Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Muscles of The Foot - Dorsal - Plantar - TeachMeA
Muscles of The Foot - Dorsal - Plantar - TeachMeA
Uploaded by
KC Dela RosaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Muscles of The Foot - Dorsal - Plantar - TeachMeA
Muscles of The Foot - Dorsal - Plantar - TeachMeA
Uploaded by
KC Dela RosaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Basics Part
| Head
of the|TeachMe
Neuroanatomy
Series | Neck | Thorax | Back | Upper Limb | Lower Limb | Abdomen | Pelvis | 3D Body
Sign Up | Log In
TeachMe Subjects Question Bank App Contact Us ' Sign Up
Anatomy
3D model is a
premium feature
Muscles of the Foot !!!!!
based on 147 ratings
Original Author(s): Jess Speller
Last updated: January 31, 2023
Revisions: 46
Home / The Lower Limb / Muscles of the Lower Limb / Muscles of the Foot
Go Premium!
Interactive 3D Advert Free
& Contents
Models %
Custom Quiz
Access over Builder
1700 multiple
choice Performance
questions tracking
Quiz
Muscles of the Foot
Upgrade to premium
!
The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups;
Question 1 of 3
extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. Already have an account?
LOG IN
Extrinsic muscles arise from the anterior, posterior and Which nerve innervates
lateral compartments of the leg. They are mainly responsible for extensor digitorum brevis and
actions such as eversion, inversion, plantarflexion and dorsiflexion of extensor hallucis brevis?
the foot.
Tibial
Intrinsic muscles are located within the foot and are responsible for
the fine motor actions of the foot, for example movement of individual
digits. Sural
In this article, we shall examine the anatomy of the intrinsic muscles of
the foot. They can be divided into those situated on the dorsum of the Deep fibular
foot, and those in the sole of the foot.
Superficial fibular
Dorsal Aspect Skip Submit
There are two intrinsic muscles located within the dorsum of the foot – Report question
the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor hallucis brevis.
They assist the extrinsic muscles of the foot in extending the toes and are
$ Recommended reading
both innervated by the deep fibular nerve.
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Dynamic evolution in mechanical
The extensor digitorum brevis is a small, thin muscle which lies characteristics of complex supporting
underneath the long extensor tendons of the foot. structures during large section tunnel
construction
Hua Jiang et al., Deep Underground
Attachments: Originates from the calcaneus and inferior extensor Science and Engineering, 2022
retinaculum. It attaches onto the long extensor tendons of the medial
Coal rock image recognition method based
four toes. on improved CLBP and receptive field
theory
Actions: Extension of the lateral four toes. Chuanmeng Sun et al., Deep Underground
Science and Engineering, 2022
Innervation: Deep fibular nerve. Additive manufacturing technology in
mining engineering research
Extensor Hallucis Brevis Xiaowei Feng et al., Deep Underground
Science and Engineering, 2022
The extensor hallucis brevis is often considered to be the medial part of
Numerical simulation of zonal disintegration
the extensor digitorum brevis muscle, rather than a separate structure. of surrounding rock in the deep-buried
chamber
Attachments: Originates from the calcaneus and inferior extensor
retinaculum. It attaches to the base of the proximal phalanx of the great
toe.
Actions: Extension of the great toe.
Innervation: Deep fibular nerve.
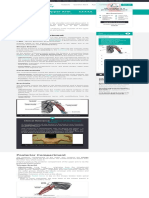
ExtensorDigitorumBrevis
ExtensorHallucisBrevis
TeachMeAnatomy
Fig 1 – The dorsal layer of foot muscles.
Plantar Aspect
There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect (sole) of
the foot.
They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot and individually to
control movement of the digits. They are innervated by the medial or
lateral plantar nerves – which are branches of the tibial nerve.
The muscles of the plantar aspect are arranged in four layers (superficial
to deep):
First Layer
The first layer contains three muscles. It is the most superficial and is
located immediately underneath the plantar fascia.
