0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views1 pageInternational Shipping Terms Explained
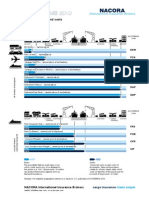
CIF, FOB, and FAS are international shipping terms that define responsibilities for delivering goods. CIF means the seller arranges and pays for transportation and insurance to the destination port, where the risk transfers to the buyer. FOB requires the seller to deliver goods to the port of shipment and load them, with risk transferring to the buyer on board. FAS requires the seller to deliver goods alongside the ship at the port of shipment, where the risk transfers to the buyer. The key difference between these terms is the point at which risk and responsibility transfers from seller to buyer.
Uploaded by
A RamasubramanianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views1 pageInternational Shipping Terms Explained
CIF, FOB, and FAS are international shipping terms that define responsibilities for delivering goods. CIF means the seller arranges and pays for transportation and insurance to the destination port, where the risk transfers to the buyer. FOB requires the seller to deliver goods to the port of shipment and load them, with risk transferring to the buyer on board. FAS requires the seller to deliver goods alongside the ship at the port of shipment, where the risk transfers to the buyer. The key difference between these terms is the point at which risk and responsibility transfers from seller to buyer.
Uploaded by
A RamasubramanianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd