Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculations of Hessians
Uploaded by
Dr. Partha Sarathi SenguptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculations of Hessians
Uploaded by
Dr. Partha Sarathi SenguptaCopyright:
Available Formats
In this chapter we will talk about calculations of hessians, molecular vibrations and vibrational Infrared
(IR) Spectra of a molecular system. We will describe a little on back ground theoretical method of
calculation for molecular vibration and take a few examples for calculations of vibrational frequency.
25.1 Theoretical Method
Mathematically, hessian is second-order partial derivatives of a function of many variables and it
describes local curvature of a function. In case of geometry optimization, it is mandatory to calculate the
second derivative of energy or hessian to check if the optimization has reached to a local minimum or a
local maximum of the energy function of coordinate variables, xi. If hessian is positive definite at x, then
the function attains a local minimum at x and if the hessian is negative definite at x, then the function
attains a local maximum at x (saddle point). On doing hessian calculations, one can easily calculate
vibrational frequency.
To a first approximation, a molecular vibration may be described in terms of a harmonic oscillator. This
can be derived simply by expanding the energy of the molecule as a function of the nuclear coordinates
in a Taylor series around the equilibrium geometry. In case of a diatomic molecule, this expansion may
be carried out in terms of inter nuclear distance, R.
E(R) = E(R0) + dE/dR (R-R0) + 1/2 d2E/dR2 (R-R0)2 + 1/6 d3E/dR3 (R-R0)3 + ..........
or,E(ΔR) = dE/dR (ΔR) + 1/2 d2E/dR2 (ΔR)2 + 1/6 d3E/dR3 (ΔR)3 + ..........
where R0 is equilibrium inter nuclear distance and ΔR = R - R0 . The first term in the second equation is
zero as this expansion is around the equilibrium geometry and at the equilibrium geometry the gradient
is zero. This leads to the harmonic approximation in terms of force constant, k when only the square
term is considered.
E(ΔR) = 1/2 d2E/dR2 (ΔR)2 = 1/2 k (ΔR)2
Based on the relation, ν = 1/2π (k/µ)1/2 vibration frequency (ν) can be calculated from force constant (k)
and reduced mass (µ) of the molecular system. Anharmonic corrections to the vibration may be
calculated by considering the higher order terms of the expansion.
25.2 Calculation of vibration frequency
The following INPUT is prepared for a hessian calculation. The input is essentially the same as in case of
geometry optimization except that the input geometrical parameters have to be the final optimized one
at the same level of theory. It is the requirement of theory as explained in the previous section that at the
equilibrium geometry only the gradient is zero. In the present case, we consider the final optimized
structure of H2O molecule calculated at B3LYP/6-31++G(d,p) for hessian calculation. The input consider
for this calculation is as follows.
********************
$SYSTEM TIMLIM=6000.0 MWORDS=11 MEMDDI=90 $END
$CONTRL SCFTYP=RHF MPLEVL=0 MAXIT=100 ICHARG=0 MULT=1
COORD=ZMT RUNTYP=HESSIAN TDDFT=NONE $END
$DFT DFTTYP=B3LYP METHOD=GRID $END
$SCF DIRSCF=.F. DAMP=.T. SHIFT=.T. $END
$BASIS GBASIS=N31 NGAUSS=6 NDFUNC=1 NPFUNC=1 DIFFSP=.T. DIFFS=.T. $END
$DATA
water: hessian//B3LYP/6-31++G(d,p)
CN 1
O
H 1 roh
H 1 roh 2 ahoh
roh=0.96 55191
ahoh=105.7086105
$END
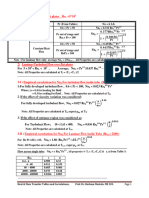
Selected portion of GAMESS ‘OUTPUT’ based on the ‘INPUT’ for hessian calculation is as follows.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NORMAL COORDINATE ANALYSIS IN THE HARMONIC APPROXIMATION
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ATOMIC WEIGHTS (AMU)
1 O 15.99491
2 H 1.00782
3 H 1.00782
MODES 1 TO 6 ARE TAKEN AS ROTATIONS AND TRANSLATIONS.