Abductor Hallucis
The abductor hallucis muscle is located on the medial side of the sole,
where it contributes to a small soft tissue bulge.
Attachments: Originates from the medial tubercle of the calcaneus, the
flexor retinaculum and the plantar aponeurosis. It attaches to the
medial base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe.
Actions: Abduction and flexion of the great toe.
Innervation: Medial plantar nerve.
Flexor Digitorum Brevis
The flexor digitorum brevis muscle is located laterally to the abductor
hallucis. It sits in the centre of the sole, sandwiched between the plantar
aponeurosis and the tendons of flexor digitorum longus.
Attachments: Originates from the medial tubercle of the calcaneus and
the plantar aponeurosis. It attaches to the middle phalanges of the
lateral four digits.
Actions: Flexion of the lateral four toes at the proximal interphalangeal
joints.
Innervation: Medial plantar nerve.
Abductor Digiti Minimi
The abductor digiti minimi muscle is located on the lateral side of the
foot. It is homologous with the abductor digiti minimi of the hand.
Attachments: Originates from the medial and lateral tubercles of the
calcaneus and the plantar aponeurosis. It attaches to the lateral base of
the proximal phalanx of the 5th digit.
Actions: Abduction and flexion of the little toe.
Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve.
Plantar
aponeurosis(cut)
Abductordigiti
minimi
Abductor
Flexordigitorum
hallucis brevis
TeachMeAnatomy
Fig 2 – The first layer of plantar muscles. The plantar aponeurosis has been cut to reveal the
underlying flexor digitorum.
Second Layer
The second plantar layer contains two muscles – the quadratus plantae
and the lumbricals. The tendons of the flexor digitorum longus (an
extrinsic muscle) also travel through this layer.
Quadratus Plantae
The quadratus plantae is a flat, square-shaped muscle with two heads of
origin.
Attachments: Originates from the medial and lateral plantar surface of
the calcaneus. It attaches to the tendons of flexor digitorum longus.
Actions: Assists the flexor digitorum longus in flexion of the lateral four
toes.
Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve.
Lumbricals
There are four lumbrical muscles in the foot. They are each located
medial to their respective tendon of the flexor digitorum longus.
Attachments: Originates from the tendons of flexor digitorum longus.
Attaches to the extensor hoods of the lateral four digits.
Actions: Flexion at the metatarsophalangeal joints and extension at the
interphalangeal joints.
Innervation:
Medial lumbrical – medial plantar nerve.
Lateral three lumbricals – lateral plantar nerve
Quadratus
plantae
Tendonsofthe
flexordigitorum
longus
Lumbricals
/TeachMeAnatomy
Fig 3 – The second layer of the plantar muscles.
Third Layer
The third layer contains three muscles. The flexor hallucis brevis and
adductor hallucis are associated with movements of the great toe. The
remaining muscle, the flexor digiti minimi brevis, moves the little toe.
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
The flexor hallucis brevis muscle is located on the medial side of the foot.
It has two heads of origin.
Attachments:
Lateral head – originates from the plantar surfaces of the cuboid and
lateral cuneiforms
Medial head – originates from the tendon of the posterior tibialis
tendon.
The fibres converge into a single muscle belly, which attaches to the
base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe.
Actions: Flexion of the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation: Medial plantar nerve.
Adductor Hallucis
The adductor hallucis muscle is located laterally to the flexor hallucis
brevis. It consists of an oblique and transverse head.
Attachments:
Oblique head – originates from the bases of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th
metatarsals.
Transverse head – originates from the plantar ligaments of the
metatarsophalangeal joints.
Both heads attach to the lateral aspect of the base of the proximal
phalanx of the great toe.
Actions: Adduction of the great toe. Supports the transverse arch of
the foot.
Innervation: Deep branch of lateral plantar nerve.
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis
The flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle is located on the lateral side of the
foot, underneath the metatarsal of the little toe. It resembles the
interossei in structure.
