishment and reliability of physical
We cannot measure risk based on only one
and logical segregation of duties
dimension. The risks may likely happen, but the
- Effectiveness of change-management
impact is immaterial. Or the risk may not likely
practices affecting the organization
happen, but the effects could be material.
Internal auditors are encouraged to remember
Risks are typically assessed along two
that a person’s behavior is determined by the
dimensions:
person and his or her environment. There a
number of different and competing forces that 1. Likelihood, or the probability that these
combine to result in the situation the individual events occur
encounters. 2. Impact, or the consequence if these events
occurred
A person’s behavior may be different in unique
situations, as the person acts in part in response Establishing objectives is a precondition to risk
to the environment. assessment.
Lewin’s equation, developed by Kurt Lewin, A risk assessment is the process of identifying,
states that behavior is a function of the person assessing, and measuring risks to the organization,
and the environment, and can be expressed in program, or process under review.
the formula:
It is imperative, however, before embarking on the
B = f(P, E) risks assessment journey, that relevant objectives
be identified.
Where B is the person’s behavior, P is the
person, and E is the environment. Risk assessment involves a dynamic and iterative
process of identifying, analyzing, and deciding how
Tone in the Middle
best to respond to these risks in relation to the
This refers to the middle management who sets achievement of objectives.
and implement ethical behavior, or the tone in
Management specifies objectives within three
the middle.
separate but related categories:
The manager determines and reinforces the
1. Reporting
values, ethics, honesty, and workplace
- reporting considerations are arranged in four
dynamics, also influences the process of getting
broad categories: internal/external and
customers and making sure they are happy.
financial/nonfinancial.
This means that the tone in the middle dictates - Auditors must remember that organizations
workplace conditions leading to customer and must meet reporting expectations beyond
employee satisfaction, turnover, profits, and the external financial reporting.
achievement of goals and objectives. - It includes reliability, timeliness,
transparency, or other terms set by
Risk Assessment
regulators, the organization’s policies or
The second component of the COSO framework other recognized standard setters.
relates to the identification, quantification, 2. Compliance
analysis, and management of organizational - Related to adherence to laws and
risks. regulations to which the organization is
subject.
Risks are those events that can jeopardize the - Compliance requirements may also include
organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. compliance with contractual terms and
The COSO indicates in its 2013 IC-IF that the conditions, service level agreements,
organization is subject to a variety of events; voluntary agreements, like corporate
some positive while others are negative. Positive sustainability reports.
3. Operation
- Effectiveness and efficiency of the
organization’s operations.
- This includes operational and financial
performance goals, safeguarding assets
against loss, damage or obsolescence, and
making sure resources are obtained
economically.
Additional:
IT Controls
- Subset of internal controls related to IT
- COBIT
- ISO 17799
- ITIL
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI)
- Used in project management, process
assessment, and performance improvement
environments.
You might also like
- Corporate Governance - Effective Performance Evaluation of the BoardFrom EverandCorporate Governance - Effective Performance Evaluation of the BoardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document11 pagesChapter 5Fav TangonanNo ratings yet
- The Executive’S Guide to Creating and Implementing an Integrated Management System: Optimally and Synergistically Incorporating Iso and Corporate Responsibility Management Standards in Response to an Ethical ImperativeFrom EverandThe Executive’S Guide to Creating and Implementing an Integrated Management System: Optimally and Synergistically Incorporating Iso and Corporate Responsibility Management Standards in Response to an Ethical ImperativeNo ratings yet
- COSCO FrameworkDocument70 pagesCOSCO Frameworkbarakkat72No ratings yet
- SIA Kel 3 FinishDocument25 pagesSIA Kel 3 FinishNugraha HaritsNo ratings yet