FREQUENCIES IN CM**-1, IR INTENSITIES IN DEBYE**2/AMU-ANGSTROM**2,
REDUCED MASSES IN AMU.
1 2 3 4 5
FREQUENCY: 27.71 0.01 0.12 1.16 13.75
REDUCED MASS: 1.04648 6.00360 5.94876 5.84117 1.00784
IR INTENSITY: 2.65180 0.00000 0.00005 0.00048 0.00095
1 O X 0.04964805 0.00001669 0.23541428 0.00000000 0.00000000
Y -0.00000012 0.23563345 -0.00001669 0.00000000 0.00000000
Z 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.23497161 -0.00093952
2 H X -0.38459053 0.00001856 0.23734907 0.00000000 0.00000000
Y 0.57327840 0.23563079 -0.00257252 0.00000000 0.00000000
Z 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.24082260 0.71157581
3 H X -0.38459025 0.00001476 0.23734910 0.00000000 0.00000000
Y -0.57327820 0.23563070 0.00253916 0.00000000 0.00000000
Z 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.24081402 -0.69705209
You might also like
- Sprague Matthew Thesis App C PDFDocument26 pagesSprague Matthew Thesis App C PDFAniello LangellaNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document10 pagesCH 2Arvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Process Control Engineering: Prof. Mahmoud A. El-Rifai Prof. Reem S. EttouneyDocument37 pagesProcess Control Engineering: Prof. Mahmoud A. El-Rifai Prof. Reem S. EttouneyCupa no DensetsuNo ratings yet
- Output 22Document16 pagesOutput 22Rockin' RobinNo ratings yet
- Uvvis Spectroscopy: Case Study - Azobenzene E/Z IsomersDocument13 pagesUvvis Spectroscopy: Case Study - Azobenzene E/Z IsomersGressya ShavanaNo ratings yet
- Help PP MEC 223Document5 pagesHelp PP MEC 223Dalia MagdyNo ratings yet
- 03 TestsDocument48 pages03 TestsPhil SunnyNo ratings yet
- Mathematical StudiesDocument56 pagesMathematical StudiesOayes MiddaNo ratings yet
- SalidaDocument47 pagesSalidaAriadna Sánchez CastilloNo ratings yet
- DTW 1Document6 pagesDTW 1suntosh_14No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Report - FinalDocument8 pagesAssignment 3 Report - FinalMustafa MogriNo ratings yet
- Line Cable Parameter Calculation User ManualDocument59 pagesLine Cable Parameter Calculation User Manualamit77999No ratings yet
- Line - Cable-Parameter-Calculation-metric MMDocument59 pagesLine - Cable-Parameter-Calculation-metric MMJoseph PoplingerNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Study by GREENEDocument12 pagesElectricity - Study by GREENEhavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Gaussian SolventDocument26 pagesGaussian SolventManoel MachadoNo ratings yet
- Sample Filter CalculationDocument20 pagesSample Filter CalculationAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Radiation Impedance of A Circular PistonDocument9 pagesRadiation Impedance of A Circular PistonTango SierraNo ratings yet
- Agua Sin DisolventeDocument18 pagesAgua Sin DisolventeDiego PalaciosNo ratings yet
- 1990 Tavoli Modal Analysis of A Hermetic Can JSVDocument5 pages1990 Tavoli Modal Analysis of A Hermetic Can JSVAnirudh SabooNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing - Type2Document60 pagesCombined Footing - Type2jobees7850No ratings yet
- 01 Driver Seat Semi-Active Vibration Control PDFDocument6 pages01 Driver Seat Semi-Active Vibration Control PDFgurudev001No ratings yet
- Three Bit Phase Shifter: MMIC Project Final Report EE525.787 Fall 2007Document16 pagesThree Bit Phase Shifter: MMIC Project Final Report EE525.787 Fall 2007eesharifNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Correlation and CovariationDocument15 pages9.3 Correlation and Covariationhadian98No ratings yet
- Multiple Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesMultiple Linear RegressionJolan MatocinosNo ratings yet