Attachments: Originates from the base of the fifth metatarsal and
attaches to the base of the proximal phalanx of the fifth digit.
Actions: Flexion of the little toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation: Superficial branch of lateral plantar nerve.
Flexordigiti
minimibrevis
Flexorhallucis
brevis
Adductorhallucis
(obliquehead)
Adductorhallucis
(transversehead)
TeachMeAnatomy
Fig 4 – The third layer of plantar muscles.
Fourth Layer
The plantar and dorsal interossei comprise the fourth and final plantar
muscle layer. The plantar interossei have a unipennate shape, while the
dorsal interossei are bipennate.
Plantar Interossei
There are three plantar interossei, which are located between the
metatarsals. Each arises from a single metatarsal.
Attachments: Originates from the medial side of metatarsals three to
five. Attaches to the medial sides of the phalanges of digits three to
five.
Actions: Adduction of the lateral three digits and flexion at the
metatarsophalangeal joints.
Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve.
Dorsal Interossei
There are four dorsal interossei, which are located between the
metatarsals. Each arises from two metatarsals.
Attachments: Originates from the lateral aspect of the metatarsals. The
first muscle attaches to the medial side of the proximal phalanx of the
second digit. The second to fourth interossei attach to the lateral sides
of the proximal phalanxes of digits two to four.
Actions: Abduction of the lateral four digits and flexion at the
metatarsophalangeal joints.
Innervation: Lateral plantar nerve.
a)DorsalInterossei b)PlantarInterossei
Fig 5 – The fourth layer of the plantar muscles. Note the unipennate shape of the plantar interossei,
and the bipennate shape of the dorsal interossei
+
Clinical Relevance: Medial Plantar Nerve
Entrapment
The medial plantar nerve can become compressed and
irritated as it passes deep to the abductor hallucis muscle.
This can cause aching, numbness and paraesthesia on the
medial side of the sole of the foot. The muscle can become
compressed during repetitive eversion of the foot, which may
occur in some sports such as gymnastics.
" Print this Article # Rate this Article
Your Health Matters
Ads By
Ikaria Lean Science Formula is a The Biggest Smile, Rejuvenated
Proven Weight Loss Shake Gums & Better Breathe
Ikaria Lean Science Formula Prodentim
Support Healthy Weight Loss Summer Near so Lose Weight
with 6 Alpine Nutrients with Alpilean's Proven Formula
Alpilean Alpilean Weight Loss
TeachMeAnatomy
Part of the TeachMe Series
The medical information on this site is provided as an
information resource only, and is not to be used or relied
on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. This
information is intended for medical education, and does
not create any doctor-patient relationship, and should not
be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and
treatment. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing
terms and conditions. If you do not agree to the
foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter this " # $ %
site.