- [GROUP 2][COMPARISON OF COSOS 2013 INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK AND 2017 ERM FRAMEWORK]Document9 pages[GROUP 2][COMPARISON OF COSOS 2013 INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK AND 2017 ERM FRAMEWORK]HƯƠNG ĐỖ MINHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document22 pagesChapter 5Jenny Lelis100% (1)
- Aud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesAud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerJazmine Arianne DalayNo ratings yet
- CoCo Framework GuideDocument2 pagesCoCo Framework GuideMaria LopezNo ratings yet
- Coso 2013Document14 pagesCoso 2013Indji TanNo ratings yet
- Romney Ais13 PPT 01Document42 pagesRomney Ais13 PPT 01Chesya Bintang CarolineNo ratings yet
- CS1 Entity Level Controls SolutionsDocument16 pagesCS1 Entity Level Controls SolutionsPakistan Breaking News100% (6)
- Fundamental Concepts of Internal ControlDocument22 pagesFundamental Concepts of Internal Controlbruh sheeshNo ratings yet
- Internal Control SystemDocument27 pagesInternal Control SystemHaidee Flavier SabidoNo ratings yet
- Coso Framework: Process, Effected by An Entity's Board of Directors, Management, and Other PersonnelDocument14 pagesCoso Framework: Process, Effected by An Entity's Board of Directors, Management, and Other PersonnelPrincess Gift ParconNo ratings yet
- A222 - Topic 7 MacsDocument26 pagesA222 - Topic 7 MacsfiqNo ratings yet
- Commission (COSO) Developed A Model For Evaluating Internal Controls. ThisDocument2 pagesCommission (COSO) Developed A Model For Evaluating Internal Controls. ThisYvonne Ryss Batuigas MendeNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Risk Management - 2017 - Appendix A COSO and ISO 31000 Framework MappingDocument9 pagesEnterprise Risk Management - 2017 - Appendix A COSO and ISO 31000 Framework MappingJesus BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Principles and Best PracticesDocument8 pagesCorporate Governance Principles and Best PracticesMarienella MarollanoNo ratings yet
- Audit Internal Chapter 6Document34 pagesAudit Internal Chapter 6Fitri NoviaNo ratings yet
- AI-X-S3-G5-Arief Budi NugrohoDocument6 pagesAI-X-S3-G5-Arief Budi Nugrohoariefmatani73No ratings yet
- What Does Coso Stand For?Document3 pagesWhat Does Coso Stand For?Frhea Love AbelloNo ratings yet
- Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesGroup Assignmentkefyalew TNo ratings yet
- Components of Internal ControlDocument13 pagesComponents of Internal ControlGamers HubNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument35 pagesInternal ControlViệt Thành NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ey Ia CosoDocument8 pagesEy Ia CosoCISA PwCNo ratings yet
- Using Coso Framework To Establish Internal Control Over Sustainability ReportingDocument11 pagesUsing Coso Framework To Establish Internal Control Over Sustainability ReportingbadrianisgmailcomNo ratings yet
- COSO framework guides internal controlsDocument3 pagesCOSO framework guides internal controlsan scNo ratings yet
- Understanding the COSO FrameworkDocument7 pagesUnderstanding the COSO FrameworkNadine VelascoNo ratings yet
- Summary CH 3Document13 pagesSummary CH 3LaksamanaNo ratings yet
- COSO control frameworks guide organizationsDocument91 pagesCOSO control frameworks guide organizationsCristina Elizalde100% (2)
- Understand Control Frameworks COSO and CoCo with thisDocument18 pagesUnderstand Control Frameworks COSO and CoCo with thisKathleen FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Organizational GovernanceDocument32 pagesOrganizational GovernancereynnedegNo ratings yet
- Criteria of Control Coco FrameworkDocument12 pagesCriteria of Control Coco FrameworkMaria LopezNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Governance ModelDocument12 pagesAn Integrated Governance Modelshifoun maafoun0% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 - Internal Control and Risk ManagementDocument34 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Internal Control and Risk ManagementMaria Elliane Querubin RosalesNo ratings yet
- PWC Pointsoffocus ExplainedDocument30 pagesPWC Pointsoffocus ExplainedshivarubanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Chapters 789Document13 pagesReviewer Chapters 789Let it beNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Risk Management StandardDocument49 pagesChapter 8 - Risk Management StandardAmmar DanialNo ratings yet
- Audit Committee Toolkit PDFDocument18 pagesAudit Committee Toolkit PDFuserNo ratings yet