- VMA2Document1,666 pagesVMA2FranciusNo ratings yet
- dt0076 Compensating For Accelerometer Installation Error Zeroing Pitch and Roll For A Reference Orientation StmicroelectronicsDocument6 pagesdt0076 Compensating For Accelerometer Installation Error Zeroing Pitch and Roll For A Reference Orientation StmicroelectronicsPatrickNo ratings yet
- Filter Design SreerafjDocument13 pagesFilter Design SreerafjPappan PreeyappettaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Basis SetsDocument8 pagesChapter - 5 Basis Setsmustafa alasadyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Distribution On A CylinderDocument7 pagesPressure Distribution On A CylinderSaahil Sankar BNo ratings yet
- Design of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital FiltersDocument16 pagesDesign of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) Digital FiltersSedat IsterNo ratings yet
- VMA1Document2,573 pagesVMA1FranciusNo ratings yet
- Output Tracking of Underactuated Rotary Inverted Pendulum by Nonlinear ControllerDocument6 pagesOutput Tracking of Underactuated Rotary Inverted Pendulum by Nonlinear ControllerImee RistikaNo ratings yet
- QuasilikelihoodDocument14 pagesQuasilikelihoodK6 LyonNo ratings yet
- Load Flow AnalysisDocument15 pagesLoad Flow AnalysisMazo Ahmed ShiponNo ratings yet
- EC3 Example ReportDocument10 pagesEC3 Example Reportscribd_namnNo ratings yet
- The Derivative2Document21 pagesThe Derivative2Desita KamilaNo ratings yet
- Opt 4-Hidroxicumarina PropertyDocument11 pagesOpt 4-Hidroxicumarina PropertyFede SiriNo ratings yet
- PCHM Final Equation SheetDocument3 pagesPCHM Final Equation SheetDanson FanNo ratings yet
- Agua Con DisolventeDocument20 pagesAgua Con DisolventeDiego PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Final Practice Problems IDocument30 pagesFinal Practice Problems IAlluri Appa RaoNo ratings yet
- Data Baru Excel 168 Obs Kelompok 6Document11 pagesData Baru Excel 168 Obs Kelompok 6Wini WachidahNo ratings yet
- PreosDocument15 pagesPreosRitesh Dev MaityNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry - Analysis of Organic CompoundsDocument7 pagesPhysical Chemistry - Analysis of Organic CompoundsChris FitzpatrickNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Oscillator and Rigid RotorDocument14 pagesHarmonic Oscillator and Rigid RotorJisu RyuNo ratings yet
- The Simple Harmonic OscillatorDocument44 pagesThe Simple Harmonic OscillatorDebora PaskarinaNo ratings yet
- Electron Spin Resonance SpectrometerDocument8 pagesElectron Spin Resonance SpectrometerSANDEEP TNo ratings yet
- JJ, Wi (: Jjo1RuDocument8 pagesJJ, Wi (: Jjo1RuSandhyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document21 pagesChapter 688alexiaNo ratings yet
- 13 Barras ProgramacionDocument6 pages13 Barras ProgramacionFabian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Vanderwall Equation MatlabDocument5 pagesVanderwall Equation MatlabSri Varalakshmi MummidiNo ratings yet
- EN 1993-1:2005/A1:2014, Eurocode 3: Design of Steel StructuresDocument2 pagesEN 1993-1:2005/A1:2014, Eurocode 3: Design of Steel StructurestomicNo ratings yet
- Peng-Robinson EOS For Z-FactorDocument29 pagesPeng-Robinson EOS For Z-FactorCHANADASNo ratings yet
- Weld CalculationDocument7 pagesWeld CalculationDenny Syamsuddin100% (1)
- VMA5Document1,146 pagesVMA5FranciusNo ratings yet
- Drag Coefficient CalculationDocument4 pagesDrag Coefficient CalculationLa Ode Ahmad BarataNo ratings yet
- Workshop 4 - Draft2Document6 pagesWorkshop 4 - Draft2Saatwick MathurNo ratings yet
- Vib Meas Ins11Document12 pagesVib Meas Ins11113314No ratings yet
- Statistics - HighlightedDocument7 pagesStatistics - HighlightedBenNo ratings yet