© TeachMe Series 2023 | Registered in England & Peer Review Team | Advertise with Us | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Acceptable Use Policy
Wales
You might also like
- Soft Tissue Mobilizazion PDFDocument55 pagesSoft Tissue Mobilizazion PDFIlinca Teodora100% (2)
- Final-Exam Neurosurgery - 2-VersionDocument6 pagesFinal-Exam Neurosurgery - 2-VersionMAMA LALANo ratings yet
- Pedagogy WheelDocument1 pagePedagogy Wheelapi-415110604100% (1)
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Document10 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 1: Transport)Gerard Selvaraj88% (26)
- Muscles of The Posterior Leg - Attachments - ActiDocument1 pageMuscles of The Posterior Leg - Attachments - ActiKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Anterior Leg - Attachments - Actio 2Document1 pageMuscles of The Anterior Leg - Attachments - Actio 2KC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Arm - Biceps - Triceps - TeaDocument1 pageMuscles of The Upper Arm - Biceps - Triceps - TeaKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Opensim: Bme 599: Modeling & Simulation of MovementDocument44 pagesIntroduction and Opensim: Bme 599: Modeling & Simulation of MovementJackelineTafurOviedoNo ratings yet
- MuscularDocument74 pagesMuscularElián LópezNo ratings yet
- Physiology: Free TemplateDocument54 pagesPhysiology: Free TemplateJaja BrillitosNo ratings yet
- Hamstring Muscles Anatomy - Google SearchDocument3 pagesHamstring Muscles Anatomy - Google SearchSunket PatelNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Powerpoint NeurocienciasDocument47 pagesPlantilla Powerpoint NeurocienciasCinthya Gómez Carmary NailsNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Powerpoint NeurocienciasDocument45 pagesPlantilla Powerpoint NeurocienciasVietnam Ibañez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Clauda Juan To PapeDocument43 pagesTrabajo Clauda Juan To Papejuan pabloNo ratings yet
- Plantilla Powerpoint Del Sistema MuscularDocument48 pagesPlantilla Powerpoint Del Sistema MuscularLimberg ArhuataNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4383182Document5 pagesSSRN Id4383182320126551001 BANKALIKITHANo ratings yet
- Pros These SDocument17 pagesPros These SArafatNo ratings yet
- U2 ADJ 03 Animal Anatomy BasicsDocument2 pagesU2 ADJ 03 Animal Anatomy BasicsMai SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Ajr 08 1316Document9 pagesAjr 08 1316EdsonR GhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ASSESSMENTS 4 5 PED 211 Principles of MotorDocument8 pagesChapter 4 ASSESSMENTS 4 5 PED 211 Principles of MotorJohn Lloyd Francis RoncalNo ratings yet
- Free Anatomy Powerpoint TemplateDocument13 pagesFree Anatomy Powerpoint TemplateLiza HeatubunNo ratings yet
- All The Muscles in The Bicep - Google SearchDocument1 pageAll The Muscles in The Bicep - Google SearchRonNo ratings yet
- What's The Five Senses - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageWhat's The Five Senses - Google Search PDFArtemis AtbaeiNo ratings yet
- Otimizacao de Barra de Direcao EsssDocument10 pagesOtimizacao de Barra de Direcao EsssGabriel Pereira FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mock MCQ Test 229 AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnatomy Mock MCQ Test 229 AnatomyBinal Morabia75% (4)
- Pengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri WidanarkoDocument74 pagesPengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri WidanarkoDaniel SihombingNo ratings yet
- Signature Info PKGDocument22 pagesSignature Info PKGPina Olson CampbellNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Shoulder Region - TeachMeAnatomyDocument1 pageMuscles of The Shoulder Region - TeachMeAnatomySunket PatelNo ratings yet
- Swimming Long Term Athlete Development Model: FemaleDocument15 pagesSwimming Long Term Athlete Development Model: FemalenccpswimmingNo ratings yet
- Sitting and Standing Work in Ergonomics Mind MapDocument1 pageSitting and Standing Work in Ergonomics Mind MapSean SuppasitNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Book DTDocument30 pagesTopic 1 Book DTgf2rxzwwrtNo ratings yet