- Meeting 4 - Comparison of Various Standards in Risk ManagementDocument21 pagesMeeting 4 - Comparison of Various Standards in Risk Managementmirza kekeNo ratings yet
- ICSPPS - Session 2.1 - Control Environment - July 25 For TR of Trainers PDODocument69 pagesICSPPS - Session 2.1 - Control Environment - July 25 For TR of Trainers PDONOR-HASHIMA SalacopNo ratings yet
- Governance Principles and Internal Audit RolesDocument6 pagesGovernance Principles and Internal Audit RolesDong-Kyun RyuNo ratings yet
- Pengendalian Internal dan Efektivitas Pemberian KreditDocument34 pagesPengendalian Internal dan Efektivitas Pemberian KreditMirah SumiyatiNo ratings yet
- ACC314 - Governance Process PresmatDocument21 pagesACC314 - Governance Process PresmatFlorenz Nicole PalisocNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Based On The Coso: ObjectiveDocument36 pagesInternal Control Based On The Coso: ObjectiveHuongTranNo ratings yet
- ERM ReviewerDocument4 pagesERM ReviewerJA Pingol PaderonNo ratings yet
- Control: Chartered Institute of Internal AuditorsDocument5 pagesControl: Chartered Institute of Internal AuditorsGNo ratings yet
- Last DayDocument2 pagesLast DaydominicNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Course Material For Corporate GovernanceDocument15 pagesWeek 7 Course Material For Corporate GovernanceemmanvillafuerteNo ratings yet
- The 17 COSO Internal Control PrinciplesDocument7 pagesThe 17 COSO Internal Control Principleseskelapamudah enakNo ratings yet
- Three Lines Model UpdatedDocument13 pagesThree Lines Model UpdatedJose David Pardo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlDocument26 pagesInternal ControlariolacmNo ratings yet
- Acctg 3116 - Internal Controls, Fraud, ErrorsDocument28 pagesAcctg 3116 - Internal Controls, Fraud, ErrorsLea Lyn FuasanNo ratings yet
- COSO - : Internal ControlDocument9 pagesCOSO - : Internal ControlRoby Gerard CorpuzNo ratings yet
- SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY WITH BUSINESS ETHICSDocument8 pagesSOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY WITH BUSINESS ETHICSCrystal ValeroNo ratings yet
- Corporate Culture:: The Second Ingredient in A World-Class Ethics and Compliance ProgramDocument8 pagesCorporate Culture:: The Second Ingredient in A World-Class Ethics and Compliance ProgramEric Nguyen Duc HieuNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance V's ManagementDocument3 pagesCorporate Governance V's ManagementDeepakNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document14 pagesUnit 3Light YagamiNo ratings yet
- Concept of MGTDocument5 pagesConcept of MGTmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Supplemental LectureDocument8 pagesSupplemental LectureBELMONTE, Christian Justin R.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Pt. 2Document8 pagesChapter 5 Pt. 2BELMONTE, Christian Justin R.No ratings yet
- Objectives and Phases of Operational AuditDocument24 pagesObjectives and Phases of Operational AuditBELMONTE, Christian Justin R.100% (1)
- Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesRisk AssessmentBELMONTE, Christian Justin R.No ratings yet
- Framework of EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesFramework of EntrepreneurshipIsmail ShahNo ratings yet
- FINAL DOCUMENT (SIP) ReportDocument16 pagesFINAL DOCUMENT (SIP) ReportSairaj MudhirajNo ratings yet
- National DanceDocument2 pagesNational DanceJohn Paul CasaclangNo ratings yet
- 12th AccountsDocument6 pages12th AccountsHarjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Study On Comparative Analysis of Icici Bank and HDFC Bank Mutual Fund SchemesDocument8 pagesStudy On Comparative Analysis of Icici Bank and HDFC Bank Mutual Fund SchemesRaja DasNo ratings yet
- IDC Infrastructure ProjectsDocument100 pagesIDC Infrastructure Projectsshashi_nspNo ratings yet
- James Shepherd LawsuitDocument22 pagesJames Shepherd LawsuitMLive.comNo ratings yet
- From Vision To Reality: GebizDocument10 pagesFrom Vision To Reality: Gebizmaneesh5100% (1)
- 12 Characteristics of Highly Qualified TeachersDocument9 pages12 Characteristics of Highly Qualified TeachersHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- MUET@UiTM2020 - Food Poisoning - Analysis & SynthesisDocument15 pagesMUET@UiTM2020 - Food Poisoning - Analysis & SynthesisNURUL FARRAH LIEYANA BT SHAMSUL BAHARINo ratings yet
- Yap vs. Lagtapon (Digest)Document2 pagesYap vs. Lagtapon (Digest)Justin IsidoroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Under Revision Wahahaha) The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Under Revision Wahahaha) The Problem and Its BackgroundAira TantoyNo ratings yet