- Sim2 Fads Vs Trends PDFDocument9 pagesSim2 Fads Vs Trends PDFMarciano MelchorNo ratings yet
- The Correlation Between Migraine Headache And.10Document6 pagesThe Correlation Between Migraine Headache And.10Luther ThengNo ratings yet
- BSBSUS601 Ass Task 1 - v2.1Document4 pagesBSBSUS601 Ass Task 1 - v2.1Nupur VermaNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument34 pagesPhilosophical Foundations of Curriculum DevelopmentAdeeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 Music 1Document2 pagesActivity Sheet 1 Music 1Enah Sazi Ale ArbalNo ratings yet
- The Power Rule and Other Rules For DifferentiationDocument23 pagesThe Power Rule and Other Rules For DifferentiationAngel EngbinoNo ratings yet
- Practice Essay For Passage TwoDocument2 pagesPractice Essay For Passage TwoVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- Salt) Base) : Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, LalitpurDocument3 pagesSalt) Base) : Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, Lalitpursachin50% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Optial ControlDocument41 pagesChapter 3 - Optial ControlNguyễn Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Study NotesDocument19 pagesCBSE Class 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Study NotesKanchana SriramuluNo ratings yet
- Responsible Management: Understanding Human Nature, Ethics, and SustainabilityDocument40 pagesResponsible Management: Understanding Human Nature, Ethics, and SustainabilityCharlene KronstedtNo ratings yet
- Technologies and Decision Support Systems To Aid Solid-WasteDocument18 pagesTechnologies and Decision Support Systems To Aid Solid-WasteNelson RiañoNo ratings yet
- SW 212 Coursework #1Document8 pagesSW 212 Coursework #1Athena EstavillaNo ratings yet
- Values Development For Citizenship TrainingDocument11 pagesValues Development For Citizenship TrainingAvril SalenNo ratings yet
- A12e IndicatorDocument2 pagesA12e IndicatorCyril J PadiyathNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker TestingDocument27 pagesCircuit Breaker TestingAjay Talajiya50% (2)
- Calculo Do SISDocument4 pagesCalculo Do SISAMINTA MANZANILLANo ratings yet
- My Strengths WorksheetDocument5 pagesMy Strengths WorksheetvilavanadonisNo ratings yet
- REELY Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletDocument2 pagesREELY Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletCERTIFIED TROLLNo ratings yet
- 2020 Oulade The Neural Basis of Language DevelopmentDocument7 pages2020 Oulade The Neural Basis of Language DevelopmentzonilocaNo ratings yet
- Pavement DesignDocument12 pagesPavement DesignTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Malaysia VBI Full ReportDocument116 pagesMalaysia VBI Full ReportHasoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument46 pagesUntitledmaqddus butoolNo ratings yet
- Oral Dosage Forms BrochureDocument20 pagesOral Dosage Forms Brochureselvi aklailia rosaNo ratings yet
- Training Evaluation Form: Seven Seas HotelDocument2 pagesTraining Evaluation Form: Seven Seas HotelPiyush SevenseasNo ratings yet
- DSP AssignmentDocument16 pagesDSP AssignmentPunitha ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Texture by The Sand Circle Method MeasurementsDocument2 pagesTexture by The Sand Circle Method MeasurementssajjaduetNo ratings yet
- The Mystery of Berry Berenson and 9-11Document5 pagesThe Mystery of Berry Berenson and 9-11HierocrypticNo ratings yet
- 41 SAfrican LJ269Document6 pages41 SAfrican LJ269Ruchira JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ifc 8thconf 4c4papDocument29 pagesIfc 8thconf 4c4papgauravpassionNo ratings yet