- Planes de Entrenamiento para Ciclistas - Strava Cuarenta y Cinco Segundos de Sprint 9Document1 pagePlanes de Entrenamiento para Ciclistas - Strava Cuarenta y Cinco Segundos de Sprint 9jhonatan pineda zuluagaNo ratings yet
- Planes and Axes of Movement - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeDocument3 pagesPlanes and Axes of Movement - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeyoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Colorful Creative Concept MapDocument1 pageColorful Creative Concept MapgabrielagonzluNo ratings yet
- Apps For AutismDocument1 pageApps For Autismapi-407131623No ratings yet
- Ijcrt 198581Document13 pagesIjcrt 198581Prajwal UtturNo ratings yet
- Types Types of Synovial Joints in The Human Skeleton - Google SearchDocument1 pageTypes Types of Synovial Joints in The Human Skeleton - Google SearchdkqjbpcwpvNo ratings yet
- Bodybuilding 6Document7 pagesBodybuilding 6CALFNo ratings yet
- Counseling Dialog System With 5W1H ExtractionDocument5 pagesCounseling Dialog System With 5W1H ExtractionWildan rafifNo ratings yet
- Bioguide-Musclemodel 0Document9 pagesBioguide-Musclemodel 0tonybony585960No ratings yet
- Built by Science Daily Trainer - Day 2, ChestDocument7 pagesBuilt by Science Daily Trainer - Day 2, ChestAlbert Tamai100% (1)
- Prosthetic Limb Design: Viren Shah E031 Datream Tanti E045 Adyant Tripathy E050Document12 pagesProsthetic Limb Design: Viren Shah E031 Datream Tanti E045 Adyant Tripathy E050MPSTME Btech CS ENo ratings yet
- 3 Fixes For Mysterious Knee, Back, and Elbow PainDocument6 pages3 Fixes For Mysterious Knee, Back, and Elbow PainPathivada LumbiniNo ratings yet
- Classroom Behavior ChartDocument2 pagesClassroom Behavior Chartsol100% (1)
- Presentation On The 6 Lenses StrategyDocument15 pagesPresentation On The 6 Lenses StrategyLana Jelenjev100% (1)
- CSS Block Plan W1Document1 pageCSS Block Plan W1Carren Joy LazoNo ratings yet
- Paralympics: 1. AssessDocument2 pagesParalympics: 1. AssessAlpesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Product Templates - PrintfulDocument1 pageProduct Templates - PrintfulFlaming nNo ratings yet
- 236 Primal Pattern Movement System Toles TDocument5 pages236 Primal Pattern Movement System Toles TTito Alho67% (3)
- Speed Distance and Time WorksheetDocument1 pageSpeed Distance and Time WorksheetShahnila AmeerNo ratings yet
- 15 Brain Exercises That Ensure Memory ImprovementDocument62 pages15 Brain Exercises That Ensure Memory ImprovementSir SuneNo ratings yet
- Ebook The Muscular System Manual The Skeletal Muscles of The Human Body PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook The Muscular System Manual The Skeletal Muscles of The Human Body PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.vann805100% (29)
- Mighty Muscles Activity Sheet - Pictures IncludedDocument6 pagesMighty Muscles Activity Sheet - Pictures IncludedamayalibelulaNo ratings yet
- Yoga Pose Classification ICIP CopyDocument6 pagesYoga Pose Classification ICIP Copyanand7992262498No ratings yet
- Create CharacterDocument5 pagesCreate CharacterRaffaele IavazzoNo ratings yet
- The Best 10 After Effects ExpressionsDocument14 pagesThe Best 10 After Effects ExpressionsJustine AlexNo ratings yet
- Rigging - Reusing Animations For Another Character - Blender Stack ExchangeDocument1 pageRigging - Reusing Animations For Another Character - Blender Stack ExchangeMed A BadaNo ratings yet
- 4 Mind-Body Exercises For Brain Health - HealthXchangeDocument1 page4 Mind-Body Exercises For Brain Health - HealthXchangeNathalie BlancoNo ratings yet
- UERM-CM 2021 EYYYYY On Twitter (ANATOMY MNEMONI 2Document1 pageUERM-CM 2021 EYYYYY On Twitter (ANATOMY MNEMONI 2KC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Spine - TeachMeSurgeryDocument1 pageExamination of The Spine - TeachMeSurgeryKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Medicowesome Glasgow Coma Scale Mnemonic 2Document1 pageMedicowesome Glasgow Coma Scale Mnemonic 2KC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Murmurs Made Easy Epomedicine 2Document1 pageMurmurs Made Easy Epomedicine 2KC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Case 12 Chest Pain - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument1 pageCase 12 Chest Pain - Knowledge at AMBOSSKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy - Neurology PreTest™ SelfDocument2 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy - Neurology PreTest™ SelfKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Gyne ReflectionDocument18 pagesGyne ReflectionKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Genital Tract Infections - GynecologyDocument17 pagesGenital Tract Infections - GynecologyKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine DisorderDocument9 pagesCervical Spine DisorderANDRE MANo ratings yet