- Illegal FishingDocument1 pageIllegal FishingDita DwynNo ratings yet
- Loan Agreement DetailsDocument21 pagesLoan Agreement DetailssherrieNo ratings yet
- Full Text of Results CPA Board ExamDocument2 pagesFull Text of Results CPA Board ExamTheSummitExpressNo ratings yet
- Annex 7 Workshop at Eastern Partnership Youth ForumDocument4 pagesAnnex 7 Workshop at Eastern Partnership Youth ForumGUEGANNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLES 7-8 - Sheet1-2Document3 pagesACCOUNTS RECEIVABLES 7-8 - Sheet1-2Astrid AboitizNo ratings yet
- Maestro-Ko: IGP - Tshirt Printing ProjectDocument4 pagesMaestro-Ko: IGP - Tshirt Printing ProjectAxel Nicerio RoveloNo ratings yet
- Tan Vs ZanduetaDocument2 pagesTan Vs ZanduetaPearl Deinne Ponce de LeonNo ratings yet
- Notes On Collective NounsDocument7 pagesNotes On Collective NounsTuisyen Dewan Hj Ali50% (2)
- An Inscribed Nabataean Bronze Object DedDocument15 pagesAn Inscribed Nabataean Bronze Object Dedejc1717No ratings yet
- Bai Tâp Anh 9 - 3-2-2021 Re - CLDocument16 pagesBai Tâp Anh 9 - 3-2-2021 Re - CLDuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Computation of Basic and Diluted Eps Charles Austin of The PDFDocument1 pageComputation of Basic and Diluted Eps Charles Austin of The PDFAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- Megastructures - Petronas Towers Malaysia - NOCHE - BT5Document3 pagesMegastructures - Petronas Towers Malaysia - NOCHE - BT5Jerick NocheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PRIME-HRMDocument50 pagesIntroduction To PRIME-HRMApril Gan Casabuena100% (7)
- Loan Policy Document 2019-20 Part-A PDFDocument176 pagesLoan Policy Document 2019-20 Part-A PDFSamiran DebnathNo ratings yet
- Imagine by John LennonDocument3 pagesImagine by John Lennonmichelle12wong4000No ratings yet
- Former Ohio Wildlife Officer Convicted of Trafficking in White-Tailed DeerDocument2 pagesFormer Ohio Wildlife Officer Convicted of Trafficking in White-Tailed DeerThe News-HeraldNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Role of SMEs in Indian Defence Industry1 PDFDocument84 pagesEnhancing Role of SMEs in Indian Defence Industry1 PDFINDIRA PALNINo ratings yet
- DRRM School Memo No. 7Document5 pagesDRRM School Memo No. 7Mime CarmleotesNo ratings yet
- Business Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionFrom EverandBusiness Process Mapping: Improving Customer SatisfactionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersFrom EverandA Step By Step Guide: How to Perform Risk Based Internal Auditing for Internal Audit BeginnersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- (ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideFrom Everand(ISC)2 CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study GuideRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- GDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekFrom EverandGDPR-standard data protection staff training: What employees & associates need to know by Dr Paweł MielniczekNo ratings yet
- The Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessFrom EverandThe Layman's Guide GDPR Compliance for Small Medium BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Audit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?From EverandAudit. Review. Compilation. What's the Difference?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Financial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksFrom EverandFinancial Statement Fraud Casebook: Baking the Ledgers and Cooking the BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electronic Health Records: An Audit and Internal Control GuideFrom EverandElectronic Health Records: An Audit and Internal Control GuideNo ratings yet
- A Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowFrom EverandA Pocket Guide to Risk Mathematics: Key Concepts Every Auditor Should KnowNo ratings yet
- GDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsFrom EverandGDPR for DevOp(Sec) - The laws, Controls and solutionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Audit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsFrom EverandAudit and Assurance Essentials: For Professional Accountancy ExamsNo ratings yet
- Executive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceFrom EverandExecutive Roadmap to Fraud Prevention and Internal Control: Creating a Culture of ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)





![[GROUP 2][COMPARISON OF COSOS 2013 INTERNAL CONTROL FRAMEWORK AND 2017 ERM FRAMEWORK]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/721464701/149x198/ce11e63250/1712667788?v=1)