- Stretches - MenDocument2 pagesStretches - MenBahak AkbaNo ratings yet
- Wrist Dropbrace Afer Radial Nerve PalsyDocument6 pagesWrist Dropbrace Afer Radial Nerve PalsyDenise MathreNo ratings yet
- 12 Filler PointsDocument15 pages12 Filler PointsSripada Lk Kingjorn100% (1)
- K-Sir Arch For Simultaneous Intrusion and Retraction of The Maxillary Anterior Teeth-A Case ReportDocument5 pagesK-Sir Arch For Simultaneous Intrusion and Retraction of The Maxillary Anterior Teeth-A Case ReportSiddarthNo ratings yet
- Peripheral CirculationDocument27 pagesPeripheral CirculationRachel ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Massage: How 2 Improve SingingDocument6 pagesLaryngeal Massage: How 2 Improve SingingAnca ONo ratings yet
- Sindesmosi Biomechanical Sequelae of Syndesmosis Injury and RepairDocument22 pagesSindesmosi Biomechanical Sequelae of Syndesmosis Injury and RepairTameemNo ratings yet
- The Five Tibetan RitesDocument14 pagesThe Five Tibetan Ritesreha-kaubaNo ratings yet
- Tendon Transfers and Upper Limb Disorders: Aws KhanfarDocument41 pagesTendon Transfers and Upper Limb Disorders: Aws KhanfarRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Kinstretch Video Are Vimeo's Part 1&2 RippedDocument3 pagesKinstretch Video Are Vimeo's Part 1&2 RippedMarcelo Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract of The PigDocument4 pagesDigestive Tract of The PiglsvcsbNo ratings yet
- Naik, S. - Biomechanics of Knee ComplexDocument25 pagesNaik, S. - Biomechanics of Knee ComplexKyle Bois100% (4)
- 6.14.19-Foot DropDocument43 pages6.14.19-Foot DropRICKSON KAWINANo ratings yet
- Textbook of Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology 2006pdf-215-231 PDFDocument17 pagesTextbook of Dental and Maxillofacial Radiology 2006pdf-215-231 PDFDania RambinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi TidurDocument25 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi TidurMuhammad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology: Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic ReflexesDocument41 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology: Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic ReflexesSyarif MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Nerve of Lower LimbDocument30 pagesNerve of Lower LimbAaminah NawazNo ratings yet
- Workbook ActivityDocument2 pagesWorkbook ActivityRisciella 18No ratings yet
- FGD - The Effectiveness of Tamsulosin in BPH Patients With LUTSDocument33 pagesFGD - The Effectiveness of Tamsulosin in BPH Patients With LUTSTrisno Fajar NursantoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Eyes and VisionDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Eyes and Visionmary krisNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination of The NewbornDocument21 pagesNeurological Examination of The Newborncristieristiie100% (1)
- PENANGANAN FRAKTUR (Time Table Hoppenfeld) - 1Document47 pagesPENANGANAN FRAKTUR (Time Table Hoppenfeld) - 1Linda SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Classification of BonesDocument3 pagesClassification of BonesJanet Floreno VillasanaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Student Sheet-1Document4 pagesHuman Body Systems Student Sheet-1Fahim JahingirNo ratings yet
- Taiho Jutsu Beginner To Black BeltDocument70 pagesTaiho Jutsu Beginner To Black Beltkalurfrnd100% (1)
- Panfacial Fractures: DR Sunil Sidana MGM Dental College and HospitalDocument54 pagesPanfacial Fractures: DR Sunil Sidana MGM Dental College and Hospitalsmartdoc3650% (2)
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument28 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringKimberlie Dela Merced Tomas100% (1)